AP II Practical 1
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
Plasma (identify/structure)
Structure: nonliving fluid matrix
The fluid backdrop/background for the formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, & platelets)
Plasma function
colorless watery fluid of blood and lymph containing no cells and in which the formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets) are suspended in.
Substances transported by blood
Carries substances, osmotic balance, lipid transport
Plasma proteins: fibrinogen (clotting of blood), defense (antibodies)
Erythrocytes structure
Biconcave discs, anucleate, essentially no organelles
Filled with hemoglobin
Spectrin and other proteins allow flexibilty
exist in blood stream=120 days
Erythrocytes (RBC) function
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide carried in blood, gas transport
Platelets function
blood clot formation/blood clotting
Leukocytes structure
complete cells (has nucleus)
part of body’s nonspecific defenses & the immune system
Leukocytes function
defense and immunity
What is the order of abundance for lymphocytes? (NEVER LET MONKEYS EAT BANANAS)
Neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
Order by size (Granulocytes + agranulocytes)
BEN= Basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils
Lymphocytes, monocytes
Neutrophils structure + image
3-5 lobed nucleys, fine reddish/violet granules
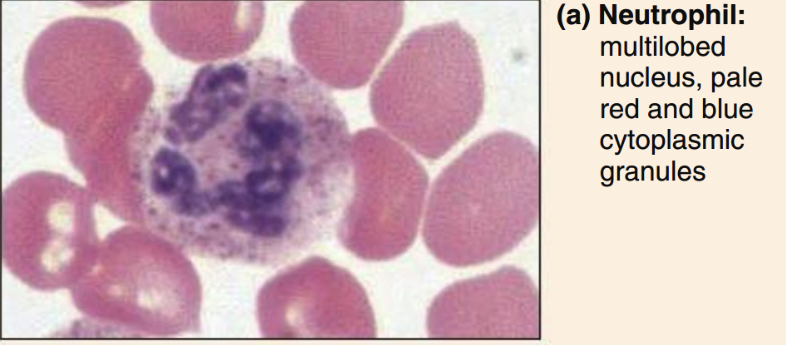
Neutrophils function
phagocytize bacteria
Eosinophils structure
bilobed nucleus, orange-pink granules
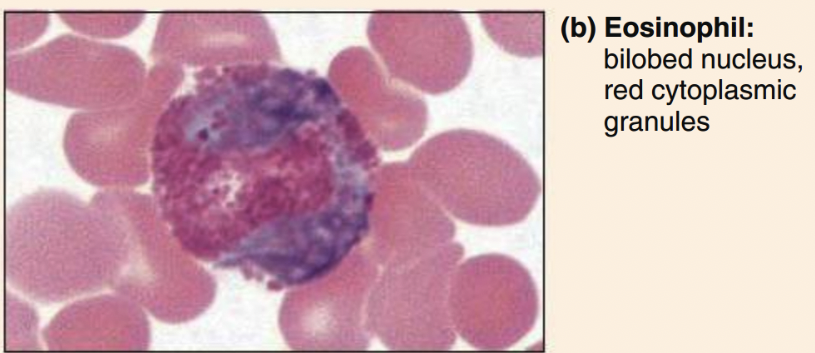
Eosinophils function
phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes. allergens, inflammatory chemicals
release enzymes to combat parasites
complex role in allergies and asthma
Basophils structure
U-shaped nucleus, dark violet granules
