Biology keystones Note
1/157
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
What are large molocules called?
Biomolecules
How many MAJOR molecules are there?
There are 4
Large substance that are like building blocks for molecules
Monomer
Energy sources
Carbohydrates
What is a good source for carbohydrates?
Bread and pasta
IN CARBOHYDRATES what are the monomers called?
Monosacchrides
What is the scientific term for Fats?
Lipids
How many monomers do Lipids/Fats have?
2
IN LIPIDS what is 1 of monomers called?
Fatty Acids
IN LIPIDS what is the other of monomers called?
Glycerol
What is a good source of Lipids?
Butter, oil, cholesterol
What do lipids make up in the cell?
Cell membrane
What are proteins good for?
Building muscle, immune system, and acting as enzymes
What food contains protein?
Meat and beans
IN PROTEIN what are the monomers called?
Amino Acids
What does a Nucleic Acid have?
DNA and RNA
IN NEUCLEIC ACIDS what is the monomer called?
nucleotide
What can have a Nucleic Acid?
Any living being/thing
What shape is an Enzyme?
Any shape as long as it has a divot
What goes into the divot?
Substrate
What can the enzyme do to the Substrate?
Build or break it
What are Enzymes made of?
Protein
What can they do to certain reactions?
They can speed it up
What is bad for enzymes?
PH and Tempature
What would happen if the Enzyme was effected?
The divot wouldn’t match with the Substrate
What does Homeo mean in Homeostasis?
Constant
What does Stasis mean in Homeostasis?
Stable
What can often trigger homeostasis?
Weather
What does the cell membrane do?
It controls what goes in and out
What kind of movement does Osmosis have?
Movement of Water
What kind of transport is Osmosis?
Passive Transport
Why would there be a low concentration of water?
Solutes could be in the water
What is a Solute?
Anything that can be dissolved (salt, sugar)
What would happen if there was solutes in the water?
The water would go towards the solute
IN THIS CASE What does Hypertonic mean?
A high concentration of solute
IN THIS CASE What does Hypotonic mean?
A low concentration of solute (opposite of Hypertonic)
What makes a Prokaryotic cell Prokaryotic?
It’s Unicellular (Single Celled)
What is an example of Prokaryotic cell?
Bacteria and Archaea
What makes a Eukaryotic cell Eukaryotic?
It can be Unicellular or Multicellular (more then one)
What is an example of Eukaryotic cell?
Fungi, Plants, and Animals
What do Pro and Eu have in common?
They have DNA, Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, and Cell membrane
What is one that they kind of have in common
Pro have Cells walls, Eu only sometimes have it (Plants and Fungal cells have them. Animal cells don’t)
What do Eukaryotes strictly have?
Nucleus and Membrane bound organelles
What do Prokaryote not have?
No Nucleus and No Membrane bound organelles
What is Photosynthesis?
It’s a process that produces oxygen
What do plants and animals need to make energy?
Glucose
What kind of energy comes from Glucose and Cellular Respiration?
ATP
What do plants need to make oxygen and sugar?
Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
How do plants capture light?
Pigment
What is one of these pigments called?
Chlorophyll
Where is the Chlorophyll located?
Chloroplast
What 2 reactions make up Photosynthesis?
Light Dependent Reaction and Light Independent Reaction
Where does the Light Dependent reaction happen?
Thylakoids
What are Thylakoids and where are they located and look like?
They contain pigment, they are in the chloroplast, and they look stacked
What happens in the Light Dependent Reaction?
It gets converted to a Chemical Reaction
What does a Chemical Reaction create?
ATP and NADPH
What happens to the water?
It gets split
What time does the Light Independent Reaction happen?
At the same time when the Light Dependent Reaction is happening
Where does the Light Independent process happen?
In the Stroma
What is the Stroma, where is it located?
It’s a fluid in the Chloroplast, it’s outside of the Thylakoids
What happens to the Carbon Dioxide?
