Acute Leukemias
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
in order to call something leukemia how many blasts should there be in the bone marrow
~20%
Leukemias (All and Aml) only affect what cell type
blasts
M0
myeloblastic with minimal maturation
What flow markers are seen in M0
CD33/34+, CD13
in order to differentiate M0 from M1you need to order
immunophenotyping
No auer rods seen
<3% blasts MPO/SBB +
5% AML
Affects adults
CD13, 34, 33+
poor prognosis
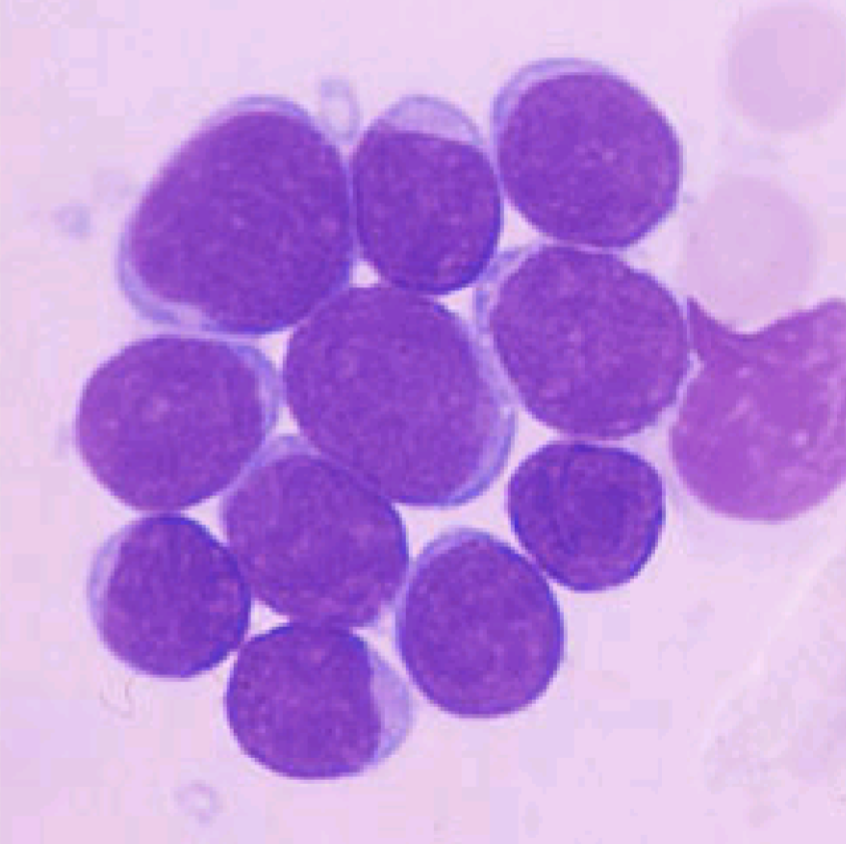
M0- AML
M1
Myeloid Leukemia w/o maturation
WBC: L, NL, H
Low Hgb/Hct
Few aurer rods
10% of the AML
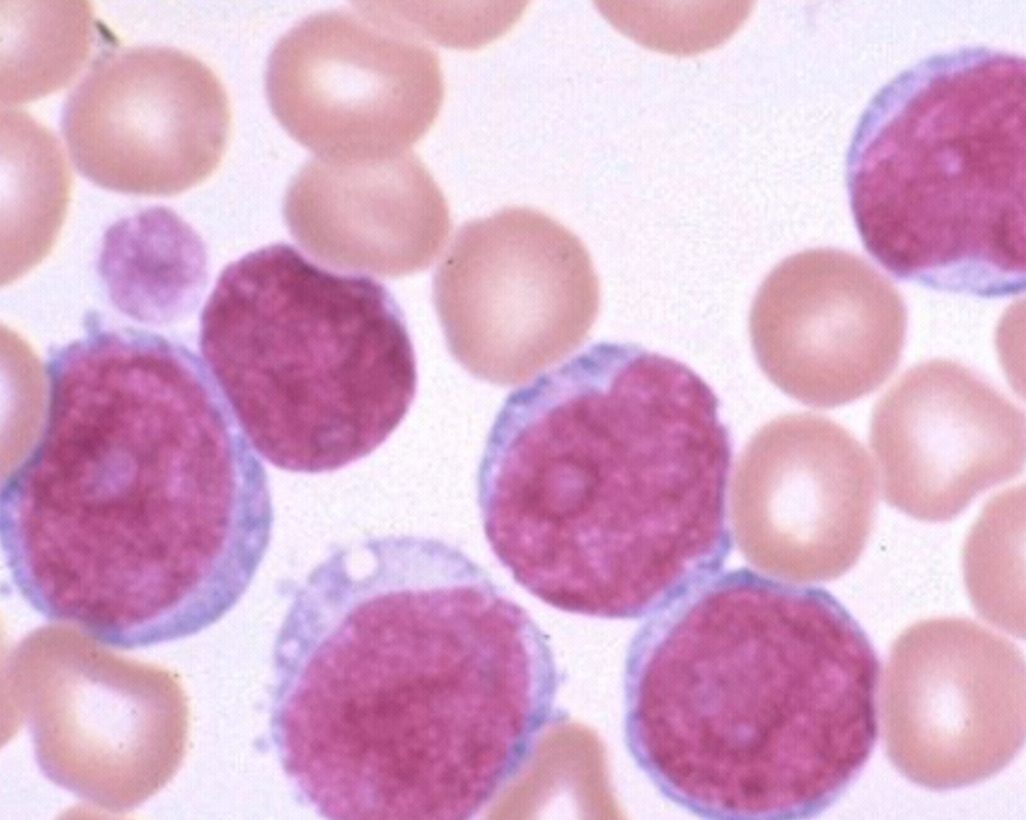
