Vesicular transport
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Name 2 ways small molecules travel across the membrane
Passive transport
Active transport
How do large molecules travel across the membrane
Using vesicles
Name 2 types vesicular transport
Exocytosis
Endocytosis
Exocytosis?
secretions of macromolecules through fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane.
Endocytosis?
cell takes in macromolecules by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane.
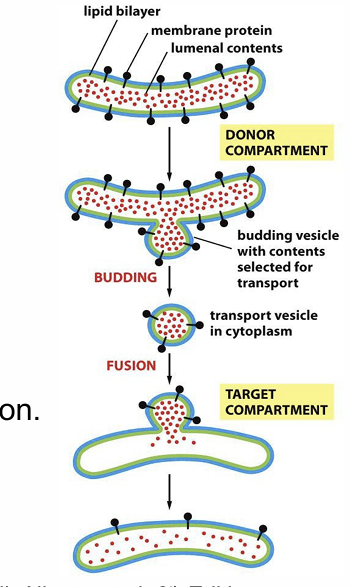
Describe process of budding and fusion
Budding from donor
Fusion with target
Membrane is transferred
Proteins retain original configuration
Soluble components transferred
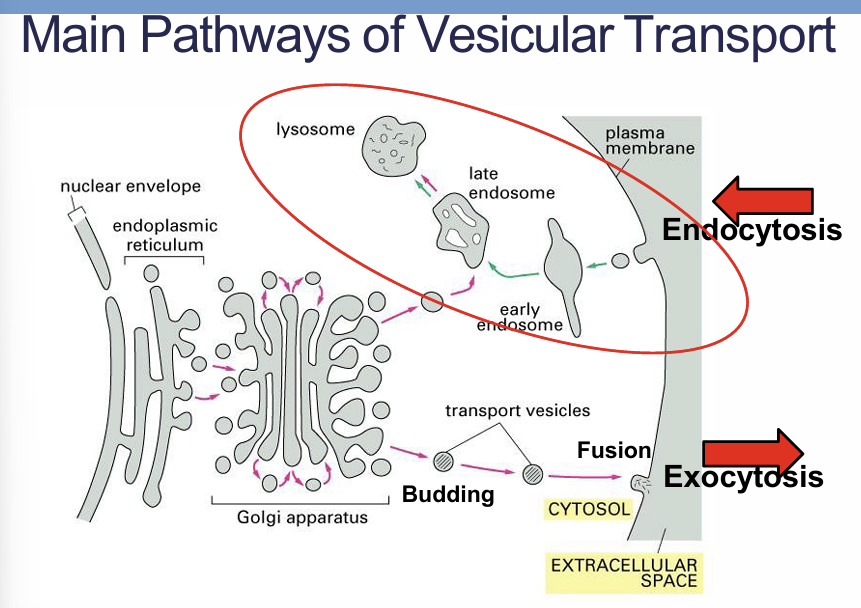
pathways
Describe composition and function of vesicles
Form part of the endomembrane system
Small membrane-bound sacs
Transport or store substances
Membrane is made of two layers = lipid bilayer
Vesicles can fuse with organelles to release their contents within the cell
Vesicles can also fuse with the cell/plasma membrane and release their contents outside of the cell
Name 6 types of vesicles
Vacuoles
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Endosomes
Transport vesicles
Secretory vesicles
Exocytosis process, name 2 types
Constitutive exocytosis
Regulated exocytosis
Constitutive exocytosis?
Steady stream of transport vesicles from trans Golgi to plasma membrane.
