PLN203 - endocrine
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
endocrine system regulates
growth
development
reporduction
uses chemical messangers to relay information and instructions between cells
what is the largest endocrine oragin
GI tract
Hypothalamus hormones
ADH
oxytocin
regulatory hormones
Pituitary gland
anterior lobe
ACTH
TSH
GH
PRL
FSH
LH
MSH
Posterior lobe
Oxytosin and ADH
Penal Gland hormone
melatonin
circadian rhythm
inhibiting reproduction
free radical protection
Parathyroid glands
PTH
parathyroid hormone
Thyroid hormones
thyroxine T4
triodothryonine T3
Calcitonin
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal Medulla
Epinephrine
Norephrine
Adrenal Cortex
cortisol
corticosterone
aldosterone
androgens
Pancreas hormones
insulin
Glucagon
Adipose tissue secretes
leptin
Direct communication
Exchange of ions and molecules between adjacent cells across gap junctions
transport cells required
Occurs between two cells of the same type
specialized and rare
moving to neighbor cells
Paracrine communication
uses chemical signals to transfer information from cell to cell within a single tissue
most common form of intercellular communication
Endocrine communication
endocrine cells release chemicals (hormones) into the bloodstream
alteration of metabolic activities in many tissues and organs simultaneously
Target cells
specific cells that possess receptors that are needed to bind and read hormonal messages
where hromones are aiming to act
Hormones
stimulate synthesis of enzymes or structural proteins
increase or decrease the rate of synthesis
turn existing enzyme or membrane channel on or off
can act to stimulate a cascade within a cell to change protein synthesis in a cell
Synaptic communication
occurs across synaptic clefts
chemical message is neurotransmitter
limited to specific area
Classes of hroomones
AA derivatives
peptide derivatives
AA chains in fragments
lipid derivatives
has lipid components
distribution of hormones
can circulate freely or travel bound to special carrier proteins
AA derivitives
molecules structurally related to AAs
derivatives of tyrosine
Thyroid hormones
catecholamines
epi, norepi, dopamine
derivatices of tryptophan
serotonin and melatonin
Peptide hormones
AA chains
synthesized as prohormones
inactive molecules converted to active hormones before or after they are secreted
Glycoproteins
Proteins that are more than 200AA long and have carbohydrate side chains
TSH, LH, FSH
