4 - CLINICAL MICROSCOPY
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
UC-3500
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
Fully Automated Urine Chemistry Analyzer
Reflectance Photometry with Colour CMOS Sensor
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
UC-3500
Principle
Glucose
Ketone
Bilirubin
Specific gravity
Protein
pH
Urobilinogen
Nitrite
Leukocyte esterase
Blood
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
UC-3500
Parameters (10)
Low
High
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
UC-3500
Quality Control
2 levels: _ (white cap) and _ (yellow cap)
Thrice a day: 6AM, 2PM, and 10PM
UF-4000
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
Urine Sediment Testing
Flow Cytometry with Hydrodynamic Focusing
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
UF-4000
Principle
RBCs
WBCs
Epithelial Cells
Casts
Bacteria
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
UF-4000
5 Main Parameters:
Low
High
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
UF-4000
Quality Control
2 levels: _ (blue) and _ (red)
Thrice a day: 6AM, 2PM, 10PM
DCA Vantage
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
Test: Urine Microalbumin-Creatinine Ratio
Spectrophotometry
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
DCA Vantage
Principle: Analyzes the intensity of light that is transmitted to the cartridge optical window and reports the results in clinically meaningful units
Clinitek Advantus
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
Test/s:
Urine Reagent Strip Testing
Urine Free Hemoglobin
Urine Myoglobin
Serum Ketone
Reflectance Photometry
Urine Analyzers (Main Machines)
Clinitek Advantus
Principle:
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Often used to detect bleeding in the digestive tract which has no other signs or symptoms
More specific to finding blood coming from the lower gastrointestinal tract than the FOBT
8 drops (alternating manner) for 5 minutes
3 drops for 5 minutes
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
Insure One: ?
Hemoccult ICT: ?
4 drops for 3 minutes
3 drops for 3 minutes
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Pregnancy Test Kits
Wondfo: ?
Rightsign: ?
3 drops for 10 minutes
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
CERTEST Kits
? for ALL CERTEST test kits
Coloured chromatographic immunoassay
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
CERTEST Kits
Principle?
H. pylori stool antigen
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
CERTEST Kits
Coloured chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of Helicobacter pylori in stool samples
The importance of H. pylori testing has increased greatly since the strong correlation between the presence of bacteria and confirmed gastrointestinal diseases (stomach and duodenum) like gastritis, peptic ulcer disease and gastric carcinoma
Fecal Calprotectin Semi-Quantitative
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
CERTEST Kits
Coloured chromatographic immunoassay for the semi-quantitative detection of human calprotectin (hCp) in stool samples that may reflect gastrointestinal inflammation caused by several pathologies (inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal cancer, and some enteropathies)
Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Semi-Quantitative
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
CERTEST Kits
Coloured chromatographic immunoassay for the semi-quantitative determination of human haemoglobin (hHb) in stool samples
Hemascreen Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Qualitative
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Stored at room temperature
Rapid, qualitative method for detecting occult blood in the stool which may be indicative of asymptomatic gastrointestinal diseases such as colorectal cancer, polyps, or colitis
2 drops of buffer for each window for 30 seconds
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Hemascreen Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Qualitative
Drops & minutes
Parascreen: Malaria Antigen Test Kit
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Rapid, qualitative, two site sandwich immunoassay utilizing whole blood for the detection of P. falciparum specific histidine rich protein-2 (Pf. HRP-2) and Pan malaria specific pLDH
