Human A&P Chapter 5
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue composed of layers of closely spaced cells that cover organ surfaces, form glands, and serve for protection, secretion, and absorption
Connective Tissue
Tissue with usually more matrix than cell volume, often specialized to support and protect organs and to bind other tissues and organs to each other
Nervous Tissue
Tissue containing excitable cells specialized for rapid transmission of coded information to other cells
Muscular Tissue
Tissue composed of elongated, excitable muscle cells specialized for contraction
Matrix
The extracellular material of a tissue, composed of fibers and ground Substance
Tissue
A group of similar cells and cell products that arise from the same region of the embryo and work together to perform a specialized structural or physiological role in an organ
Epithelium
Covers the body surface (skin), lines body cavities, forms the external and internal linings of many organs, and constitutes most gland tissue. They are avascular (without blood vessels)
Basement Membrane
Layer between an epithelium and underlying connective tissue
Simple Epithelium
Every cell is anchored to the basement membrane
Stratified Epithelium
Some cells rest on top of other cells and don't contact the basement membrane
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Single layer of thin cells, shaped like fried eggs with bulge where nucleus is located; nucleus flattened in the plane of the cell
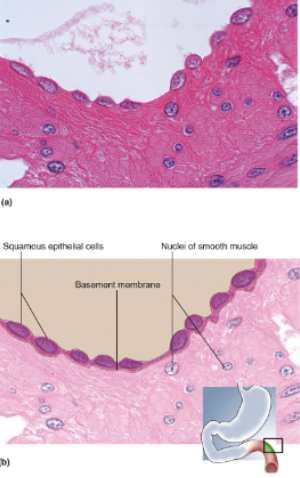
Location of simple squamous epithelium
Air Sacs (alveoli) of lungs; glomerular capsules of kidneys; some kidney tubules; inner lining of heart & blood vessels: serous membranes of stomach, intestines, and some other viscera; surface mesothelium of pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, and mesenteries
Function of simple squamous epithelium
Allows rapid diffusion or transport of substances through membrane; secretes lubricating serous fluid.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Single layer of square or round cells; in glands, cells often pyramidal and arranged like segments of an orange around a central space; spherical, centrally placed nuclei
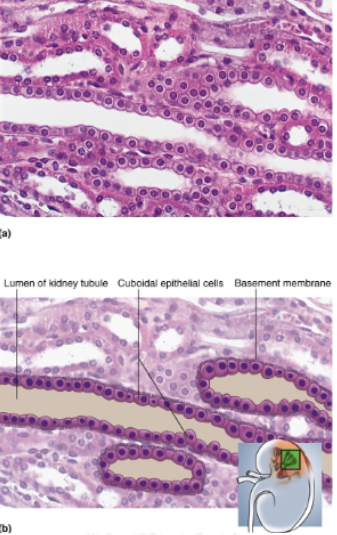
Location of simple cuboidal epithelium
Liver, thyroid, mammary, salivary, and other glands; most kidney tubules; bronchioles
Function of simple cuboidal epithelium
Absorption and secretion; production of protective mucous coat; movement of respiratory mucus
