Week 1d: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Who invented the MRI technology?
Felix Block & Edward Purcell
- They used it to determine the structure of molecules

Who created MRI for medical use?
Paul Lauterbur & Sir Peter Mansfield

What is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)?
MRI is a cross sectional imaging technology that uses a magnetic field and radio frequency signals to cause hydrogen nuclei to emit their own signals, which then are converted to images by a computer
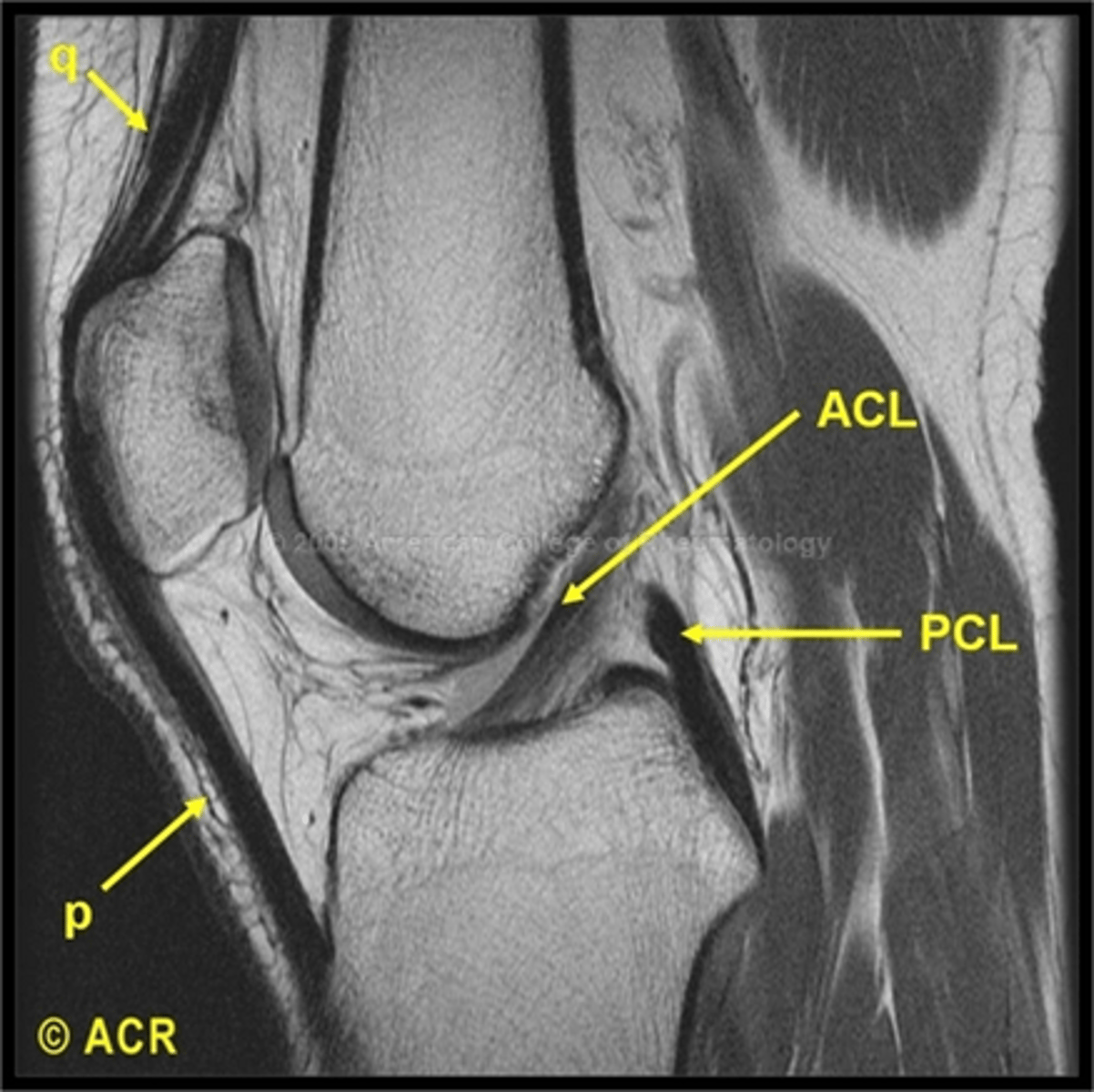
What are the three basic components of the MRI?