M1 diff/CBC
M1 BM
hyper cellular marrow
Blasts >90% of WBC
Later grans <10%
Decreased Megs ad nrbc
CD13, 33, 34+
M1 Stains that are +
MPO
SSB
SpEst
M2
Myeloid with maturation
WBC H
Low Hgb/HCt
Low Plt
Auer rods seen most of the time
Dysplasia frequent
30-45% of the AML
HIGH BLASTS
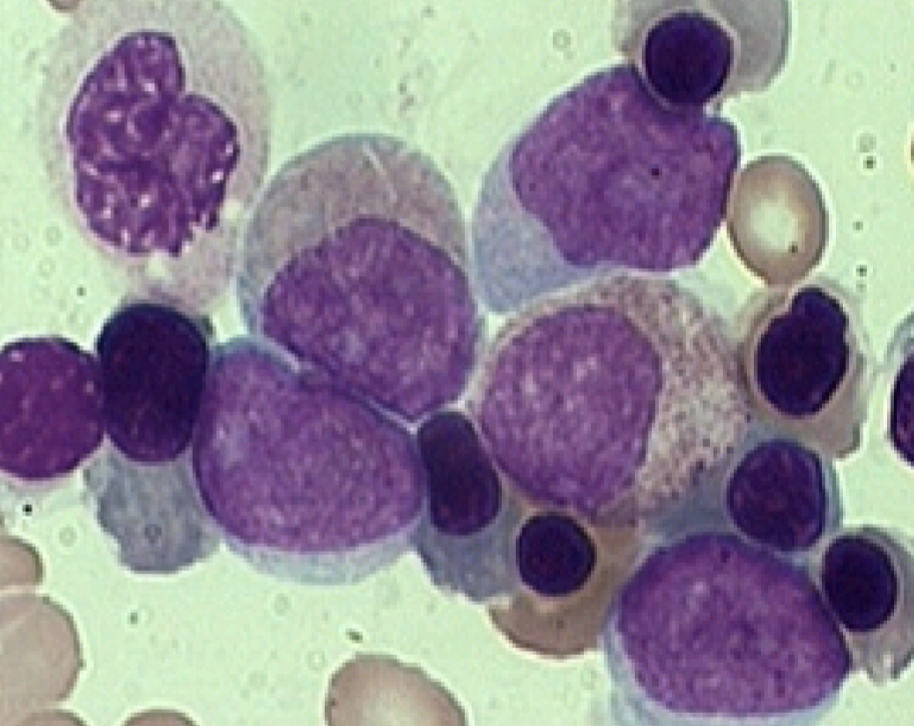
M2 CBC/diff
M2 BM
Hypercellular
Blasts>20%
Blasts <90% of WBC
Later gans >10%
Monocytes<20%
M2 + stains
MPO
SBB
spest
Cyto genetics of M2 needed to seperate from M3, what does M2 have
t(8:22) sometimes (indicated better prognosis)
CD13, CD33
CD34±
CD19 and CD3-
M3 is
HYPER GRANULAR acute proglanulocytic Leukemia
M3 CBC/diff