Short polypeptides/small proteins
all proteins secreted by hypo, heart, thalamus, pancreas, posterior pitutary
Short chain polypeptides
ADH (oxytocin and vasopressin)
small proteins
GH and prolactin
Glycoproteins
200+ AA long which have carbohydrate side chains
Thyroid stimulating hormone
leutinizing hormones
follicle stimulating hormone
Short chain polypeptides
only 9 AAs
ADH
Vasopressin and oxytocin
acts on nephron for the regulation of kidney fluid balance
reduces how often you have to pee
Small proteins
200 AAs ish
GH and prolactin
Lipid derivitives
Eicosanoids - 20 carbon fatty acid
Steroid hormones
derived from cholesterol
Eicosanoids
20 carbon Fatty acid
paracrine factors coordinate cellular activities and effect enzymatic processes in extracellular fluids
some have secondary roles as hormones
Second group is Prostaglandins
coordination of local cellular activities
converted to thromboxjnes and prostacyclins which have paracrine effects
Prostoglandins
second group of Eicosanoids
primarily involved in coordination of local cellular activities
in some tissues these are converted to thromboanes and prostacyclins which have pancrean effects
Leukotrienes
eicosanoids with a secondary role as hormones
Steroid hormones
cholesterol derivatives
released by
reproductive organs (androgens, estrogens, progestines)
cortex of adrenal gland (corticosteroids)
kidneys (calcitriol)
bound to transport proteins in the plasma so they are able to remain in circulation longer than free hormones
Free Hormones
remain functional less than an hour
diffuse out of bloodstream and bind to receptors on target cells
broken down and absorbed by cells in the liver and kidneys
broken down by enzymes in the plasma or intersitial fluids
Distribution of thryoid and steroid hormones
remain in circulation longer because they are bound
enter the bloodstream
99% will attach to special transport proteins
Albumin binds these hormones
Albumin
hormone binding agent that transports hormones through the blood
Hormone receptor
the part of a protein molecule that binds strongly to a molecule
responds to several different hormones which are similar in shape and side
this is why supplements work by mimicking hormones to bind receptors and trigger the cascades
the presence or absense of these is what determines hormone sensitivity
Up and downregulation of receptor numbers
when there is too much of a hormone there will be less receptors making the cell less sensitive to the hormone
