Medicine - Dental Cardiology
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
the left heart sends blood to…?
the right heart sends blood to…?
left → systemic
right → lungs
which component of the cardiac system do myocardial infarctions affect?
coronary arteries
which component of the cardiac system does cardiomyopathy affect?
myocardium
which component of the cardiac system do arrhythmias affect?
conduction system
which component of the cardiac system do regurgitation/stenosis endocarditis affect?
valves
there is a left and right coronary artery. which one covers more of the heart and therefore has larger effects if something’s wrong with it?
left (but both equally important)
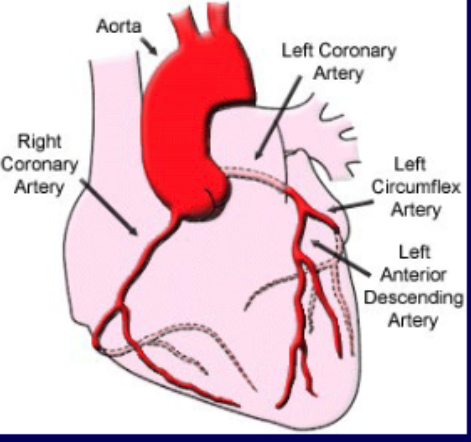
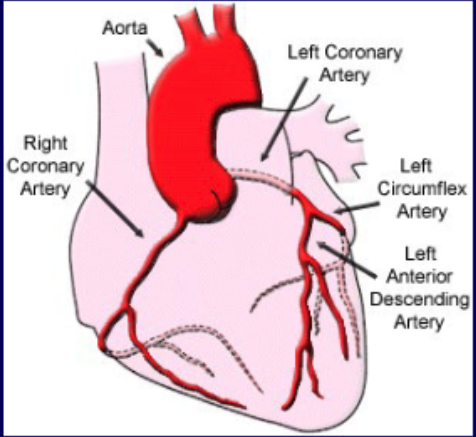
what coronary vascular territory is supplies by the left anterior descending a.?
Anterior wall and septum
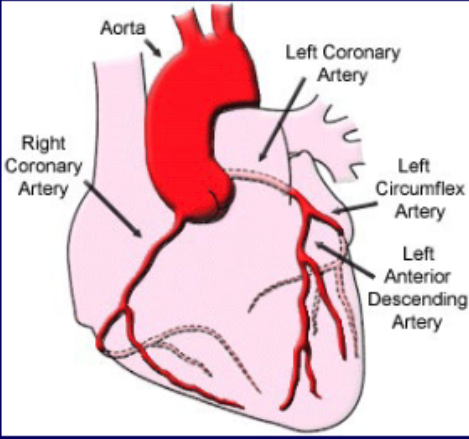
what coronary vascular territory is supplies by the left circumflex a.?
lateral wall
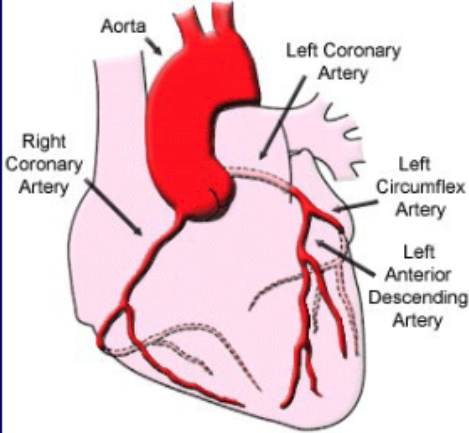
what coronary vascular territory is supplies by the right coronary a.?
inferior wall and right ventricle
atherosclerosis leads to…?