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Single layer of tall, narrow cells; oval or sausage shaped nuclei, vertically oriented, usually in basal half of cell; often shows a brush border of microvilli; ciliated in some organs; may possess goblet cells
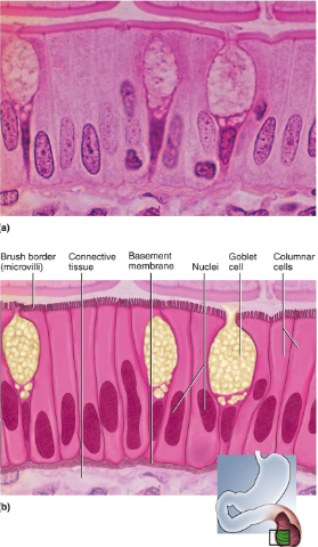
Location of simple columnar epithelium
Inner lining of stomach, intestines, gallbladder, uterus, and uterine tubes; some kidney tubules
Function of simple columnar epithelium
Absorption; secretion of mucus and other products; movement of egg and embryo in uterine tube
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Looks multilayered; some cells do not reach free surface, but all cells reach basement membrane; nuclei at several levels in deeper half of epithelium; often with goblet cells; often ciliated
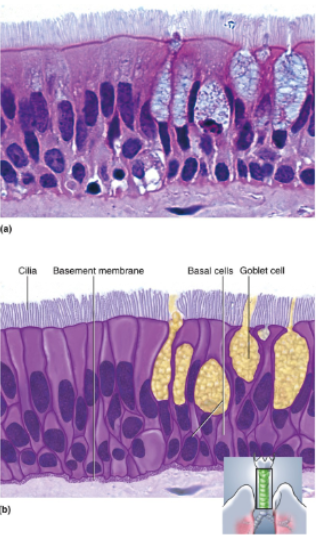
Location of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Respiratory tract from nasal cavity to bronchi; Portion of male urethra
Function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Secretes and Propels mucus
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Keratinized)
Multiple cell layers with cells becoming increasingly flat and scaly toward surface; surface covered with a layer of compact dead cells without nuclei; basal cells may be cuboidal to columnar
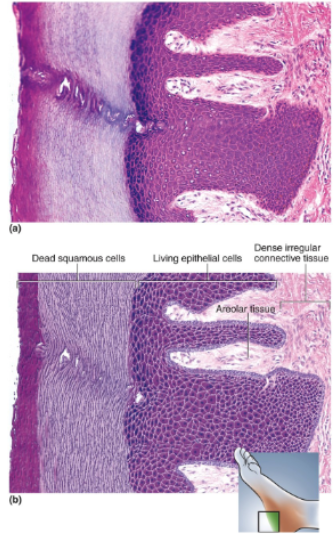
Location of stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized)
Epidermis, palms and soles are especially heavily keratinized
Function of stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized)
Resists abrasion and penetration by pathogenic organisms; retards water loss through skin
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Nonkeratinized)
Same as keratinized epithelium but without the surface layer of dead cells
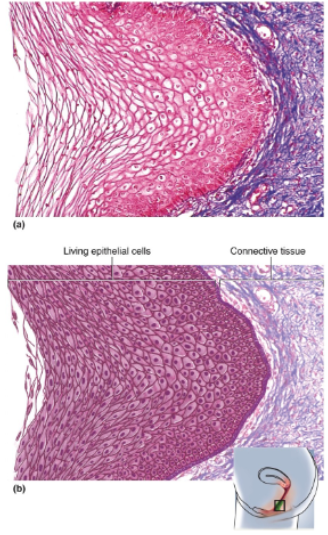
Location of stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized)
Tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, anal canal, vagina
Function of stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized)
Resists abrasion and penetration by pathogenic organisms
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Two or more layers of cells; surface cells square or round
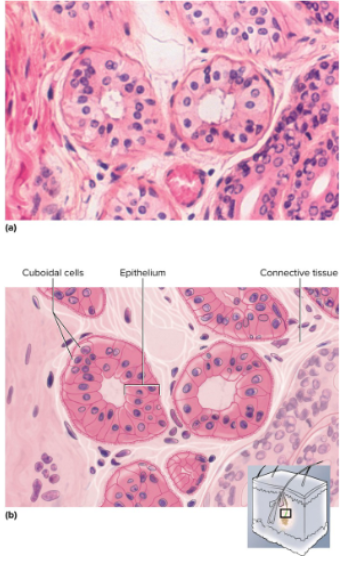
Location of stratified cuboidal epithelium
Sweat gland ducts; egg producing vesicles (follicles) of ovaries; sperm
Function of stratified cuboidal epithelium
Contributes to sweat secretion; secretes ovarian hormones; produces sperm
Transitional Epithelium
Multilayered; surface cells change from round to flat when stretched
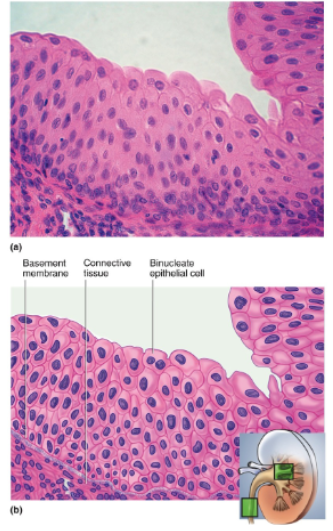
Location of transitional epithelium