when there is too little there will be an increase in the number of receptors making the cell more sensitive to the small amount of the hormone
Leptin and up and down regulation
the issue isnt that there is a deficiency in leptin it is that cells have downregulated the receptors that are meant to trigger a response to leptin meaning that cells are less responsive to the present leptin
Catecholamines and peptide hormones (receptors)
not lipid soluble
unable to penetrate plasma membrane
must bind to an extracellular receptor to trigger a cascade that can change transcription and translation
Eicosanoids and plasma membrane receptors
lipid soluble
diffuse readily across the plasma membrane to each receptor proteins that are on the innner surface of plasma membrane (intracellular receptors)
First and second messangers
bind to receptors in the plasma membrane
cannot have direct effects on the activities inside the target cell
intracellular intermediary to exert effects on the cell
First messanger
leads to a second
can act as an enzyme activator, inhibitor, or cofactor
may or may not want the doors to be open
- feedback with multiple doors to open and close
results in change in rates of metabolic reactions
Main second messangers
Cyclic-AMP (cAMP)
Adenosine mono phosphate
ATP derivitive
Cyclic-GMP (cGMP)
GTP derivative
Calcium Ions
Ca++
Amplification process
binding of a hormone to a receptor
triggers a cascade throughout the cell by releasing thousands of second messangers in the cll
magnifies the effect of the hormone on the target cell
DOWN regulation of hormone receptors
presence of a hormone triggers a decrease in the number of hormone receptors
when levels of a hormone are high the cells become less sensitive to them
UP regulation of hormone receptors
absence of hormone triggers an increase in the number of hormone receptors
when levels of particular hormones are low, cells become more sensitive to them
What substance activates protein kinases and thus acts as a secondary messanger?
A. insulin
B. ACTH
C. Epinephrine
D. c-AMP
E. two of the above
G-protein
enzyme complex that is linked to a membrane receptor
involved in the link between the first and second messengers
G proteins and cAMP
adenylate cyclase is activated when a hormone binds a receptor at the membrane surface and creates a change in the concentration of second mesanger cAMP in the cell
this increases the metabolic activity within a cell
Adenylate cyclase