New lipids and proteins are continuously supplied to the plasma membrane for membrane growth, rejuvenation and remodelling
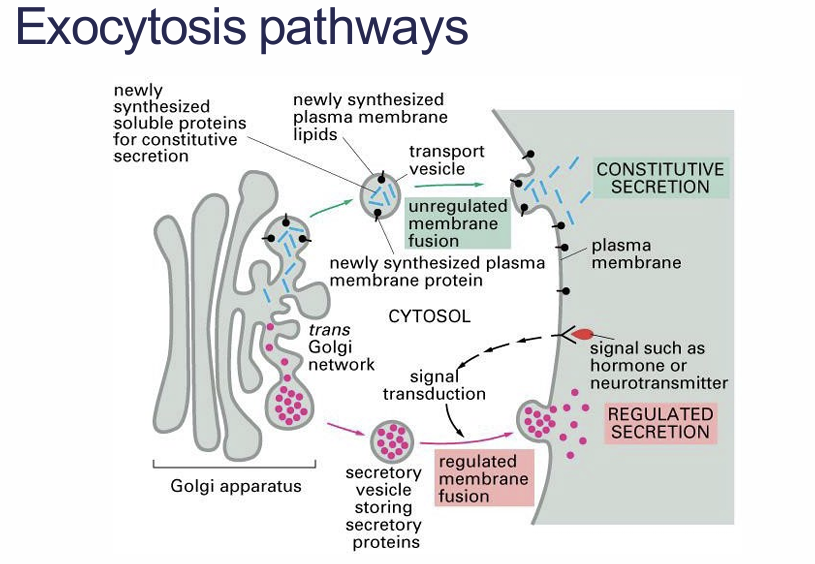
Regulated exocytosis?
Functions only in cells specialised for secretion.
Lots of secretory vesicles found in specialised secretory cells hormones, mucous, digestive enzymes
Extracellular signal will stimulate their fusion with the plasma membrane and release into the extracellular fluid
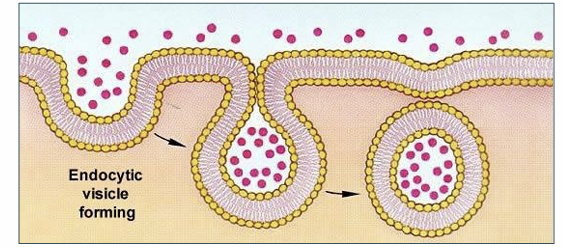
Endocytosis?
New vesicles are formed by the plasma membrane. • It is the reverse process of exocytosis, using different proteins. • Plasma membrane pinches in to form a vesicle containing extracellular material. • Three types of endocytosis.
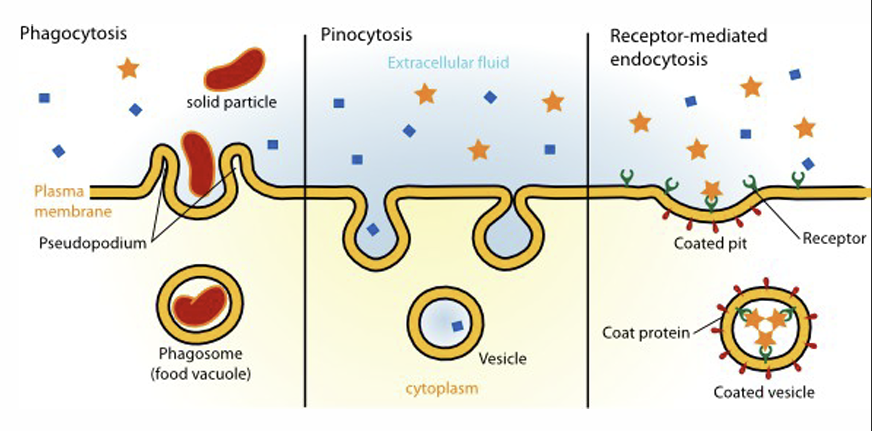
Name 3 types of endocytosis and describe
PHAGOCYTOSIS is engulfment of a particle, usually food or microorganisms, by wrapping cell membrane around it to form a vacuole.