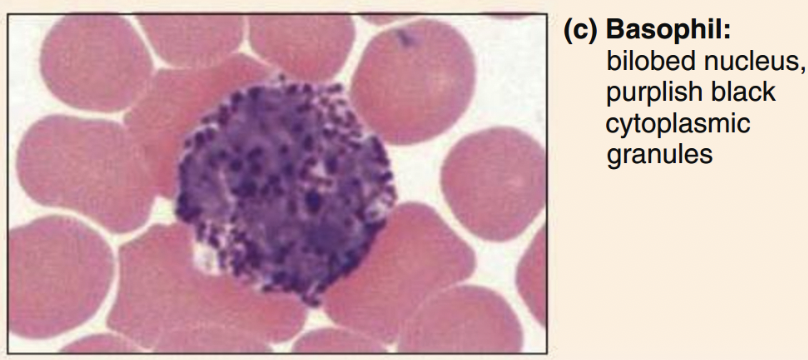
Basophils function
secrete histamine and heparin (anti-coagulant)
promote blood flow and travel of other WBCs
Lymphocytes structure
classic= oval/round nucleus, scant cytoplasm
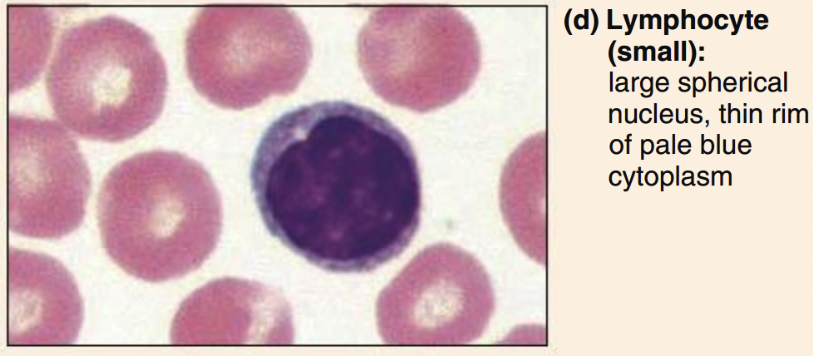
Lymphocyte function
specific immunity
mount immune response by direct cell contact or antibodies
What are the 2 types of lymphocytes and functions
T cells function in the immune response
B cells give rise to plasma cells, which produce antibodies
Monocytes structure
ovoid/kidney/horseshoe nucleus, abundant cytoplasm
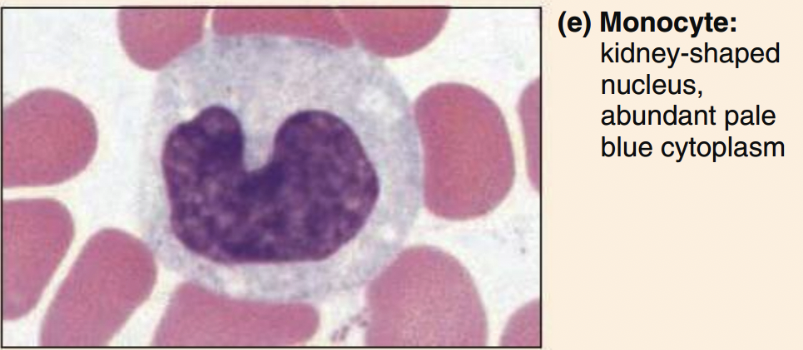
Monocytes function
phagocytize pathogens and debris
present antigens
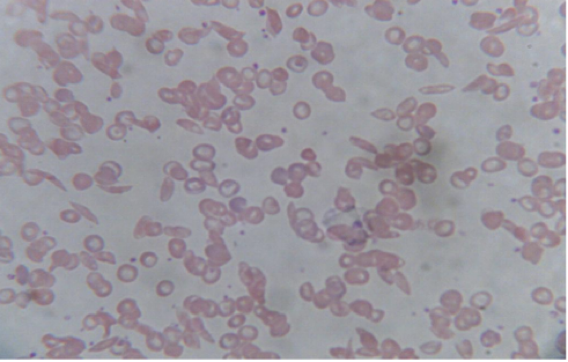
Sickle cell anemia
RBCs are curved or crescent shaped
Cells cannot get enough oxygen since capillaries get blocked by crescent-shaped cells
Pernicious anemia (vitamin B12 deficiency)
RBCs are macrocytic (larger than normal)
Unusual oval shape
Results from deficiency of vitamin B12
Lack of intrinsic factor needed for absorption of B12
Iron-deficiency anemia
RBCs are microcytic (smaller than normal)
Hypochromic (lacking significant pigmentation)
Causes: secondary result of hemorrhagic anemia, inadequate intake of iron-containing foods, impaired iron absorption
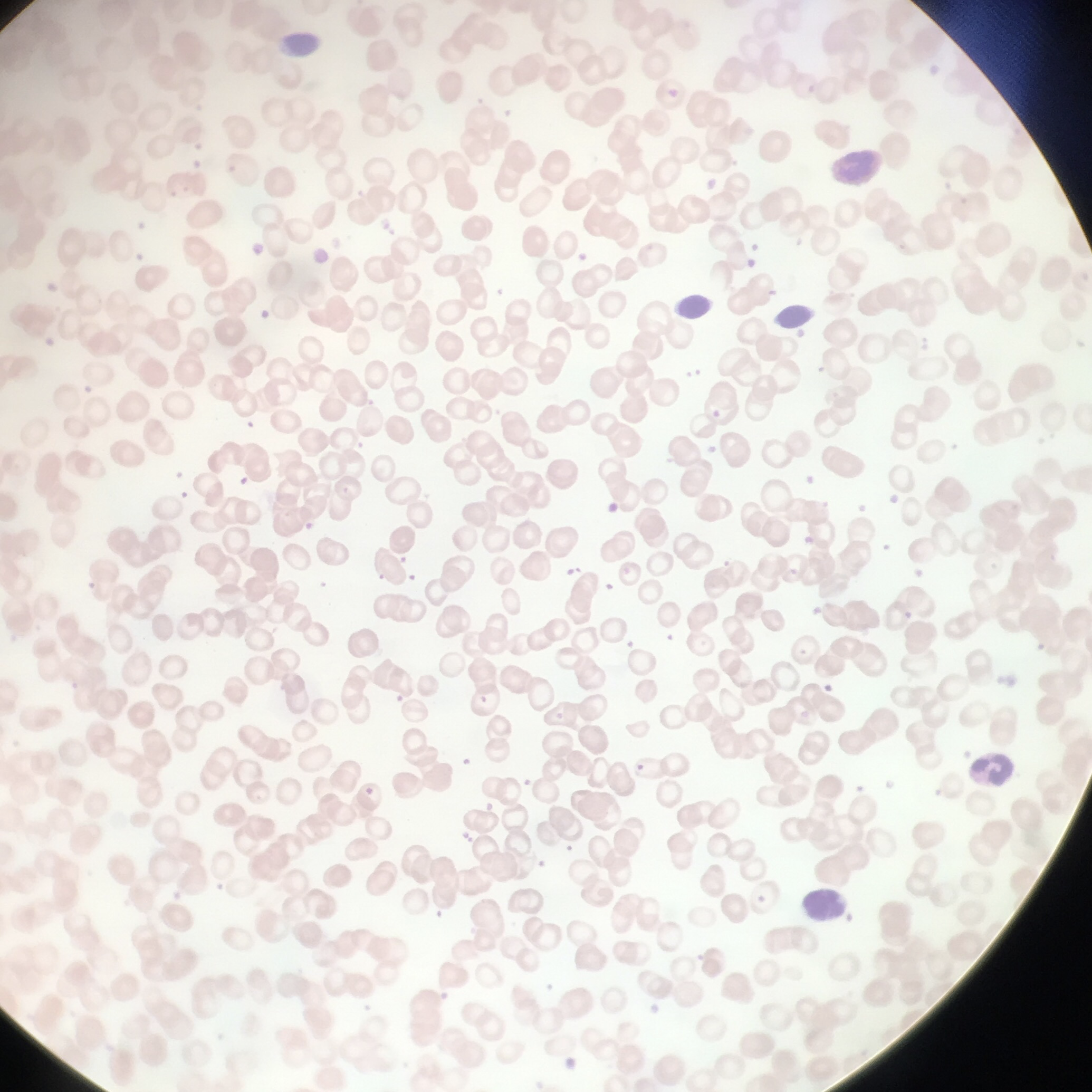
Eosinophilia
abundance of eosinophils
Occurs with caused by parasitic infections & allergies
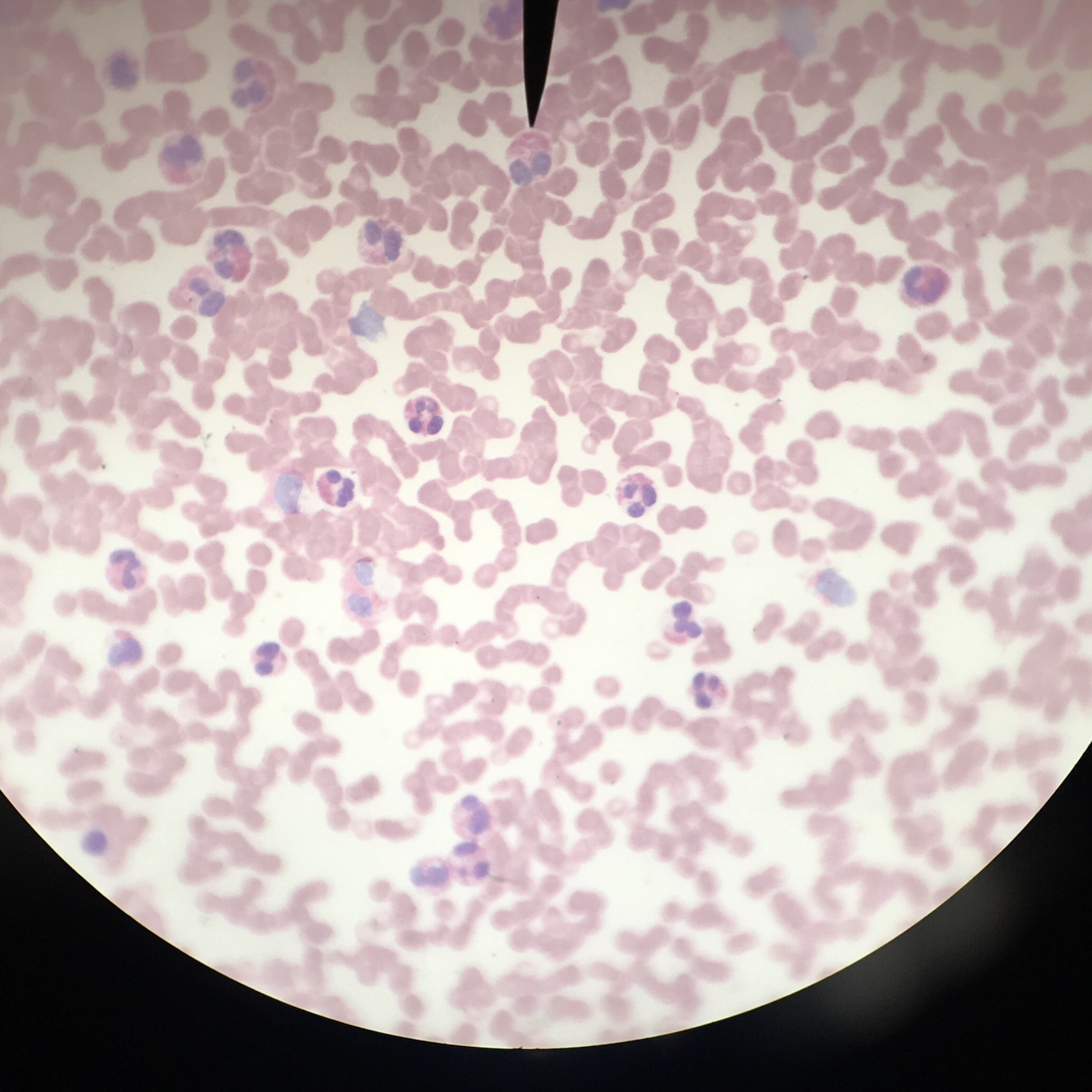
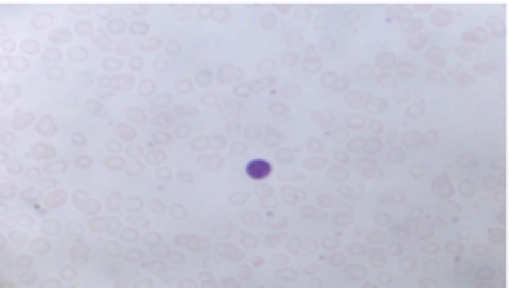
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
increased number of mature B lymphocytes
normal WBC range is 4-10k, patients with leukemia can have WBC counts > 100 k
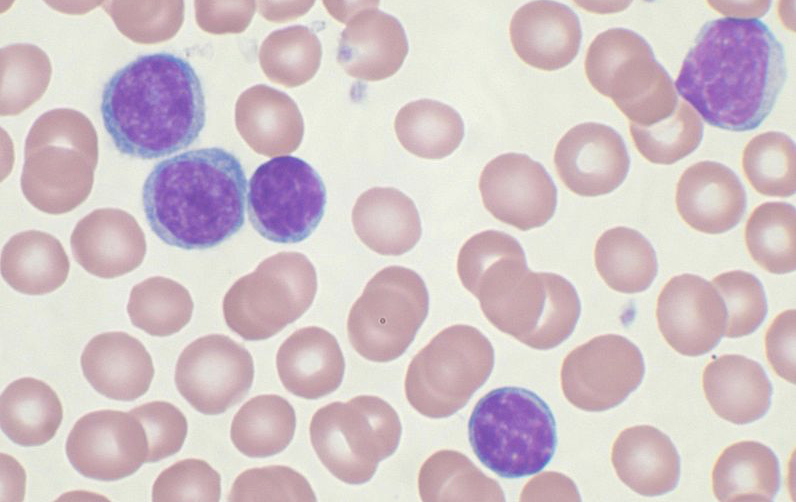
Why do we measure hematocrit and what does it tell us?
to measure percentage of RBCs in a volume of blood
Provides information on quantity