is activate when the g-protein is activated through the binding of a hormone
it is responsible for converting ATP into cAMP (second messenger)
this allows the opening of ion channels and the activation of enzymes and metabolic activity within the cell
What hormones can bind to produce cAMP
Epinephrine and norephrine if they bind to a beta receptor
calcitonin
PTH
ADH, ACTH, FSH, LH, TSH
glucagon
Hormones binding to lower cAMP
bind to gprotein
cAMP is broken down by PDE creating AMP
this reduces enzyme activity within the cell
inhibitory effect
Epinephrine or norephrine if it acts on alpha cells
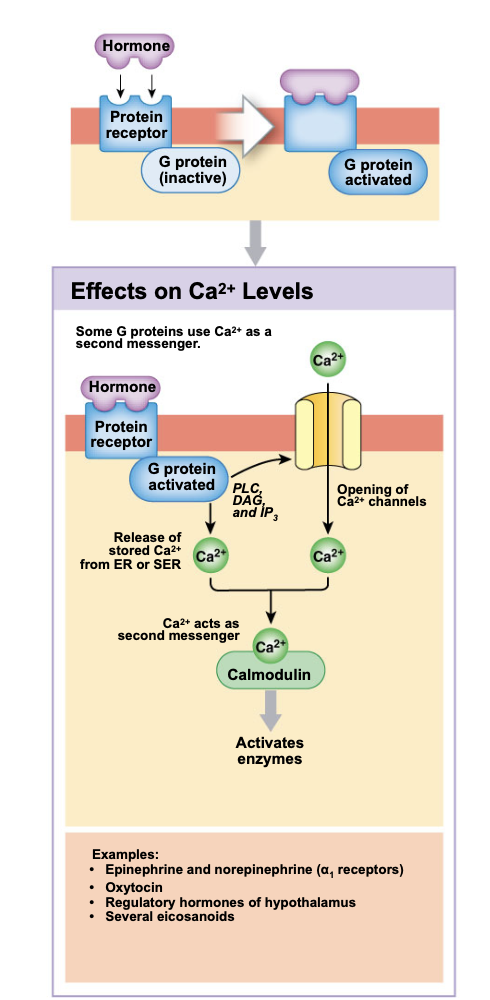
G-proteins and calcium ions downstream events
Activated g proteins trigger the openign of Ca++ ion channels in the membrane
releases calcium ions fron intracellular stores
activates PLC (phospholipase C)
triggers receptor cascade
DAG and IP3 are created from membrane phospholipids
may further activate more calcium ion channels through PKC
may activate calmodulin creating further changes in the cell
What happens when adenylate cyclase is acivated?
ATP is consumed
cAMP if formed
Hormones and intracellular receptors
alter the rate of DNA transcription in the nucleus
changing the patterns of protein synthesis
directly affects the metabolic activity and structure of the target cell
includes steroids and thyroid hormones
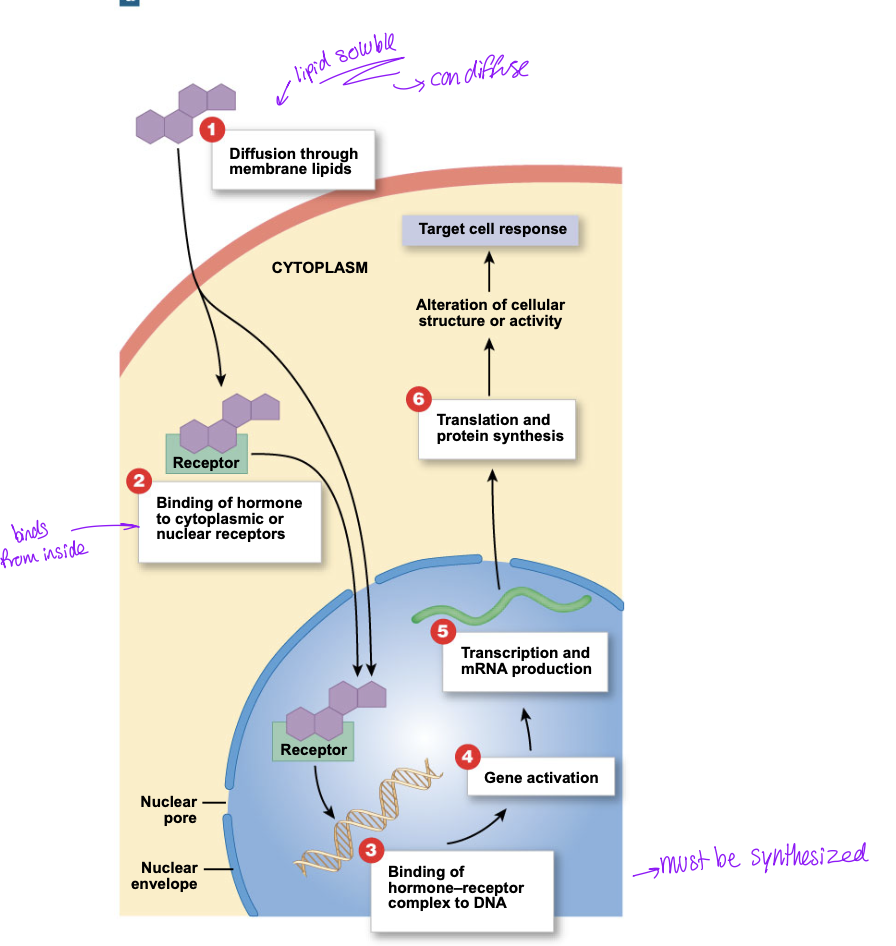
Steps of intracellular hormone binding
Diffusion through membrane lipids
lipid soluble so can diffuse through
binding of a hormone to a cytoplasmic or nuclear receptor
hormone receptor complex binds to DNA
gene activation
transcription of mRNA product
translation and protein synthesis
alteration of cellular structure or activity on target cell
Second option for intracellular hormone binding
hormone receptor complex must bind both a nucleus receptor and one at the mitochondria
the nucleus will continue in to bind DNA, alter transcription of mRNA, synthesis proteins and alter the structure of activity
the mitochondria hormone receptor complex will increase the production of ATP which is required to power the target cell responses by providing cell energy
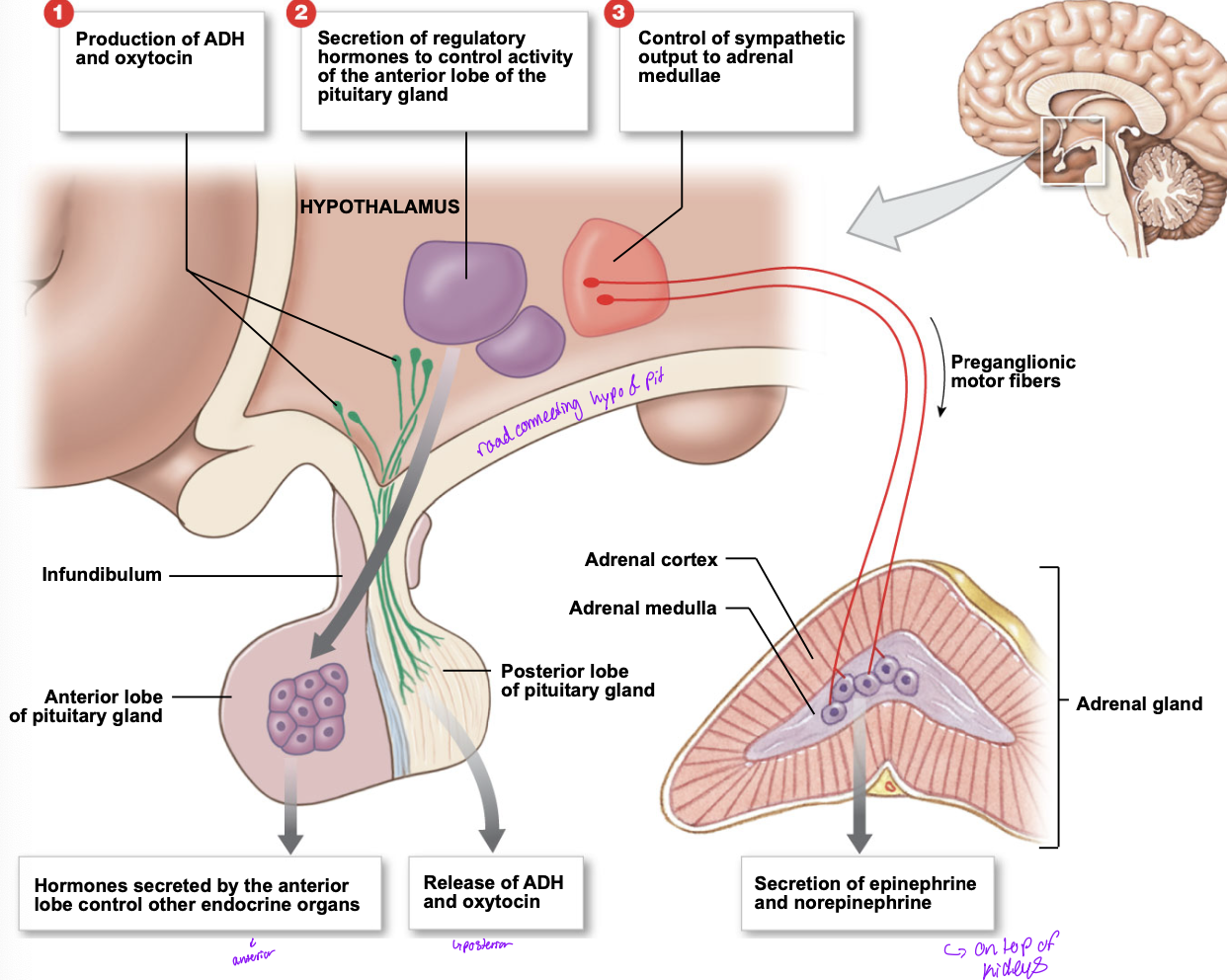
3 mechanisms for hypothalamic control over endocrine function
production of ADH and oxytosin
hypothalamus acts directly onto the posterior lobe of the pituirary gland
Secretion of regulatory hormones to control the activity of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
