Qualitative Analysis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Reducing sugar
If the oxygen on the anomeric carbon (C-1/C-2) of a sugar is not attached to any other structure, that sugar can act as a?
Ex. Glucose and Fructose
Sucrose is a reducing sugar
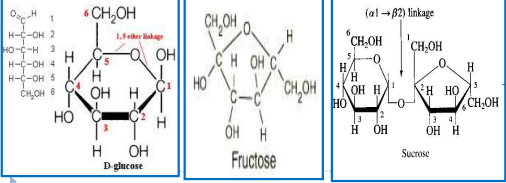
Monosaccharide and Disaccharide
Are white crystalline solids that are soluble in water.
Polysaccharides
is an amorphous solid substance that is slightly soluble to insoluble to water
Glucose, Fructose, Mannose
Image shows a needle shaped crystal formation.
Galactose
Image shows a balls with thorny edge shaped crystals
Xylose
Image shows a fine long needle shaped crystals
Maltose
Image shows a sunflower shaped crystals
Molisch, Anthrone test
General Tests for carbohydrates (2)
Iodine test
Test for starch and glycogen (1)
Moore’s, Benedicts, Fehling’s, Picric acid Test
Test for reducing sugars (4)
Barfoed’s Test
Test to distinguish reducing monosaccharides from reducing disaccharides.
Seliwanoff'‘s Test
Test for ketones
Bial’s, Seliwanoff’s Test
Test for pentoses
Molisch Test
GENERAL TESTS FOR CARBOHYDRATES
Conc. H2SO4 hydrates glycosidic bonds to yield monosaccharides which in the presence of an acid get dehydrated to form furfural and its derivatives. These products react with sulphonated α-naphthol to give a purple complex.
Remember:
7 Test tubes
1 mL of the following: 1%
Xylose, Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Starch, Distilled water.
3 drops of Molisch Reagent + 10 drops Conc. H2SO4, 45 degree angle
Precautions:
α-naphthol solution is unstable and should be prepared fresh.
Conc. H2SO4 should be along the sides of the test tubes causing minimal disturbance to the contents in the tube.
Anthrone Test
GENERAL TESTS FOR CARBOHYDRATES
In this the furfural produced reacts with anthrone to give bluish green colored complex
Iodine Test
TEST FOR STARCH AND GLYCOGEN
forms colored adsorption complexes with polysacchaides. Starch gives blue color with iodine, while glycogen reacts to form reddish brown complex. Hence it is useful, convenient and rapid test for detection of amylase, amylopectin and glycogen.
Moore’s Test
TESTS FOR REDUCING SUGARS
Carbohydrates containing free aldehyde group are being liberated with the influence of concentrated alkali in the presence of heat. This will subsequently polymerize forming a resinous substance — a caramel.
Remember:
5 test tubes
12 drops each; 1%
Glucose, Galactose, Fructose, Sucrose, Distilled water
12 drops of 10% NaOH + heat 3 min
Repeat with 1% Ba(OH)2 solution
Procedure:
All monosaccharide and disaccharide (except sucrose) will give a Positive result since they are reducing sugars
Polysaccharide and sucrose will not give a positive result because they are non-reducing sugars
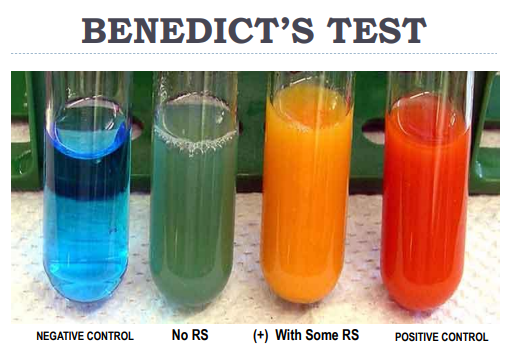
Benedict’s Test
TESTS FOR REDUCING SUGARS
Reagent contains CuSO4, Na₂CO₃ and Na Citrate. Carbohydrates bearing a free carbonyl group will be oxidized and in turn reduce Cu2+ to produce a reddish-orange colored complex in the presence of alkaline environment.
Remember
8 test tube
1 mL of : 1%
Xylose, Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Starch, Hydrolyzed starch, Distilled water.
3 ml of Benedicts Reagent + Heat 5 min + Set aside for 10 mins. + observe
Ex. (picture)
Negative control = no sugar
No RS = There is sugar but not reducing sugar
With some RS = Not many for ex. glucose conc.
Positive = Super conc sugar that is present in solution.
Fehling’s Test
TESTS FOR REDUCING SUGARS
Fehling’s reagents comprises of two solution Fehling’s solution A and solution B
Fehling’s solution A
is aqueous CuSO4
Fehling’s solution B
is alkaline sodium potassium tartrate (Rochelle salt).
Rochelle salt acts as the chelating agent in this reaction.
Formation of red precipitate of cuprous oxide denotes the presence of reducing sugar.
Procedure:
8 Test tubes
1 mL of : 1%
Xylose, Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Starch, Hydrolyzed starch, Distilled water
0.5 mL FA + 0.5 mL FB + Heat boiling bath for 5 min + Set aside for 10 mins + Observe

Picric Acid Test
TESTS FOR REDUCING SUGARS
The reducing sugars react with picric acid to form a red colored complex. Appearance of red color Picramic Acid in an alkaline environment (Na₂CO₃ ) would indicate the presence of reducing sugars. This is a very sensitive chemical test for the presence of reducing sugars
Procedure:
8 Test tubes
1 mL of saturated picric acid to
1mL of the following; 1%
Xylose, Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose Distilled water
+ 0.5mL of 10% Na2CO3 + Heat in a boiling water 30-45 Until mahogany red solution + observe
Barfoed’s Test
TEST TO DISTINGUISH REDUCING MONOSACCHARIDES FROM REDUCING DISACCHARIDES
Barfoed’s reagent: cupric acetate in acetic acid, reduces copper (II) ions. A disaccharide is a weaker reducing agent than monosaccharide, so it will reduce copper in a slower rate. Monosaccharides usually react in about 1 - 2 min while the reducing disaccharides take much longer time between 7 - 12 min.
Reducing sugars will result in brick red ppt in the solution
Procedure:
6 Test tubes
1ml of the following : 1%
Xylose, Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose
3mL of Barfoeds reagent + Heat in water bath 5min + Set aside 10 min + observe
Seliwanoff’s Test
TEST FOR KETONES
This test is used to distinguish aldoses from ketoses. Ketoses undergo dehydration to give furfural derivatives, which then condense with resorcinol to form a cherry red complex.
With ketoses the reagent produces a deep red color rapidly, while with aldoses a light pink color develops over a longer period of time
Procedure:
6 Test tubes
3 ml of Seliwanoff;s rgnt + 1 mL of the following; 1%
Xylose, Glucose, Fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose
+ Heat water bath 3 min
Bial’s Test
TEST FOR PENTOSES
This test is useful in distinguishing pentoses sugar from hexoses sugars.
Pentoses form furfural in acidic medium which condense with orcinol in presence of ferric ion to give blue green colored complex which is soluble in butyl alcohol.

Seliwanoff’s Test
TEST FOR PENTOSES
Add 1.5 mL of Bial’s reagent to 1 mL of the following solutions.
Heat with some agitation directly over the burner flame.
Hold the tube at a diagonal and heat along the sides of the tubes rather that at the bottom to prevent eruption of the liquid.
Stop heating when the mixture begins to boil.