Chem Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:55 AM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
\- deltaH
endothermic
2
New cards
\+ deltaH
exothermic
3
New cards
lattice energy
energy required to separate a mole of an ionic solid into gaseous ions
4
New cards
Coulomb's law
energy of attraction = (charge 1 x charge 2)/distance
5
New cards
______ matters more than _______ for Coulomb's law
charge, distance
6
New cards
potential energy of covalent bonds (+ or -)
negative
7
New cards
bond order
# of bonds/# of locations
8
New cards
bond energy
energy required to overcome the electrostatic attraction of a bond and separate it
9
New cards
high bond order = ______ bond length = ______ bond energy
short, high
10
New cards
network covalent solids
a continuous network of covalent bonds
11
New cards
electronegativity
a value describing how well an atom can attract electrons in a molecule
12
New cards
electron affinity
amount of energy released when an electron is added to an atom
13
New cards
non-polar covalent bond
electrons shared equally
14
New cards
polar covalent bond
unequal sharing of electrons
15
New cards
polar covalent bonds have a ______ difference
electronegativity
16
New cards
metallic bonding has a _______ of ______ electrons
sea, delocalized
17
New cards
free radical
a molecule with an odd number of electrons
18
New cards
resonance structures
an average of all possible resonance structures
19
New cards
formal charge equation
valence electrons - 1/2(bonding electrons)-nonbonding electrons
20
New cards
formal charge rules for deciding structure
smaller better, more negative formal charge on more electronegative atom, charges add up to overall molecule charge
21
New cards
2 bonding groups (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
linear, linear, 180
22
New cards
3 bonding groups (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
trigonal planar, trigonal planar, 120
23
New cards
2 bonding groups, 1 lone pair (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
trigonal planar, bent,
24
New cards
4 bonding groups (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
tetrahedral, tetrahedral, 109.5
25
New cards
3 bonding groups, 1 lone pair (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal,
26
New cards
2 bonding groups, 2 lone pair (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
tetrahedral, bent,
27
New cards
5 bonding groups (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal, 90 and 120
28
New cards
6 bonding groups (electron, molecular, & bond angle)
octahedral, octahedral, 90
29
New cards
levels of repulsion
lone pair > triple bond > double bond > single bond > free radical
30
New cards
isomers
same chemical formula, different shapes
31
New cards
cis isomers
molecules on same side of central atom
32
New cards
trans isomers
molecule on different sides of central atom
33
New cards
hybrid orbitals does not form _____ _______, just different ________
new orbitals, orientations
34
New cards
2 bonds
sp hybrid
35
New cards
3 bonds
sp2 hybrid
36
New cards
4 bonds
sp3 hybrid
37
New cards
5 bonds
sp3d hybrid
38
New cards
6 bonds
sp3d2 hybrid
39
New cards
sigma bonds
end-to-end overlap of single bonds
40
New cards
pi bonds
sideways overlap between double (1) and triple (2) bonds
41
New cards
alkanes
single bonds, saturated
42
New cards
alkenes
double bonds, unsaturated
43
New cards
alkynes
triple bonds, unsaturated
44
New cards
free rotation only in _____ bonds
sigma
45
New cards
1 carbon root
meth-
46
New cards
2 carbon root
eth-
47
New cards
3 carbon root
prop-
48
New cards
4 carbon root
but-
49
New cards
5 carbon root
pent-
50
New cards
6 carbon root
hex-
51
New cards
7 carbon root
hept-
52
New cards
8 carbon root
oct-
53
New cards
9 carbon root
non-
54
New cards
10 carbon root
dec-
55
New cards
alkane suffix
-ane
56
New cards
alkene suffix
-ene
57
New cards
alkyne suffix
-yne
58
New cards
aromatic hydrocarbons
6 carbon ring of delocalized electrons
59
New cards
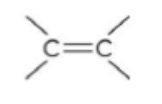
alkene
60
New cards
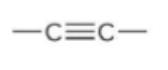
alkyne
61
New cards
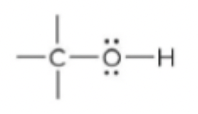
alcohol
62
New cards
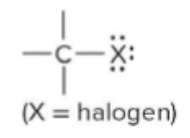
haloalkane/halide
63
New cards
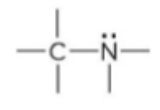
amine
64
New cards
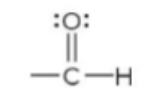
aldehyde
65
New cards
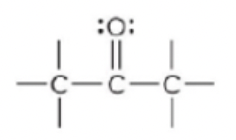
ketone
66
New cards
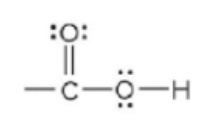
carboxylic acid
67
New cards
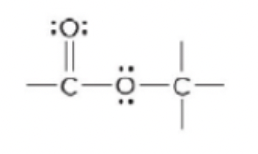
ester
68
New cards
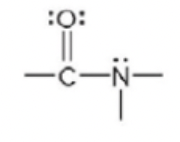
amide
69
New cards
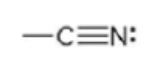
nitrile
70
New cards
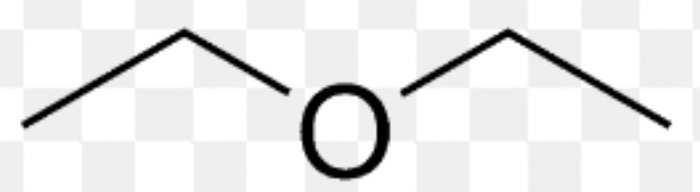
ether
71
New cards
primary alcohol
carbon bonded to 2H and 1 other C
72
New cards
secondary alcohol
carbon bonded to 1H and 2 other C
73
New cards
tertiary alcohol
carbon bonded to 3C
74
New cards
primary amine
1 bond between C&N
75
New cards
secondary amine
2 bonds between C&N
76
New cards
tertiary amine
3 bonds between C&N