The test may also be used for the differentiation of P. falciparum and other material species (P. malariae, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. knowlesi) and for the follow up of antimalarial therapy in whole blood samples
sandwich immunoassay
5 uL of blood with 2 drops of buffer for 20 minutes
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Parascreen: Malaria Antigen Test Kit
Principle
Drops and minutes
Operon: Simple H. pylori
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Simple/Stick H.pyl* and Simple H.pyl-Tf are non-invasive rapid tests that can identify both active H. pylori infection and the presence of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract quickly, safely, easily, affordably and reliably
4 drops for 15 minutes
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Operon: Simple H. pylori
Drops & minutes
Operon: Simple Calprotectina
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
immunochromatographic assay is a rapid test for the semi-quantitative detection of human Calprotectin in fecal samples as an indicator of the gastrointestinal inflammation present in various pathologies (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, colorectal cancer)
immunochromatographic assay
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Operon: Simple Calprotectina
Principle
MRP8 and MRP14
neutrophil
3 drops for 10 minutes
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Operon: Simple Calprotectina
Calprotectin is a heterocomplex with antimicrobial properties comprised of two calcium-binding proteins (?) present in the cytoplasm of neutrophils
The presence of calprotectin in feces is a consequence of _ migration into the gastrointestinal tissue due to an inflammatory process
Drops and minutes
Wondfo: Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Semi-Quantitative
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
_ test uses immunochromatographic sandwich method, which employs two specific monoclonal antibodies to selectively identify hemoglobin in test samples
It is a rapid immunochromatographic direct binding test for the visual detection of hemoglobin in fecal samples
immunochromatographic sandwich method
3 drops for 10 minutes
Most Commonly Performed Special Tests
Wondfo: Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Semi-Quantitative
Principle
Drops & minutes
Brown, Yellow Brown, Light Brown, Dark Brown, Greenish Brown, Greenish Black, Reddish
Hard, Formed, Soft, Mushy, Loose, Watery
Fecalysis
Examine the gross appearance of the sample according to:
Color: (8)
Consistency: (6)
Mucus: Present (+) or Absent (-)
NSS
Lugol’s iodine
LPO, HPO
Fecalysis
Procedure:
Get 1 slide. Using a marker, Write the patient’s initial at the side of the glass slide
Place 1 drop of _ on one part of the slide and another drop of _ _ on the area opposite to NSS
With an applicator stick, poke at various parts of the stool sample. Make sure to touch the portions with blood or mucus
Make a smooth uniform emulsion in both solutions
Place the coverslips in both emulsion (avoid air bubbles)
Examine both emulsions under _ to screen and detect the presence of helminth eggs and larvae. View under _ for greater morphologic details and better identification
Entamoeba coli
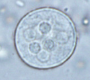
Entamoeba histolytica
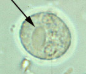
Blastocystis hominis
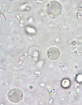
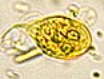
Giardia lamblia cyst and trophozoite
Calcium Oxalate
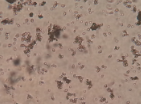
Amorphous Urates & Amorphous Phosphates
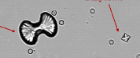
Triple Phosphate

Ammonium Biurate
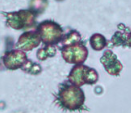
Hyaline Cast

Fine Granular Cast
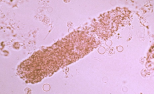
Coarse Granular Cast
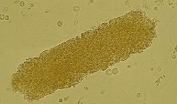
Mucus Threads
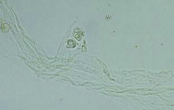
Sperm
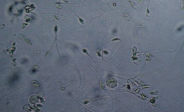
RBCs
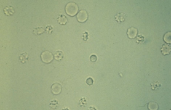
WBCs
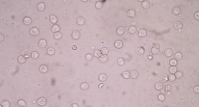
Fat Globules
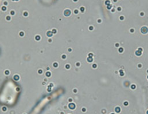
Yeast Cells
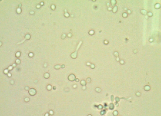
Budding Yeast Cells
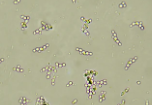
Yeast Cells with Hyphae
8 drops, 5 mins (alt manner)
3 drops, 5 minutes
Special Tests | |||