What does hematocrit NOT tell us?
the QUALITY
Component parts of of a hematocrit
Plasma, Buffy coat (leukocytes and platelets), and erythrocytes
Hematocrit formula
% HEMATOCRIT= (RBC height/ total column height) x 100
Where is the apex and base?
apex= bottom (point of maximum impulse)
Base= top “broader”; (conducting system of heart)
Pericardium (fibrous + parietal pericardia) anatomy
superficial fibrous pericardium
Deep 2-layer pericardium
Parietal layer - lines the internal surface of the fibrous pericardium
Visceral layer (epicardium)-lines the surface of the heart
separated by the fluid-filled pericardial cavity
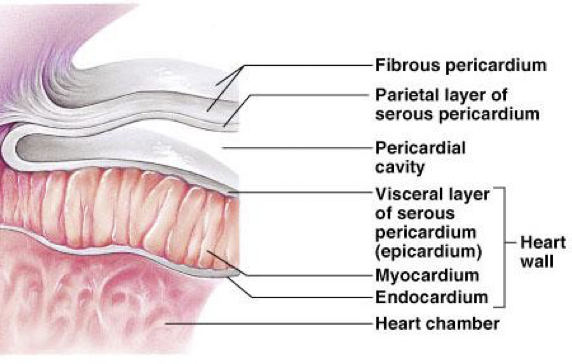
Pericardium function
protects and anchors heart
Prevents overfilling of heart with blood
Allows heart to work in friction-free environment (serous pericardial fluid)
Heart Walls
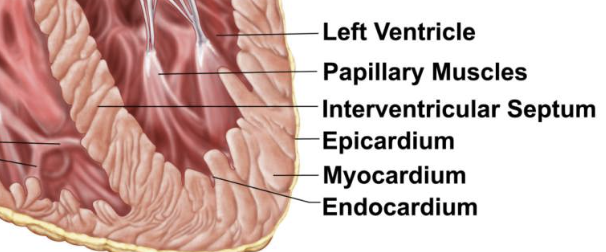
Epicardium (visceral pericardium)
outer visceral layer of the serous pericardium
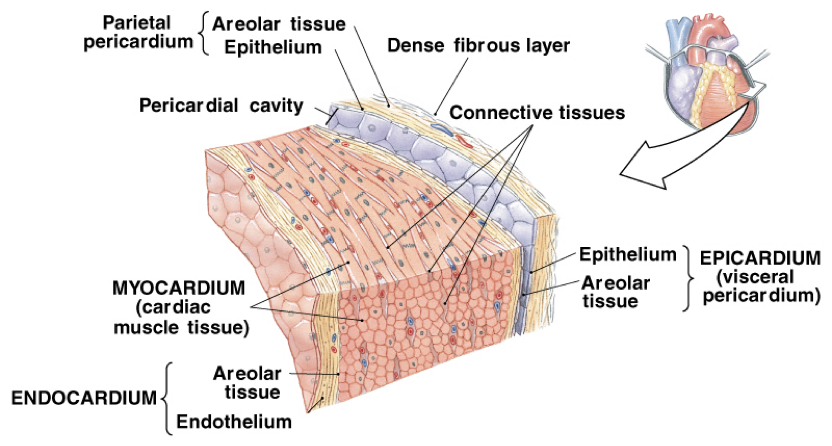
Myocardium (cardiac muscle)
cardiac muscle layer forming the bulk of the heart
Middle layer, thickest layer
Reinforced with fibrous skeleton of the heart (crisscross, interlacing layer of connective tissue)
Provide scaffolding for the heart chambers; assist in contraction and relaxation of the cardiac walls
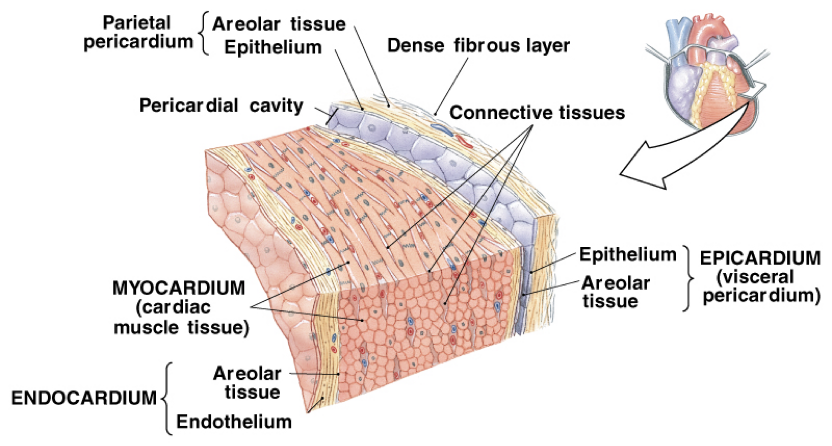
Endocardium
endothelial layer of the inner myocardial surface
covers heart valves and is continuous with the inner lining of the great vessels
composed of simple squamous epithelium on areolar connective tissue
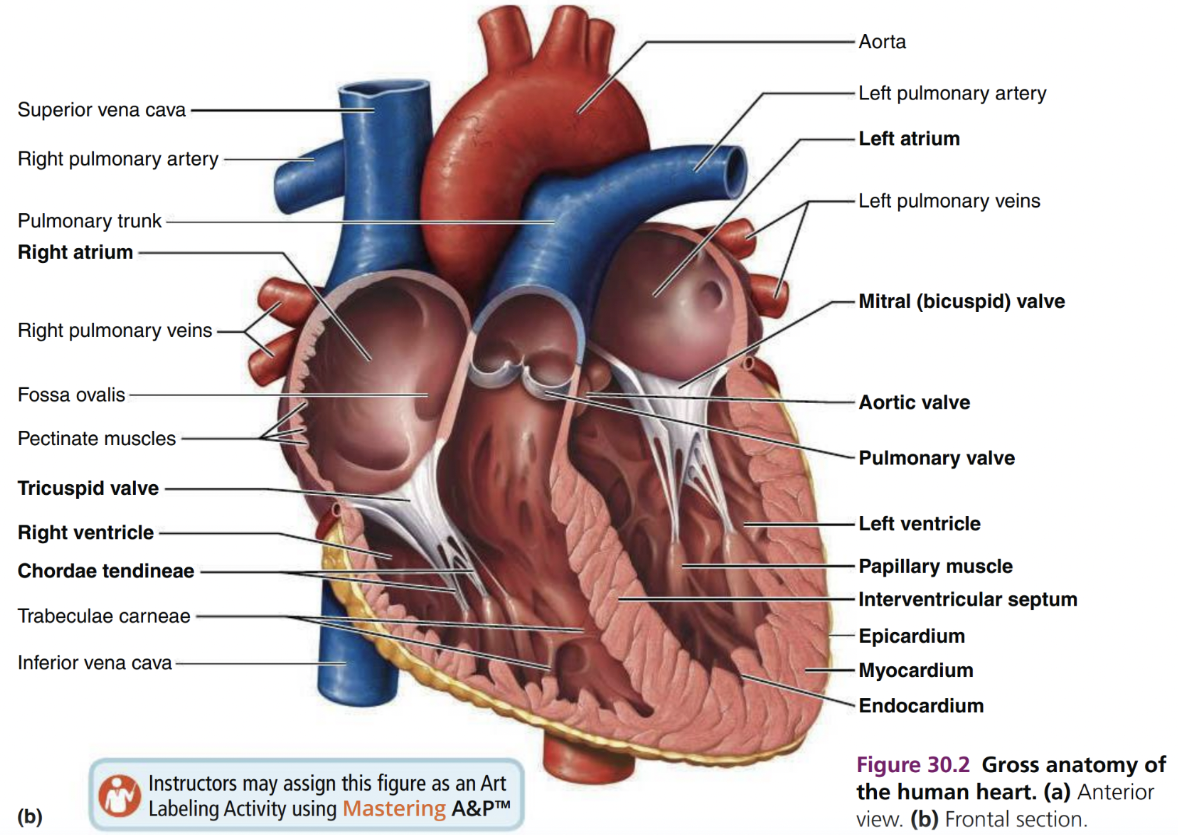
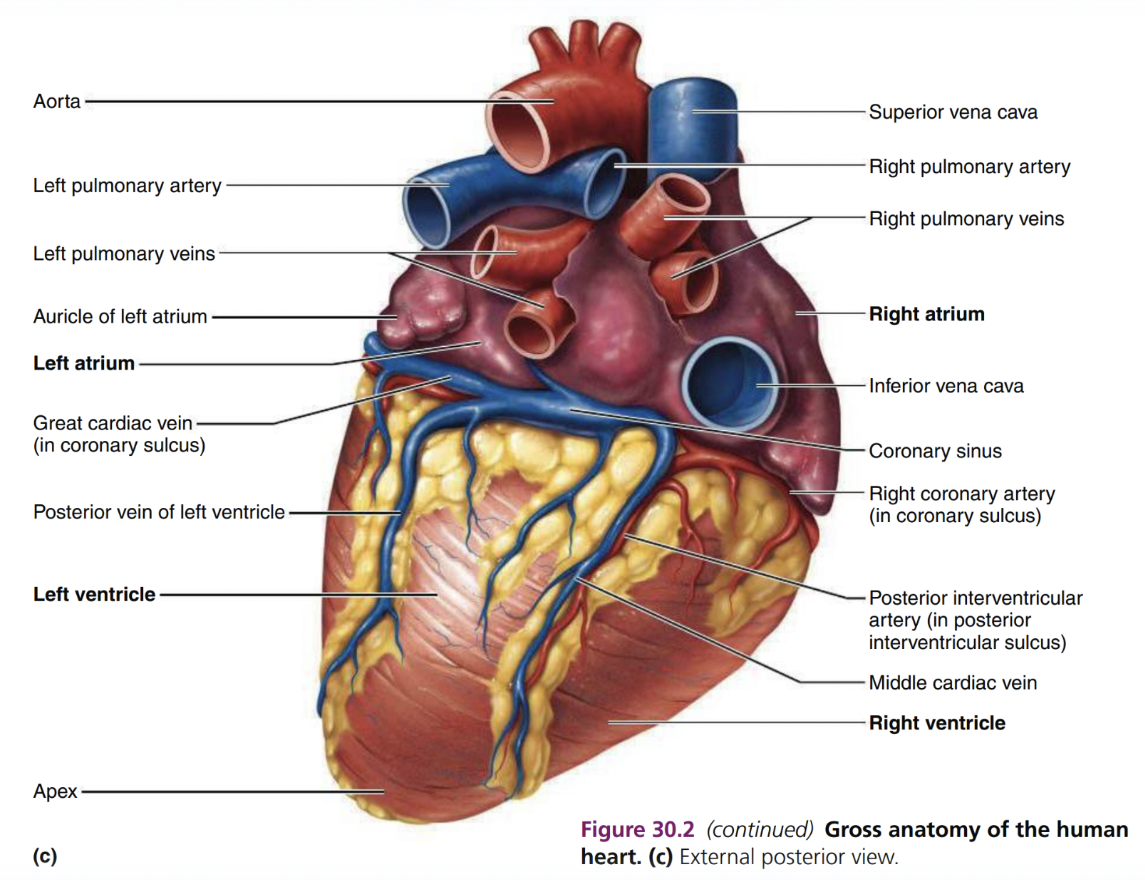
Left and right atria*
receiving chambers of the heart
pectinate muscles mark atrial walls
blood enters right atria from superior and inferior vena cava and coronary sinus
blood enters left atria from pulmonary veins
