Neuro Quiz 4 🧠4️⃣
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
we got this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
the structures past the tympanic membrane are called the…
middle ear
what is the scientific term for the ear canal?
external auditory meatus
name ALL structures present in the middle ear
the ossicles, tympanic membrane, tympanic cavity
name ALL structures present in the inner ear
semicircular canals, cochlea, vestibule
name ALL structures in the outer ear
external auditory meatus, pinna, concha
main purpose of external auditory meatus
protects tympanic membrane
The tympanic membrane is ________ (concave or convex?)
concave
The tympanic membrane is attached to the _______ bone
malleus
what is the main purpose of the Eustachian tube?
connects middle ear and nasopharynx, equalizes air pressure
The vestibule plays a role in sensing ____ ______, maintaining _________, and detecting ____ acceleration.
head position, equilibrium, linear
Semicircular canals are ____ _____ canals that detect ______ acceleration of the head and help maintain _______.
fluid filled, rotational, balance
The cochlea is a small, shell-shaped part of the ____ _____ that is approximately ___ mm long in humans, forming a somewhat _____-shaped spiral with ____ turns
inner ear, 35, cone, 3/4th
what is the main purpose of the scala media?
house the organ of Corti, separate the other two membranes
The three parts of the cochlea are the ….
scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani.
the Basilar membrane separates the…
scala tympani and scala media
Reissner’s membrane separates the ….
scala vestibuli and scala media