Test | Principle | Drops and Reading Time | Detects: |
Fecal Immunochemical Tests (FIT) | |||
Insure One | ? | Detects bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract | |
Hemoccult ICT | ? | ||
4 drops, 3 minutes
3 drops, 3 minutes
Pregnancy Test Kits | |||
Wondfo | ? | ||
Rightsign | ? | ||
Coloured Chromatographic Immunoassay
3 drops, 10 minutes
CERTEST KITS | |||
H. pylori stool antigen | ? | ? | H. pylori – gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastric carcinoma |
Fecal Calprotectin Semi-Quantitative | Human calprotectin – inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal cancer, enteropathies | ||
Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Semi-Quantitative | Human hemoglobin | ||
2 drops for each window, 30 secs
Sandwich Immunoassay
5 uL of blood w/ 2 drops of buffer for 10 minutes
4 drops, 15 minutes
Other Test Kits | |||
Hemascreen Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Qualitative | ? | Colorectal cancer, polyps, or colitis | |
Parascreen: Malaria Antigen Test Kit | ? | ? | P. falciparum (histidine rich protein-2) Pan malaria (pLDH) |
Operon: Simple H. pylori | ? | H. pylori infection | |
Operon: Simple Calprotectin | Immunochromatographic Assay | 3 drops, 10 minutes | HCP – ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s Disease, colorectal cancer MRP8, MRP14 |
Wondfo: Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Semi-Quantitative | Immunochromatographic Sandwich Method | 3 drops, 10 minutes | Visual detection of hemoglobin in fecal samples |
Immunochromatographic Assay
3 drops, 10 minutes
Immunochromatographic Sandwich Method
3 drops, 10 minutes
Other Test Kits | |||
Hemascreen Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Qualitative | 2 drops for each window, 30 secs | Colorectal cancer, polyps, or colitis | |
Parascreen: Malaria Antigen Test Kit | Sandwich Immunoassay | 5 uL of blood w/ 2 drops of buffer for 10 minutes | P. falciparum (histidine rich protein-2) Pan malaria (pLDH) |
Operon: Simple H. pylori | 4 drops, 15 minutes | H. pylori infection | |
Operon: Simple Calprotectin | ? | ? | HCP – ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s Disease, colorectal cancer MRP8, MRP14 |
Wondfo: Fecal Occult Blood (FOBT) Semi-Quantitative | ? | ? | Visual detection of hemoglobin in fecal samples |
Total Cell Count
Differential Count
Additional Notes
Body Fluids Cell Count & Gross Examination
_ _ _ – uncentrifuged
_ _ – centrifuged
NSS
Glacial Acetic Acid
Crystal Violet
Additional Notes
Body Fluids Cell Count & Gross Examination
Reagents used:
_
_ _ _ – lyses RBC
_ _
NSS
glacial acetic acid
crystal violet
Additional Notes
Body Fluids Cell Count & Gross Examination
Total Cell Count – _
All body fluids – _ _ _
Synovial fluid – _ _ (prevents mucin clot and clumping)
double sequential enzymatic reaction
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Glucose
Diazo reaction
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Bilirubin
sodium nitroprusside reaction
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Ketone
pKa change of polyelectrolyte
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Specific gravity
protein error of indicators
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Protein
double indicator system
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
pH
Greiss reaction
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Nitrite
pseudoperoxidase activity of Hgb
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Blood
leukocyte esterase activity
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Leukocyte esterase
Ehrlich reaction
Additional Notes
Reagent Strip Parameters:
Urobilinogen
Uric Acid
Acidic
_ _ | _ | Rhombic, four-sided flat plates (whetstones), wedges, rosette |
Amorphous Urates
Acidic
? | ? | Yellow-brown granules Refrigeration: Pink sediment |
Amorphous Phosphate
Alkaline
Refrigeration: White sediment |
Calcium Oxalate
Acidic/Alkaline
Dihydrate: Octahedral envelope Monohydrate: Dumbbell-shaped (ethylene glycol “antifreeze” poisoning) |
Calcium Phosphate
Alkaline
Thin prism in rosette form |
Triple Phosphate
Alkaline
AKA “Ammonium Magnesium Phosphate” or “Struvite” Coffin lid |
Ammonium Biurate
Alkaline
Thorny apples Most often encountered in old specimen |
Calcium Carbonate
Acidic/Alkaline
Dumbbell or spherical shape |