coronary artery disease (CAD)
70%+ blockage has hemodynamic effects
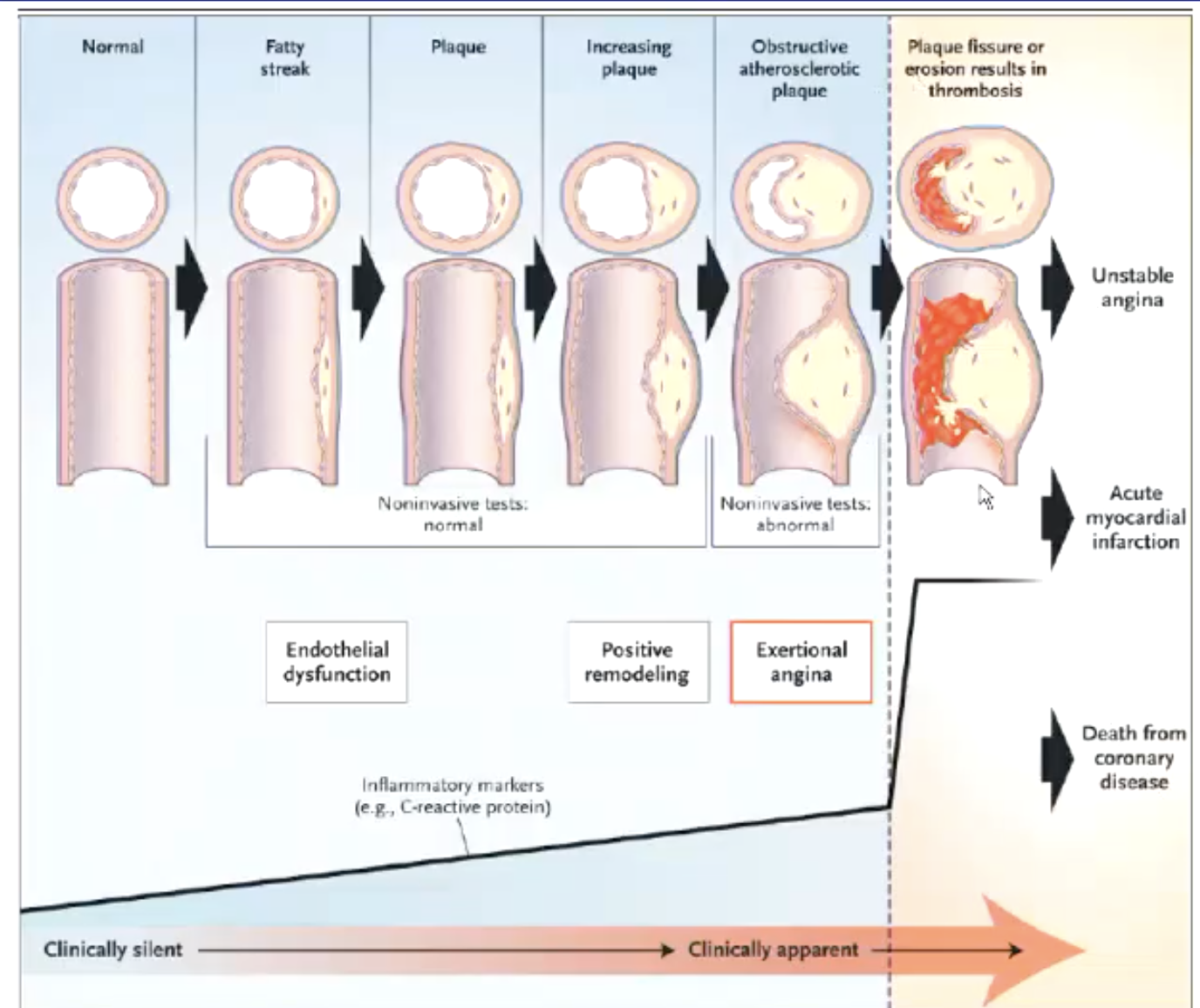
how do pts with atherosclerotic disease present?
chest pain aka angina (most common symptom)
t/f: chest pain or angina from cardiac heart pain can radiate to the jaw or may even be primarily located in the jaw
true
characteristics of chest pain/angina
does not move around
reproducable
pts describe as a discomfort (not a pain)
can radiate down left arm
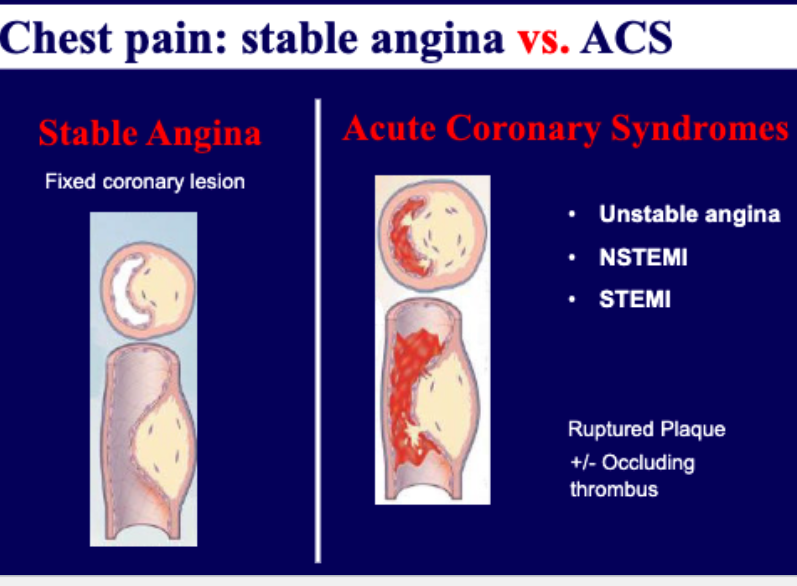
what is the difference between stable angina vs acute coronary syndromes?
stable → fixed coronary lesions
acute → ruptured plaque + occluding thrombus
unstable angina
NSTEMI/STEMI (myocardial infarction)
what are risk factors of developing atherosclerotic disease?