The oval window is a small membrane-covered opening that connects the…..
middle ear to cochlea
The round window is a small, flexible membrane at the….
end of the cochlea
The round window allows ____ inside the _____ to move
fluid, cochlea
The basilar membrane in the cochlea is organized _______, meaning different regions respond to different sound frequencies.
tonotopically
In the basilar membrane, high frequencies resonate at the___ of the cochlea, while low frequencies resonate at the ___.
base, apex
Movement of the basilar membrane stimulates ______ _________
hair cells
Outer Hair Cells (OHCs) are arranged in ____ rows
three
what is stereocilia and why is it important
tiny hairs that detect sound vibrations and help convert them into signals for the brain
Inner Hair Cells (IHCs) are arranged in ___ row
one
Nerve cells in the cochlea join to form the ______ _____, sending sound to the _____
cochlear Nerve, brain
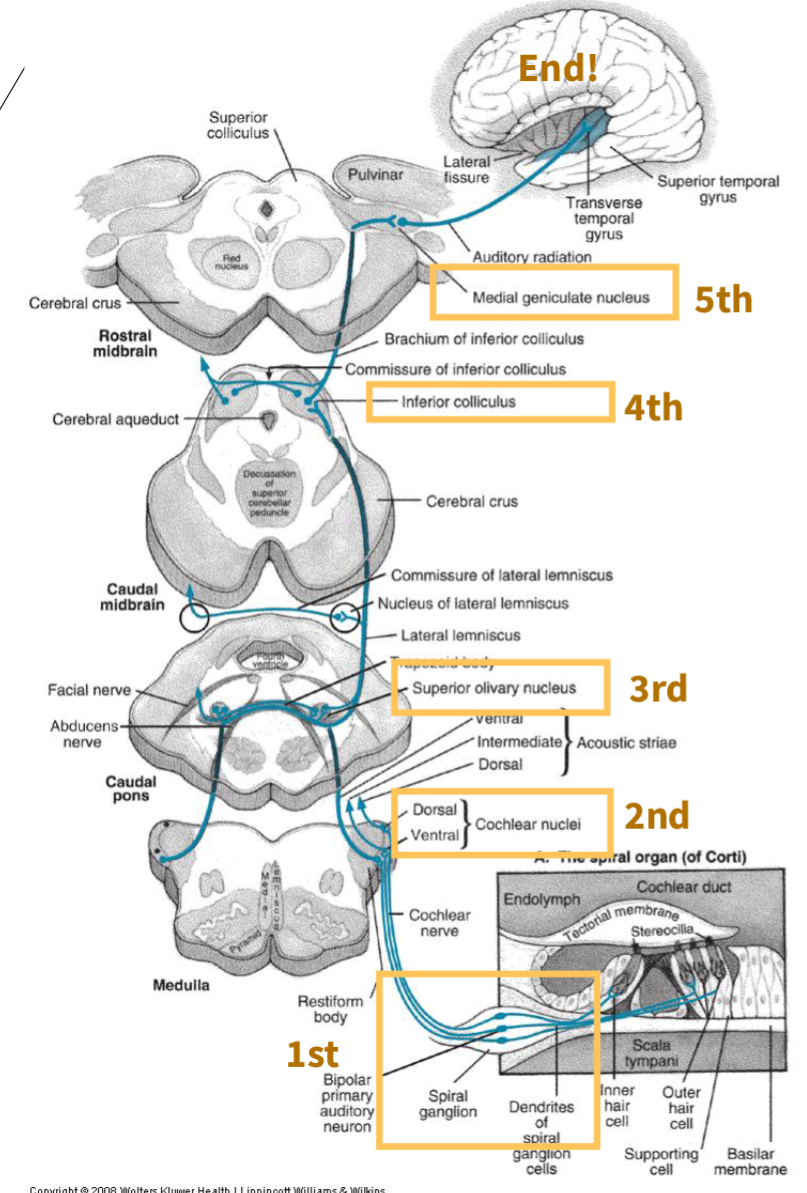
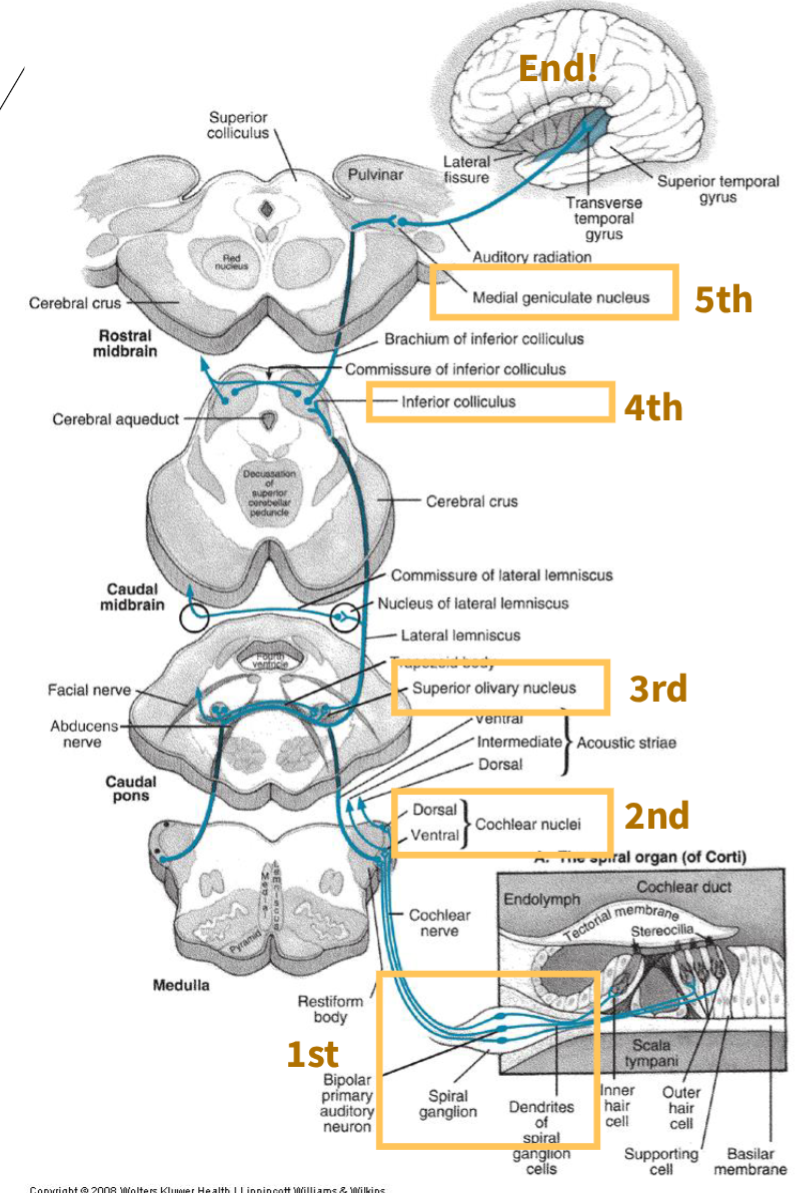
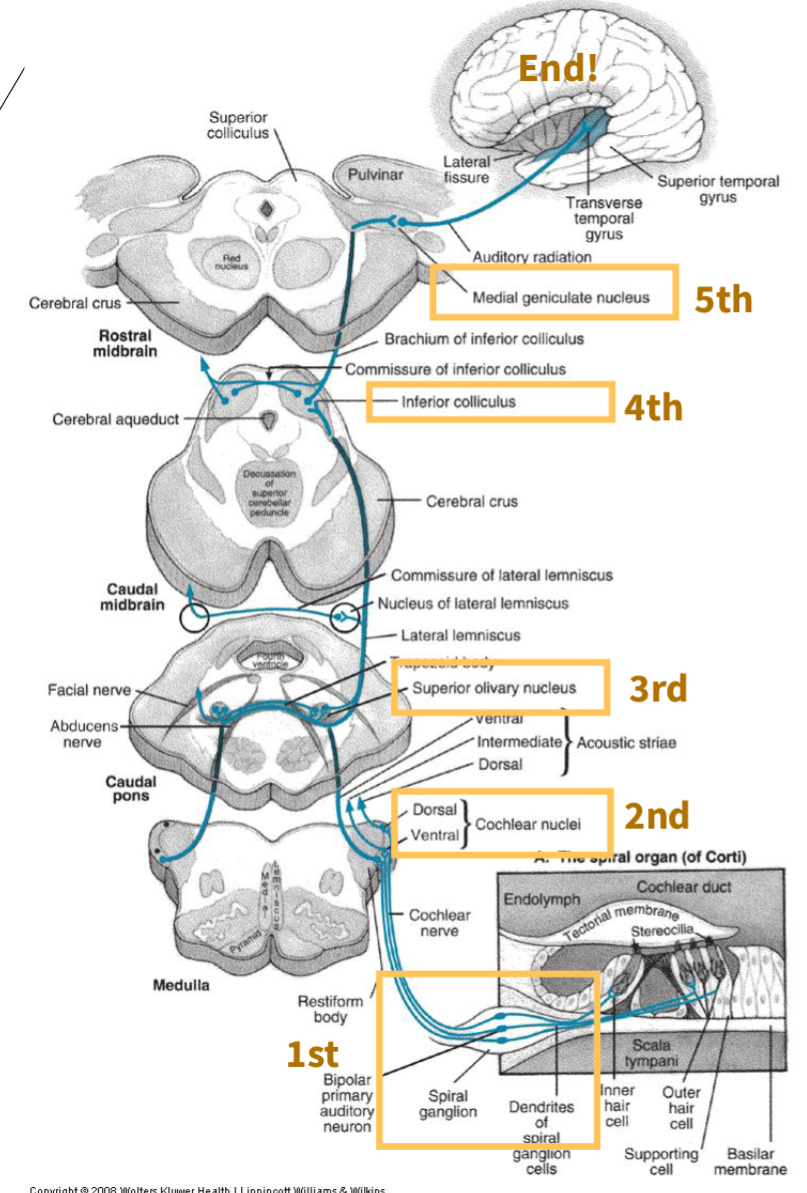
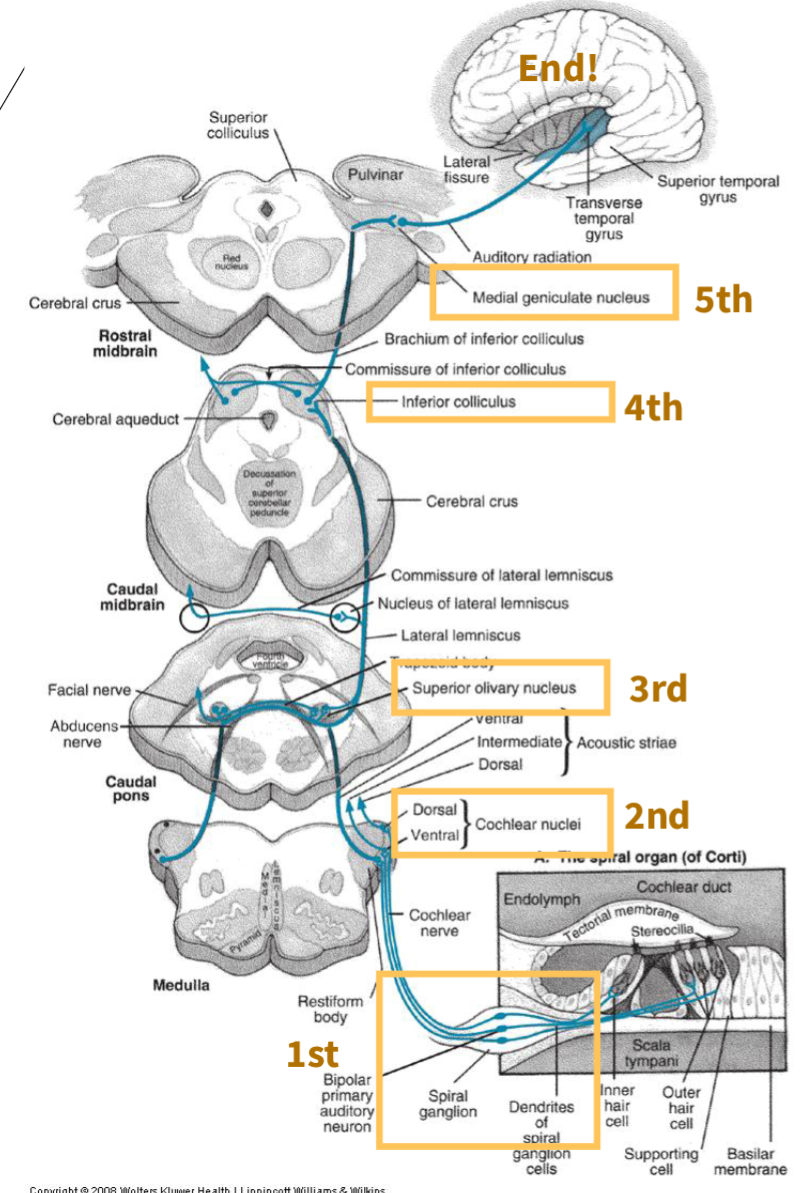
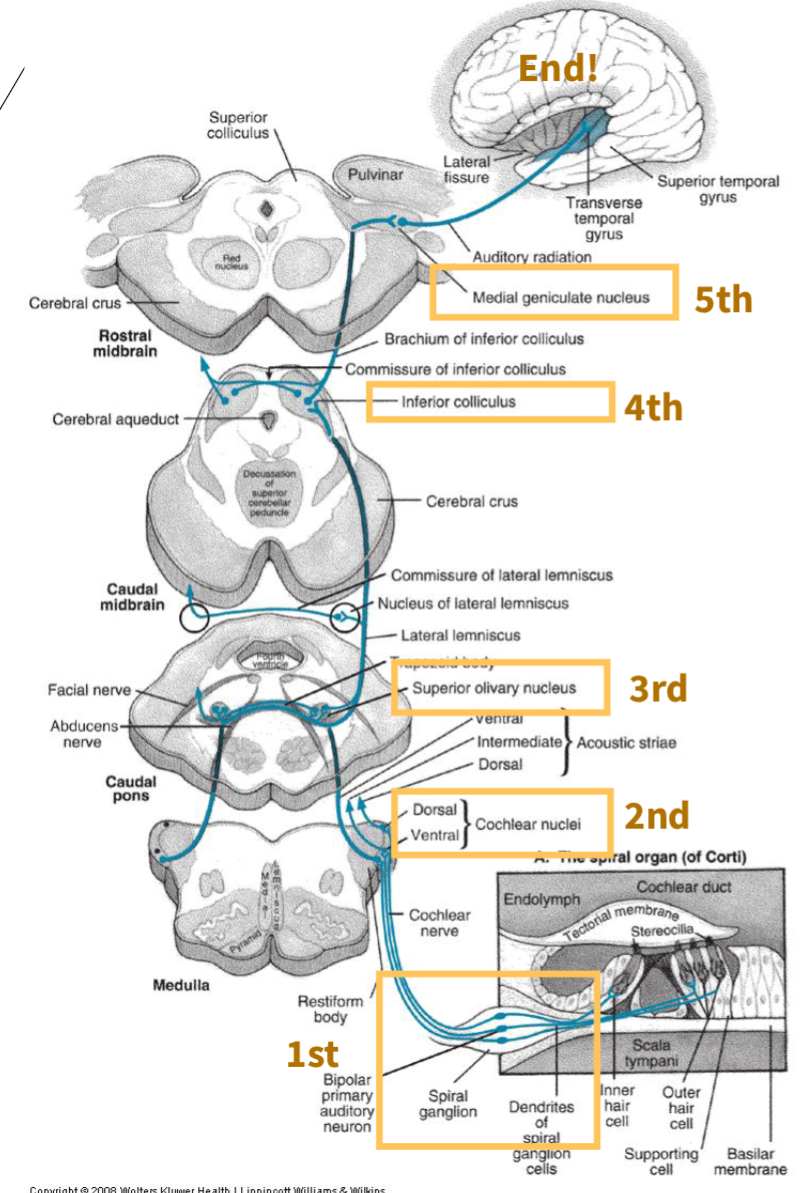
there are ____ neurons of the central auditory pathway
5
CAP First order neuron?
spinal ganglion
CAP Second order neuron?
Cochlear nuclei
CAP Third order neuron?
Superior olivary complex (first site where binaural [both ears] information is processed)
CAP Fourth order neuron?
Inferior colliculus (midbrain structure where some fibers cross to the opposite side)
CAP Fifth order neuron?
Medial geniculate nucleus (thalamus, relays auditory information to the cortex)
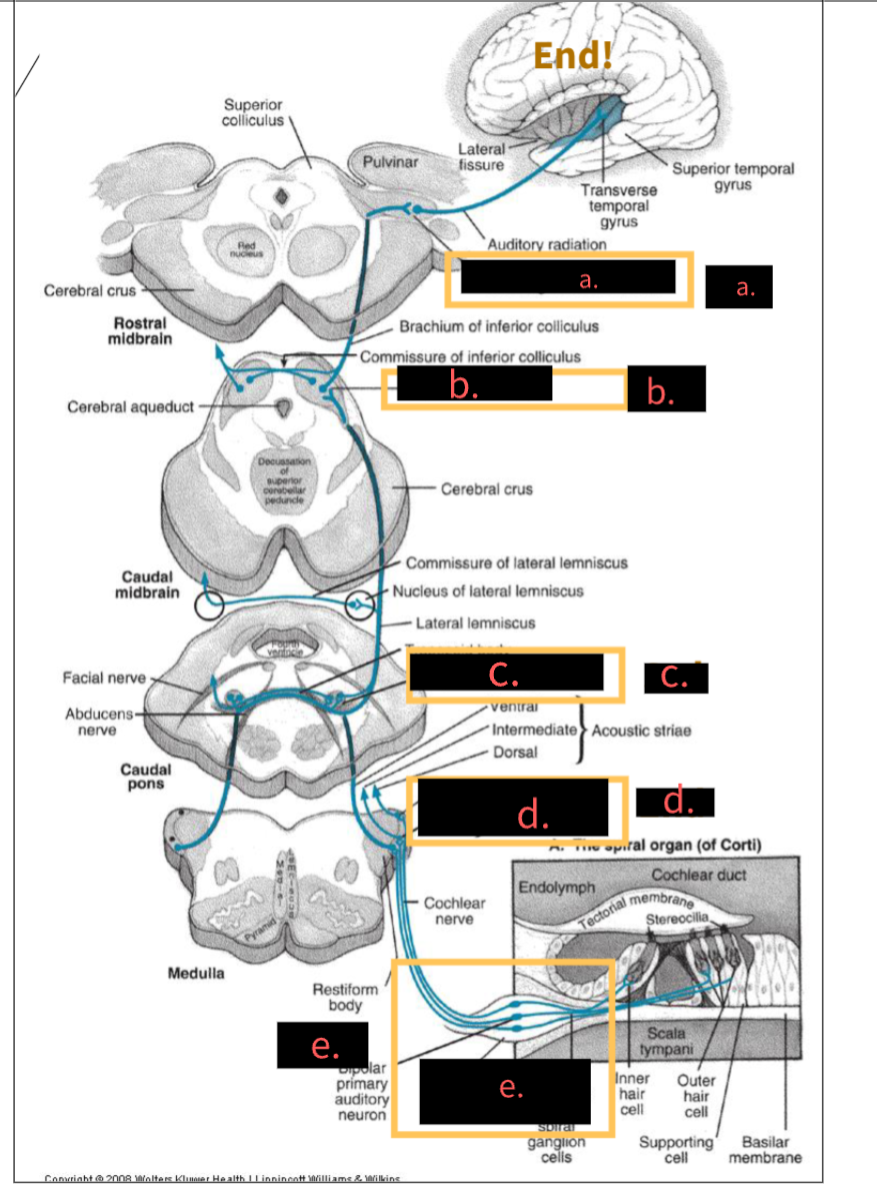
what is this image depicting?