hormones secreted by anterior lobe controle other endocrine organs
control of the sympathetic output to adrenal medullae
secretion of epinephrine and norephtine
Neuroendocrine reflexes
pathways including both neural and endocrine components
commands issued by changing
amount of hormone secreted
pattern of hormone release
hypothalamic and pituitary hormones released in sudden bursts
frequency changes the response of target cells
Pituitary gland location and structure
aka hypophysis
dural sheet locks it into position
isolates it from the cranial cavity
hangs inferior to hypothalamus
connected by the infundibilum
Pituitary gland hormones
releases 9 important peptide hormones
hormones bind to membrane receptors
use cAMP as a second messanger
what are the subsets of the anterior lobe
pars tuberalis
pars distalis
other put hormones
pars intermedia
secretes MSH
Anterior lobe of the pituitary
aka adenohypophysis
hormones turn on endocrine glands or support other organs
split into 3 regions
pars distalis
pars tuberalis
pars intermedia
Hypophyseal portal system
median eminence
swelling near attachment of the infundibulum
where hypothalamic neurons release regulatory factors
go into intersital fluids through fenestrated capillaries
window into capillaries of the portal system in pituitary
Portal Vessels
BV link two capillary networks
whole complex is a portal system
ensures that regulatory factors reach their target cells before entering the general circulation
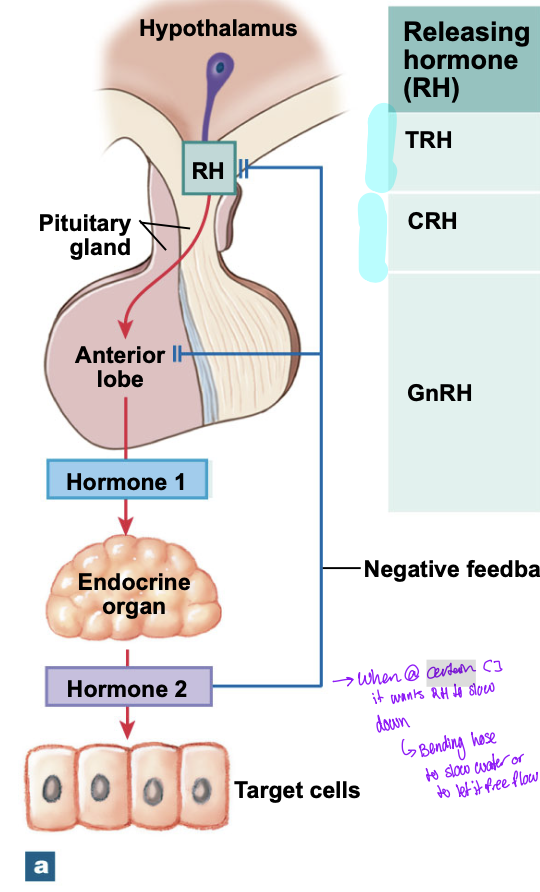
two classes of hypothalamic regulatory hormones (acting on anterior lobe)
RH
stimulate the synthesis and secretion of one or more hormones at the anterior lobe
IH
prevents the synthesis and secretion of hormones from the anterior lobe
Rate of secretion is controlled by negative feedback
Feedback control of the endocrine system
RH from hypothalamus goes to anterior lobe → releases hormone 1 → acts on endocrine organ → releases hormone 2 → acts on target cells
Hormoen 2 will also loop back up to the anterior lobe and the hypothalamus to prevent the syntehesis of more hormone 1
blocking its own production
when it reaches a certain concentration it wants the RH to not over produce
Examples of endocrine feedback
TRH (RH) → TSH (hormone 1 from pituitary) → thyroid gland (endocrine target organ) → thyroid hormones (hormone 2 from target organ)
CRH (RH) → ACTH (Hormone 1 from pituitary) → adrenal cortex (target organ) → glucocorticoids (hormone 2 from target organ)