Age (M>45, F>55)
Hypertension
Hyperlipidemia
Tobacco use
Family History (M<55, F<65)
Diabetes
50 year old gentleman with hypertension and diabetes comes into your office for tooth extraction. During the procedure, he develops chest pain.
What are the proper steps of management for pts with acute chest pain?
1. Stop the procedure
2. Give sublingual nitroglycerin
3. Give aspirin
4. Transfer to Emergency Department/Call EMS
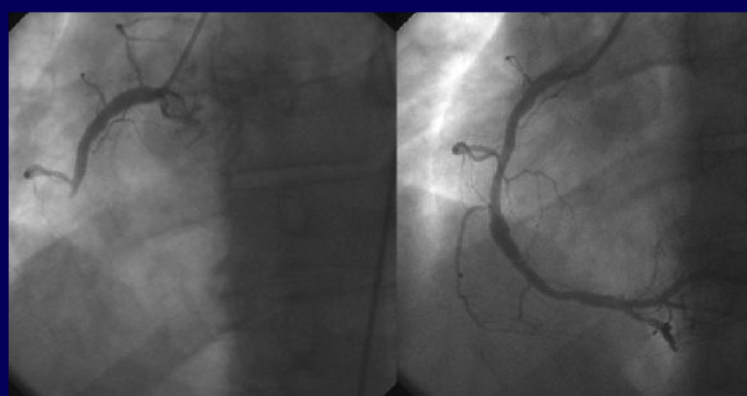
what procedure is performed to assess and treat myocardial infarctions?
cardiac catheterization (left image shows blockage, right is after being fixed there is blood downstream)
stenting
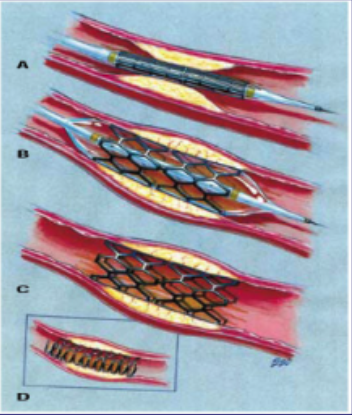
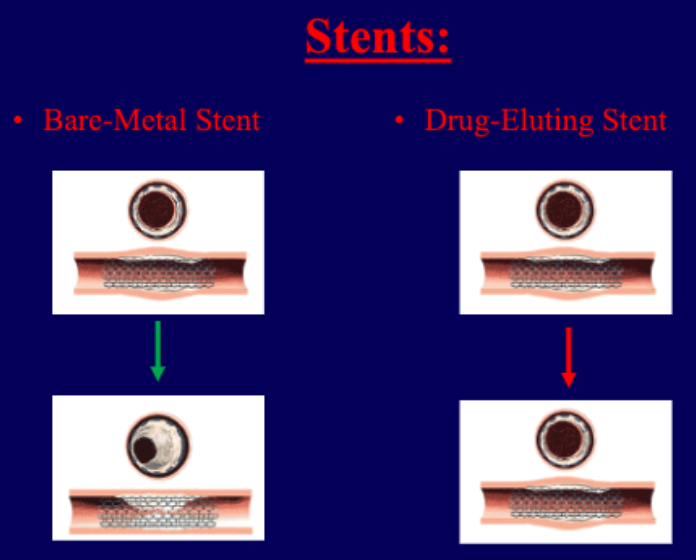
what are the types of stents used to treat myocardial infarctions?
bare-metal stent
can sometimes cause excessive wound healing that can block artery
drug-eluting
can prevent excessive wound healing but sometimes more likely to develop thrombus (anti-platelet meds needed)
50 year old patient returns to your clinic to have tooth extracted. He received a drug eluting stent for his myocardial infarction two months ago.
What is the best step to take?