Urinary tract (part of kidney, ureter, bladder, part of urethra)
Function of transitional epithelium
Stretches to allow filling of urinary tract; protects underlying tissues from osmotic damage by urine
Connective tissue
Generally occupy less space than the extracellular matrix, usually their cells are not in direct contact with each other
Fibroblasts
Produce the fibers and ground substances that form the matrix
Fibrous connective tissue, adipose tissue, supportive connective tissues, and fluid connective tissue
Four broad categories of connective tissue
Areolar Tissue
Loose arrangement of collagenous and elastic fibers, scattered cells of various types; abundant ground substance, numerous blood vessels
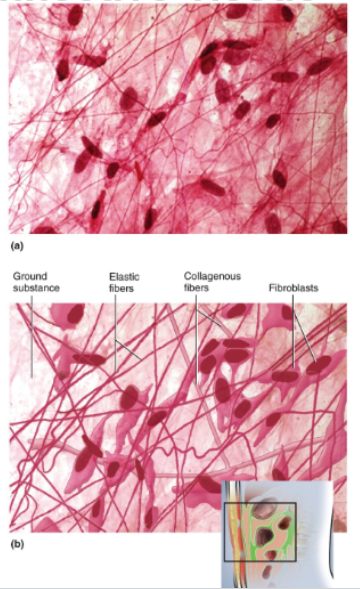
Location of areolar tissue
Underlying nearly all epithelia; surrounding blood vessels, nerves, esophagus, and trachea; fascia between muscles; mesenteries, visceral layers of pericardium and pleura
Function of areolar tissue
Loosely binds epithelia to deeper tissues; allows passage of nerves and blood vessels through other tissues; provides an arena for immune defense; blood vessels provide nutrients and waste removal for overlying epithelia
Reticular Tissue
Loose network of reticular fibers and cells, infiltrated with numerous leukocytes, especially lymphocytes
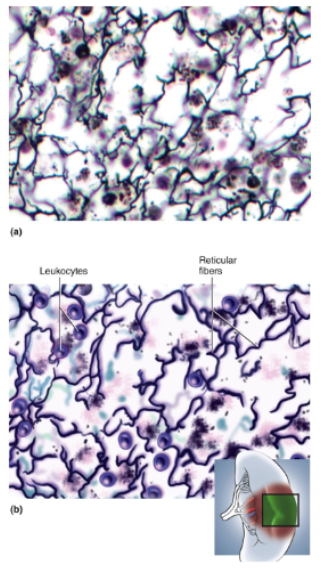
Location of reticular tissue
Lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow
Function of reticular tissue
Forms supportive stroma (framework) for lymphoid organs
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Densely packed, parallel, often wavy collagen fibers; slender fibroblast nuclei compressed between collagen bundles; small amount of open space (ground substance); scarcity of blood vessels
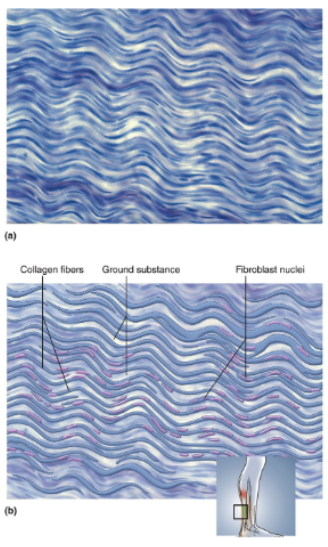
Location of dense regular connective tissue
Tendons and ligaments.
Function of dense regular connective tissue
Ligaments tightly bind bones together and resist stress; tendons attach muscle to bone and transfer muscular tension to bones
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Densely packed collagen fibers running in random directions; not a lot of open space (ground substance); few visible cells; scarcity of blood vessels
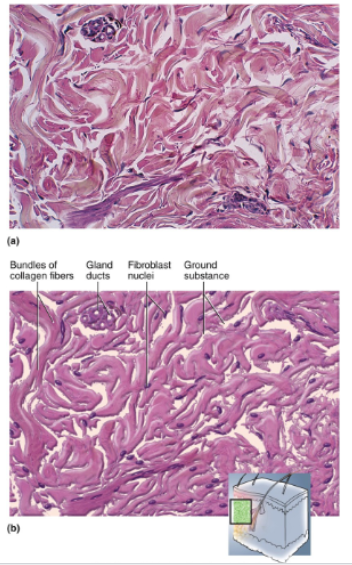
Location of dense irregular connective tissue
Deeper portion of dermis of skin; capsules around viscera such as liver, kidney, spleen; fibrous sheaths around cartilages and bones
Function of dense irregular connective tissue
Withstands stresses applied in unpredictable directions; imparts durability to tissues.
