Chapter 3: Nervous System Organization
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/79
Last updated 5:11 AM on 8/14/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
nuclei
clusters in the cortex that organize neurons
2
New cards
tracts
fiber pathways that form from the long-distance connections between neurons and cells
3
New cards
anatomical reference to body parts
rostrum (beak), caudum (tail), dorsum (superior), and ventrum (inferior)
4
New cards
anterior
structures that are in front
5
New cards
posterior
structures that are behind
6
New cards
lateral
structures that are at the side
7
New cards
medial
structures are at the center/between
8
New cards
coronal
a section that reveals a frontal view
9
New cards
horizontal
a section that reveals a dorsal view
10
New cards
sagittal
a section that reveals a medial view
11
New cards
ipsilateral
structures that lie on the same side of the nervous system and body (e.g. left arm is ipsilateral to the left leg)
12
New cards
contralateral
structures that lie on the opposite side of the nervous system and body (e.g. left arm is contralateral to the right leg)
13
New cards
bilateral
structures that lie in each hemisphere of the nervous system and body (e.g. the lungs are bilateral structures)
14
New cards
proximal
structures close to one another (e.g. the shoulder is proximal to the elbow)
15
New cards
distal
structures far away from one another (e.g. the hand is distal to the shoulder)
16
New cards
afferent
any movement towards a brain structure (e.g. sensory pathways that carry messages from the body towards the brain and spinal cord)
17
New cards
efferent
any movement away from a brain structure (e.g. motor pathways leading to the body from the brain and spinal cord)
18
New cards
precentra gyrus
a part of the brain responsible for motor ability
19
New cards
parasympathetic nerves
calming nerves that tell the organs when to rest and digest
20
New cards
sympathetic nerves
arousing nerves that tell the organs when to fight and flee
21
New cards
meninges
a triple-layered set of membranes within the bony case enclosing the CNS
22
New cards
dura mater
tough layer of tissue enclosing the brain in a loose sack
23
New cards
arachnoid membrane
a very thin sheet of delicate tissue that follows the brain’s contours
24
New cards
pia mater
a moderately tough tissue that clings to the brain’s surface
25
New cards
booid-brain barrier
protects the CNS by limiting the movement of chemicals from the rest of the body into it and by protecting it from toxic substances and infection.
26
New cards
astroglia
glial cells that stimulate the cells of capillaries to form tight junctions with one another to prevent many blood-borne substances from crossing from the capillaries into the CNS tissue
27
New cards
anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
irrigates the medial and dorsal parts of the cortex
28
New cards
middle cerebral artery (MCA)
irrigates the lateral surface of the cortex
29
New cards
posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
irrigates the ventral and posterior surfaces of the cortex
30
New cards
neural stem cell
a germinal cell that the brain originates in
31
New cards
progenitor cells
migrate and act as precursor cells
32
New cards
blasts
non dividing primitive nervous system cells
33
New cards
sensory receptor
a cell that transduces sensory information into nervous system activity
34
New cards
bipolar neuron
a cell body with a dendrite on one side and an axon on the other (found in the retina)
35
New cards
somatosensory neuron
projects from a sensory receptor in the body into the spinal cord. its dendrite and axon are connected so messages don’t have to pass through the body, speeding up information conduction
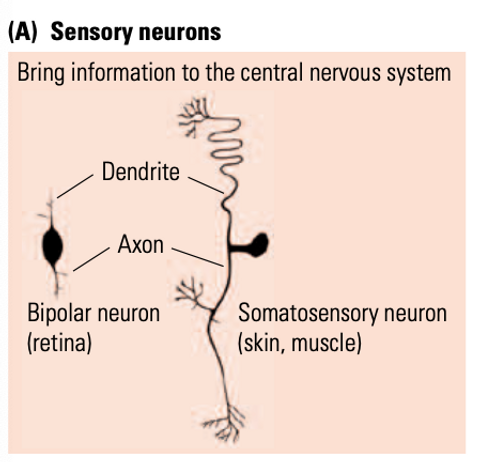
36
New cards
interneurons
links up sensory and motor neuron activity in the CNS
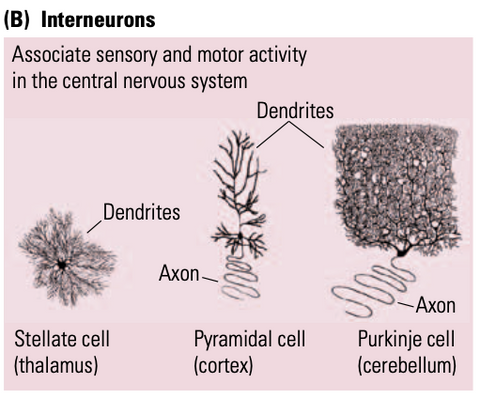
37
New cards
motor neurons
located in the brainstem and spinal cord, and project to facial and body muscles (the final common path because all movement is produced through them)
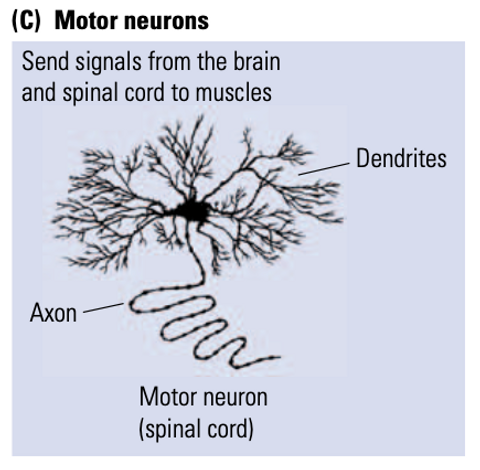
38
New cards
gray matter
color comes from the capillaries and neuronal cell bodies that predominate there; this makes up the cortex
39
New cards
white matter
consists of axons that extend from these cell bodies to form connections with neurons in other brain areas
40
New cards
reticular matter
contains a mixture of cell bodies and axons which gives it a net-like appearance, or mottled gray and white.