The Scanner
- Contains the primary magnetic field, the radiofrequency coils and the gradient coils. (The patient slides into the scanner gantry)
The Operator Console
- The technician selects the imaging protocols
The Computer
- Converts data from the radiofrequency receptors into images
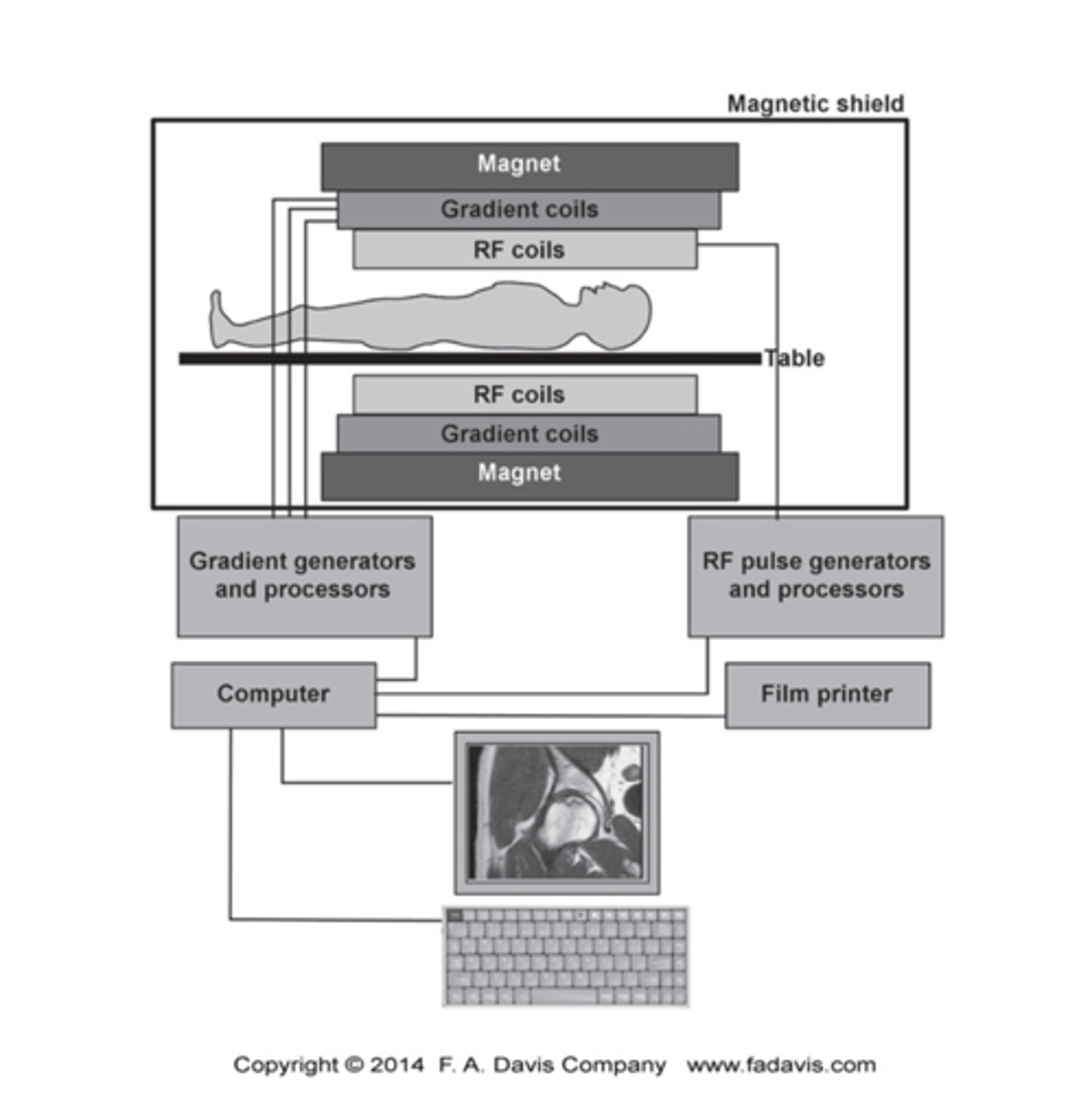
What is the substance in the body that MRI affect?
MRI is based on signals from hydrogen nuclei in water molecules because it consists of only one proton
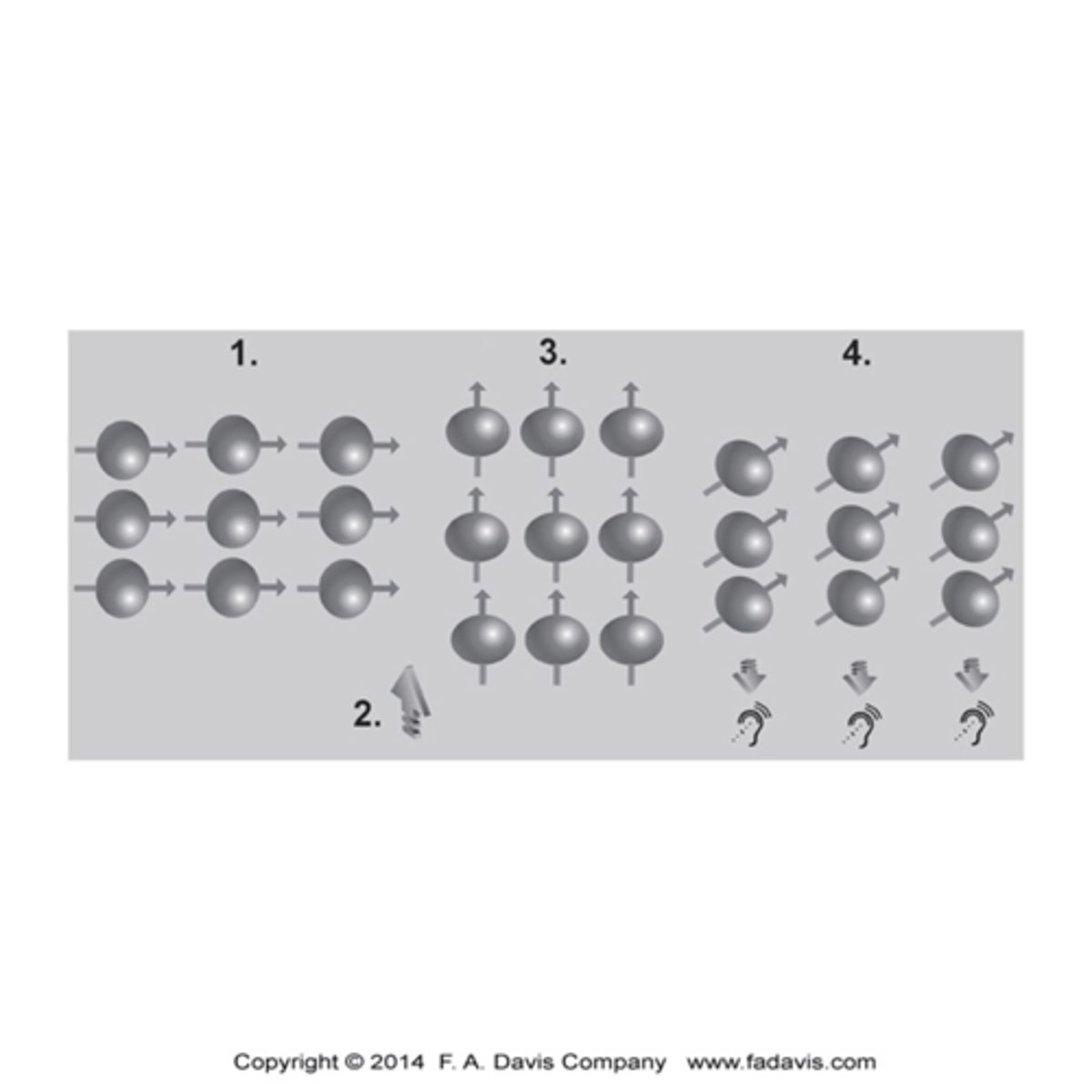
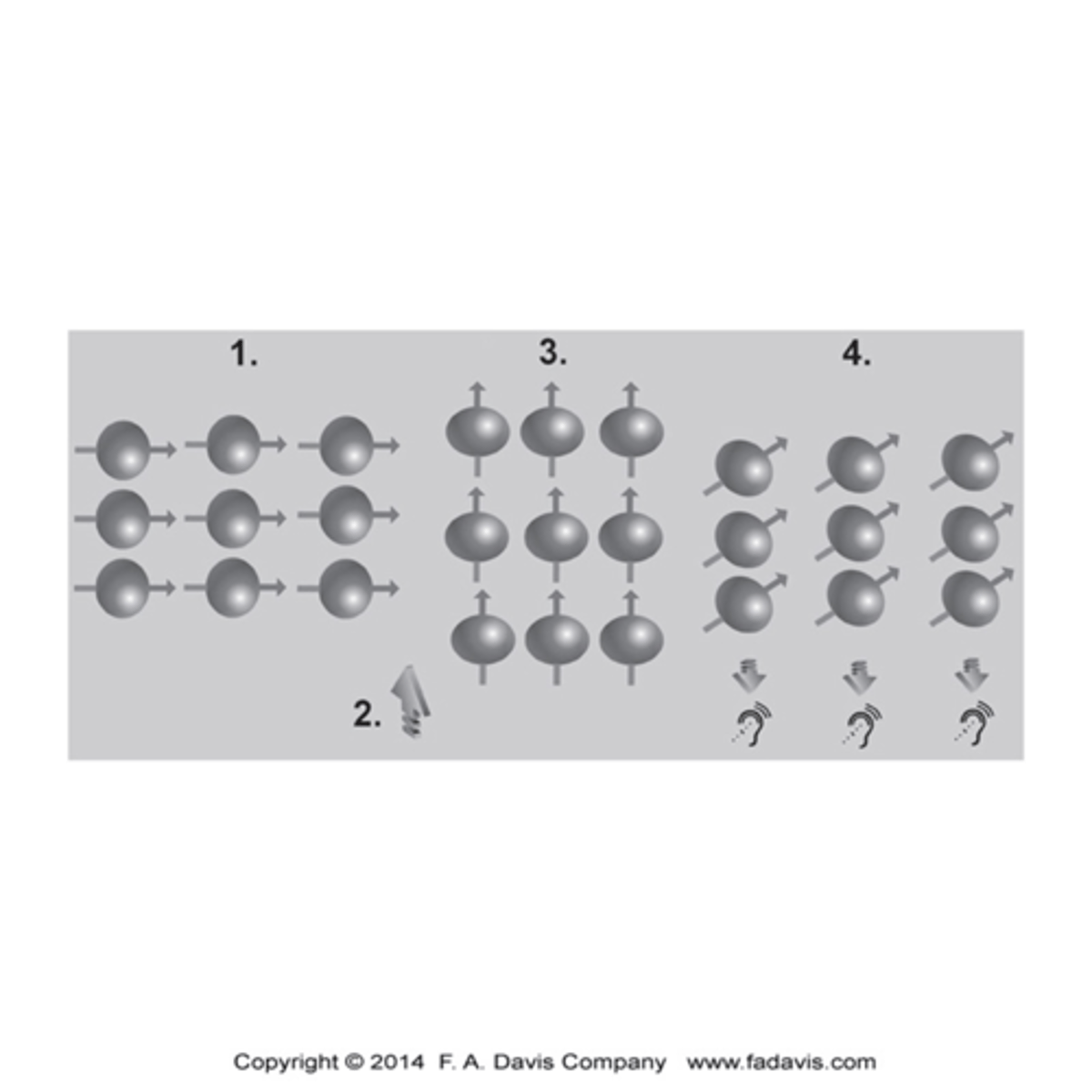
What is magnetic resonance?