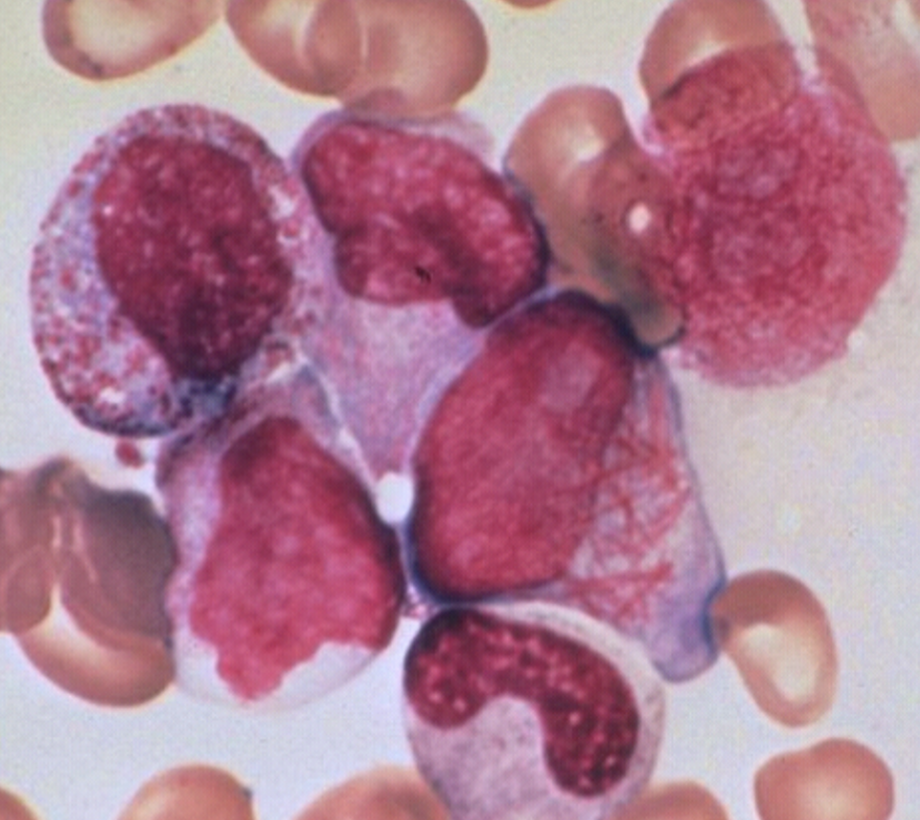
WBC low
Bundles of Auer rods seen
Nucleus is kidney shaped or bilobed
70% of M3 are hyper granular
M3m
Microgranular promyeloctic
WBC: high
Blasts resemble monos with ilobed irregular nucleus
dust like granular
auer rods possible
MArrow is hyper granular
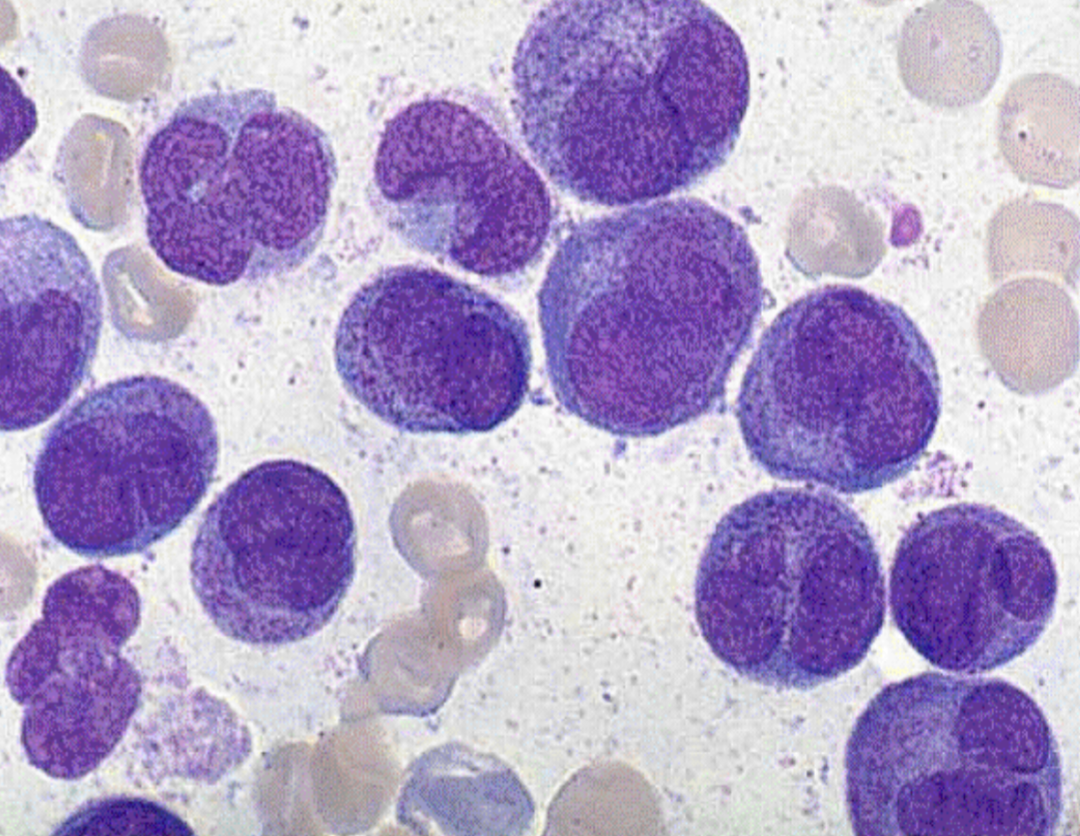
M3m CBC/diff/BM
ALL M3 have + stains
MPO
SBB
Spest
What is diagnostic in M3
t(15:17)
What other tests do you run for M3
DIC complications
genetics
MPO
FISH for PML/RARa
CD13, CD33+/CD34- (flow)
M4
Acute Myeloonocytic Leukemia or Naegeli type
M4 CBC/diff
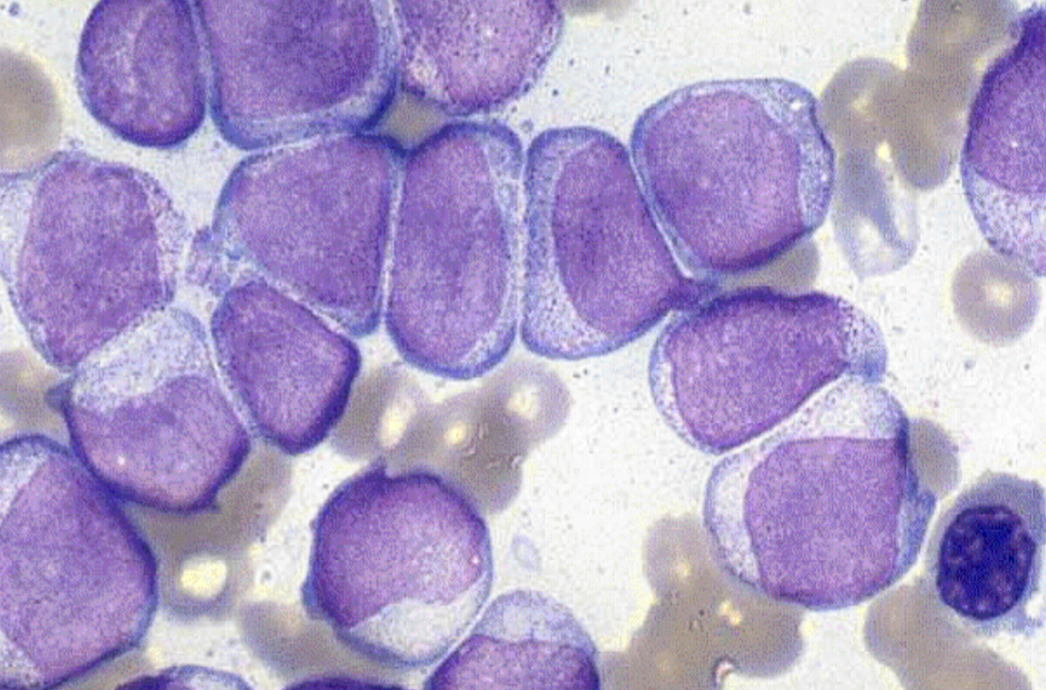
WBC: H
H-H: LOW
PLt: LOW