Interatrial septum —> septum that divides the heart longitudinally/separates atria
left and right auricles
Right auricle= remnant of the fetal RA
Left auricle=remnant of fetal LA
Auricles can relieve high atrial pressure by increasing the atrial capacity at times of stress, acting as overflow vessels
Left and right ventricles
discharging chambers of the heart
force blood out of the heart into large arteries that emerge from its base
Right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary trunk
Left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta
Interventricular septum
separates the ventricles
Interatrial septa
separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Superior vena cava + inferior vena cava
returning blood to the heart
Pulmonary veins
carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
Pulmonary trunk and pulmonary arteries
trunk; splits into right and left pulmonary arteries
arteries: carry deoxygnated blood from heart to lungs
Aorta function
carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
Atrioventricular (AV) valves (tricuspid valve/bicuspid or mitral valve)
lie between the atria and ventricles
prevent backflow into the atria when ventricles contract
chordae tendineae anchor AV valves to papillary muscles
lub
Tricuspid Valve (AV valves)
prevents the backflow of blood as it is pumped from thr RA to the RV, it keeps blood from blocking the RV.
Bicuspid/Mitral Valve
regulates blood flow from the LA to LV; keeps the blood from blocking the LA
Semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic)
aortic lies between the left ventricle and aorta
pulmonary lies between the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
Semilunar valves prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles
dub
Pulmonary SL valve
prevents backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles
