Canadian Citizenship Test
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1215
Magna Carter was signed
1497
first North American expedition of John Cabot, marking the beginning of European exploration of Canada
1534-1542
Jacques Cartier made 3 voyages to North America and claimed the land for King Francis I of France
1550s
the name “Canada” starts appearing on maps
1604
Acadians — descendants of French colonists — began settling in the Maritimes. The first European settlements in Canada — namely, in present-day Nova Scotia — are established by French explorers, Pierre de Monts and Samuel de Champlain
1700s
French & British fight for control of North America.
1759
British defeat the French in the Battle of the Plains of Abraham in Quebec city, marking the end of the French empire
1755-1764
Great Upheaval: the British forcefully removed Acadians from the Maritimes
1763
Royal Proclamation of 1763 is signed by King George II, which established the basis for negotiating treaties with the Aboriginals & guaranteed territorial rights to them
1774
British Parliament passes the Quebec Act, which conforms the principles of British institutions to the realities of governing a French/Catholic-majority province. ⇒ allowed religious freedom for Catholics + restored French Civil law while permitting British Criminal Law
1776
13 British colonies south of Quebec declare independence and formed the United States
1791
Constitutional Act is passed which divided the Province of Quebec into Upper Canada and Lower Canada. The name Canada became official
1800s-1980s
federal government ran residential schools to assimilate Aboriginal children into mainstream Euro-centric Canadian culture
1807
British parliament prohibits the buying and selling of slaves
1812
US tries to conquer Canada after resentment due to British interference with American shipping, beginning the War of 1812
1813
The Americans burned the Government House and Parliament Buildings in York (now Toronto) → 1814 Major General Robert Ross went form Nova Scotia and burned the White House + other public buildings in Washington DC
1832
Montreal stock exchange opens
1833
British Parliament abolished slavery throughout the Empire
1840
Lower and Upper Canada are merged into the Province of Canada, following rebellions and reformist movements.
July 1, 1867
British North America Act is passed, making Canada a self-governing dominion composed of Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia and New Brunswick.
1870
Manitoba and the Northwest Territories join Canada
1871
British Columbia joins Canada
1873
PEI joins Canada
1880
Arctic islands are transferred to NWT (North West Territories)
1898
Yukon Territory joins Canada
1905
Alberta & Saskatchewan join Canada
1916
Manitoba becomes the first province to grant women the right to vote
1917
Canadian Corps capture Vimy Ridge in WWI
1918
most Canadian female citizens aged 21 and over were granted right to vote in federal elections
1921
Agnes Macphail became first woman MP
1940
employment insurance (EI) is introduced + Quebec granted women the right to vote
June 6, 1944
D-Day Invasion in which Canadian soldiers helped capture Juno Beach from German troops
1944-1945
Canadian army liberated the Netherlands from Nazi occupation
1948
Japanese Canadians gain right to vote
1949
Newfoundland and Labrador join Canada
1960
Aboriginal people are granted the right to vote
1969
Official Languages Act is passed, which guarantees French and English language services in Canada.
1970
Canada helped found La Francophonie — an international association of French-speaking countries
1980
Terry Fox begins a “Marathon of Hope” across Canada to raise money for cancer research.
1982
Constitution of Canada was amended to entrench the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. July 1, which was previously known as Dominion Day, became known as Canada Day.
1988
Canada begins free trade with the US
1999
Nunavut joins Canada
2006
House of Commons recognize that Quebecois form a nation within United Canada
2008
Canadian government apologized to former students of Aboriginal schools
Sir Leonard Tilley
Father of Confederation; suggested the term “Dominion of Canada”, which was written into the constitution
Sir John Alexander Macdonald
Father of Confederation; First Prime Minister of Canada; on the $10 bill
Sir George-Etienne Cartier
Father of Confederation; he led Quebec into confederation and helped negotiate the entry of the Northwest Territories, Manitoba, and British Columbia into Canada
Lord Durham
recommended that the Upper and Lower Canada be merged and given responsible government
Louis Riel
Father of Manitoba; led an armed uprising against the Dominion in 1870 but fled to the US
Sir Wilfred Laurier
first French-Canadian prime minister since Confederation; on the $5 bill
General Sir Arthur Currie
Canada’s greatest soldier
Dr. Emily Stowe
first Canadian woman to practice medicine in Canada; founder of the women’s suffrage movement
Sir Sandford Fleming
invented the worldwide system of time zones.