auer rods may be present
immature grans
increase in : monos, prosmonos, blasts/hybrids
15-25% AML
CD13, CD33, CD14, CD64+
M4 BM
Later grans >20% but <80% of WBC
Monocytic line > 20% but <80% of WBC
Often marrow monos are lower than blood amount
M4 + stains
PAS
SBB
SPEST
Nsest
M4 eo
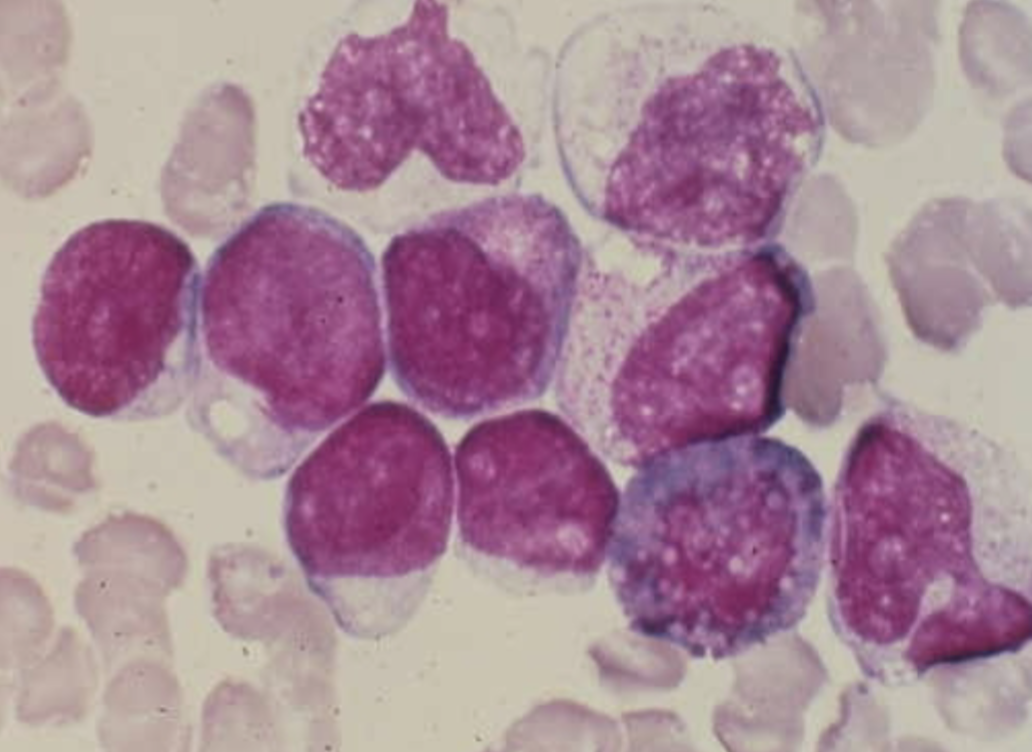
EOS increased in marrow and blood >5% but <30%
Inversion or translocation of long arm Ch. 16
M5a
Acute Monocytic Leukemia or Schillings type
M5a CBC/diff
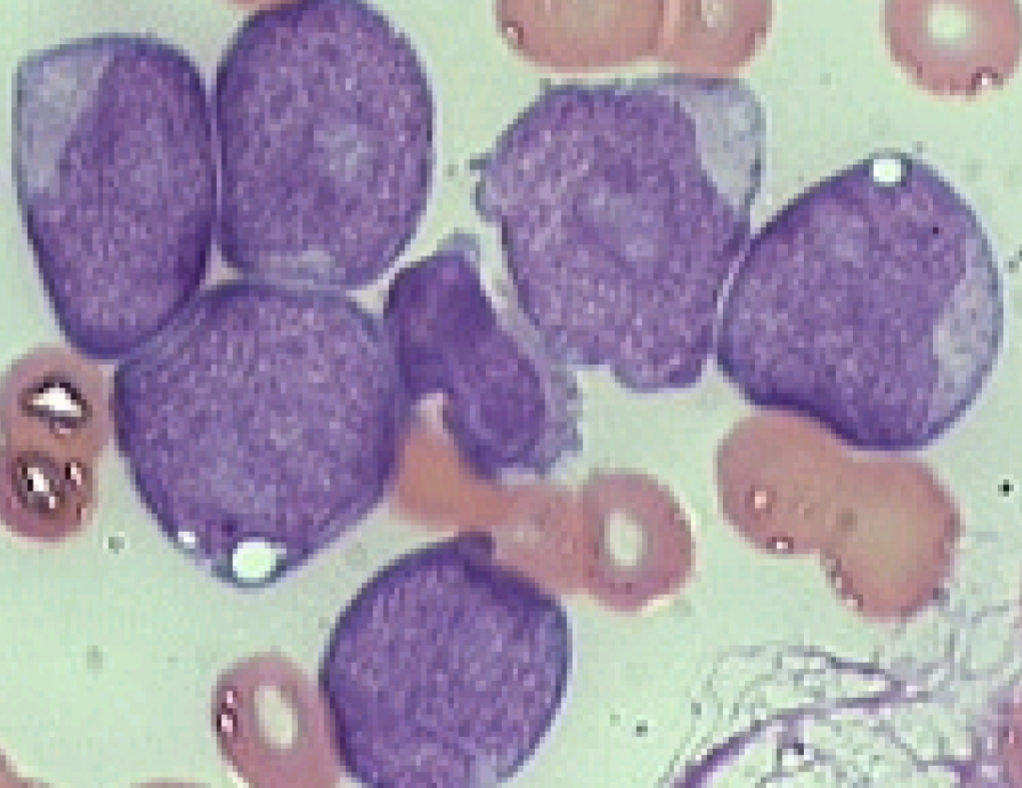
WBC varies
Younger ages
5-8% of AML
Monoblasts >80%
round or oval nucleus/occ
fold
lots of cytoplasm
few granules
pseudopods poss.