2. PINOCYTOSIS is the same process except that fluids are taken into small vesicles.
3. RECEPTOR-MEDIATED ENDOCYTOSIS is where receptors in a receptor-coated pit interact with a specific protein, initiating formation of a vesicle
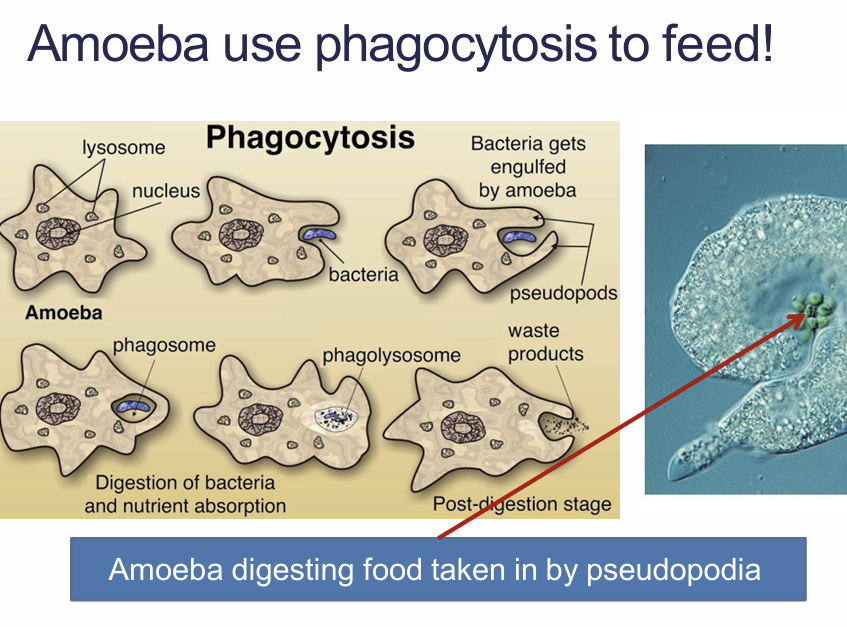
Phagocytosis?>
• A cell engulfs a particle, wrapping pseudopodia around it and packaging it into a membrane enclosed sac large enough to be classified as a vacuole. • The particle is digested after the vacuole fuses with a lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes
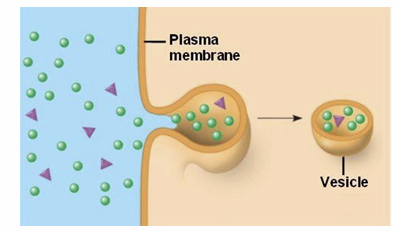
Pinocytosis?
The cell ‘gulps’ droplets vesicles. of extracellular fluid in tiny • Example: Droplets of extracellular fluid enters the cells via small vesicles. • Pinocytic vesicles are returned to the cell surface after ingestion.
Receptor mediated endocytosis
Selective uptake of specific macromolecules from extracellular fluid occurs via receptor proteins in the membrane. Ligands bind to these receptors, which are clustered in ‘coated pits’—areas lined on the cytoplasmic side with special proteins.
Example: Cholesterol, carried in the blood as low-density lipoproteins (LDLs), binds to LDL receptors on the membrane.
Name 3 types of coated vesicles
CLATHRIN
COP I
COP II
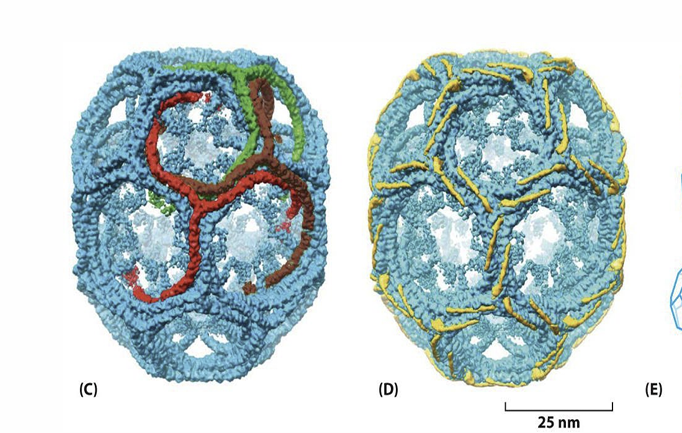
Clathrin?
comprised of 3 light chains and 3 heavy chains. • Clathrin coated vesicles traffic between the golgi network and the lysosomes; and between the plasma membrane and the endosomes. • Triskelions form a framework of hexagons and pentagons to form coated pits on the membrane surface.
Formation of a clathrin coated vesicle process?
Molecules bind to surface receptors of the plasma membrane proteins located in areas of clathrin-coated pits. 2. Pits bud to form clathrin-coated vesicles. 3. Fusion with endosomes or lysosomes
Endosomes?
Endosomes appear as a complex membrane tubes and larger vesicles. • Two populations of endosomes: set of connected • Early endosomes Late endosomes (near nucleus) Endosome – main sorting station in the endocytic pathway