41
New cards
ganglia
clusters (layers or nuclei) within the PNS
42
New cards
nerves
fibers and fiber pathways that enter and leave the CNS
43
New cards
ventricles
four prominent pockets of the hollow region in the tube of the brain; where CSF flows through; “lateral ventricles” (first and second) form C-shaped lakes underlying the cerebral cortex and third and fourth ventricles extend into the brainstem and spinal cord, and are connected by the cerebral aqueduct
44
New cards
dermatome
skin cut body segments that encircles the spinal column
45
New cards
posterior root
strands of fiber that converge from information being brought in by the body’s sensory receptors from afferent fibers
46
New cards
anterior root
strands of fiber that converge from information being brought out towards the muscles from the efferent fibers
47
New cards
reflexes
specific movements elicited by specific forms of sensory stimulation.
48
New cards
flexion
reflexes that bring the limb toward the body and away from injury in response to pain and temperature
49
New cards
extension
reflexes that extend the limb outward, away from the body in response to fine touch and muscle receptors
50
New cards
cranial nerves
12 pairs that convey sensory (s) and motor (m) signals to and from the head. one set controls the left side, the other set controls the right (olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abdunces, facial, auditory vestibular, glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory, and hypoglossal)
51
New cards
referred pain
pain that’s perceived as coming from the outer parts of the dermatome
52
New cards
brain stem
consists of the diencephalon, the midbrain, and the hindbrain
53
New cards
hindbrain
consists of the cerebellum, recticular formation, the pons, and the medulla
54
New cards
cerebellum
plays a role in motor coordination, motor learning, and may coordinate other mental processes
55
New cards
reticular formation
maintains “general arousal” or consciousness (RAS)
56
New cards
pons
bridges inputs from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain through its nuclei
57
New cards
medulla
regulates vital functions like breathing and the functioning of the cardiovascular system
58
New cards
midbrain
consists of the tectum and the tegmentum
59
New cards
tectum
a posterior sensory component, and the roof of the third ventricle.
60
New cards
superior colliculi
structure of the tectum that receives projections from the retina
61
New cards
inferior colliculi
structure of the tectum that receives projections from the ear
62
New cards
tegmentum
an anterior motor structure, and the floor of the third ventricle
63
New cards
substantia nigra
black substance that connects ot the forebrain and rewards behaviors such as approaching desired objects
64
New cards
periacqueductal gray matter (PAG)
controls species-typical behaviors (e.g. sexual) and modulates pain responses
65
New cards
diencephalon
consists of the hypothalamus, thalamus, and the epithalamus
66
New cards
hypothalamus
takes part in nearly all aspects of motivated behavior—feeding, sexual behavior, sleeping, temperature regulation, emotional behavior, and movement.
67
New cards
thalamus
serves as a hub for the cortex, which relays information through it, and other brain regions. lateral geniculate body (LGB) receives visual projections; medial geniculate body (MGB) receives auditory projections; and ventrolateral posterior nuclei (VLP) receives touch, pressure, pain, and temperature projections from the body
68
New cards
epithalamus
secretes melationin, which influences daily and seasonal body rhythms
69
New cards
habenula
regulates hunger and thirst
70
New cards
pineal gland
influences daily and seasonal biorhythms
71
New cards
forebrain
consist of the basal ganglia, the limbic system, and the neocortex
72
New cards
basal ganglia
a collection of nuclei that form a circuit with the cortex thats associated with movement and learning. includes the putamen, the globus pallidus, and the caudate nucleus
73
New cards
limbic system
plays a role in self-regulatory behaviors such as emotion, personal memories, spatial behavior, and social behavior. consists of the amygdala, the hippocampus, and the cingulate cortex
74
New cards
amygdala
participates in emotion
75
New cards
hippocampus
participates in personal memory and spatial navigation
76
New cards
cingulate cortex
invilved in sexual behavior, among other social interactions
77
New cards
neocortex
the heavily wrinkled outer part of the forebrain that contains six layers of cells (gray matter)
78
New cards
primary areas
receives projections from the major sensory systems or send motor projections to the muscles
79
New cards
secondary areas
adjacent to and interconnected with primary areas, and involved in elaborating information received from or sends commands to primary areas
80
New cards
tertiary areas (association cortex)
mediates complex activities such as language, planning, memory, and attention