Rare Auer rod seen
M5a BM
Differ from M5b in that the majority of monocytic cells are monoblasts (>80%)
<20% granulocytes
Appearance of the abnormal cells varies from case to case
- CD13, CD33, CD36 pos
M5b CBC and diff
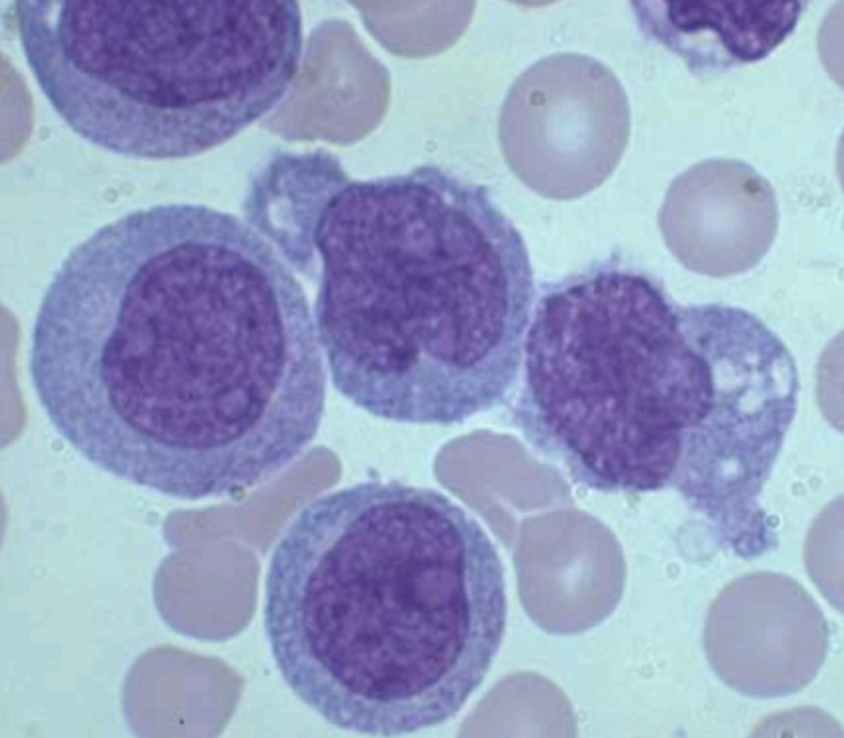
Mature monos more numerous in blood than marrow
Majority of monocytic cells are promonocytes <20% granulocytes
CD13, CD33, CD36 pos
3-6% of AML
Promonocytes:
fine chromatin;
cerebriform shape
cytoplasm more gray
few fine granulesMature monos often
have extreme folding
and irregularity
M5a and b are + for what stains
PAS
SBB
NSEST
Non-sp becomes neg. when NaF added
What genetic abnormality is likely with M5a and b