Matthew Evans & Henry Woodward
invented the first light bulb and sold the patent to Thomas Edison
Dr. Wilder Penfield
the greatest living Canadian; brain surgeon at McGill.
Dr. John A. Hopps
invented the first cardiac pacemaker
Lieutenant Alexander Roberts Dunn
first Canadian to win the Victoria Cross
Reginald Fessenden
contributed to the invention of the radio and also sent one of the world's first wireless voice messages
John Graves Simcoe
Upper Canada’s first Lieutenant Governor and founder of Toronto
Rick Hansen
circled the globe in a wheelchair to raise funds for spinal cord research
Marjorie Turner-Bailey
Olympian + descendant of black Loyalists (escaped slaves and freed men and women of African origin who fled to Canada from America in the 1780s)
Sir Guy Carleton (Lord Dorchester)
Governor of Quebec, defended rights of the Canadiens, defeated American military invasion of Quebec in 1775, and in 1782 - 1783 supervised the Loyalist migration to Nova Scotia and Quebec
Sir Louis-Hippolyte La Fontaine
a champion of French language rights and democracy, became first head of a responsible government in Canada in 1849
Rights & freedoms entrenched in the Charter:
Mobility rights → live, work and move anywhere
Aboriginal peoples’ rights → any rights in Charter will not subvert rights/freedoms of Aboriginal peoples
Official Language & Minority Language Rights → French & English have equal status
Multiculturalism → pluralistic society in which one can enjoy their heritage & culture
Freedom of conscience → freedom to hold any ethical beliefs, regardless of whether or not they are religious
Freedom of religion
Freedom of thought, belief & opinion and expression
Freedom of speech
Freedom of the press
Freedom of peaceful assembly
Freedom of association
Yellow = Magna Carta
Responsibilities of citizenship:
Obeying the law
Taking responsibility for oneself and one’s family
Serving on a jury
Voting in elections
Helping others in the community
Protecting and enjoying our heritage and environment
Canada is a Constitutional Monarchy
Canada is the only constitutional monarchy in North America = has a hereditary Sovereign (queen/king) who rules according to the Constituion (rule of law)
Canada has 3 founding peoples
Aboriginal, French & British
There are 3 sub-groups of Aboriginal people:
Indian/First Nations → all Aboriginals who are not Metis or Inuit (65%)
Inuit (the people) → live in small, scattered villages across the Arctic (4%)
Metis → mixed Aboriginal & European ancestry; they live predominantly in the prairie provinces and speak Michif (30%)
Anglophones + Francophones
18 million Anglophones in Canada
7 million Francophones in Canada
New Brunswick is the only bilingual province
Acadians
descendants of French colonists who settled in the Maritime provinces
Quebecers
people of Quebec, vast majority French Speaking + descendants from French settlers from 1600s and 1700s
Underground Railroad
The Underground railroad was a Christian anti-slavery network that helped slaves escape into free states and Canada
Slaves escaped from the US by following the “North Star” into Canada and settled in Canada via the Underground railroad
War of 1812
ensured that Canada would remain an independent country from the US
Responsible government
ministers of the Crown must have the support of a majority of elected representatives in order to govern
Canada has a system of responsible government today: if a government loses a confidence vote, it must resign
The Head Tax
a race-based entry fee that Chinese nationals had to pay to enter Canada
Remembrance Day
November 11th every year
1980 and 1995 Separatist Movements
There were 2 referendums for Quebec sovereignty in 1980 and 1995 ⇒ Quebec sovereignty was defeated both times + in 1982 the Constitution was amended without Quebec’s agreement
Thanksgiving
2nd Monday of October
Federal State
Canada is a federal state, where power is shared between the federal and provincial governments.