Central Auditory Pathway neurons
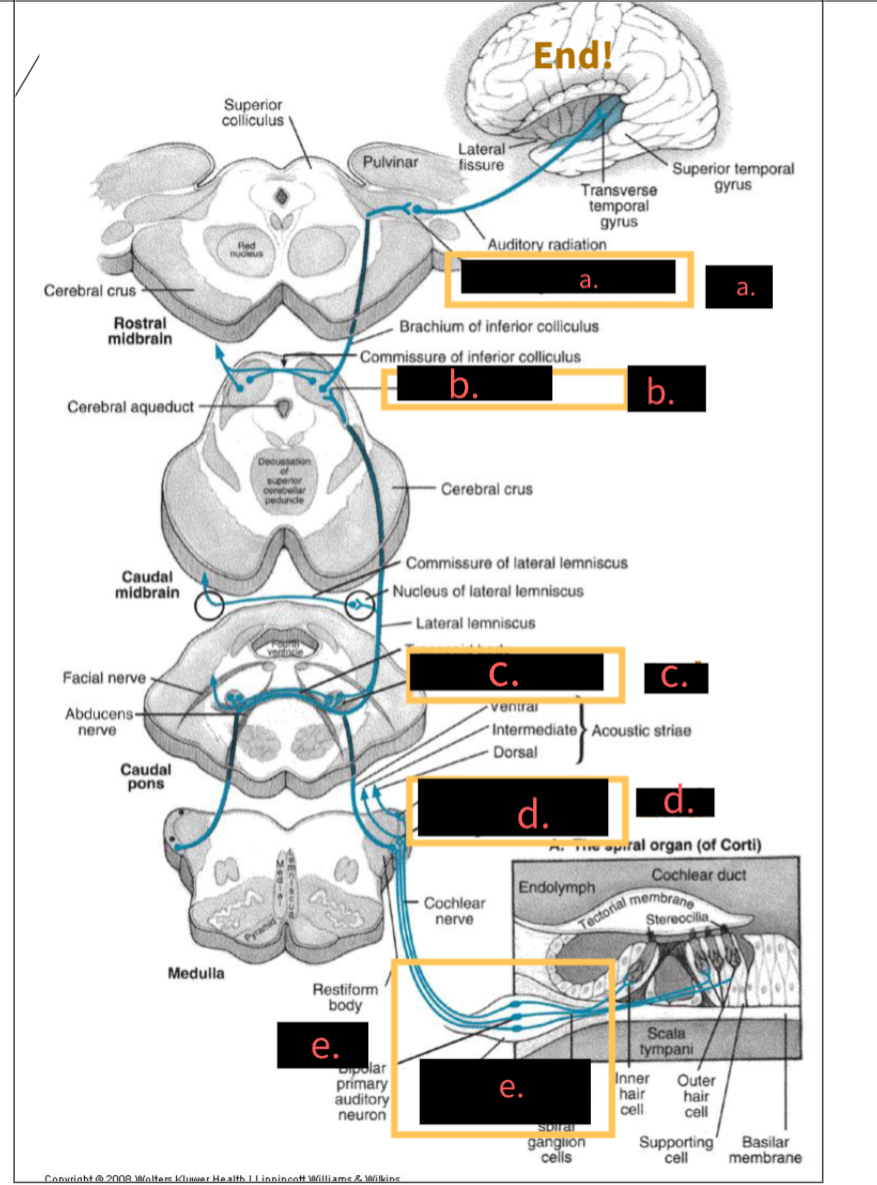
What structure is indicated by the letter A?