11q23(MLL)
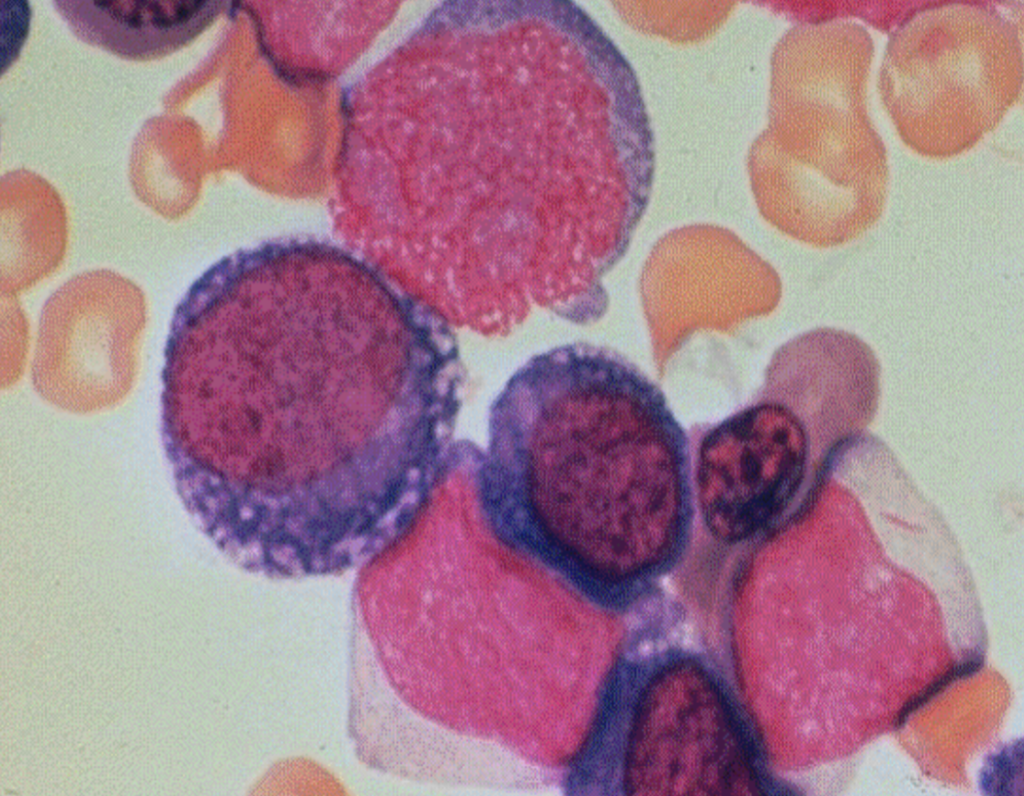
WBC can be elevated otherwise blood is panocytopenic
Glycophorin A pos. on flow
multinucleation
RBC show macrocytic anemia, HJ bodies, baso stipling, ringed sideroblasts, and ansiopoik
M6 Erythroleukemia
What stains will be + in M6
PAS
MPO/SBB
NSE and resistant to NaF
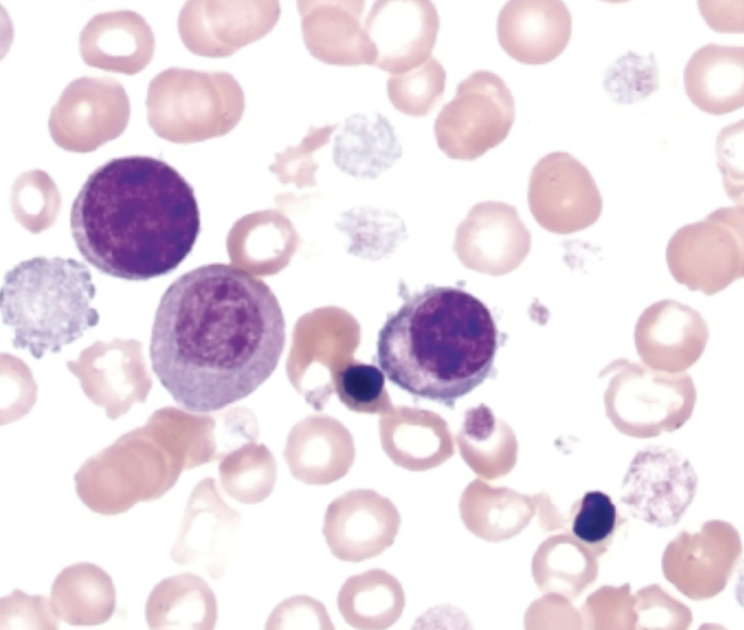
WBC low
Plt varies but atypical and bizarre
>50% of blasts are megakaryoblasts
Adults and children
3-5% of AML
Poor prognosis, particular in
infant with t(1;22).May be associated with marrow
fibrosisIf dry tap, >50% megakaryocytic
cells of any stageFlow for CD41+