A. Stop aspirin
B. Stop clopidogrel (Plavix)
C. Stop both aspirin and clopidogrel
D. Postpone tooth extraction
E. Extract the tooth without interruption of anti-platelet therapy and use local measures to control bleeding
E. Extract the tooth without interruption of anti-platelet therapy and use local measures to control bleeding
According to the ADA, what is the recommendation of pts on anti-coagulant and platelet management needing dental procedures.
for most patients, it is not necessary to alter anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy prior to dental intervention.
typical pt → no need to discontinue meds (use local measures to control bleeding)
procedure with high risk of bleeding → consult with pt’s physician
Uninterrupted dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin AND clopidogrel) fo Bare-metal stents should be done for at least how long?
Minimum 1 month
Uninterrupted dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin AND clopidogrel) fo Drug-Eluting Stents should be done for how long?
Minimum 12 months (newer DES may be able to tolerate 6 months)
t/f: Do not discontinue aspirin or other antiplatelet therapy without first discussing with the patient’s cardiologist.
true. aspirin and Clopidogrel (Plavix), Prasugrel (Effient), and Ticagrelor (Brilinta)
what are some anti-platelet agents used as medical therpay for coronary artery disease?
aspirin, Plavix, etc
what are some lipid-lowering agents used as medical therpay for coronary artery disease?
statins
what are some beta-blockers used as medical therpay for coronary artery disease?
“olol”: metoprolol, atenolol
what are some ACE-inhibitors/ARBs used as medical therpay for coronary artery disease?
“pril/sartan”: lisinopril, losartan
what are some nitrates used as medical therpay for coronary artery disease?
nitroglycerin
what are cardiomyopathies?
Abnormality of heart muscle function
Cardiomyopathies can result in …?
abnormal contraction, abnormal relaxation, or both
cardiomyopathy Clinically manifests as …?
congestive heart failure
what is the difference between ischemic cardiomyopathy vs non-ischemic cardiomyopathy?
ischemic
caused by heart attacks, CAD (coronary disease)
responsible for 50% of all heart failures
non-ischemic
caused by Hypertension, Valve disease, Genetics, Viral infection, Arrythmia, Alcohol, Infiltrative disease, Chemotherapy
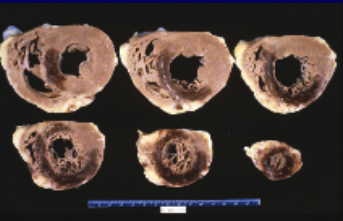
ischemic cardiomyopathy
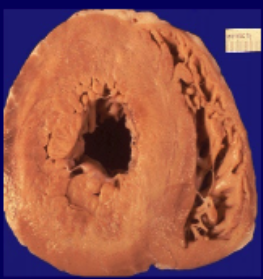
non-ischemic cardiomyopathy
what are things to consider when treating cardiomyopathies?
• Symptoms from volume overload: diuretics
• Prevent remodeling: beta-blockers, ace-inhibitors
• Devices: defibrillators, “resynchronization therapy”
t/f: Treatment of cardiomyopathies are tailored to the specific patient and the cardiomyopathy
true
A 76 year-old gentleman with a longstanding history of coronary artery disease and an ischemic cardiomyopathy presents for a planned procedure. He had been instructed to hold his aspirin by his cardiologist, but misunderstood and accidentally held all his medications.
You notice he wears flip-flops because he cannot wear his shoes because of swelling. He cannot speak full sentences because he is very short of breath, and when you recline the chair to begin the procedure, he sits upright because he cannot breathe properly
t/f: Heart failure is a chronic disease, often with a waxing and waning course. Patients will develop exacerbations with episodes of acute decompensated heart failure for various reasons
true
t/f: Patients in decompensated heart failure should undergo (nonemergent) procedures.
false. Patients in decompensated heart failure should not undergo (nonemergent) procedures and should be quickly evaluated and treated
how many leads are there when taking an electrocardiography?
12
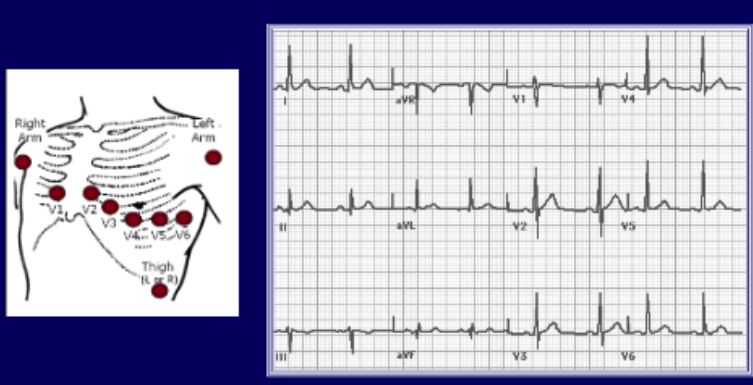
what information can we get from an EKG?