5th, Medial geniculate nucleus
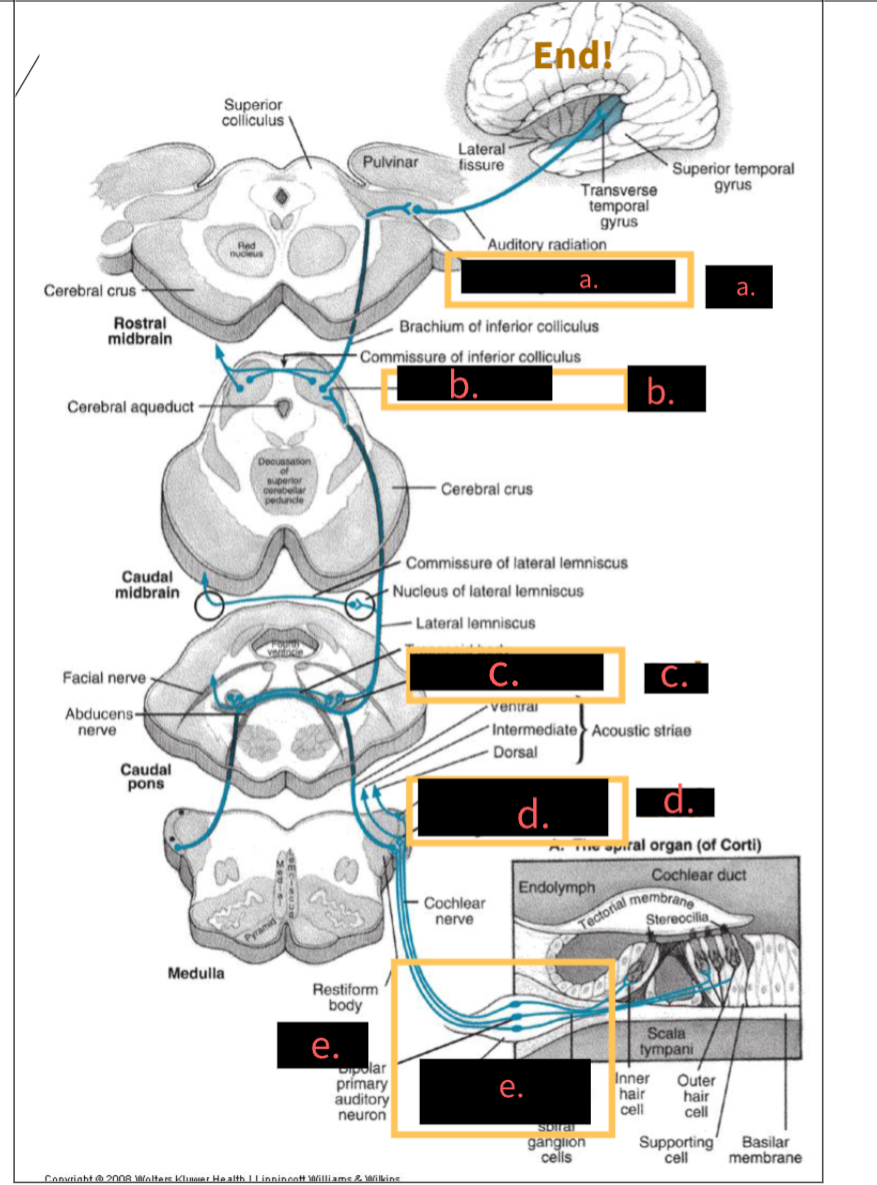
What structure is indicated by the letter B?
4th,Inferior colliculus
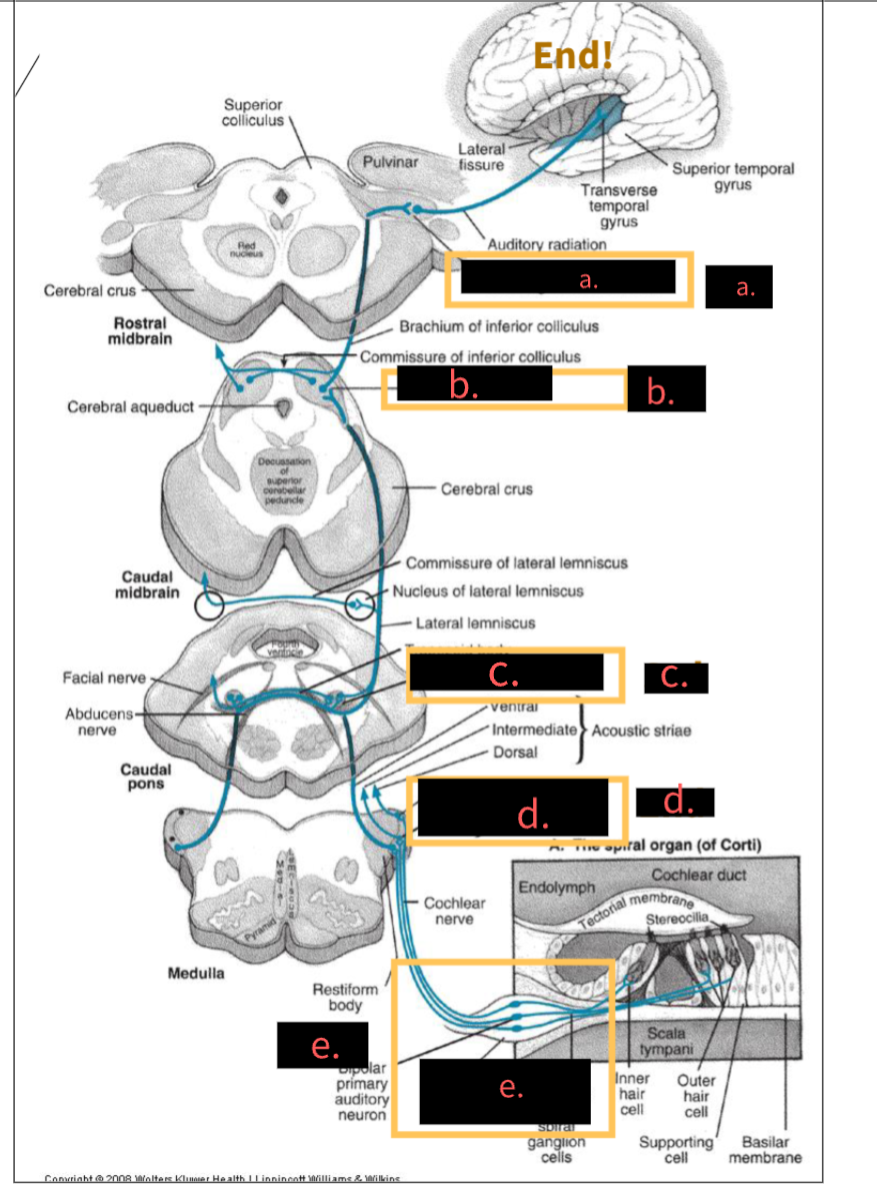
What structure is indicated by the letter C?