M7 - Acute Megakaryocytic Leukemia
What stains are positive for M7
NSEst weak
Any leukemia with two phenotypic markers for B and T cells is considered
Biphenotypic
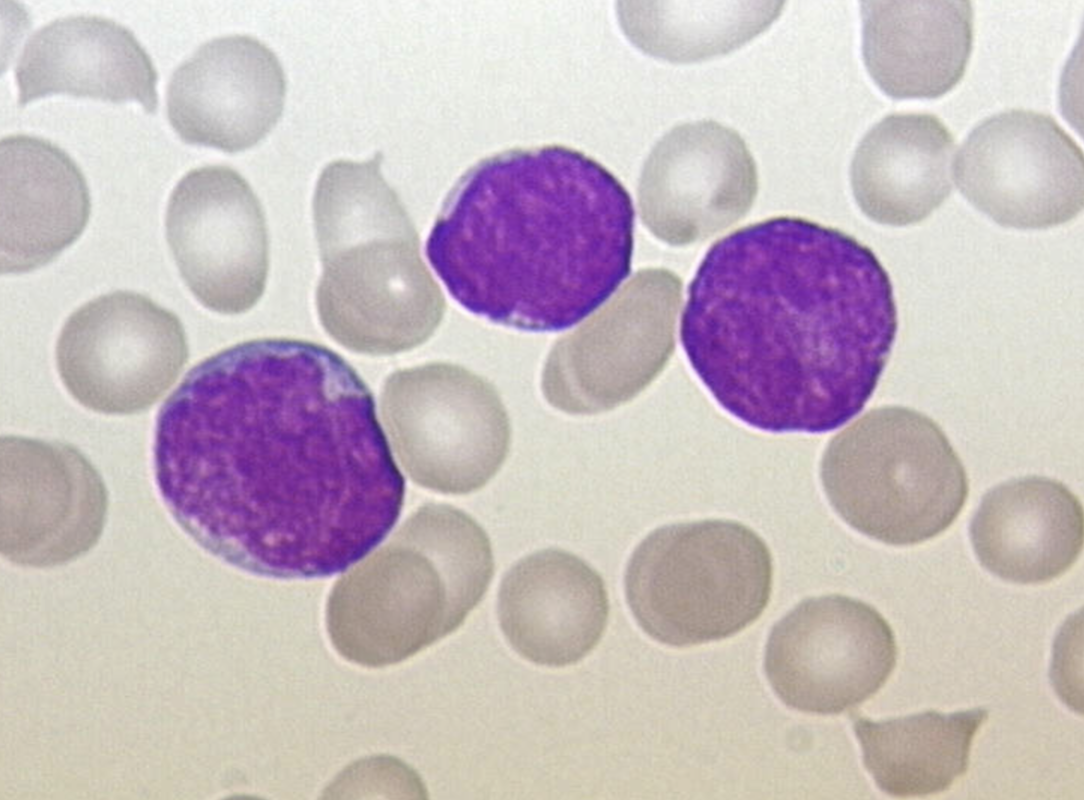
WBC increased half the time, normal or decreased the other half
>65% lymphoblasts
Small size (up to 2x lymph size)
High N/C ratio - scant cytoplasm
Nucleus is round with occ. cleft or indent
Homogenous chromatin
Inconspicuous nucleoli
Fairly uniform population
Cytoplasm may have vacuoles
L1
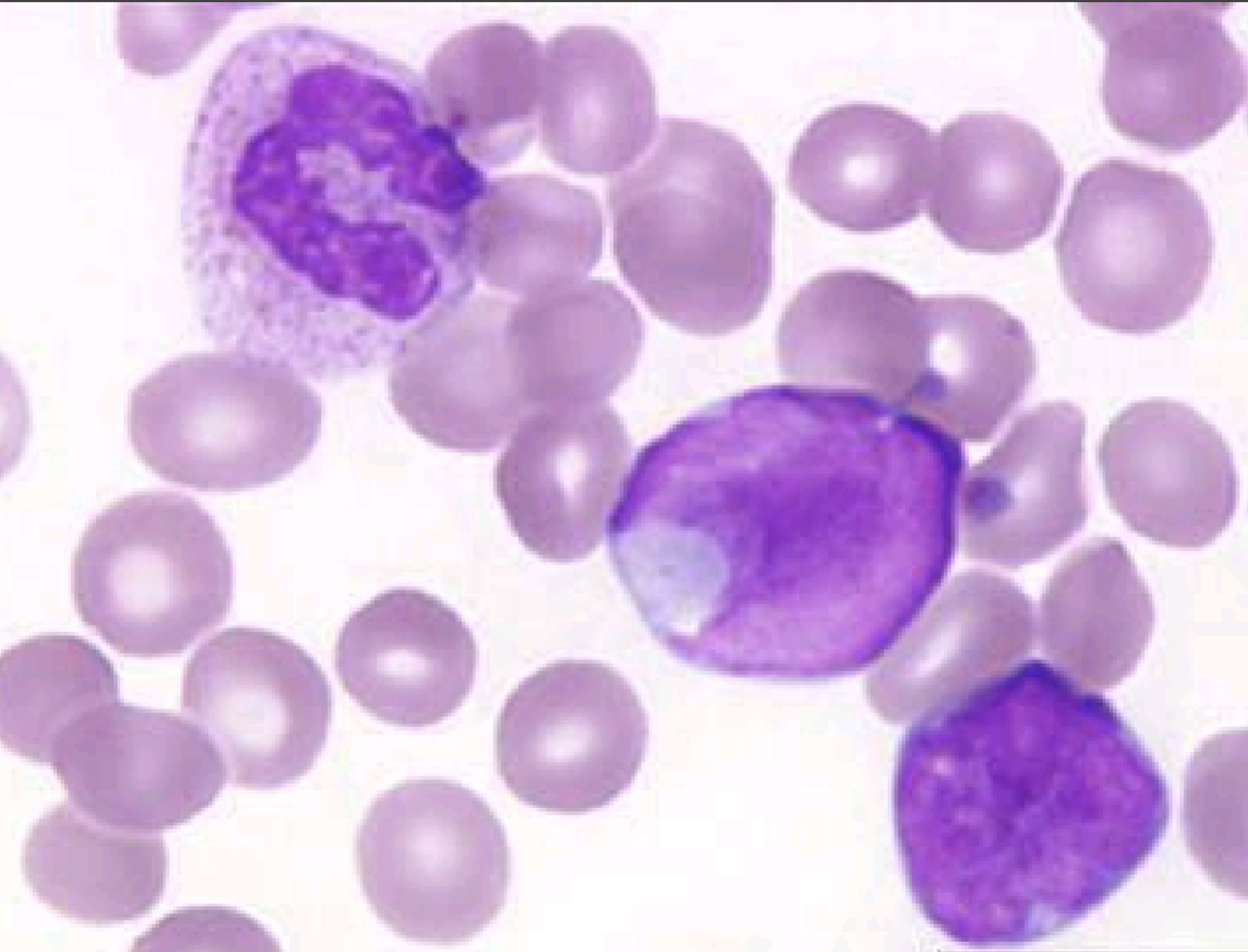
WBC increased half the time, normal or decreased the other half
>65% lymphoblasts
Mixture of blast sizes - majority > 2x lymph