The process by which nuclei, aligned with and external magnetic field, absorb and release energy
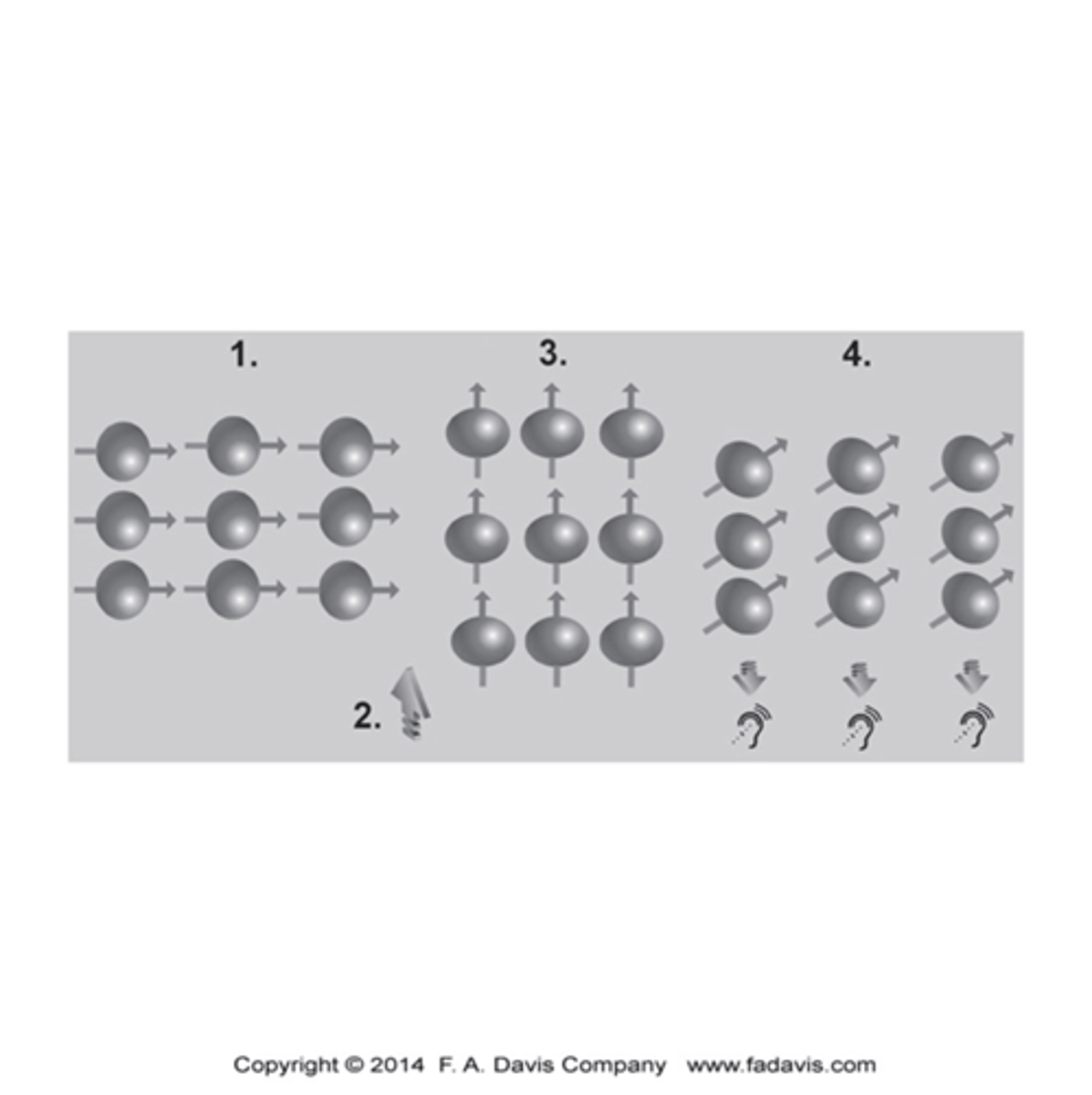
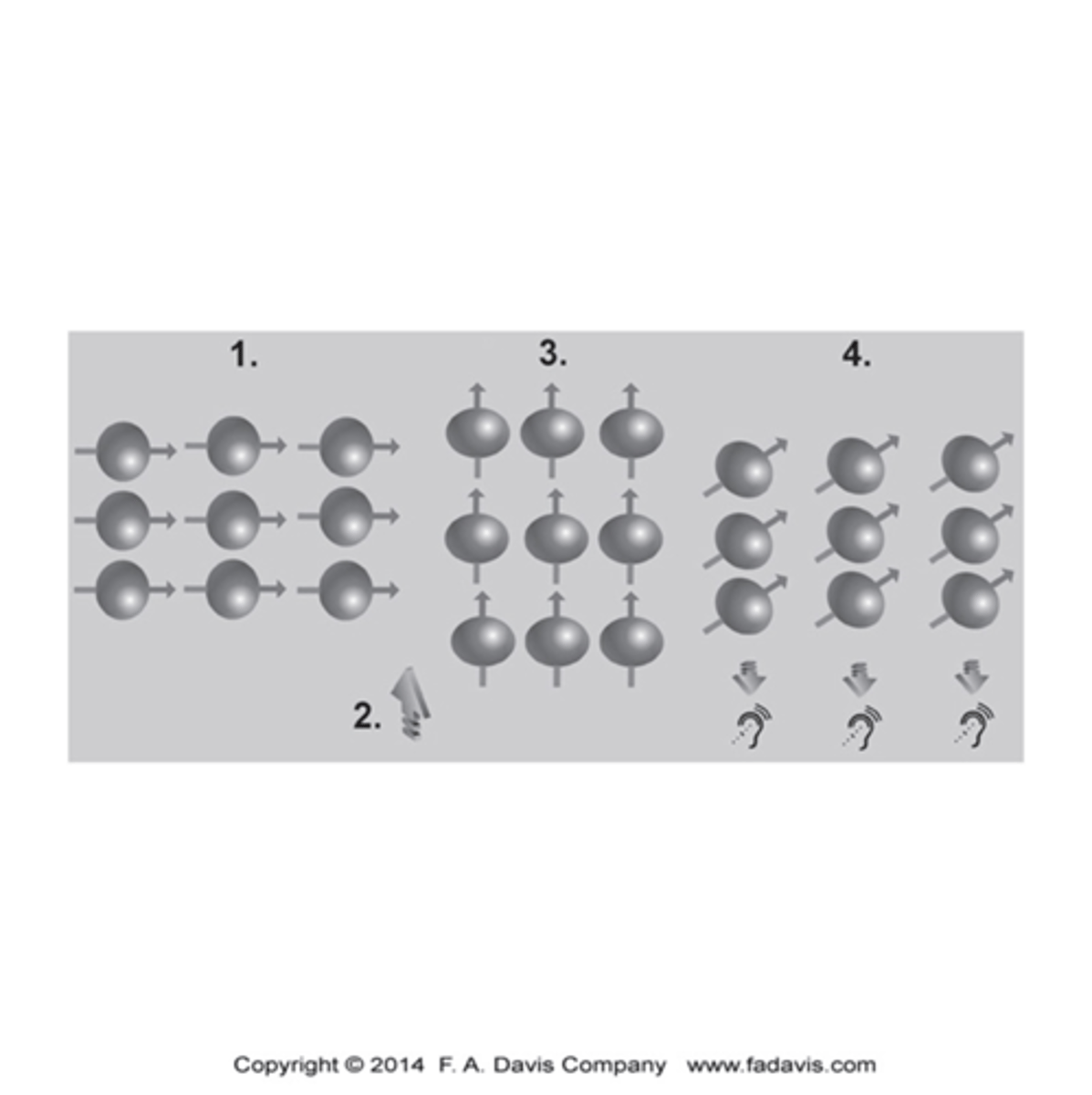
Steps to an MRI?
1.The magnetic field in the scanner causes the hydrogen nuclei in water molecules to align relative to the field.
