Carbohydrates - The Energy Nutrient
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
carbohydrates are made up of
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
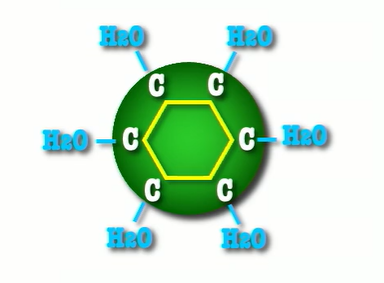
carbohydrates represent the ___’s energy, trapped in a ring of_____atoms that have been_______ with water.
sun , carbon, hydrated
(T/F) About half our energy nutrient comes from carbs.
True.
What are the three levels of carbohydrate structure?
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
The basic unit of all carbohydrates is a _______ that contains potential energy which comes from the sun.
monosaccharide
(T/F) Any foods with monosaccharides contains simple sugars.
True.
three examples of monosaccharides
fructose, glucose, galactose
Sucrose is ____ and _____ connected via a bond.
glucose, fructose
sucrose is a
disaccharide
maltose
breakdown unit from starch - two glucose units bonded together
lactose is a _______ made up of _____ and ______.
disaccharide, glucose, galactose
starch
hundreds of glucose in long chains
fiber
hundreds of glucose units or other monosaccharides linked in long chains. the linkage between sugar units is not digestible by human enzymes.
Which of the following statements about fiber are true? Check all that apply.
a. Fiber contains energy that is physiologically available to humans.
b. Humans have the enzymes to digest the polysaccharide starch, but not fiber.
c. Fiber supplies 4 calories per gram that is available to humans.
d. The basic unit of fiber is an amino acid.
e. Fiber contains potential energy.
b, e
glycogen
storage form of carbohydrate found in animals (including humans)
What is glycogen? Check all that apply
a. Glycogen is a monosaccharide
b. Glycogen can be found in many food sources.
c. Glycogen is stored in the muscle and liver of humans and other animals.
d. Glycogen is a type of polysaccharide.
e. Glycogen is an animal/human “starch” made from glucose units.
C, D, E
What type of carbohydrate is plain white pasta?
? saccharide
poly
What type of carbohydrate does this pile of fruit represent?
poly, mono
What type of carbohydrate does this pile of bread represent?
poly
What type of carbohydrate is found in dairy, like this yogurt?
dissacharide
What type of carbohydrate do energy drinks represent?
mono, di
What type of carbohydrate do diet drinks represent?
none
salivary amylase
substance produced from the saliva glands that begins the digestion of starch into simple sugars, such as maltose and dextrin
What puts a stop to the salivary amylase?
stomach acid, it disrupts the saliva enzyme
Which organ secretes the majority of digestive enzymes to break down the energy macronutrients?
pancreas
What is the end product of carbohydrate digestion?
individual monosaccharides
lactose intolerance
not enough or complete lack of lactase to break down the disaccharide lactose
water-insoluble fibers and sources
cellulose, hemi-cellulose
structural components on the plant cell wall
sources: whole grains, vegetables, beans
Why is water-insoluble fiber important?
It draws water in and ends up bulking up the stool which pushes against the walls of the intestinal tract, speeding the passage of waste. This means potential carcinogens that could disrupt cells and lead to cancer pass through the intestinal tract much faster due to the fiber. It makes it easier to poop.
Water-insoluble fiber holds _______, bulks up the intestines, and ________ passage of waste.
water, speeds up
What are food sources high in water-insoluble fiber?
whole grains, beans, vegetables
Name three benefits of consuming water-soluble fiber.
Helps relieve constipation
Lower risk of colon cancer
Lower incidence of large intestinal problems such as hemorrhoids and diverticulus
water soluble fibers refers to
gums and pectins
water soluble fibers are often used as
thickening agents
water soluble fibers sources
fruits, oats, beans
What effect does water soluble fiber have in the body?
Gel-like effect that slows gastric emptying, creating greater feelings of fullness. It slows the release of glucose into your circulation, helping with better blood-glucose regulation. Lowers risk of type II diabetes.
Water soluble fiber mixes with the chewed food in the stomach and forms a ___. This can bind a fatty substance called _________, lowering the amount that enters your circulation.
gel; cholesterol
What hormone allows glucose to enter the cell?
insulin
Type I diabetes is from
lack of insulin (no way to get glucose into the cells so it accumulates in the blood stream)
Type II diabetes is from
cell receptors no longer responding to insulin (insulin resistance)
the pancreas overcompensates and sends out even more glucose because none of it is getting into the blood cells
too much glucose in the blood stream can result in
cardiovascular disease
poor circulation (maybe even amputation)
loss of eyesight
easily get infections like UTI (poor circulation and sugar rich blood)
wounds wont heal
improved insulin action
receptor “hearing” improves with…
30-60 mins of daily exercise
What are the end products of carbohydrate aerobic energy metabolism?
Energy (4 calories/g)
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Water (H2O)
What kind of scenarios can lead to carbohydrate depletion (glycogen running out!)
Fasting >1 Day
No carb / Low carb diet
No insulin (diabetes)
What happens to energy metabolism after a prolonged fast? Check all that apply
a. Nitrogen levels in the urine decrease
b. When glycogen stores run out, we can make our own glucose from amino acids by breaking down body protein. The resulting nitrogen is excreted through the urine.
c. Your body first uses your glycogen stores for energy.
d. Nitrogen levels in the urine increase.
b, c, d
What are some of the drawbacks of a low-carb diet? Check all that apply.
Constipation
Muscle loss
Bad breath
Initial rapid water loss instead of sustainable weight loss
intrisic sugar
sugar found naturally in foods
We store carbohydrates as ______ in the _____ and _____.
glycogen, muscle, liver
gluten
protein complex found in wheat, rye, and barley