1. Rate & rhythm
2. Axis & intervals
3. Hypertrophy
4. ST-T abnormalities
what heart rate is classified as tachycardia?
HR > 100 beats per minute
what heart rate is classified as bradycardia?
HR < 60 beats per minute
what’s a normal heart rate?
60-100 bpm
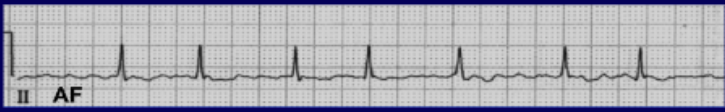
If you see the following on an EKG, what arrhythmia is the heart in?
• Lack of P waves
• Irregularity of R waves (irregularly irregular)
atrial fibrillation
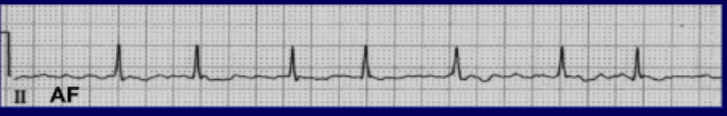
atrial fibrillation
• Lack of P waves
• Irregularity of R waves (irregularly irregular)
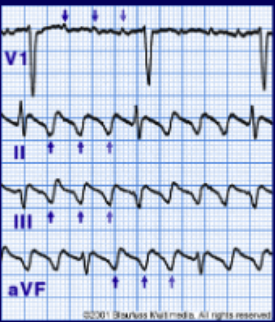
If you see the following on an EKG, what arrhythmia is the heart in?
saw-tooth
shaped P-waves
atrial flutter
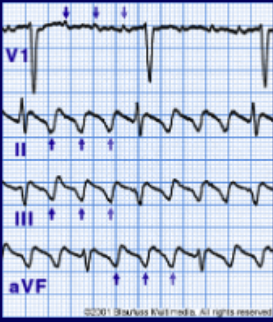
atrial flutter
saw-tooth shaped P-waves
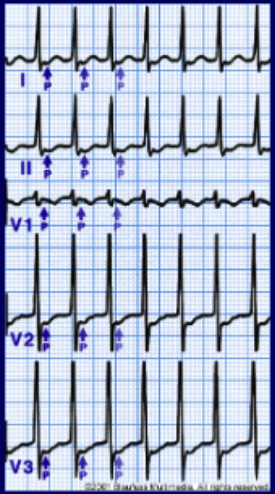
narrow complex tachycardia
narrow QRS complex
rhythm must be coming from atrium (supraventricular)
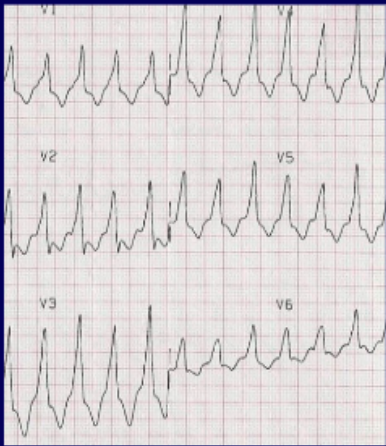
wide complex tachycardia
wide QRS complex
rhythm comes from ventricle (ventricular tachycardia)
t/f: arrhythmias coming from the ventricles are more life-threatening than those coming from atrias.
true
when reading an ECG, the QRS complex should be how long?
<120 ms (3 small boxes)
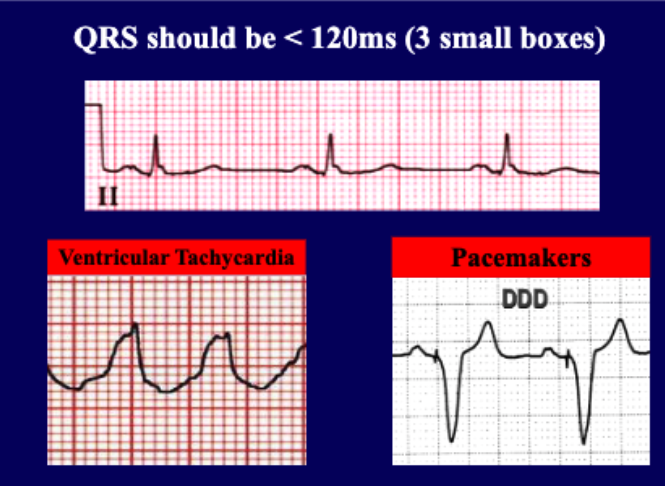
if you notice wide complex tachycardia, we should suspect what condition?
