12U Biology- Homeostasis: A Fine Balance
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
homeostasis
process by which a constant internal environment is maintained despite changes in the external environment
internal environment
refers to the fluid between our cells (etracellular fluid)
sensor
detects change
integrator
processes info
effector
produces response
negative feedback
process by which a mechanism is activated to restore conditions to their original state
positive feedback
process by which small effect is amplified
Endotherms
organisms that are capable of generating enough heat through metabolism to regulate their own tempurature
Ectotherm
organims that depend on the environment around them to regulate their body tempuratures; unable to generate their own body heat; majority of animals
Thermoregulation
process of keeping body at a constant tempurature
Hypothalamus
monitors body tempuature, sends nerve impulses to skin
Vasodilation
blood vessels supplying blood to skin SWELL/ dialate so more heat is carried by blood to skin where it can be lost to the air
Vasocontriction
blood vessels SHRINK down to reduce heat loss through skin when body temperature is back to normal
Osmosis
water moves from a high concentration to a low one BUT this means it is moving from a low solute concentration to a high one
Osmotic pressure
pressure that results from difference in water concentration on two sides of a membrane
Osmoregulation
regulating osmotic pressure of bodily fluids and cells
Hyperosmotic
higher concentration of solutes
Hypo osmotic
lower concentration of solutes
Iso osmotic
equal solute concentration on both sides of membrane
Glomerulus and Bowman’s Capsule
Filters blood, allowing waste products and excess water; then collects the filtered fluid, known as glomerular filtrate, which eventually forms urine.
Proximal Tubule
It reabsorbs most of the filtered water, essential nutrients like glucose and amino acids, and ions such as sodium and potassium. It also secretes waste products like urea and creatinine. Additionally, helps regulate the body's pH balance and maintains osmolarity by reabsorbing solutes. Overall, it plays a crucial role in urine formation.
Descending limb of the loop of Henle
Permeable to water. It is responsible for reabsorbing water from the filtrate, which helps in concentrating the urine. NaCl becomes concentrated
Ascending limb of the loop of Henle
responsible for reabsorbing sodium and chloride ions from the filtrate. It plays a crucial role in the formation of concentrated urine by creating a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney. Permeable to NaCl, resulting in diffusion of NaCle out of the
Distal Tube
selective reabsorption, active + passive transport, nutrients move from blood into filtrate, helps regulate K+ and NaCl
Collecting Duct
urine formation
Afferent
blood going in
Efferent
blood going out
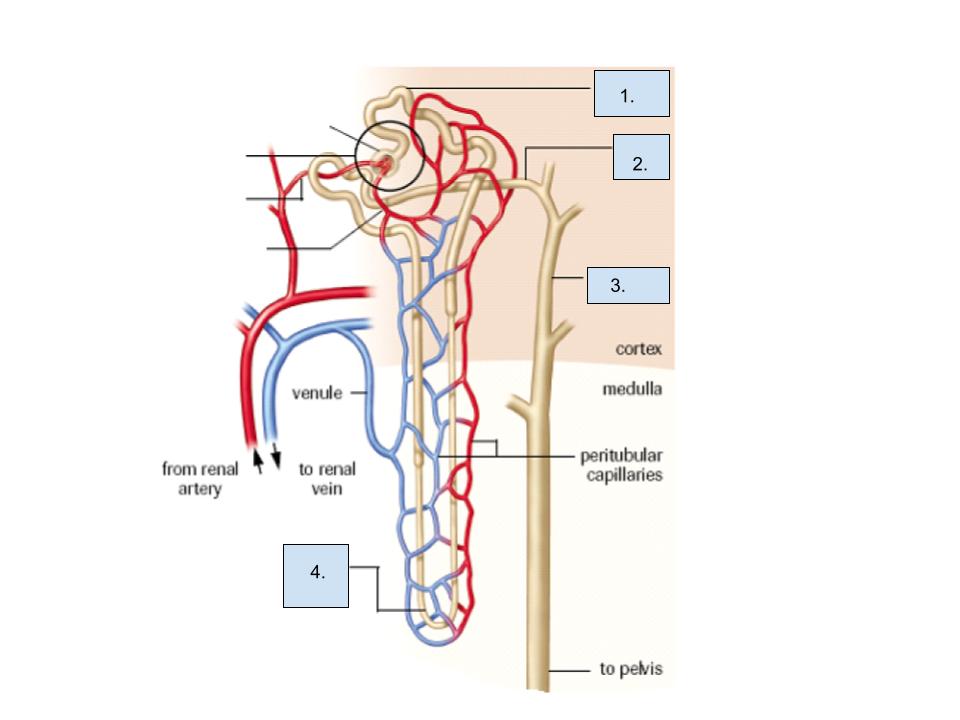
What is label 1?