2.A pulse of radiofrequency waves is applied, and this pulse knocks the protons out of alignment, and energy is absorbed in the process.
3.After the radiofrequency pulse is turned off, the protons realign with the magnetic field and release their absorbed energy
4.Because each soft tissue has a different amount of water content, it will absorb and release energy at different rates.
5.The measurement of the differences in these energy levels is what is used to create the image.
What are the two types of weighted images?
T1 & T2 weighted sequences
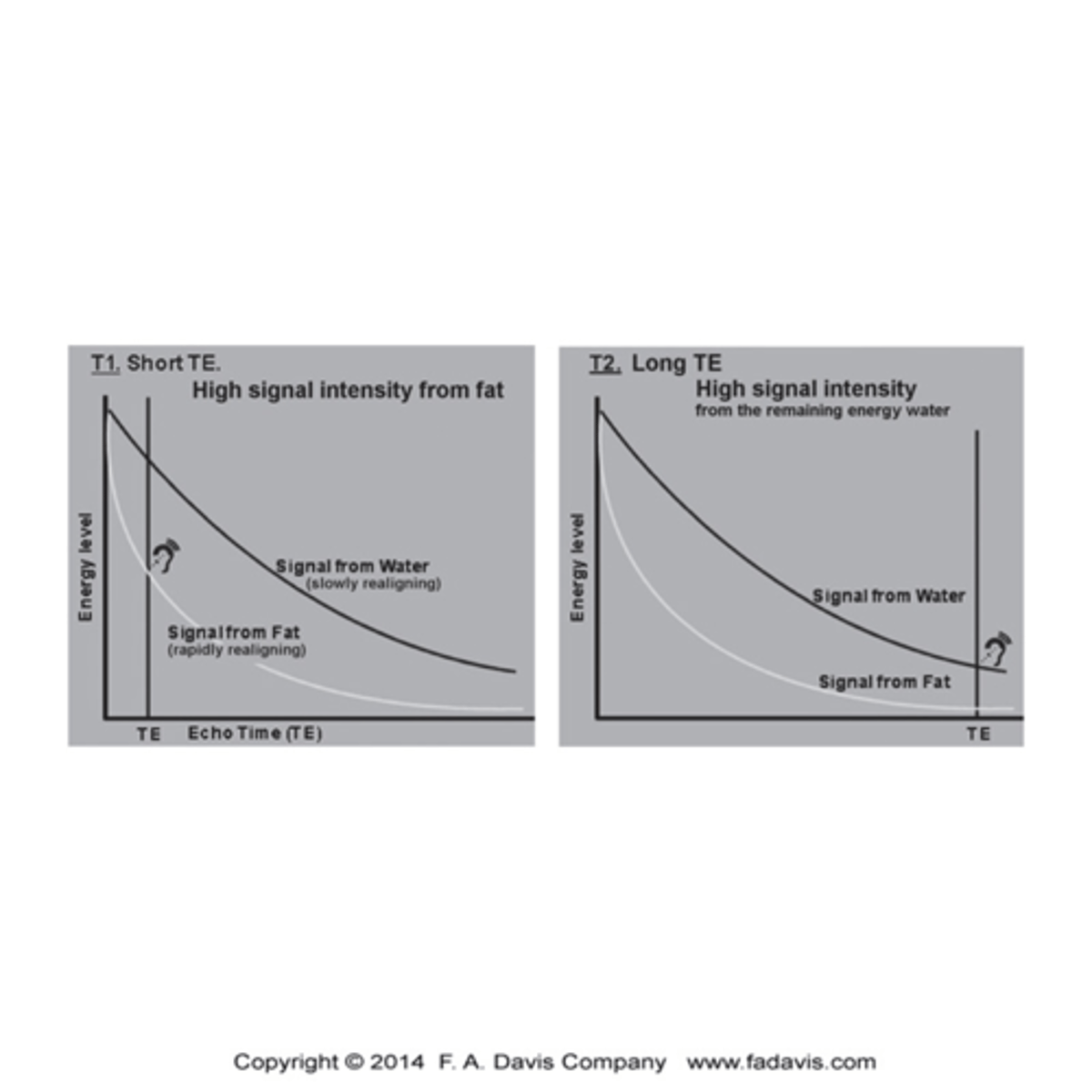
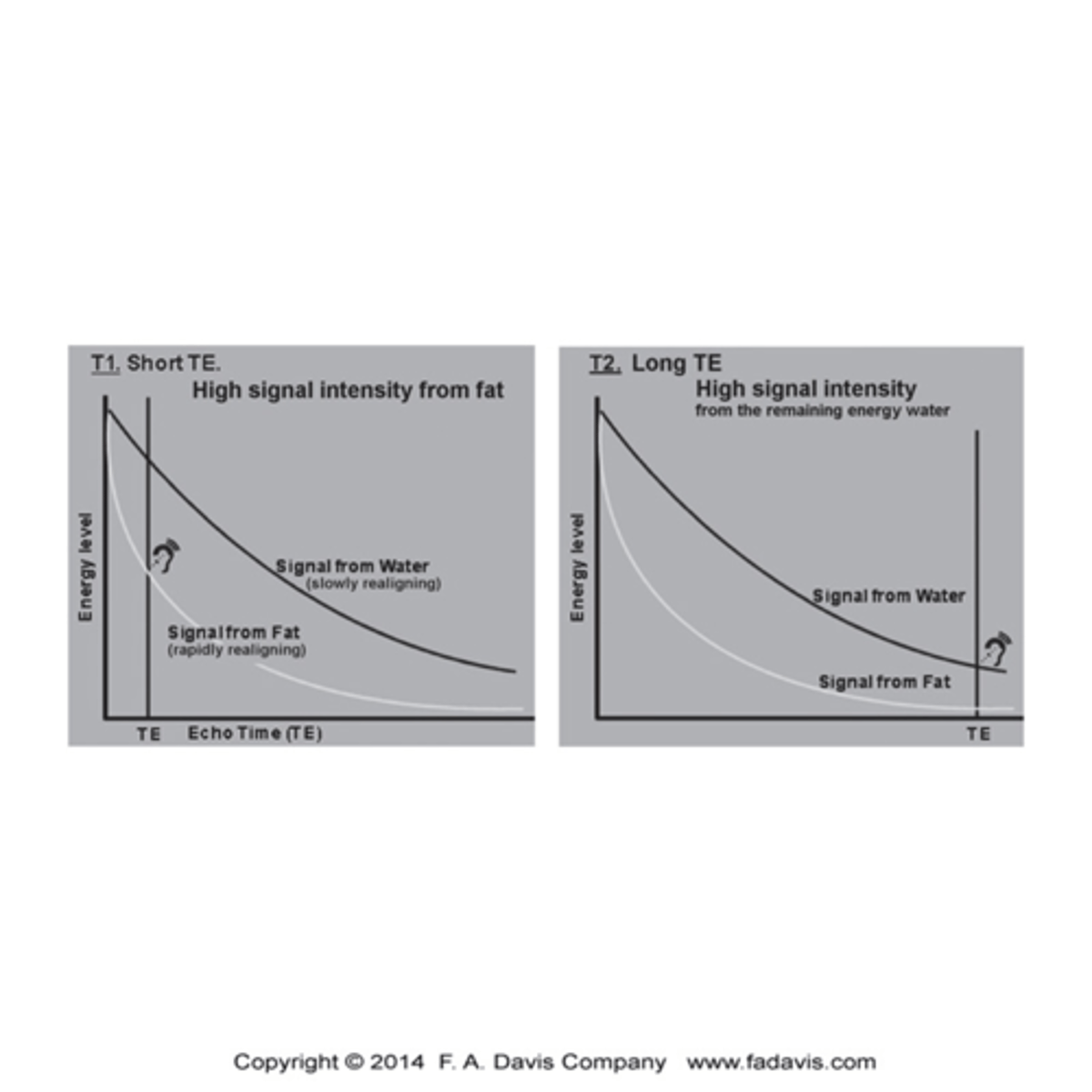
What is a T1 sequence?