ventricular tachycardia
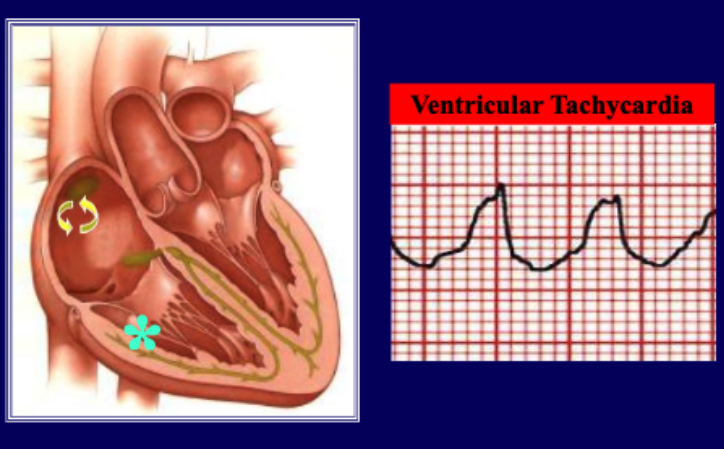
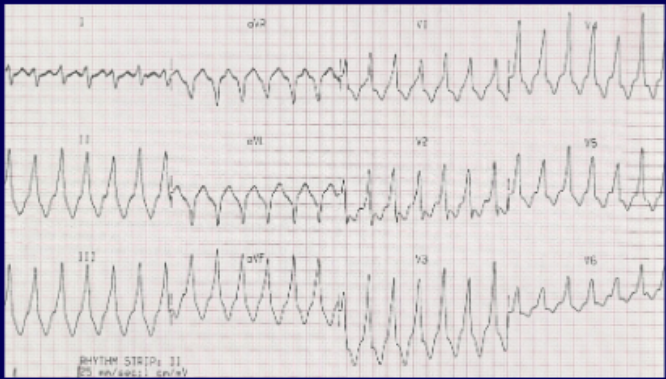
WIDE COMPLEX TACHYCARDIA
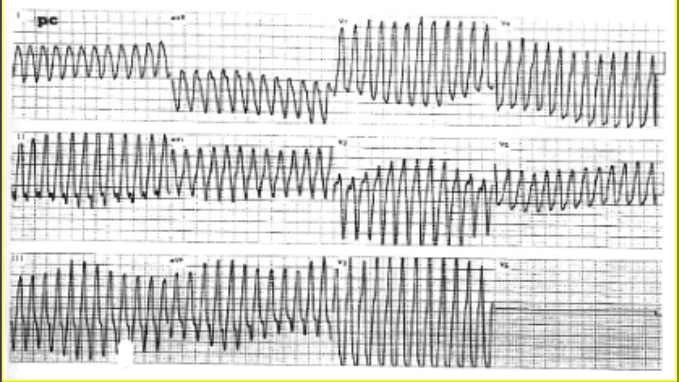
WIDE COMPLEX TACHYCARDIA
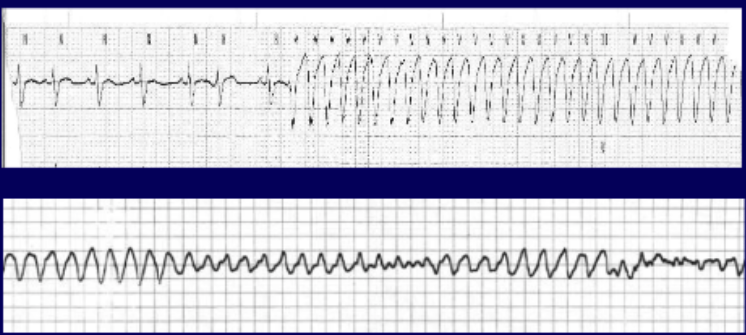
22 yo male basketball player with tooth fracture. He is rambling about nearly passing out at practice and his recent “decline in game”. Half listening, you figure you’ll quiet the excuses. You inject a subcutaneous anesthetic (the mixture contains epinephrine). He suddenly complains of: “racing heart rate and dizziness”. He looks diaphoretic, pale....then blacks out.