Feedback of endocrine system with releasing and inhibition hormones from hypothalamus
GH-RH (hypo) → anterior lobe → GH → Liver → Somatomedins → growth of muscle and other tissues
GH-IH blocks the production of GH from the anterior lobe
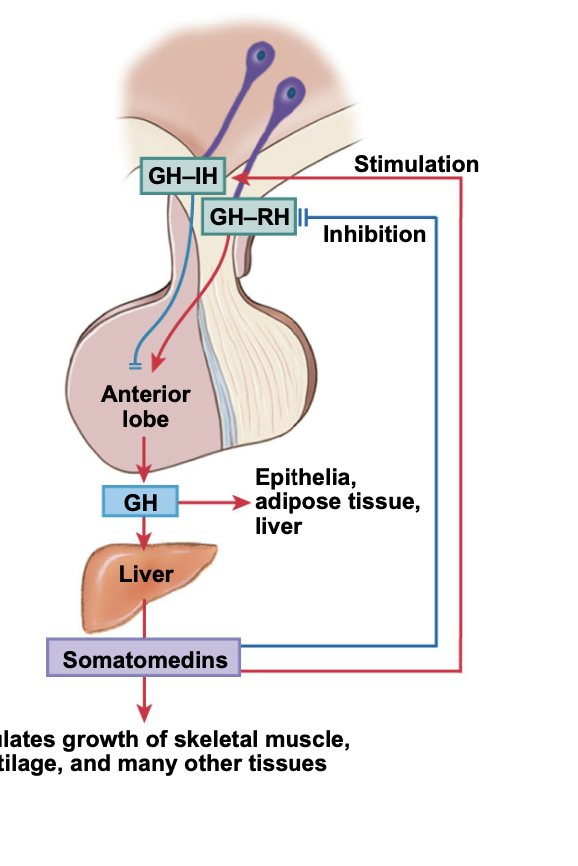
If the median eminence of the hypo was destroyed the hypo could no longer control the secretion of
TSH, ACTH, P…
Posterior lobe
neurohypophysis
containes unmyelinated axons of th ehypothalamic neurons
supraoptic and paraventricular neuclei manufactor
ADH (Acts on kidneys)
OXT (acts on smooth muscle in males and uterine smooth muscles in females)
Change in blood osmotic pressure would more affect the secretion of
ADH
want to produce more ADH to stop the body from urinateng as much (water retention)
thyroid gland
lies anterior to the thyroid cartilage of the larnyx
consists of two lobes connectd by narrow isthmus
thyroid follucles
hollow spheres lined by cuboidal epothelium
cells surround follicle cavity that contains viscous colloid
surrounded by capillaries that deliver nutrients and regulatory hormones and accept secretory produces and metabolic wastes
Thyroglobulin
globular protein made by the thyroid
synthesized by follicle cells
secreted into colloid of thyroid follucles
molecules contain amino acid tyrosine
Thryoxine
T4
Tetraiodothyronine
contains 4 iodine ions
Triiodothronine
T3
contains 3 iodine ions
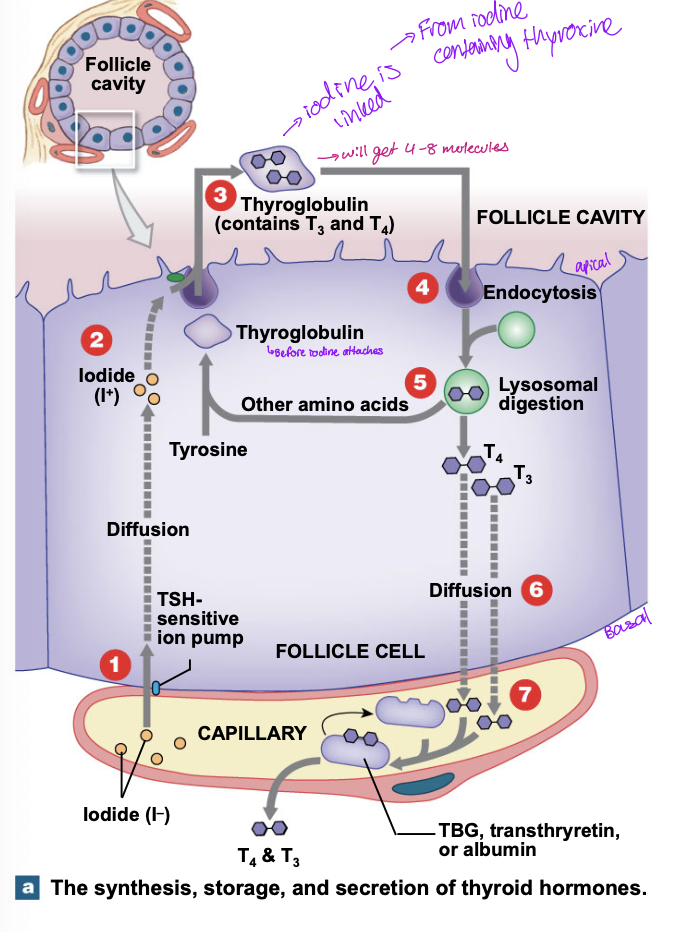
Where does the chemical reaction between thyroglobulin and iodine take place
in the lumen of the thryoid follicle
Production of thyrpod hormones
diffuseion of iodine through a TSH sensitive ion pump
Iodine diffuses through to the apical surface of the folicle cell
tyrosine portion of thyroglobin binds the iodine atoms
iodine containing thyrosine molecules links to form T3 and T4
follucle cells move the thyroglobin from the follicles by endocytosis
lysosome cells break down thryoglobulin and the AA and thyroid hormones enter the cytoplasm
released t3 and t 4 diffuse from follicle cell into bloodstream and bind transport proteins
Regulation of thyroid secretion
Homeostasis = normal T3 and T4 concentrations, normal body temp
Homeostasis disturbed (lower T3 and T4 in blood or low body temperature)
hypo releases TRH to act on the anterior lobe
Anterior releases TSH to act on thyroid gland to release T3 and T4
homeostasis restored
TBG (Thyroid binding globulins)
plasma proteins that bind abotu 75% of T4 and 70% of T3 entering the bloodstream