Adipose Tissue
Dominated by adipocytes, large, empty looking cells with thin margins; tissue sections often very pale because of scarcity of stained cytoplasm; adipocytes shrunken; nucleus pressed against plasma membrane; blood vessels present
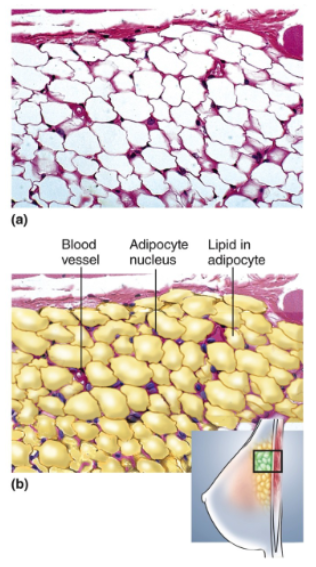
Location of adipose tissue
Subcutaneous fat beneath skin; breast; heart surface; mesenteries; surrounding organs such as kidneys and eyes
Function of adipose tissue
Energy Storage; thermal insulation; heat production by brown fat; protective cushion for some organs; filling space, shaping body
Hyaline Cartilage
Clear, glassy matrix, often stained light blue or pink in tissue sections; fine, dispersed collagen fibers, not usually visible; chondrocytes enclosed in lacunae, often in small clusters of three or four cells; usually covered by perichondrium.
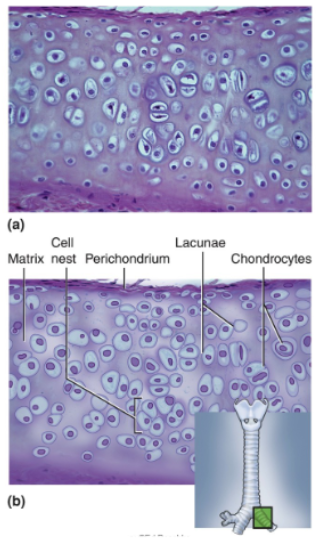
Location of hyaline cartilage
Over the ends of bones at movable joints; supportive rings and plates around trachea and bronchi; boxlike enclosure around larynx; much of the fetal skeleton; and a coastal cartilage attaches the end of a rib to the breastbone
Function of hyaline cartilage
Eases joint movements; holds airway open during respiration; moves vocal cords during speech; a precursor of bone in the fetal skeleton and the growth zones of long bones of children
Elastic Cartilage
Elastic fibers form weblike mesh amid lacunae, always covered by perichondrium.
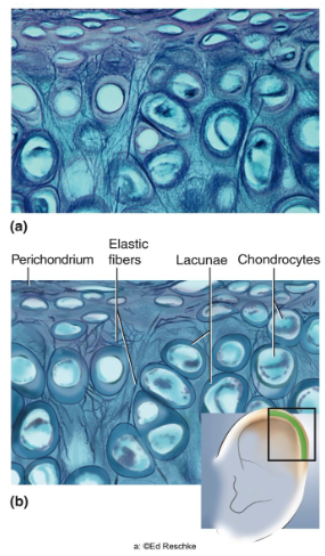
Location of elastic cartilage
External ear; epiglottis
Function of elastic cartilage
Provides flexible, elastic support
Fibrocartilage
Parallel collagen fibers similar to those of tendon; rows of chondrocytes in lacunae between collagen fibers; never has a perichondrium
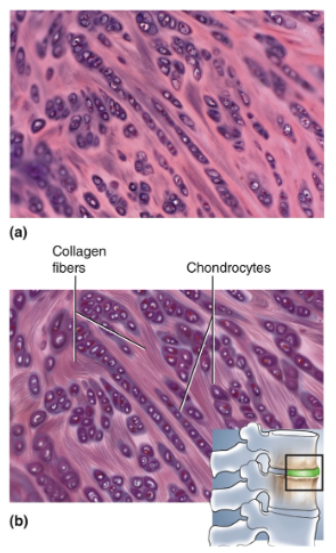
Location of fibrocartilage
Pubic Symphysis, intervertebral discs, menisci, in knee joint
Function of fibrocartilage
Resist compression and absorbs shock in some joints; often a transitional tissue between dense connective tissue and hyaline cartilage
Bone
Calcified matrix arranged in concentric lamellae around central canals; osteocytes in lacunae between adjacent lamellae; lacunae interconnected by delicate canaliculi
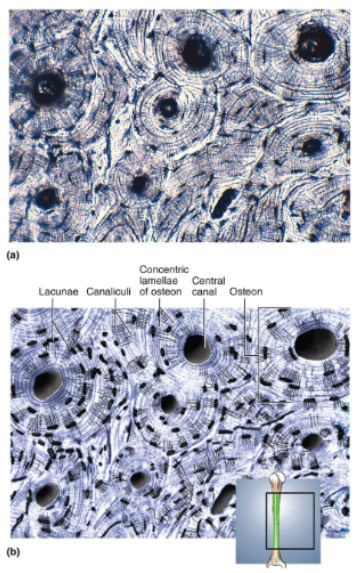
Location of bone
Skeleton
Function of bones