What should be done next? (tachycardia)
AED (shock, if advised)
transfer
in young athletes, what may herald an underlying cardiac condition?
pre-syncope or syncope
consider avoiding ________ if history suggests cardiac disease.
epinephrine
t/f: ventricular tachycardia from epinephrine is common.
false. very rare
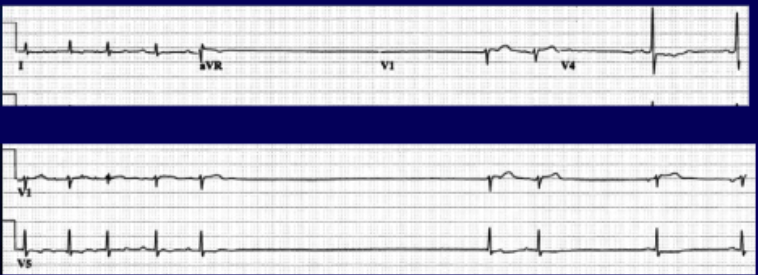
22 yo male basketball player with tooth fracture. He is rambling about nearly passing out at practice and his recent “decline in game”. Half listening, you figure you’ll quiet the excuses. You inject a subcutaneous anesthetic (the mixture contains epinephrine). He suddenly complains of lightheadedness. He is pale and intermittently alert before ultimately blacking out.
What should be done next? (bradycardia)
• STOP procedure for any pauses > 3 seconds or if heart rate is persistently less than 40.
• Transfer patient
• Transcutaneous pacing
74 year old gentleman sees you for a dental procedure that requires electrocautery. He had a ventricular tachycardia cardiac arrest 5 years ago during a heart attack, for which he has an ICD.
Does he need endocarditis prophylaxis prior to dental work for his ICD implanted 5-years ago?
No (not routinely recommended after 6 months)
Can electrocautery alter the ICD programing?
yes. Electrocautery can produce chatoic electric wave throughout body. ICD recognizes this and thinks pt is having heart attack and will shock the pt.
What must be done when working with electrocautery in a pt with an ICD?
• Put a magnet over the device and proceed with electrocautery freely.
• Proceed with cautery, but use short bursts (< 30 seconds). → not super recommended
• Delay procedure until you’ve spoken to patient’s cardiologist
what disables ICD shocks?
magnets
In some ICDs, magnet over the device > 30 seconds permanently disables it
If magnet is used, device should be interrogated before monitoring discontinued
Some dental chairs contain magnets located in the headrest. If the pacemaker or defibrillator is programmed not to respond to a magnet, patients may sit in these chairs. If the implanted device is programmed to respond to a magnet and the magnet power is greater than or equal to _____ — patients should not sit in these chairs as device function/programming may be affected
10 Gauss (1 mTesla)
t/f: Typically pacemakers do not need to be turned off before electrocautery, but it is better to consult with the cardiologist
true
what is valvular heart disease: stenosis?
scar tissue forms around aortic valve
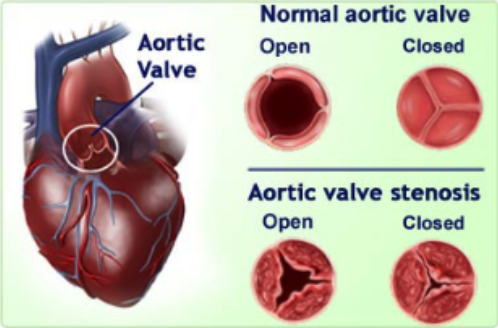
A cardiac murmur represents turbulent blood flow usually from …?
a stenotic or regurgitant valve
An _________ can be helpful in evaluation, as distinguishing between an innocent murmur and a pathological murmur can be difficult for even well trained physicians
echocardiogram
what kind of problem are valve diseases? what is the treatment?
mechanical problem
treatment = surgery
what are the 2 types of prosthetic valves?
mechanical
last longer (15+ years) → younger people
requires lifelong anticoagulation (coumadin, warfarin)
most commonly used
bioprosthetic (pig or cow)
does not need anticoagulation
does not last long (10 years) → older people

what are some prosthetic valve complications?
Thrombosis
Thromboembolism
Endocarditis
Peri-valvular leak
Hemolysis
56 year old female with a mechanical mitral valve presents with “bad gingivitis.” She has a procedure with you scheduled for next week that will involve tissue removal. She also wants you to do a “thorough cleaning”. She is on Coumadin and her INR today is 3.5.
what is the INR goal for all mechanical valves?
2.5 to 3.5
who are low-risk patients for mechanical valve thrombosis?
Bi-leaflet aortic valve AND no history of stroke, atrial fibrillation, left ventricular dysfunction or hypercoagulable state
who are high-risk patients for mechanical valve thrombosis?
• Mechanical valve in Mitral Position
• More than one mechanical valve
for low risk pts, what guidelines should be followed with warfarin and heparin use?