Federal Jurisdiction / Responsibilities
defence
foreign policy
interprovincial trade and communications
currency
criminal law
citizenship
Provincial Jurisdiction / Responsibilities
municipal government
education
health
natural resources
property & civil rights
highways
Canada is a parliamentary democracy
: the people elect representations to the provincial/territorial/federal legislatures.
representatives are responsible for:
passing laws
approving and monitoring expenditures
keeping government accountable
Cabinet Ministers
responsible to elected representatives = must retain “confidence of the House”
have to resign if they aredefeated in non confidence vote
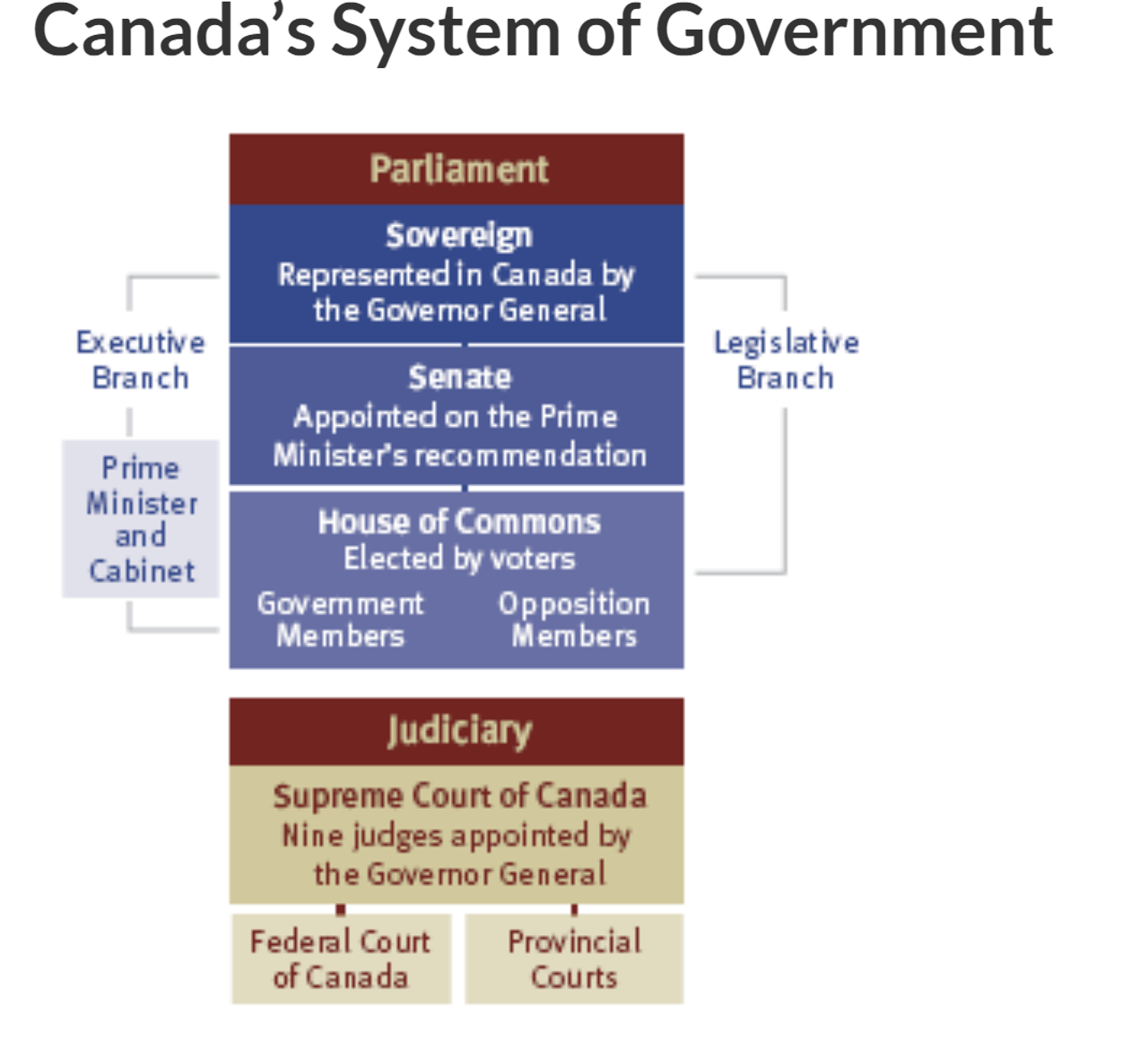
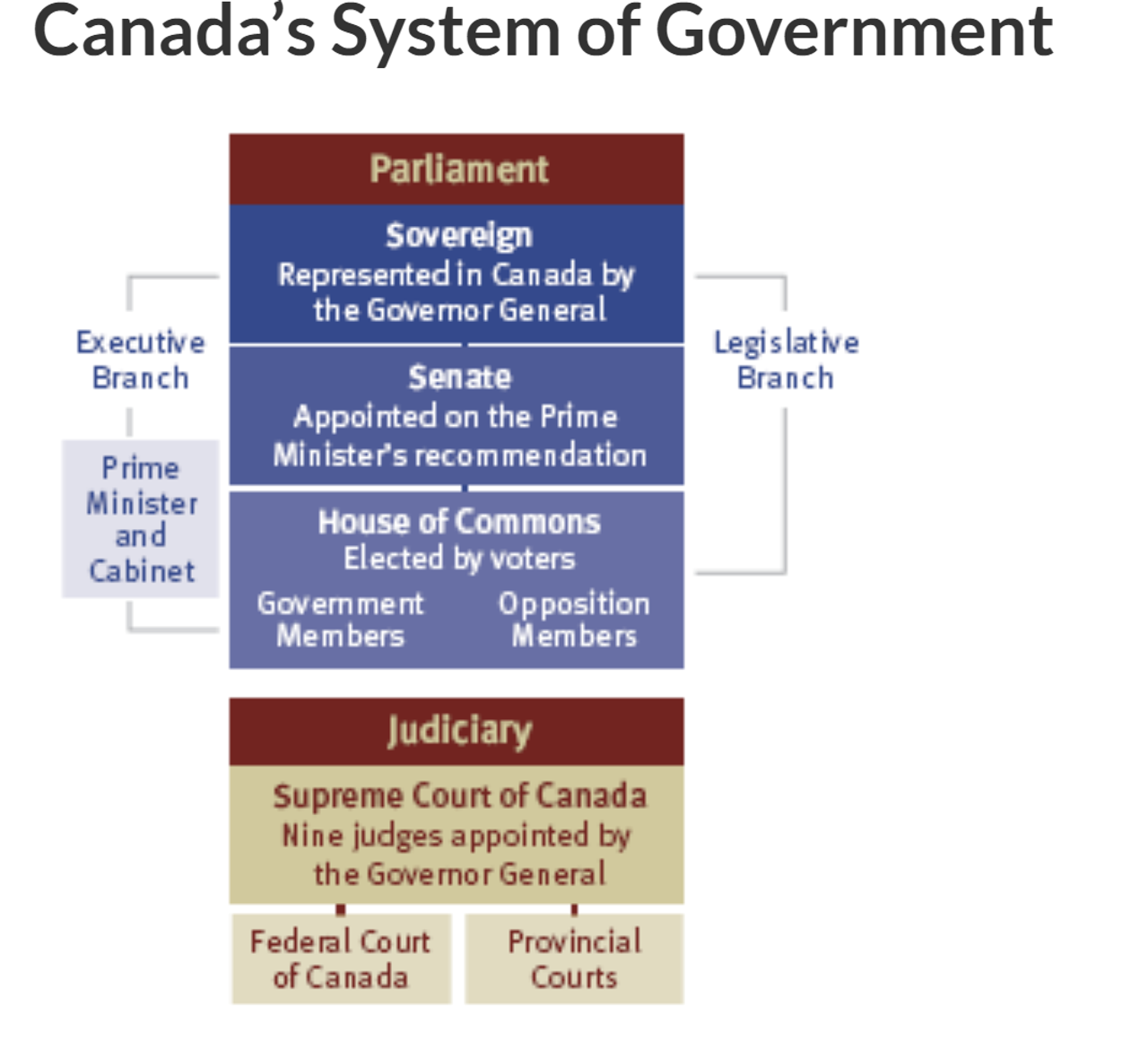
3 parts of the federal parliament:
Sovereign = head of state - currently King Charles III
Senate = made up of senators + consider and review bills (proposals for new laws)
Senators are appointed by the Governor General on the advice of the Prime Minister; they serve until age 75.