Physical support of body; leverage for muscle action; protective enclosure of viscera; reservoir of calcium and phosphorous
Blood
Erythrocytes appear as pale pink discs with light centers and no nuclei; leukocytes are slightly larger, are much fewer, and have variously shaped nuclei, usually stained violet; platelets are cell fragments with no nuclei, much smaller than erythrocytes
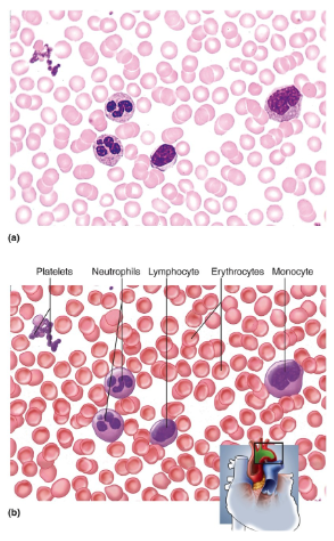
Location of blood
Contained in heart and blood vessels.
Function of blood
Transports gases, nutrients, wastes, chemical signals, and heat throughout the body; provides defense leukocytes; contains clotting agents to minimize bleeding; platelets secrete growth factors that promote tissue maintenance and repair
Collagen
The most abundant protein in the body, forming the fibers of many connective tissues in places such as the dermis, tendons, and bones
Reticular Fibers
Thin collagen fibers coated with glycoprotein. They form a spongelike framework for such organs as the spleen and lymph nodes and constitute part of the basement membranes underlying epithelia
Elastic Fibers
Thinner than collagenous fibers, and they branch and rejoin each other along their course. Made of a protein called elastin coated with a glycoprotein. Stretches and recoils like a rubber band
Collagenous Fibers
Fibers made of collagen that are tough, flexible, and resist stretching. Makes up tendons, ligaments, and deep layer of skin
Neurons (nerve cells), neuroglia (glial cells), dendrites (receives signals from other cells), neurosoma (cell body)
Cell types that compose nervous tissue
Nervous Tissue
Most sections show a few large neurons, usually with rounded or stellate cell bodies and fibrous processes (axon and dendrites) extending from the cell bodies; neurons are surrounded by a greater number of much smaller glial cells, which lack dendrites and axons
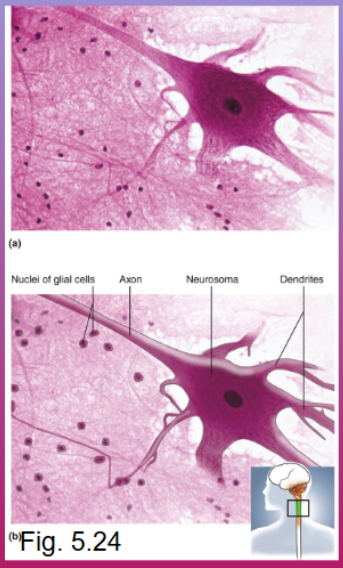
Location of nervous tissue
Brain, Spinal Cord, nerves, ganglia.
Function of nervous tissue
Internal Communication
Skeletal Muscle
Long, threadlike, unbranched cells (fibers), relatively parallel in longitudinal tissue sections; striations; multiple nuclei per cell, near plasma membrane
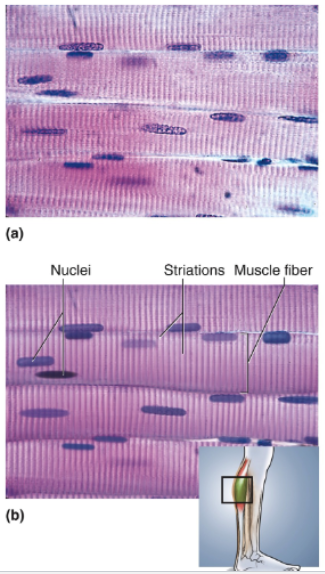
Location of skeletal muscle
Mostly attached to bones but also in the tongue, esophagus, and encircling the lips, eyelids, urethra, and anus.