for high risk pts, what guidelines should be followed with warfarin and heparin use?
heparin bridge

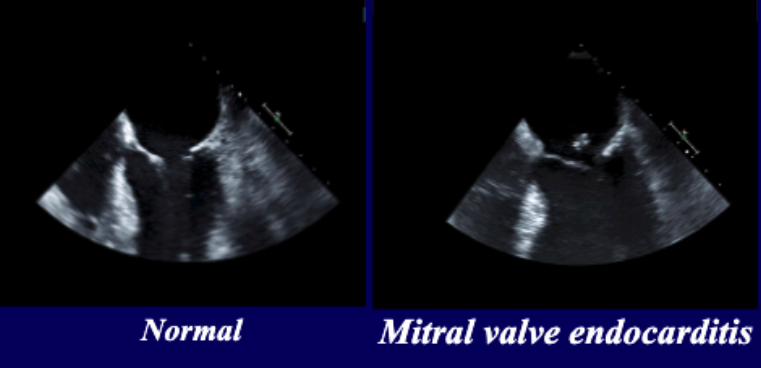
what are risk factors for endocarditis?
• Structural Heart Disease
• Prosthetic heart valves
• IV drug use
• HIV+
• Hospital-Acquired
• Hemodialysis
• Pacemakers
• Poor dental hygiene
• Prior history of endocarditis
% of all endocarditis cases have preexisting structural abnormality
75%
what are typical organisms that cause endocarditis?
• Strep. viridans
• Staph. aureus
• Strep. bovis
• Enterococcus
• HACEK group
what are clinical manifestations of endocarditis?
• Fever (most common)
• Anorexia, malaise, weight loss, night sweats (in subacute cases)
• Murmur
• Heart failure
• Conduction abnormalities
how do we diagnose endocarditis?
2 major duke Criteria
or
1 major + 3 minor duke criteria
what are major duke criteria for diagnosing endocarditis?
Persistently positive blood cultures with a
typical micro-organism
Evidence of endocardial involvement
Echocardiographic evidence of vegetation
New murmur consistent with valvular regurgitation
what are minor duke criteria for diagnosing endocarditis?
• Fever
• Single positive blood culture
• Predisposing condition (IV drug use, cardiac abnormality)
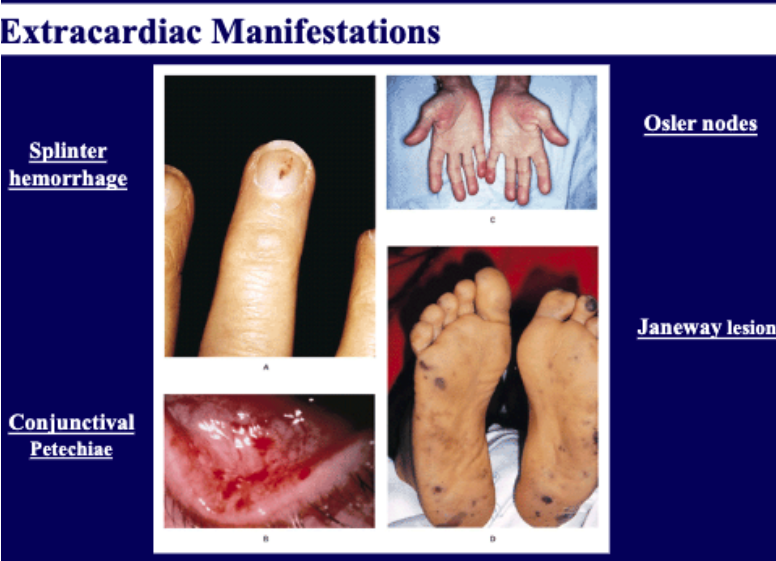
• Embolic event (embolic stroke, pulmonary infarcts, renal infacts, conjuctival hemorrhages, Janeway lesions)
• Immunologic phenomenon (Glomerulonephritis, Osler’s node, Roth’s spot)
what are some extracardiac manifestations of endocarditis?
t/f: Endocarditis is a common disease
false. uncommon
t/f: Endocarditis more likely to result from random daily activity bacteremia than from dental procedure
true
what are some indications for antibiotic prophylaxis?
• Prosthetic valve or material
• Previous endocarditis
• Congenital HD (like cyanosis)
• Cardiac transplant with valvulopathy
chest pain is a symptom of …?
myocardial infarction
t/f: Do not interrupt aspirin and antiplatelet agents in patients who recently received coronary stents
true
t/f: Do not interrupt anticoagulation in patients with high risk mechanical valves – discuss procedural planning with cardiologist
true
t/f: Most patients do not need endocarditis prophylaxis. However, you MUST know the four groups of patients where it is recoemmended
true
• Prosthetic valve or material
• Previous endocarditis
• Congenital HD (cyanotic)
• Cardiac transplant with valvulopathy