3rd, Superior olivary complex
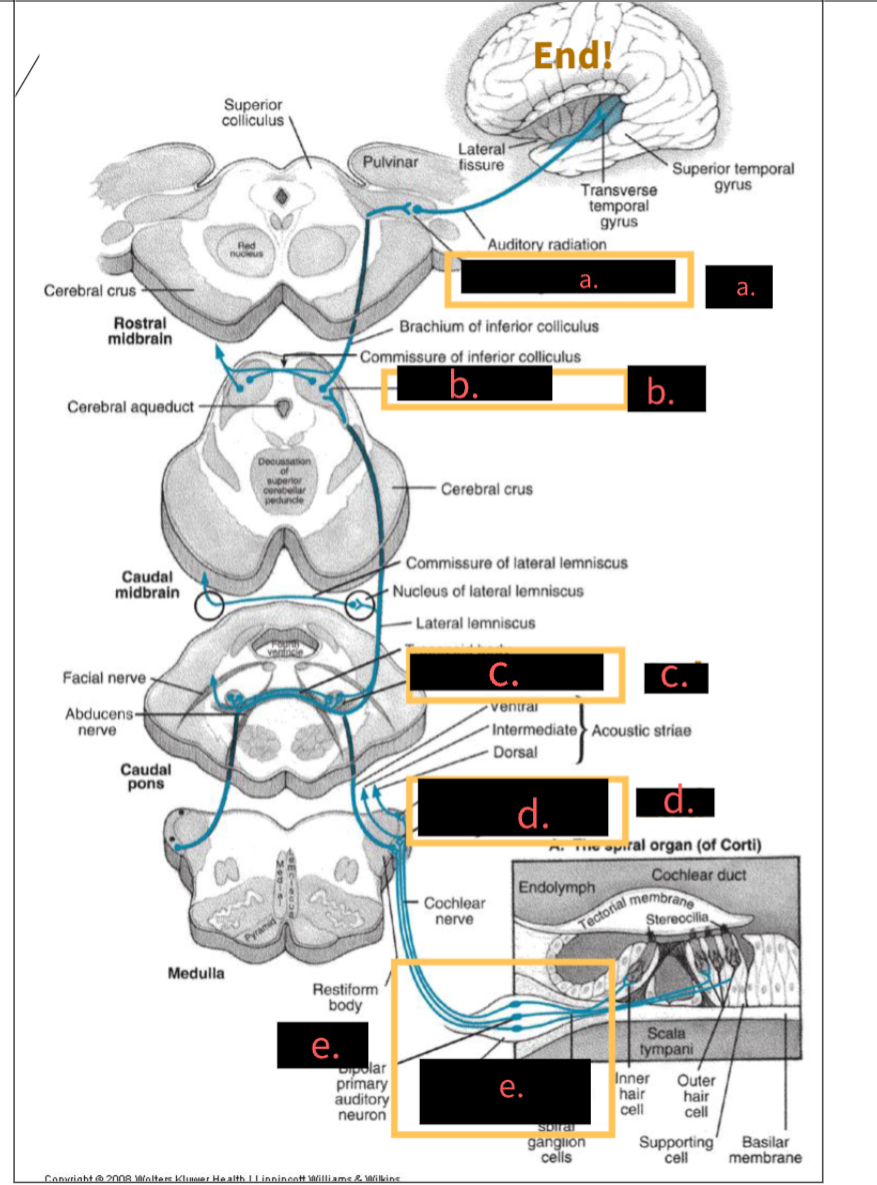
What structure is indicated by the letter D?