Function of skeletal muscle
Body movements, facial expressions, posture, breathing, speech, swallowing, control of urination and defecation, and assistance in childbirth; under voluntary control
Cardiac Muscle
Short Cells (Cardiomyocytes) with notched or slightly branched ends; less parallel appearance in tissue sections; striations; intercalated discs; one nucleus per cell, centrally located and often surrounded by a light zone
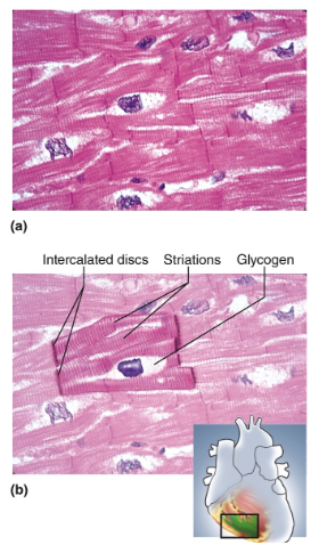
Location of cardiac muscle
Heart
Function of cardiac muscle
Pumping of blood; under involuntary control
Smooth Muscle
Short fusiform Cells overlapping each other; nonstriated; one nucleus per cell, centrally located
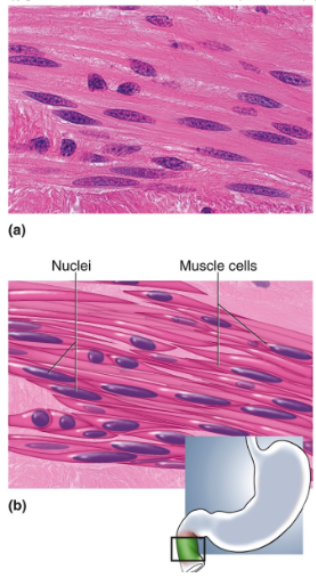
Location of smooth muscle
Usually found as Sheets of tissue in walls of blood vessels and viscera such as the digestive tract; also in the iris and associated and with hair follicles; involuntary Sphincters of urethra and anus
Function of smooth muscle
Swallowing; contractions of stomach and intestines; expulsion of feces and urine; labor contractions; control of blood pressure and flow; control of respiratory airflow; control of pupillary diameter; erection of hairs; under involuntary control
Cellular junctions
The connections between one cell and another
Tight Junction
A junction in which the plasma membranes of two adjacent cells come very close together and are linked by transmembrane cell. Prevents molecules from passing in between cells
Desmosomes
A patchlike intercellular junction that mechanically links two cells together; not continuous and can’t prevent substances from passing around them and going between the cells, but keep cells from pulling apart and enable a tissue to resist mechanical stress
Gap Junctions
A junction between two cells consisting of a pore surrounded by a ring of proteins in the plasma membrane of each cell; allows solutes to diffuse from the cytoplasm of one cell to the next.
Gland
A cell or organ that secretes substances for use elsewhere in the body or for elimination as waste. Composed mostly of epithelial tissue, but usually have a supportive connective tissue framework and capsule
Exocrine Glands
A gland that secretes its product into another organ or onto the body surface, usually by way of a duct, an epithelial tube that conveys their secretion to the surface
Endocrine Glands
A ductless gland that secretes hormones into the bloodstream
Simple Gland
Gland with a single unbranched duct.
Compound Gland
Gland with a branched duct.
Tubular Gland
Gland with the duct and secretory portion of uniform diameter
Acinar Gland
Gland with secretory vesicles that form a sac
Tubuloacinar Gland
Gland with secretory cells in both the tubular and acinar portions
Eccrine, apocrine, holocrine
Modes of secretion
Eccrine Glands
Pertaining to gland cells that release their products by means of exocytosis. Found all over the body, produce a more water substance (sweat)
Apocrine Glands
Pertaining to certain sweat glands with large lumens and relatively thick, aromatic secretions and to similar glands such as the mammary gland. Secretes proteins and fatty acids
Holocrine Glands
Gland in which cells accumulate a product and then the entire cell disintegrates