Transthyretin (thryoid binding prealbumin-TBPA) and albumin
binds the remaining thyroid hormones
0.3% of T3 and 0.03% of T4 are unbound
TSH
absence causes thyroid follicles to becone inactive
neither synthesis or secretion occurs
binds membrane receptors
activates key enzymes in thyroid hormone production
Marty feldman
graves disease
effects the thyroid gland
Functions of thyroid hormones
enters target cells by transport system
affect most cells in body
bind to receptors in:
cytoplasm
surfaces of mitochondria
nucleus
In children essential to normal development of
skeletal, muscular and nervous system
Calorigenic effect
cell consumes more energy resultin in increased heat generations
cell consumes too much energy
Responsible for strong, immediate and short lived increase in rate of cellular metabolism
dysfunction of thyroid can mess with body fitness
Effects of thyroid hormones
elevates rates of oxxygen consumption and energy consumption - raises body temperature
increases heart rate and force of contraction; generally results in rise in blood pressure
increases sensitivity to sympathetic stimulation
maintains normal sensitivity of respiratory centers to changes in oxygen and CO2 concentrations
stimulates RBC formation and thus enhances oxygen delivery
stimulates activity in other endocrine tissues
accelerates turnover of minerals in bone
Thyroid C cells and calcitonin
c (clear) cells aka parafollicular cells
produce calcitonin (CT)
helps regulate concentrations of Ca++ in body fluids
inhibits osteoclasts which slows the rate of Ca++ release from bone
stimulates Ca++ excretion by the kidneys
Thyroid hormone action involves all steps except
A. binding to hormone receptor in plasma membrane
B. specific transport into target cell (can diffuse)
C. binding to a cytoplasmic receptor protein
D. activation of specific gene
E. avation of mitochondria
Goitrogens
compound metabolized to thicyanate and blocks thyrodial uptake of iodine
some species of millet and cruciferous vegetables also contain goitrogens
soybean isoflavones may inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis
most goitrogens are not of clinical importance unless they are consumed in large amounts and there is a coexisting iodine deficiency
Iodine functions
essential for T3 and T4
T4 is abundant in blood
T3 is the active form of hormone
conversion of T4 to T3 requires selenium
Thyroid function wihtout sufficient dietary iodine