sizeMod to large amount of cytoplasm
Nuclear indentation and clefting very common (stretched appearance)
Heterogeneous chromatin distribution
Larger, visible nucleoli
L2
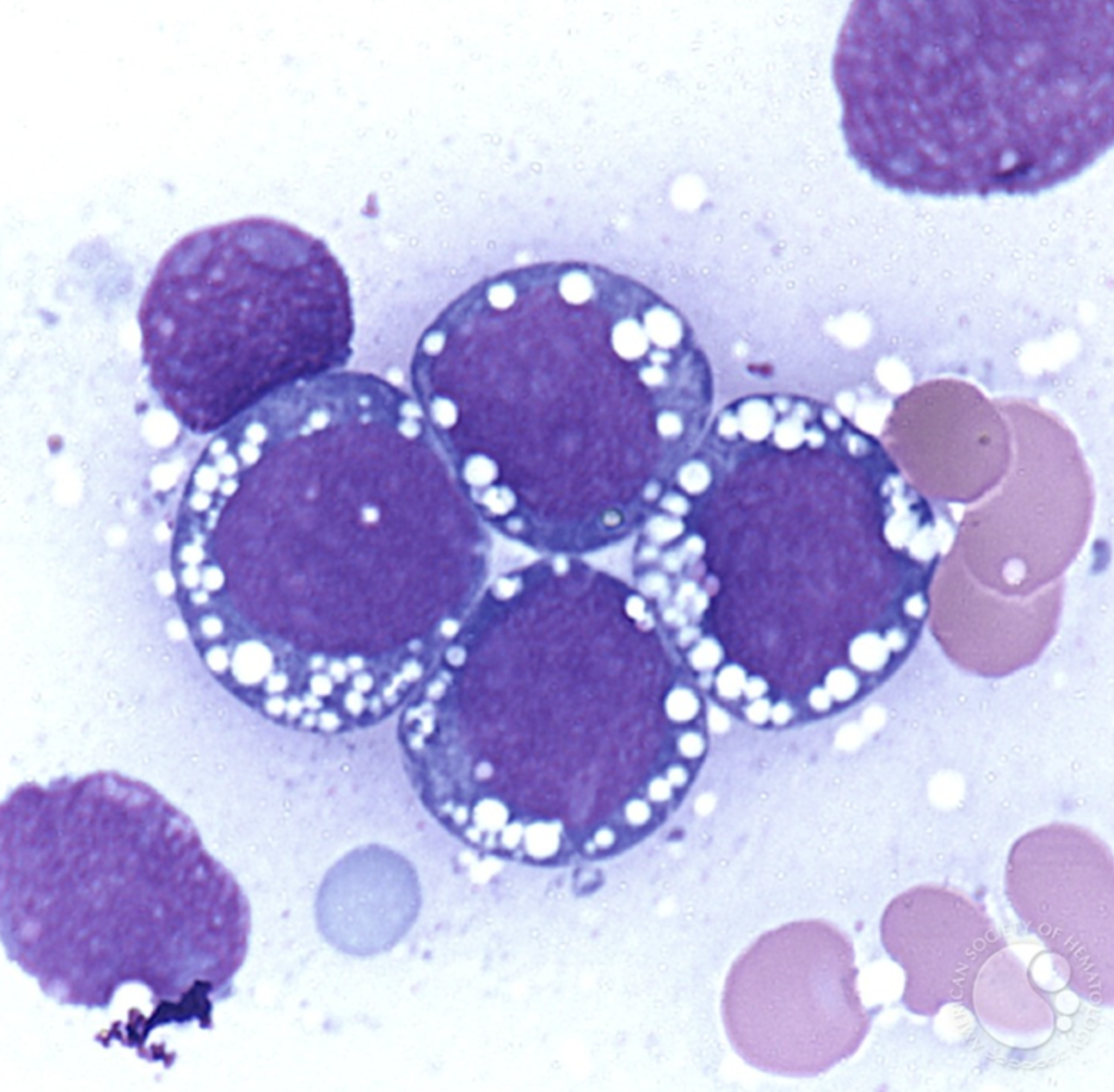
WBC increased half the time, normal or decreased the other half
>65% lymphoblasts
Large size blasts
Moderate N/C ratio
Nucleus is oval or round
Semi-coarse chromatin
One or more prominent nucleoli
Cytoplasm is medium to intensely blue with prominent vacuoles
L3 or Burkitts lymphoma
What stains are + in ALL
Tdt most of the time
PAS sometimes
what is the prfered method of diagnosis for ALL
immunophenotyping to determine B cell, Tcell, or hybrid