Aortic SL valve
prevents blood from flowing back into the LV and keeps it moving towards the body
Chordae tendinae
help prevent the valve cusps from averting into the atrium
Papillary muscles
located in ventricles; attach to the cusps of the av valves via the chordae tendineae
contraction of the papillary muscles opens these valves; relaxation closes these valves
Pulmonary circulation
Blood flow through the right side of the heart
1. The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body via the venae cavae (superior
vena cava and inferior vena cava) and the coronary sinus.
2. From the right atrium, blood flows through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
3. From the right ventricle, blood flows through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary
trunk.
4. The pulmonary trunk branches into left and right pulmonary arteries, which carry blood
to the lungs, where the blood unloads carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen.
5. Oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart via four pulmonary veins.
Systemic circulation
- Blood flow through left side of the heart
6. Oxygen-rich blood enters the left atrium via four pulmonary veins.
7. From the left atrium, blood flows through the mitral valve to the left ventricle.
8. From the left ventricle, blood flows through the aortic valve to the aorta.
9. Oxygen-rich blood is delivered to the body tissues by the systemic arteries.
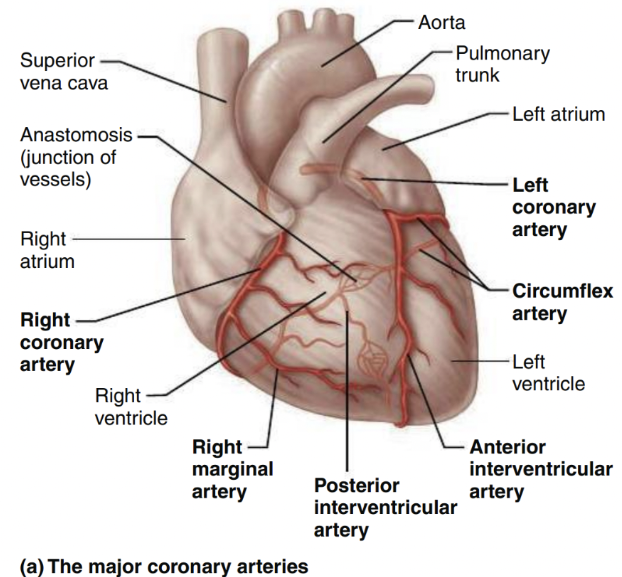
Cardiac Circulation (artery)
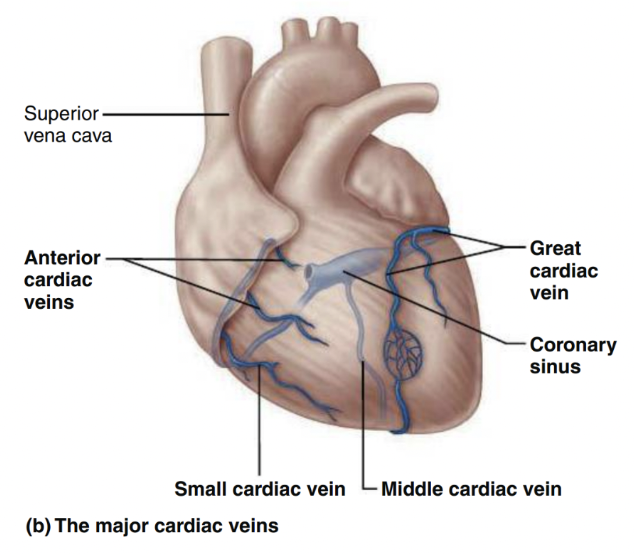
Cardiac Circulation (veins)
Foramen ovale vs. Fossa ovalis (fetal remnant)
Foramen Ovale → a flaplike opening in the interatrial septum
○ Shunts blood entering the RA into the LA (R → L shunt)
○ The LV then pumps the blood out the aorta to the systemic circulation.
