Nasopharynx & Oropharynx
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the three paired pharyngeal constrictor muscles that make up the pharynx
Superior, middle, and inferior pharyngeal constrictors
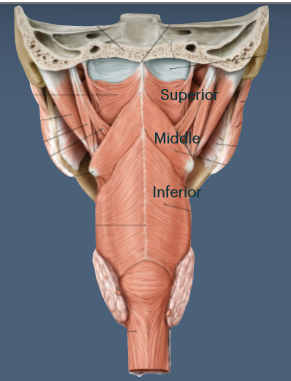
How are the 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles connected to each other
Posteriorly by the pharyngeal raphe.
What nerve innervates the pharyngeal constrictor muscles
CN X
What muscle opens the eustachian tube
Salpingopharyngeus
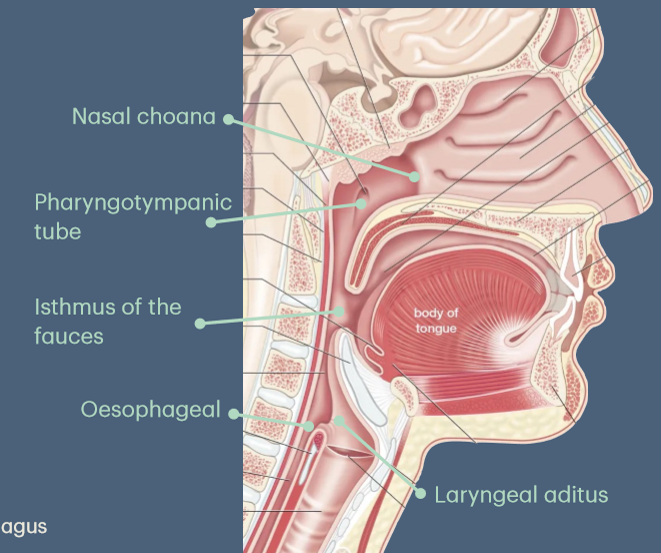
Name the 5 pharyngeal openings
Nasal choanae – from nasal cavities.
Pharyngotympanic (Eustachian) tubes – from the middle ear.
Isthmus of fauces – from the oral cavity.
Laryngeal aditus – from pharynx to larynx.
Oesophageal opening – from hypopharynx to oesophagus.
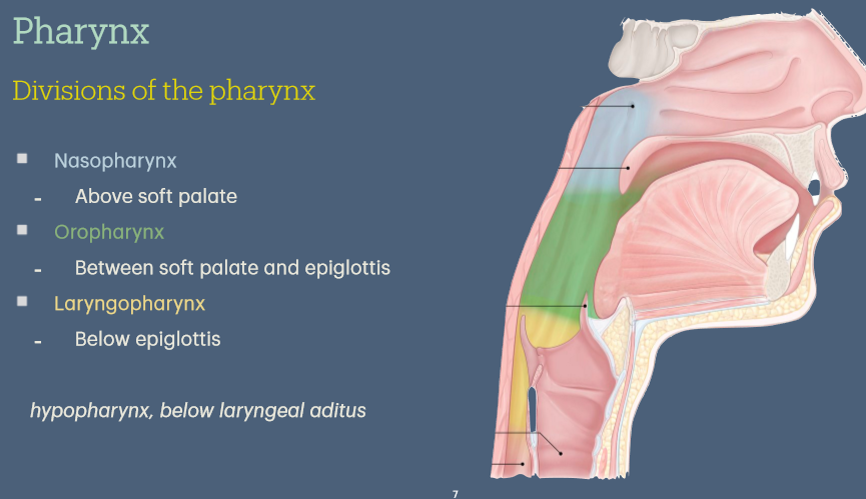
Where do each of the divisions of the pharynx start & stop
The area of pharynx beneath the oropharynx is called the hypopharynx. The first part of the hypopharynx, opposite the laryngeal opening is called the laryngopharynx. The hypopharynx proper lies behind the larynx and before the commencement of the oesophagus
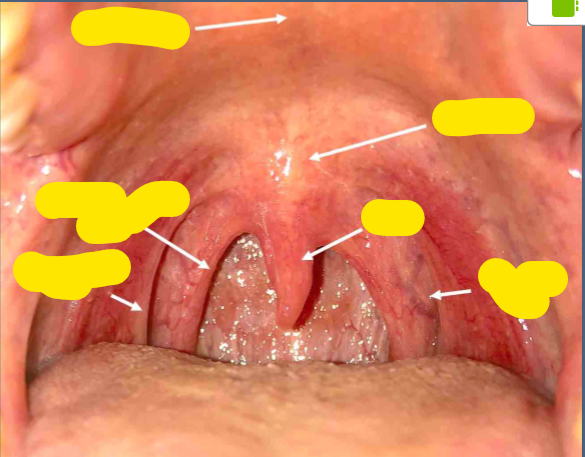
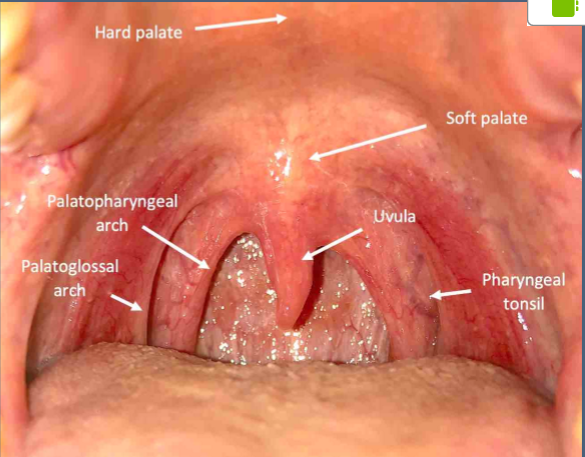
Lymphoid tissue surrounding external pharyngeal openings forms what structure
Waldeyer’s ring
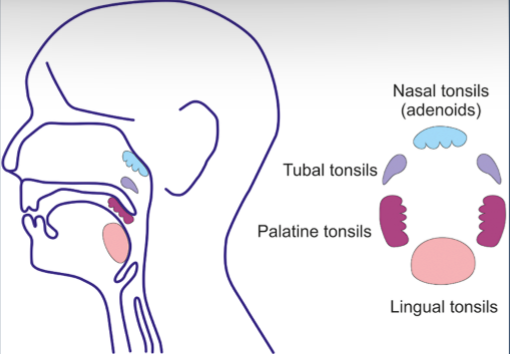
What tonsils make up Waldeyer’s ring
How does the pharynx change shape and disposition?
Through activities like breathing, chewing, and swallowing.
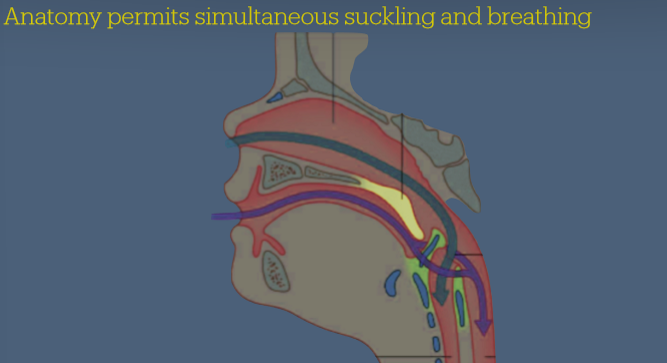
How does the paediatric pharynx differ from adult
What nerves are involved in the gag reflex (afferent & efferent)

Why is the gag reflex important in clinical evaluation?
It is used to assess neurological function, particularly after a stroke, and its absence is a criterion in determining brain death.