Marketing Chapter 1-3
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is Marketing?
Marketing is the process of creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value to satisfy customer needs.
What are the Core Concepts of Marketing?
Needs, Wants, Demands: Understanding what customers require, desire, and can afford.
Target Market: Specific group of customers a company aims to serve.
Value Proposition: Unique benefits offered to satisfy customer needs better than competitors.
Marketing Mix (4Ps): Product, Price, Place, Promotion—tactical tools to deliver value.
Customer Relationship Management: Building and maintaining long-term customer loyalty.
Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning (STP): Dividing markets, choosing segments, and positioning offerings for maximum impact.
Evolution of Modern Marketing thought
Production Era: Focus on mass production; good products sell themselves.
Sales Era: Emphasis on aggressive selling and promotions.
Marketing Era: Focus shifts to meeting customer needs and wants.
Societal Era: Balances customer satisfaction with social responsibility and sustainability.
Digital Era (modern): Uses technology and data analytics for personalized marketing and engagement.
key aspects of each Orientation
Production, Sales, Market, and Value-Based.
Understand the role of co-creation
is a collaborative process where customers and businesses jointly create products or services.
What does it mean to be Value Driven?
Focus on delivering real customer benefits perceived as worth more than the cost.
Use data to meet needs, lower costs, and build loyalty.
Connect with customers through meaningful experiences, not just selling products.
concepts related to Societal Welfare
more holistic view of marketing that goes beyond simply buyer and seller but includes impact on community/society as well.
Marketing is about
Creating:, Capturing:, Communicating: and Delivering Value:
What is Marketing Strategy?
is a long-term plan to achieve marketing goals by understanding customer needs and gaining competitive advantage.
Components of “Marketing Strategy”
•Job #1:
•Identify market segments
•Job #2
•Define target market(s)
•Job #3:
•Craft Unique Selling (Value) Proposition that offers a sustainable competitive advantage
•Job #4:
•Implement the marketing strategy & tactics
•Job #5:
•Measure, monitor, course correction
Strategic Planning versus Tactical Planning
Strategy= goal/ a plan designed to achieve
a major or overall aim.
Tactic= actions to achieve that goal/a specific action designed to
obtain a particular result.
sustainable competitive advantage
•Unique
•Superior
•Long term
Gaining Competitive advantage
Competitive advantage is what makes a company better than its rivals, allowing it to offer superior value or lower cost.
gain it by:
Cost Leadership: Being the lowest cost producer.
Differentiation: Offering unique, high-quality products.
Focus: Targeting a specific market niche better than competitors.
Components of a Marketing Plan
Plan – Planning, Implementation & Control
Mission, Objectives, SWOT analysis
Mission: Defines the firm’s purpose and what it wants to accomplish now.
Objectives: Specific, measurable goals that guide the firm's actions.
SWOT Analysis: Assesses internal Strengths and Weaknesses, and external Opportunities and Threats to inform strategy.
Portfolio analysis
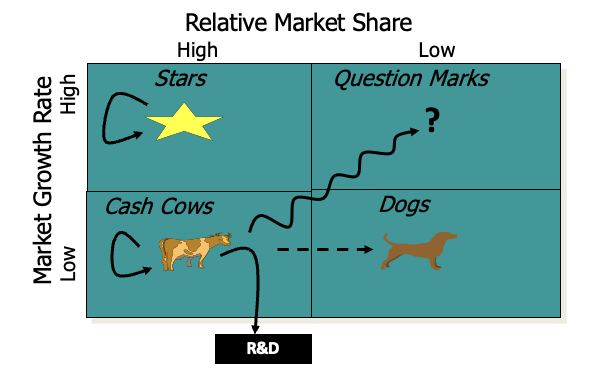
understand the basic characteristics of each and the strategy associated with each (e.g., Build, Hold, Milk/Harvest, Divest
Stars: High market share, high growth;
Strategy: Build by investing heavily for growth and leadership.
Cash Cows: High market share, low growth;
Strategy: Hold or Milk by maximizing profits with minimal investment.
Question Marks: Low market share, high growth;
Strategy: Build or Divest—invest to grow market share or phase out if unsuccessful.
Dogs: Low market share, low growth;
Strategy: Divest or phase out as they drain resources, unless strategically needed.