○ @ birth/ shortly after: the foramen ovale closes and becomes the fossa
ovalis
Ductus arteriosum vs. Ductus ligamentum (fetal remnant)
Ductus Arteriosum → fetal shunt that connects the pulmonary trunk to the
aorta
○ Blood that does enter the RV is pumped out of the pulmonary trunk, and
encounters this short vessel that connects the pulmonary trunk and the
aorta.
○ @ birth/ shortly after: the ductus arteriosus collapses and is converted
to the fibrous ligamentum arteriosum
○ In newborns with critical congenital heart defects (CHDs), a medication/
naturally-occurring hormone called Prostaglandin E1 is infused to maintain
ductal patency.
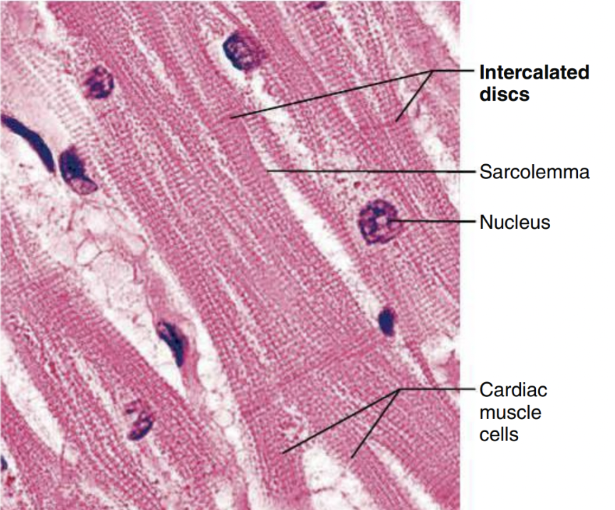
Cardiac muscle with intercalated discs (function)
support synchronized contraction of cardiac muscle tissue
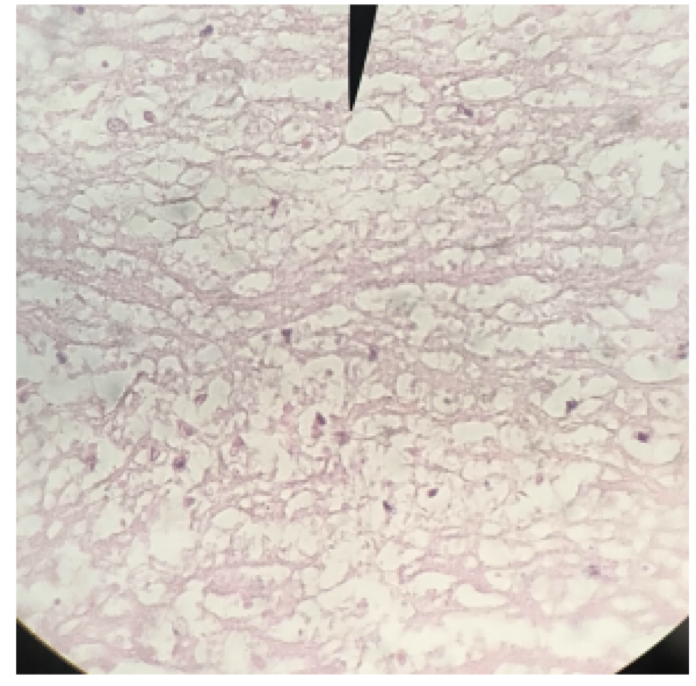
Myocardial infarction
cardiac muscle been replaced by connective tissue
scar tissue doesn’t contract, can’t help the heart to pump
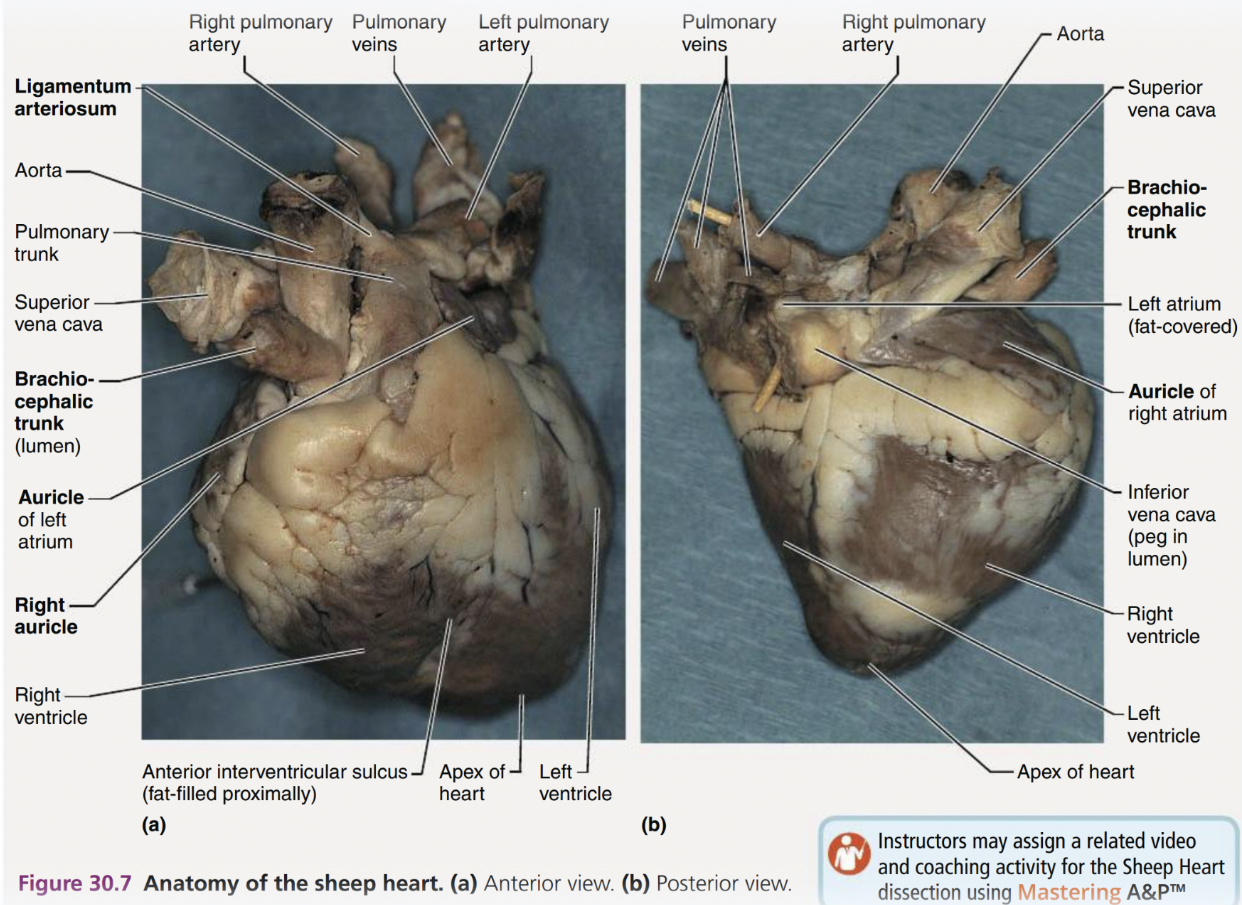
Sheep Heart
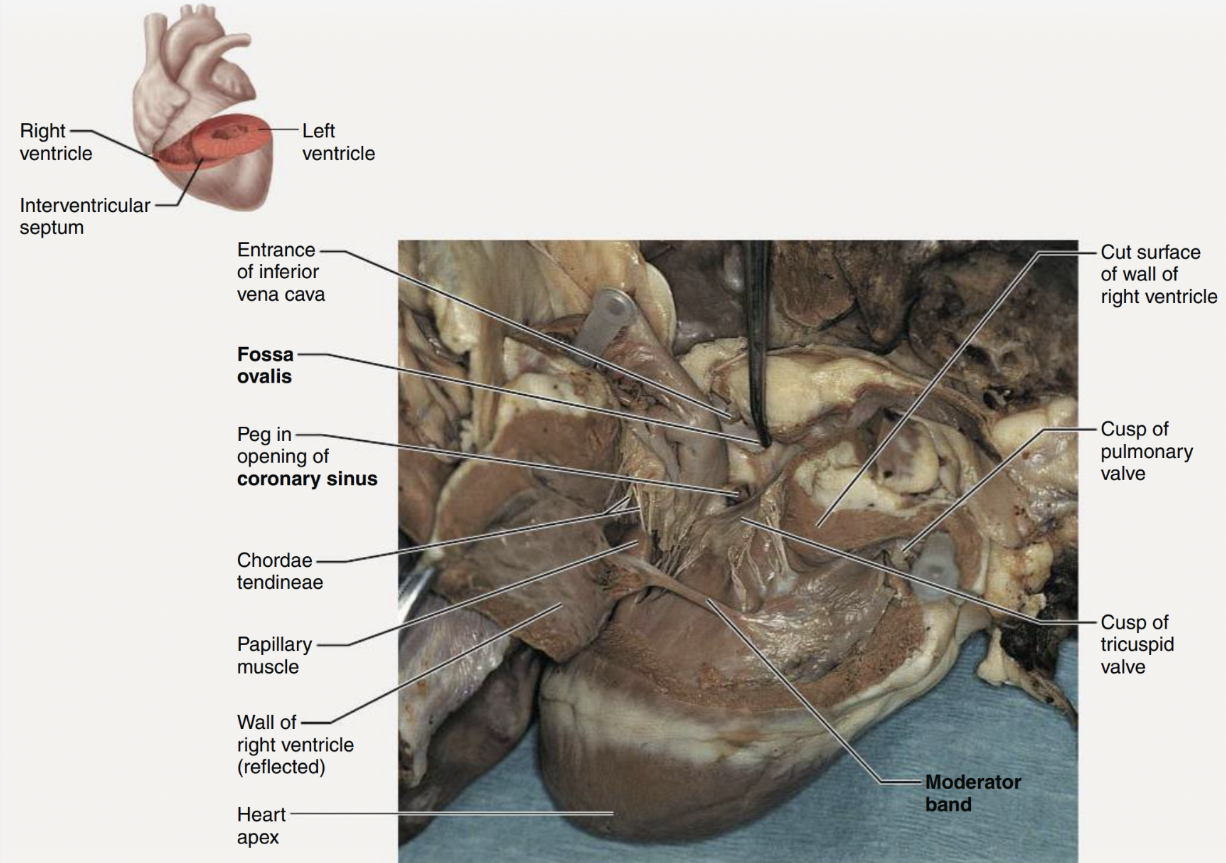
Sheep Heart 2
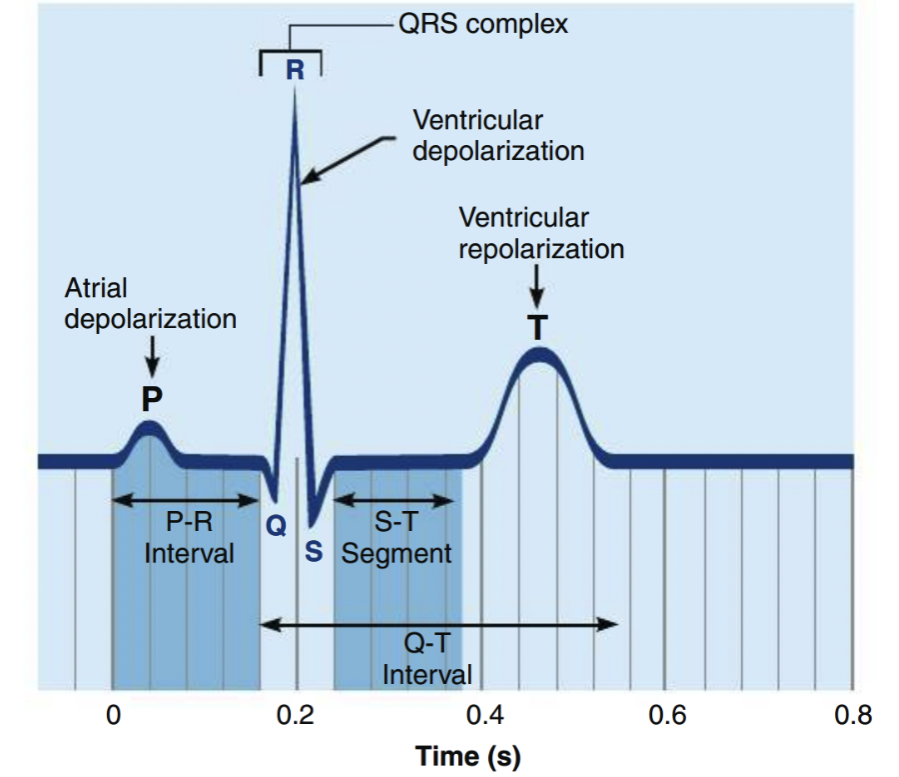
Normal ECG
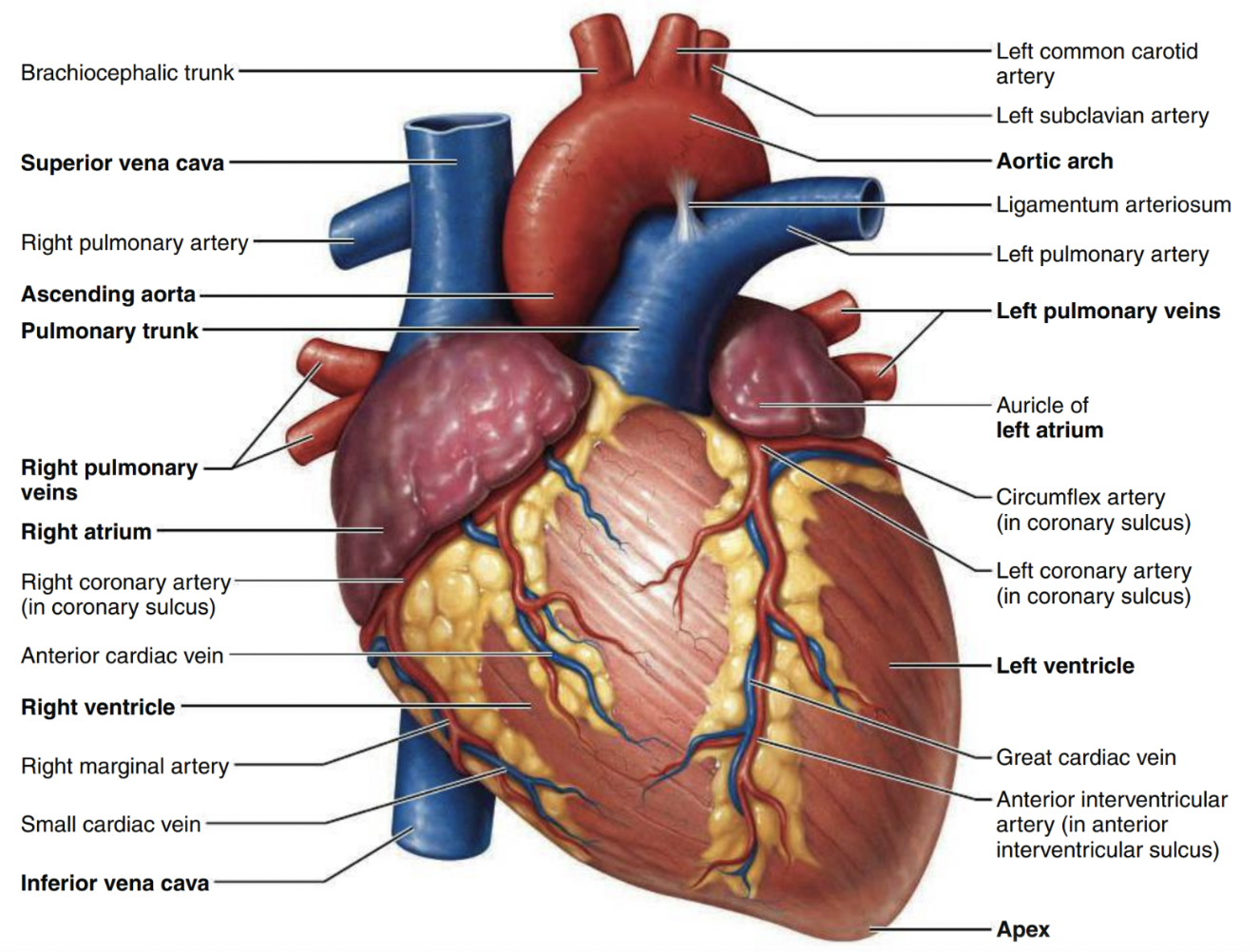
Heart diagram
Heart Diagram 2
Heart Diagram 3
Tunica intima/interna endothelium (location)
the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein
Tunica intima/interna *function*
contains endothelium
Lines all lumen cell walls
forms slick surface that minimizes blood friction
Tunica media (smooth muscle layer) (location)
muscular middle layer
Tunica media (smooth muscle layer) function*
responsible for maintaining bp and continuous blood circulation by vasoconstriction or vasodilation
Tunica externa/adventitia *fibrous connective tissue (location)
outermost layer
Tunica externa/adventitia (fibrous connective tissue) function
-composed of large, loose woven collagen fibers that protect/reinforce the vessel
structure of artery (know to compare with vein)
Arteries:
arteries contains 3 layers (interna, media, and externa)