Provide excellent resolution of the Anatomy
- Characterized by Short TE (time to echo time the echo is captured) and TR (time to repetition - time at which the RF pulse is repeated toa gain displace the protons)
- Signal is caught early and big difference between fat (brighter-high signal intensity) and water (low intensity)
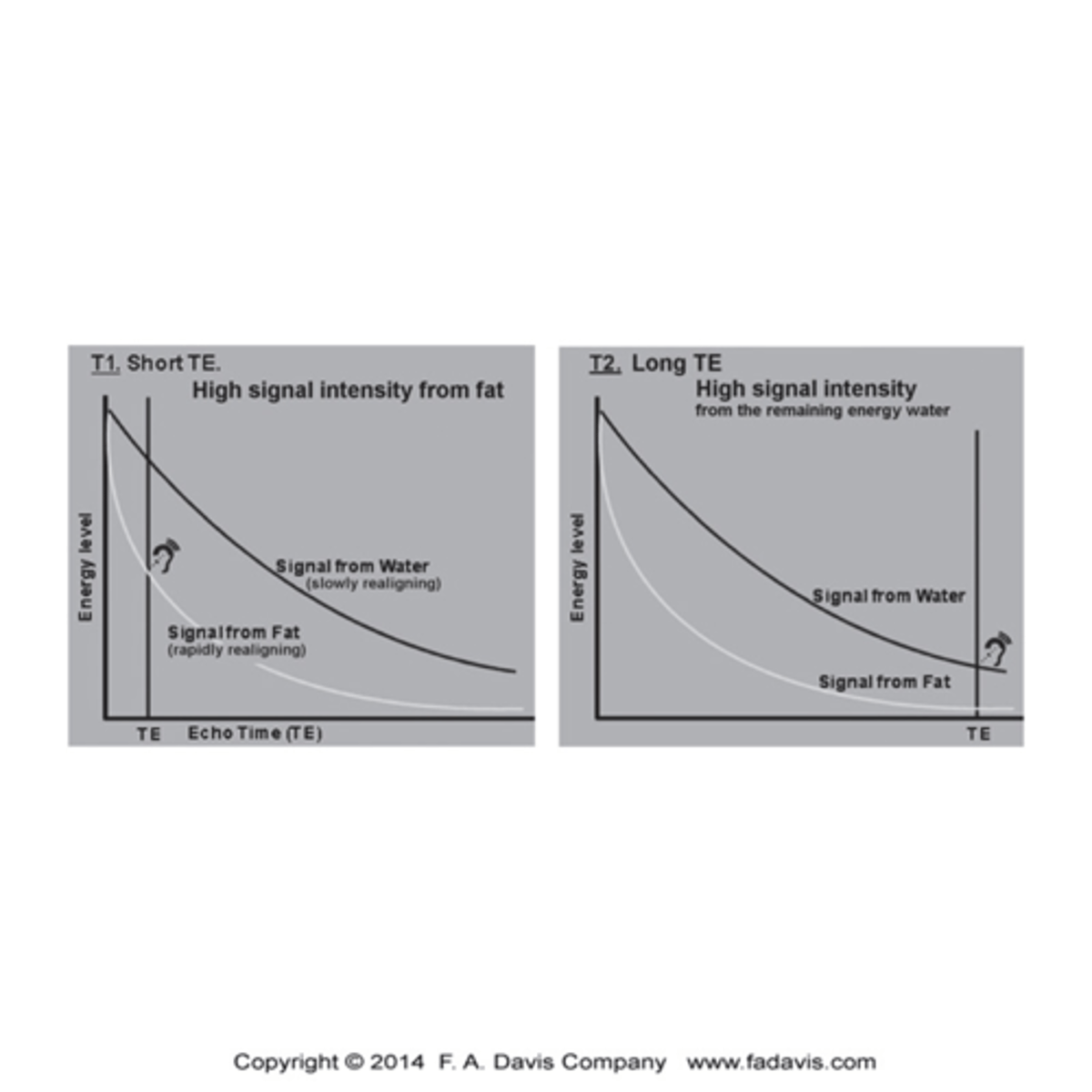
What is T2 sequence?
- Make the signal form water the brightest,
- Signal is measured late, those reluctant to give up energy are imaged, and water is slow (high signal intensity) and fat is quick (low signal intensity)
- This sequence is most valuable for identifying pathology that has a component of edema or inflammation
*ALL ABOUT H2O
What does the term protocol refer to?
Refers to combination of sequences performed during an MRI procedure for the body part being examined.
The combinations depend on the body part and the suspected pathology
What are the two most important parameters for creating contrast in the images?
- TE (time to echo)
- TR (Time to repetition)
What is SE (spin echo)?
The SE is characterized by a 90 degree RF pulse flip, followed by T1 relaxation and T2 decay, aided by a 180 degree re-phasing pulse
What is GRE (gradient echo)?
GRE is very different; it is characterized by the RF only partially flipping the magnetic vector (between 0 - 90).
- Advantage is fast image acquisition, high resolution and thin slices, and high contrast between fluid and cartilage
What are the two types of weighted images used in MRI?
SE (Spin echo)
GRE (gradient echo)
What is TE (time to echo)?
TE is the time in which the echo is captured
TR is the time at which the RF pulse is repeated to again displace the protons
What do the ABCDs Stand for?
- Alignment/Anatomy
- Bone signal
- Cartilage
- eDema
- Soft Tissues
What is the contrast material used in MRI with contrast?
Includes a contrast medium, usually gadolinium based
What is the contrast material used in MRI Arthrography?
