NET4007: Exam Set #2
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam Set made from review slides 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
2. Apply DCT to 8x8 blocks.
3. Quantize the DCT coefficients.
4. Zig-zag ordering and Run-Length Encoding (RLC).
5. Entropy coding (e.g., Huffman coding).
What is chroma subsampling in JPEG?
Chroma subsampling (e.g., 4:2:2 or 4:4:4) reduces color resolution while preserving luminance detail, as human vision is less sensitive to color variations.
What are the storage advantages of Color Look-up Tables (LUTs)?
For a 640x480 8-bit image, LUTs reduce storage to ~300 kB compared to ~921.6 kB for 24-bit images.
How do you decide the number of colors for a LUT?
The number of bits determines the table size: an n-bit LUT can index (2^n) colors. For example, 8-bit LUTs support 256 colors.
- P-frames: Predicted using past frames.
- B-frames: Bidirectionally predicted using past and future frames.
What is the role of chroma subsampling in MPEG?
MPEG employs chroma subsampling (e.g., 4:2:0) to increase color quality
Explain briefly the basic idea behind Information Theory. (5 points) Why is it needed in multimedia compression?
Information theory is an organizing strategy for data. It allows us to store and transmit large amounts of data like videos and music files in a much smaller form, saving space and bandwidth.
Calculate the entropy of “GOOGLE”. (20 points)
Unique Characters and Their Frequencies:
G: 2
O: 2
L: 1
E: 1
Total Characters: 6
Probabilities of Each Character:
P(G) = 2/6 = 1/3
P(O) = 2/6 = 1/3
P(L) = 1/6
P(E) = 1/6
Entropy Formula:
Entropy (H(S)) = - Σ P(x) * log2(P(x))
H(S) = -(1/3 log2(1/3) + 1/3 log2(1/3) + 1/6 log2(1/6) + 1/6 log2(1/6))
H(S) = -(2/3 log2(3) + 1/3 log2(6))
H(S) ≈ -(2/3 1.585 + 1/3 2.585)
H(S) ≈ -1.917
H(S) ≈ 1.917 bits/character
Encode “GOOGLE” using Huffman coding algorithm.
Frequency Table:
G: 2
O: 2
L: 1
E: 1
Huffman Code:
101011001000
Average Code Length:
(1*2 + 2*2 + 1*3 + 1*3)/6 = 2 bits/character
Close to the 1.917 bits/character for entorpy
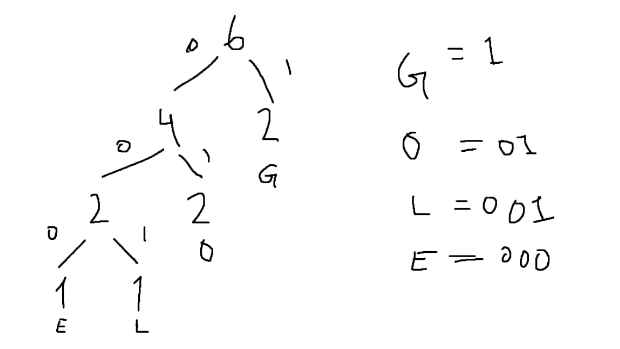
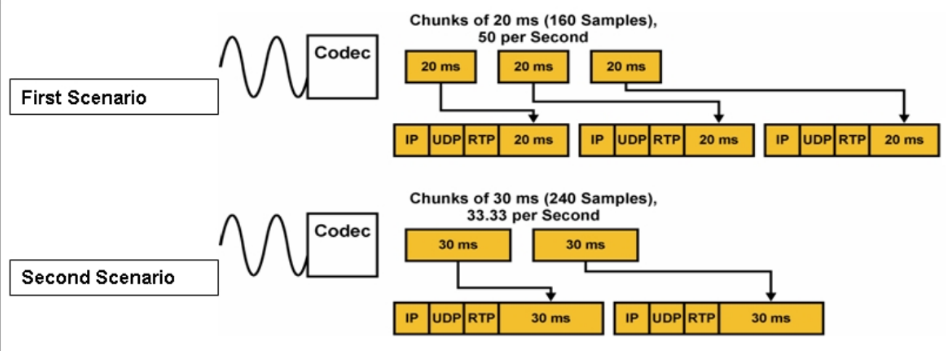
Refer to the following exhibit. On the basis of the two scenarios, which statement is true about the impact of the VoIP packet size and rate on network performance? (10 points)
(a) The first scenario introduces smaller IP overhead and lower bandwidth consumption but will increase the delay for the voice packets.
(b) The first scenario introduces additional IP overhead, which results in higher bandwidth consumption needed to transport the voice packets.
(c) The first scenario introduces the VoIP packets transportation at lower packet rate, which results in higher bandwidth consumption to transport the voice packets.
(d) The second scenario introduces additional IP overhead, which results in higher bandwidth consumption needed to transport the voice packets.
(b) The first scenario introduces additional IP overhead, which results in higher bandwidth consumption needed to transport the voice packets.
Suppose we have available 24 bits per pixel for a color image. However, we notice that humans are more sensitive to R and G than to B – in fact, 1.5 times more sensitive to R or G than B. How could we best make use of the bits available? (15 points)
Since humans are 1.5 times more sensitive to R and G than to B, so we assign that proportional weight of 1.5 to R and G and just 1 to B, summing the total weights to 4.
Using these weights the 24 bits are allocated as (1.5 / 4) * 24 = 9 bits to R and G each, and (1 / 4) * 24 = 6 bits to B.
If the block size of a 2D DCT transform is 8 x 8, and we use only the DC components to create a thumbnail image, what fraction of the original pixels would we be using? (15 points)
Each 8x8 block, which without transforming will contain 64 pixels, contributes to just one DC component, representing the average intensity of the block. This means that for every 64 pixels in the original image, only 1 value is retained. This means that the fraction of the original pixels used is 1/64, or approximately 1.56%.
Identify two differences between Fourier transform and Wavelet transform. (15 points)
Fourier transform breaks down a signal into its different frequency components using infinite sine and cosine waves
Wavelet transform uses finite, discrete wavelets that can adapt their scale, allowing it to provide spatial and frequency information.
Your task is to create a new image-compression standard based on JPEG, for use with images that will be viewed by an alien species. What part of the JPEG workflow would you likely have to change? (15 points)
the colour space transformation and quantization steps are tailored to human vision. For an Alien it would need to be tailored to their visual perception
2. Prediction using motion vectors (MC-based).
3. Derivation of the prediction error (the difference).