proximal tubule
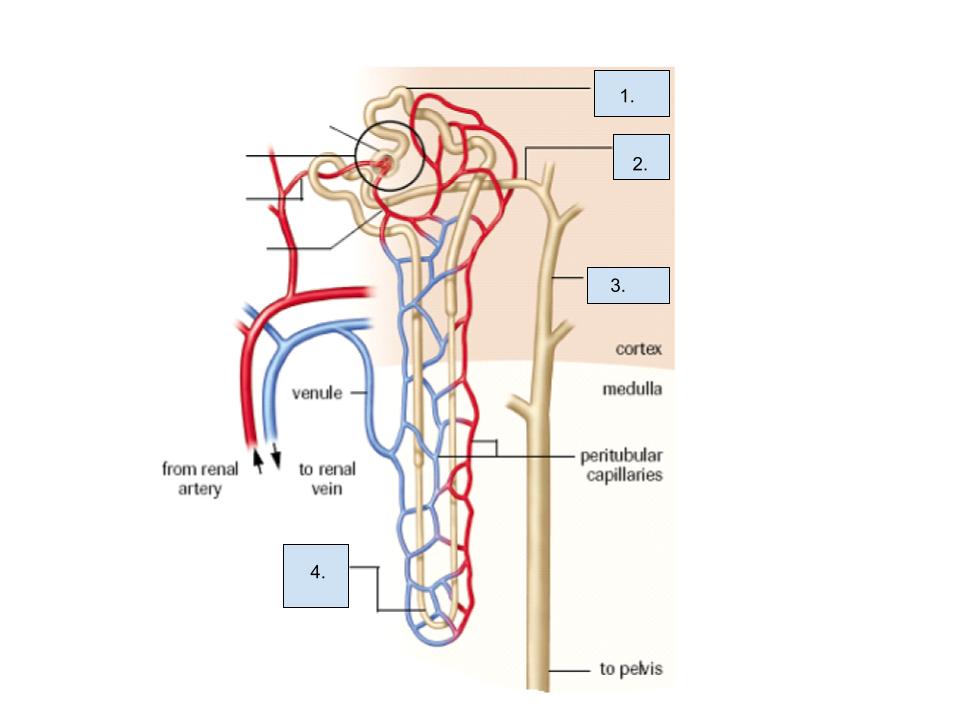
What is label 2?