there is no negative feedback from T3 and T4 resulting in excess TSH being released into the thyroid and creating a goiter
cretenism
hyperthyroidism
Parathyroid glands
4 glands
embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
only 1.6g
PTH is produced
produced by parathyroid cells in response to low Ca++ concentrations
calcitonin antagonist
wants to release more Ca++ from blood
PTH
produced in parathyroid chief cells
responds to low Ca++ in blood
takes Ca++ from the bones
acts on the nephron distal conv tube to enhance Ca++ reabsorption to reduce the urinary losses
Effects of PTH
stimulates the osteoclasts and inhibits osteoblasts
higher turnover of minerals and more release of Ca++ from bone
reduction in the rate of calcium deposition in the bone
Enhances reabsorption of Ca++ at the kidneys reducing the urinary losses
distal convoluted tubule
stimulating formation and secretion of calcitriol by the kidneys
effects complement or enhance PTH
also enhances Ca++, PO4- - - absorption by the digestive tract
Regulation of rising levels of blood calcium
thyroid produces calcitonin → increases the excretion of calcium by the kidneys and deposition of calcium into the bones → homeostasis restored and the calcium levels decline
Regulation of declining Calcium ion levels in blood
Parathyroid produces PTH → acts to activate osteoclasts and limit osteoblast usage + also increases the reabsorption of Ca from the kidneys + increased calcitriol production causes Ca reabsorption by digestive system → blood homeostasis is restored
Normal levels 8.5-11 mg/dL
Follicular epithelium
produces T3 and T4
targets most cells
for energy utilization, o2 consumption, growth and development
stimlated by TSH from the anterior lobe of pituitary
C cells
Calcitonin
bone, kidneys
decreases Ca++ concentrations in the body fluids
stimulated by elevated blood Ca++ levels; actions are opposed by PTH
Adrenal Glands
lie on the superior border of each kidney
divided into
Superficial adrenal cortex
inner adrenal medulla
Adrenal cortex
stores lipids especially cholesterol and fatty acids
manufactures steroid hormones (corticosteroids)
Inner adrenal medulla
secretory activities controlled by sympathetic division of ANS
fight or flight
Production of epinephrine and norepinephrine
metabolic changes which persist for several minutes
Adrenal cortex subregions
zona glomerulosa
zona fasciculata
zona reticularis
Zona glomerulosa (adrenal cortex outer region)
mineralocorticoids
aldosterone