thick, elastic muscular walls
valves are absent
blood flows under high pressure
thick tunica media tends to be heavier due to more smooth muscle and elastic tissue
carry oxygenated blood from heart to various parts of the body
structure of vein (know to compare with artery)
carry blood from body organs toward heart for purification
all veins carry deoxygenated blood except pulm. vein
thin, non-elastic walls
valves are present to prevent backflow
blood flows under pressure
Ascending aorta
sits atop of the left ventricle and arches posteriorly
carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to the rest of your body
aortic arch
curved segment that gives the aorta cane shape, bridges ascending and descending aorta
distributes oxygenated blood to the brain, head, and arms
brachiocephalic artery
first branch of the aortic arch (right)
supplies oxygen/nutrients to upper right arm, right side of brain, face, and neck
carries blood to right subclavian and right common carotid
Right common carotid artery
in the neck, branches from brachiocephalic artery
supplies oxygen-rich blood to the right side of head/neck
Internal and external carotid
division of the common carotids, either side of the neck
Internal artery serves brain and gives rise to the ophthalmic artery
External carotid artery supplies the tissues external to the skull
Right subclavian artery
branches off from the brachiocephalic, below clavicle
oxygenated blood from heart to right side of head, neck, and arms
Vertebral artery
runs up the posterior neck to supply the cerebellum and the posterior cerebral hemispheres
Axillary artery
runs through the axilla, gives off several branches to the chest wall and shoulder girdle
supplies blood to shoulder, chest, and arm
Brachial artery
continuation of the axillary artery in armpit/shoulder and ends at cubital fossa
delivers blood to biceps, brachialis muscles, elbow, triceps, basically arm muscles
Radial and ulnar arteries