distal tube
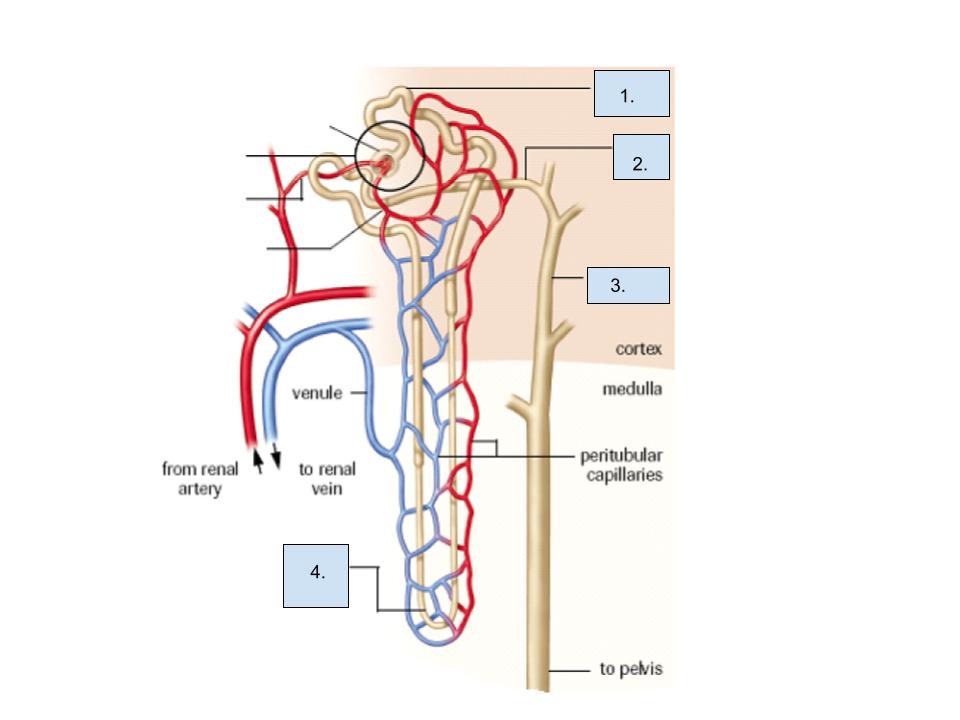
What is label 3?
collecting duct
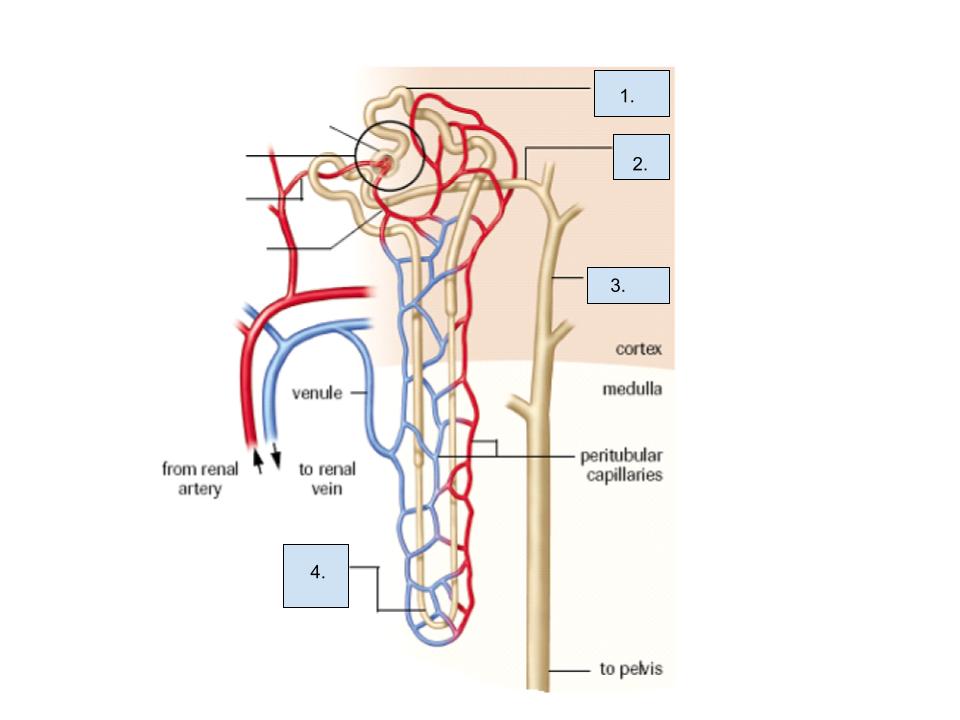
What is label 4?
loop on Henle