Growth Strategies
Market Penetration: Increase sales of current products in existing markets (e.g., more promotions or ads).
Market Development: Enter new markets with existing products (new geographic areas or customer segments).
Product Development: Create new products for current markets to meet evolving needs.
Diversification: Introduce new products into new markets; highest risk but potential high reward.
Macro versus Micro (Immediate) Environment
Micro Environment: Immediate factors close to the company—customers, suppliers, competitors—that directly affect daily operations and are somewhat controllable.
Macro Environment: Broader societal forces—economic, political, technological, cultural—that influence all businesses, are uncontrollable, and shape long-term strategies.
How do these factors influence marketing: Social trends, Tech advances, economic, and political legal
Social Trends: Shape what consumers want and how brands engage (e.g., social media, cultural shifts).
Technology: Enables new marketing channels, data use, and customer interactions.
Economic: Affects consumers' spending power and demand for products.
Political-Legal: Regulates marketing practices and product availability.
Defining Consumer Behavior
Thoughts, feelings, actions, and marketing strategies and tactics
Consumer Decision Process
Need recognition
Information research
Evaluation of alts: impacted by beliefs, attitudes, and purchase intentions
Decision Rules: Compensatory and non compensatory
What are “heuristics” and why do consumers rely on them?
Heuristics are mental shortcuts or rules of thumb that help consumers make quick decisions with less effort.
They simplify complex choices by using previous experiences, simple cues (like brand or packaging), or feelings.
Consumers rely on heuristics to save time and reduce cognitive load when facing many options or limited information.
While useful, heuristics can sometimes lead to biases or errors in judgment.
Post-Purchase stage – Cognitive dissonance, Satisfaction and Loyalty
Post-Purchase Stage: Involves consumers’ thoughts and feelings after buying.
Customer Satisfaction: Occurs when product meets or exceeds expectations, leading to repeat purchases and positive word of mouth.
Cognitive Dissonance: Buyer’s remorse or doubt if the product doesn’t meet expectations, causing discomfort.
Loyalty: Satisfied customers become loyal, repurchase, and recommend the brand, which benefits marketers.
Marketers reduce dissonance by setting realistic expectations, offering guarantees, and maintaining contact post-sale.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Psychological: Motivation (needs), perception, learning, beliefs, and attitudes shape how consumers think and feel about products.
Personal: Age, lifestyle, economic status, occupation, and personality affect preferences and buying power.
Social: Family, friends, reference groups, and social roles influence opinions and behaviors.
Cultural: Culture, subculture, and social class guide values and consumption patterns.
Economic: Income and overall economic conditions determine purchasing ability.
Technological: New technologies change how consumers get information and buy products.
Maslow’s Hierarchy
Physiological (basic survival like food, water)
Safety (security, job stability)
Love/Belonging (friendship, family)
Esteem (status, respect)
Self-Actualization (personal growth, fulfilliment)
components of attitude
Attitude is a person’s lasting evaluation, feeling, and behavioral tendency toward an object or idea.
Cognitive Component: Beliefs or thoughts about a product, brand, or issue (e.g., thinking a movie is highly rated).
Affective Component: Emotions or feelings about the object (e.g., excitement or dislike based on past experiences or marketing).
Behavioral Component: Actions or intentions based on beliefs and feelings (e.g., deciding to watch a movie or buy a product).
Reference Groups: Friends, family, celebrities, or communities that influence attitudes and buying decisions by shaping beliefs, emotional reactions, and behaviors (e.g., following friends’ advice or imitating group trends).
Involvement and Consumer Buying Decisions
High involvement leads to extended problem solving—consumers research, evaluate options, and seek information for risky or significant purchases.
Low involvement results in limited or habitual decision making—consumers rely on routine, make quick choices, or respond to simple cues like brands or endorsements.
Extended versus Limited Problem Solving versus Routine/Habitual buying
Extended Problem Solving: High involvement; consumers research, compare options, and invest time/effort (e.g., buying career clothing).
Limited Problem Solving: Moderate involvement; consumers rely on prior experience, spend some effort (e.g., impulse grocery buys).
Routine/Habitual Buying: Low involvement; minimal thought, quick decisions (e.g., fast food).