2nd, Cochlear nuclei
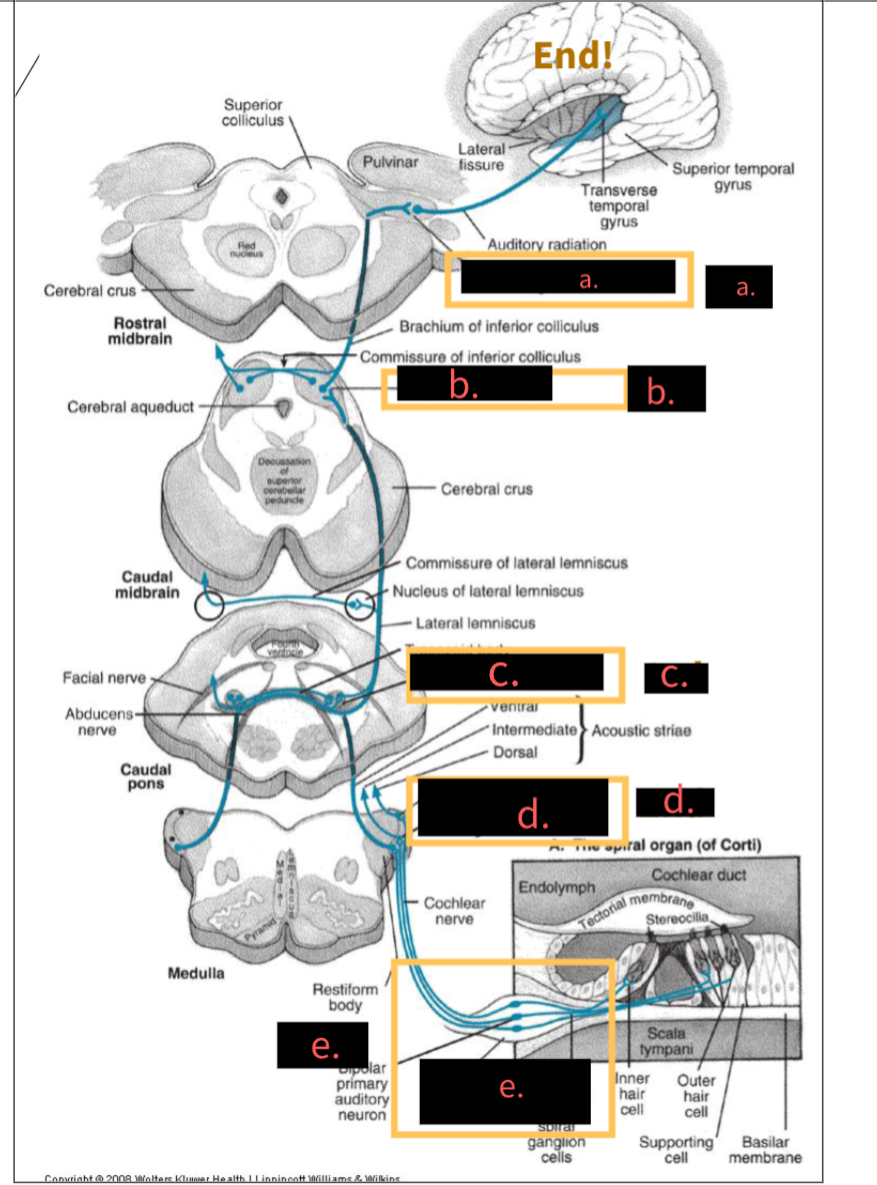
What structure is indicated by the letter E?
1st, spinal ganglion
What are the two reasons for bilateral input in the CAP?
the presence of accessory nuclei related to ascending pathways
the bilateral representation of impulses from both ears
what feedback system provides a mechanism for regulating selective attention?
auditory modulation
Unilateral lesion to auditory cortex or its pathways causes….?
little to no hearing loss, but will have impaired ability to tell direction and distance of sounds.
Nerve deafness happens when…
the cochlea’s receptor cells or the cochlear nerve become damaged
Nerve Damage hearing loss effects
might cause hearing loss that can affect both ears, depending on how severe the damage is.
Unilateral leison to the hair cells, their ganglion, cochlear nerve, or cochlear nuclei causes…
hearing loss in that same ear. Does not usually cause serious hearing loss.
what are the two main functions of the vestibular system?
Keep the head & body balanced
Keep the eyes steady while the body is making small movements
Excessive vestibular stimulation causes…
vertigo
the vestibulospinal pathway’s main function is….
equilibrium
Equilibrium depends on…
visual, proprioceptive, and vestibular senses
which otolith organ is almost in the horizontal plane
Utricle
which otolith organ is almost in the vertical (sagittal) plane
Saccule
Inside each of the utricle and saccule is a small thickened area called the ______
macula
The macula helps detect _____ _______
linear acceleration
The cranial nerve associated with the vestibular system is Cranial Nerve ____ , also called the _____________ nerve.
VIII (8), Vestibulocochlear
Lateral vestibulospinal tract controls …….
posture and balance
Medial vestibulospinal tract controls controls….
cervical spinal cord, position/muscles of the head
Retina contains 2 types of photoreceptors, called….
rods and cones
The first-order neurons in the retina are the ________ ____, and the second-order neurons are the _______ ______ whose axons form the optic nerve.
bipolar cells, ganglion cells
Visual Pathway First Stop
Optic nerves
Visual Pathway Second Stop
optic chiasm
Visual Pathway Third Stop
optic tracts
Visual Pathway Fourth Stop
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
Visual Pathway Fifth Stop
optic radiations
Visual Pathway Final Destination
occipital lobe
Binocular field = seen by …
both eyes while focusing on an object
Monocular field = seen by…
lateral portion of the visual field
anopsia means
loss of any field of vision
Monocular blindness = blindness in…
one eye due to damage before the decussation
Bitemporal hemianopsia = blindness in…
temporal fields of both eyes due to damage to the optic chiasm
Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia = blindness in….
visual field opposite the side of lesion due to damage
to the fibers before the LGN
Quadrantanopsia = blindness in…
one fourth of visual field in both eyes due to damage to optic radiations in one hemisphere