It changes to it’s more usable and organic form via Enzymes
What does that process make in the end?
Glucose
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Triphosphate
What does the formula of Cellular Respiration look similar to?
Photosynthesis
What is one difference that Cellular Reparation CAN do but Photosynthesis CAN’T
Break glucose
What is unique about a flower glucose
It makes and breaks glucose
What are the 3 steps in Cellular Respiration?
Glycolysis, Kreb Acid Cycle, and Electron Transport Chain
Where does the Glycolysis take place?
Cytoplasm
What happens in the Cytoplasm?
Glucose gets converted into a more usable formula called Pyruvate form ATP and NADH
Where does the Kreb Acid Cycle take place?
Mitochondria
What happens in the Mitochondria?
The Mitochondria oxidize Pyruvate to create 2 ATP, 5 NADH, and 2 FADH
Where does the Electron Transport Chain take place?
Mitochondria
What happens in the Mitochondria?
The NADH AND FADH Transport electrons to electron carriers
Where do those Electron carriers bring the electrons to?
ATP Synthase
What does ATP Synthase make?
ATP
Where is the DNA located?
Nucleus
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
What does DNA control?
It controls all your traits (height, hair color, eye color)
Does every cell in you body have DNA?
Yes
Is your DNA code turned on all the time?
No
What does Gene Regulation mean?
DNA code can be turn on/off
What category in the 4 major molecules does DNA fall under?
Nucleic Acid
What shape is DNA
Double Helix
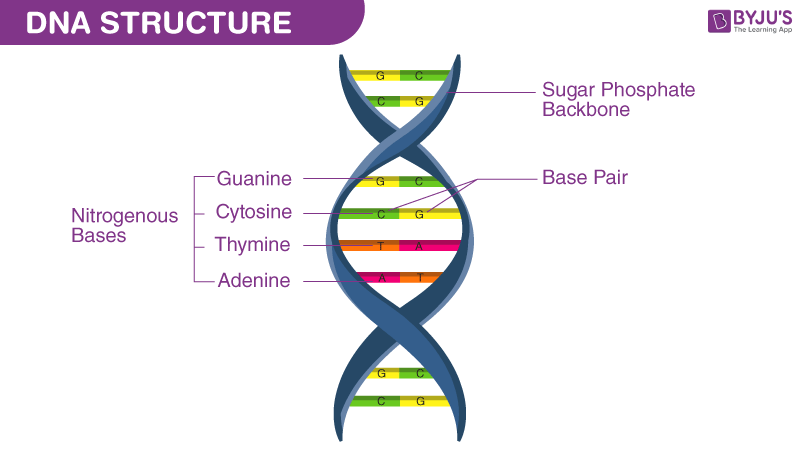
There are 4 bases in the DNA structure, what are they called?
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine
Which of the 4 bases go together?
A → T
G → C
What is holding the DNA strucutre?
Hydrogen bonds
What would happen if you didn’t have RNA
You wouldn’t be able to get the genetic message to your cells to create your traits
What does RNA stand for?
Ribonucleic Acid
What are the 4 bases for RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, and Cytosine
Which of the 4 bases go together?
A → U
G → C
Where does RNA start and where does it go and why?
It starts in the Nucleus and travels out to deliver messages of the DNA
How many types of RNA are there?
3
What are the 3 RNA types
mRNA (message), tRNA (transport), and rRNA (ribosome)
What does DNA code proteins to do?
Make pigment (color)
Protein makes color because it was coded to do so. What is that process called?
Protein Synthesis
How many steps does Protein Synthesis have?
2
What are those 2 steps called?
Transcription and Translation (in that order)
What is the difference between them?
Transcription = Transcribes the DNA into a message (mRNA)
Translation = Translates the DNA message into a protein
What happens when the mRNA sends that message?
The tRNA carries an Amino Acid and bases to plug into the RNA
What happens it pairs up?
The tRNA will drop off the Amino Acid