ulnar follows the ulnar bone on the pinky side
supplies oxygen to ulnar nerve, wrist bones/joints, fingers
Radial follows the radial bone on the thumb side
supply blood to lateral part of forearm, wrist, hand, thumb-side
Left common carotid artery
branches off the aortic arch, middle branch
supplies left side of head and neck
Left subclavian artery
branches off aortic arch
delivers to left arm, neck, head, and brain
Circle of Willis
encircles the pituitary gland and optic chiasma
unites the brains anterior and posterior blood supplies
provides alternative route for blood flow when one of the contributing arteries is obstructed (collateral blood low)
Descending aorta
begins at aortic arch and courses downwards through thoracic cavity
supplies blood to your chest wall, organs, and tissues
Celiac trunk
upper abdomen
carries blood to parts of your digestive system (liver, gallbladder, spleen, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, duodenum)
Left gastric (celiac) artery
supplies to stomach and esophagus
common hepatic (celiac) artery
branches into hepatic artery proper (supplies liver, gallbladder, and stomach), and gastroduodenal artery (supplies stomach, pancreas, and duodenum)
splenic artery
branches to the spleen and stomach
Superior mesenteric artery
supplies most of the small intestine and first part of the large intestine
in midsection of digestive tract
Renal arteries
kidneys
Gonadal arteries
supplies to the ovaries and testes
abdominal area, below the renal arteries
Inferior mesenteric artery
supplies distal portion of the large intestine
abdominal, lumbar vertebra
Common iliac arteries (not found in cat)
supplies pelvic organs, lower abdominal wall, and lower limbs
internal and external iliac arteries
internal supplies the gluteal muscles
external supplies the anterior abdominal wall and lower limb
Femoral arteries/deep
upper part of thigh, near groin
supply lower extremities with oxygenated blood/nutrients
deep: supply to deep structures of the thigh