Inject diluted gadolinium into a joint to distend the joint, and highlight tears of capsule
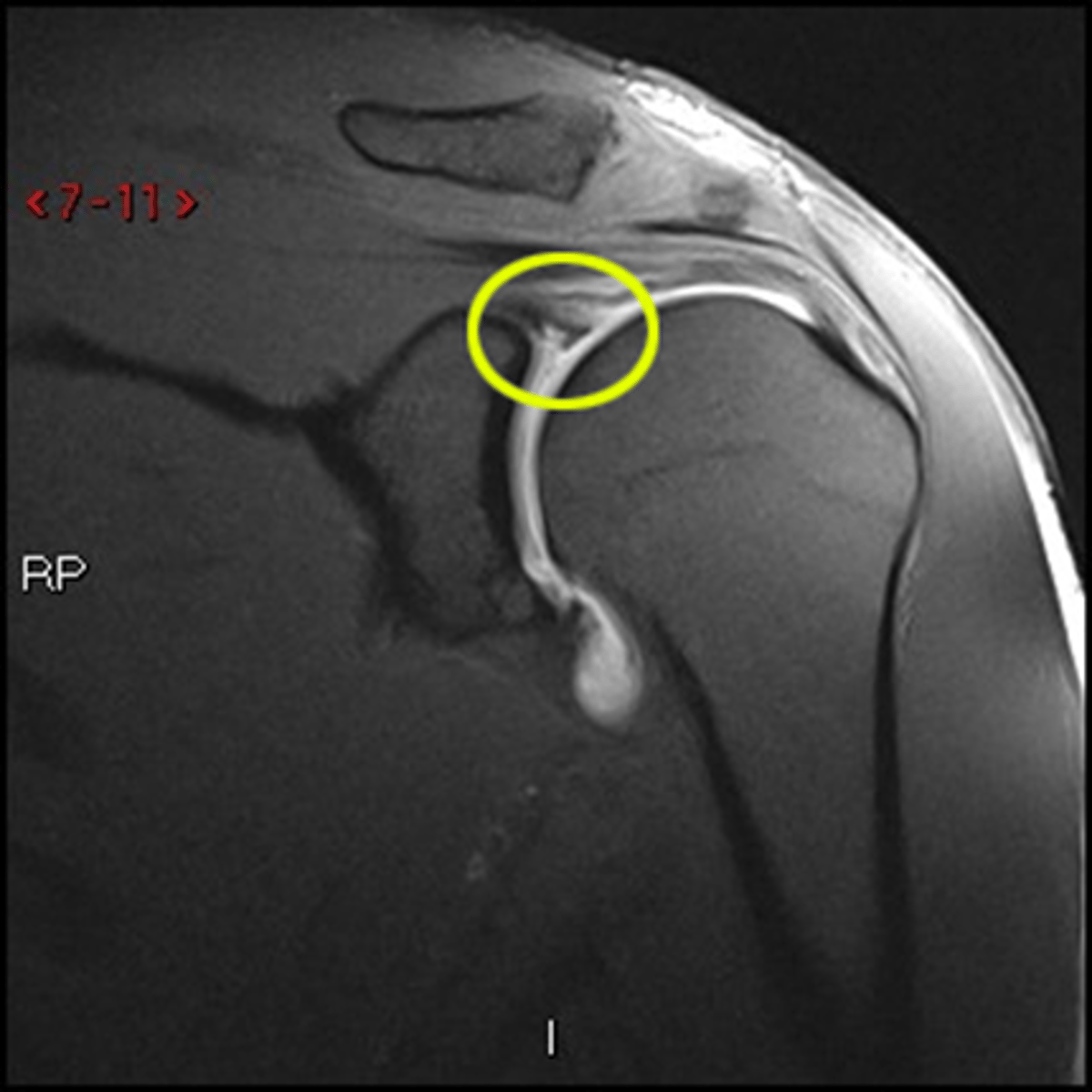
What is the contrast material used in MRI Myelography?
It is non-invasive with no contrast, sequences are used for the CSF (spinal stenosis)
Intensity of MRI signals are recorded as a _____ scale, High intensity signal is _____ and low signal intensity is _______?
Gray; Bright (White); Dark (Black)
What are some low signal intensity and high density structures?
- Cortical Bone
- Ligaments and Tendons
What are some high signal intensity and low density structures?
- CSF and Synovial Fluid
- Fat and Yellow Bone marrow
What are the different factors that tissue contrast is based on?
- Difference in T1 and T2 sequences
- Proton (H) density
- Difference used in protocols to employ the contrast for different tissues
What are the 3 factors under Alignment/Anatomy?
- General Skeletal Architecture
- General contour of bone
- Alignment of Bones to adjacent bones
What are the 3 factors under Bone Signal?
- General Bone Density
- Textural abnormalities
-Local Bone Density Changes
What are the 3 factors under Cartilage?
- Joint space width
- Subchondral bone
- Epiphyseal Plates
What are the advantages of MRI?
- Excellent resolution of all soft tissue
- No ionizing radiation
- Sensitive to detect change in bone marrow-tumor, stress fracture, avascular necrosis
What are the structures under Soft Tissues?
Muscles, Fat pads and lines, Joint capsules, Periosteum, Miscellaneous
What are the disadvantages of MRI?
- Poor imaging of bone which has water content
- Expensive
- Time consuming
- Claustrophobic for patients
What are the Contraindications for of MRI?
- Cardiac pacemakers
- Ferromagnetic intracranial aneurysm clips
- Metal foreign body in eye or orbit
- Orthopedic hardware
- Iron in pigments of tatoos
- Cochlear implants
- Fetus during pregnancy
- Allergy to gadolinium or risk of nephrogenic fibrosis