asynchronous week 5 micronutrient malnutrition
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
describe and evaluate factors related to iron deficiency: how much we need, dietary sources, who is at risk, consequences, how can we detect
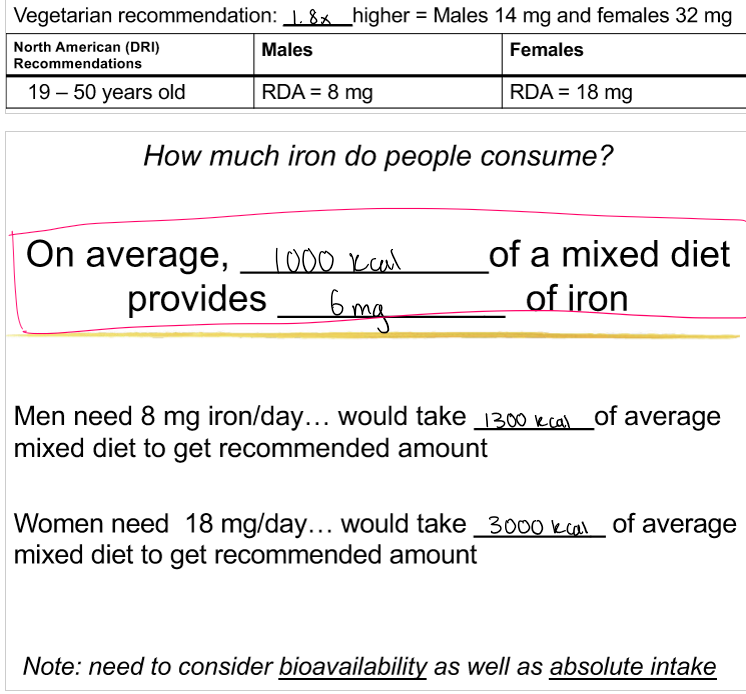
how much needed:
dietary sources: liver, beef, pork, blood, dried beans fruits, iron fortified foods (cast iron), spinach
who is at risk: children, mothers
consequences: children’s learning, premature birth, maternal deaths, lowers productivity = loss of GDP
how can we detect: biochemical blood test etc, clinical pale conjunctiva
identify describe and evaluate strategies that could reduce iron deficiency and improve iron status
change diet to increase iron intake and absorption
iron in animal tissue
40% heme 60% non heme
iron in plant foods
100% non heme
HEME more absorbable
vitamin C
fortification
add iron to wheat flour
micronutrient powder MNP packets
control hookworm
wear shoes
identify and justify WHO reccomendations for zinc supplementation during acute diarrheal episodes in children; evaluate one approach to increase adherence to this reccommendation in rural Zambia
10-14 days zinc supplementation
piggy backig on coca cola supply chain to get ORS and zinc into rural zambia
the actual success came from an effective value chain, not promoted through coke distribution
describe causes and consequences of iodine deficiency at different stages of life
pregnancy: leads to 20 million infacts per year born with cognitive and growth impairments
children: cretinism (stunted physical and mental growth)
goiter: swelling of thyroid gland 90% caused by iodine deficiency
describe and evaluate the impact of fortification as a strategy to reduce the global prevalence of iodine deficiency
iodine in table salt (only ¾ of the world using it)
fortification programs aren’t always mandatory
levels of fortification may vary
Uk has never regulated iodization of salt and it is limited