House of Commons = representative chamber: made up of members of parliament elected by people every 4 years = consider and review bills
7 steps for a bill to become a law:
First reading → bill is read for the first time and printed
Second reading → members debate the bill’s principle
Committee stage → committee members study the bill, clause by clause
Report stage → members can make other amendments
Third reading → members debate and vote on the bill
Senate → bill follows a similar review process in the senate
Royal assent → Governor general signs off after the bill is passed by both houses
Governm
The sovereign is represented in Canada by the Governor General, who is appointed by the sovereign on advice of the PM for 5 years.
Lieutenant General
The sovereign is represented in each province by a Lieutenant General, who is appointed by the Governor General on advice of the PM for 5 years.
There are 3 branches of government:
Executive
Legislative
Judicial
MLA
Each provincial and territorial government has an elected legislature where provincial and territorial laws are passed + members of legislature are called members of Legislative Assembly (MLAs)
Comissioner in 3 Territories (Northwest Territories, Yukon, Nunavut)
In the 3 territories, the Commissioner represents the federal government and plays a ceremonial role (analogous to the Lieutenant Governor)
Supreme Court of Canada
The supreme court of Canada has 9 justices appointed by the Governor General.
Federal Elections
Typically, federal elections are held on the 3rd Monday of October every 4 years following the most recent election — although, the PM can ask the Governor General to call an election earlier.
In order to vote, you must be on the voters’ list (National Register of Electors) — a database of eligible voters maintained by Elections Canada.
When an election is called, Elections Canada mails all eligible voters a voter information card which details where and when to vote.
Official Opposition
The Official Opposition is the party with the highest number of MPs of all the non-governing parties.
Current Government
Head of State: King Charles III
Monarch (Queen or King) defined by constition and constitutional convention
Governor General: Mary Simon
representative of Queen of Canada
Head of Government/Prime Minister: Justin Trudeau
Political Party in Power: Liberal Party
Leader of the Opposition: Pierre Poilievre
The name of the party representing Her Majesty’s Loyal Opposition is: Conservative Party
names of opposition parties + leaders:
New Democratic Party, Jagmeet Singh
Bloc Québécois, Yves-François Blanchet
Green Party of Canada, Elizabeth May
Member of Parliamment (MP) in Ottawa: Joyce Murray, Liberal Party
Federal Electoral District: Vancouver Quadra
Current Provincial Government
The name of the representative of the King for my province is…
Janet Austin
The representative of the King in my province, the Lieutenant Governor, is…
Janet Austin
The Head of Government (the Premier) is…
David Eby
The name of the provincial party in power is…
New Democratic Party
The names of the provincial opposition parties and leaders are…
Kelvin Falcon, BC United
Green Party of BC, Sonia Furstenau
Conservative Party of British Columbia, John Rustad
My provincial representative is…
David Eby (Vancouver-Point Grey constituency)
Municipal Government
The name of the municipality where I live is…
Technically UBC does not fall under any municipality. (See https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/it-takes-a-village-how-ubc-became-canada-s-largest-community-without-a-municipal-government-1.4845987)
But you can say Vancouver
The name of the head of the municipal government (mayor or reeve) is…
Mayor Ken Sim (ABC Vancouver party)
Key Facts: Justice System
Justice system operates on the presumption of innocence.
Courts settle disputes, whereas the police enforce the laws.
Ontario and Quebec have their own police forces; the RCMP plays the role of the provincial police in other provinces.
Key Facts: Canadian Symbols
The Union Jack is our Royal flag.
The national motto of Canada is a mari usque ad mare, which means “from sea to sea”.
Hockey is the national winter sport.
Lacrosse is the national summer sport.
The national anthem of Canada is “O Canada”.
The royal anthem of Canada is “God Save the Queen (or King)” — it may be sung to honour the sovereign.
The Victoria Cross is the highest Canadian honour.
Key Facts: Canada’s Economy
Canada’s largest trading partner is the US.
The US and Canada share the largest bilateral trading partnership in the world.
The US-Canada border is the world’s longest undefended border.