Recording from an Auditory Nerve Fiber: Background Information
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Bipolar neurons that make up the VIIIth nerve have two auditory nerve fibers...
called axons
If voltage is high enough...
an action potential occurs
What is amplitude?
amount of displacement
The amplitude (amount of displacement) of the traveling wave is...
relatively low at the base and then grows to its peak at the stimulus frequency location, then decays rapidly
Traveling Wave in the Cochlea
the motion of the stapes footplate results in the motion of the basilar membrane (up and down) which causes voltage changes in the hair cells which results in stimulation of the VIIIth nerve
What causes the motion of the basilar membrane?
the motion of the stapes footplate
When the basilar membrane goes up...
the stereocilia moves away from the modiolus
When the stereocilia bend towards the tallest row (away from the modiolus) this triggers...
the excitatory phase of the hair cells. This occurs when the basilar membrane moves towards the scala vestibuli
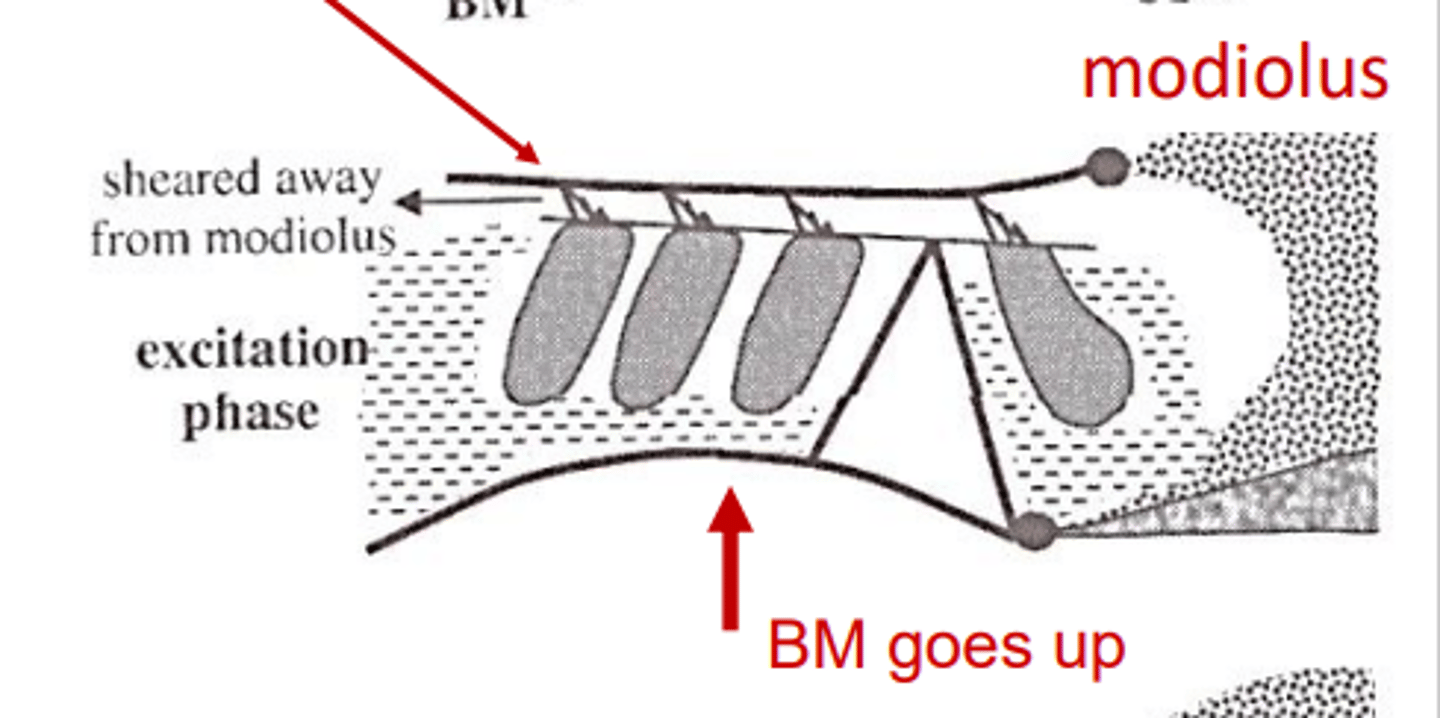
During the excitatory phase of the hair cells, the hydromechanical energy is...
transduced into neural energy as the signal moves into the afferent nerve fibers
A single nerve fiber (axon) is also called a...
"single-unit"
Recordings require...
microelectrodes with extremely fine tips
What do the recordings from a nerve fiber record?
the discharge patterns and sensitivity of a nerve fiber
What is the simplest method of analysis of neural activity?
spike rate function
What does the analysis of the discharge (temporal) pattern require?
the determination of some form of histogram
Histogram
reveals details of a neuron's response to the stimulus
What is the time scale divided into?
"bins"
A histogram is a...
graphic display of a single neuron's response to repeated presentations of a given stimulus
What is the vertical axis on a histogram?
usually some measure of the number of responses
The vertical axis of a histogram may represent...
frequency of responses, percentage of responses, or just the number of neural discharges
Numerous presentations of the stimulus and repeated sampling of the discharges generally are...
required to obtain sufficient data to reveal the characteristic discharge pattern of a given neuron
When is the single-unit recording useful?
when determining how the auditory system is able to discriminate between sounds of different frequencies
Rose et al (1967) stated that...
"There is strong evidence that for [sinusoidal] stimuli the spiral ganglion neurons transmit to the cochlear nuclear complex information concerning frequency by means of a period-time code."
Rose et al (1967) Study
-tonal stimuli presented at 80 dB SPL and 1 second in duration (10 stimuli per histogram)
-33 squirrel monkeys
-VIIIth nerves were exposed
-a microelectrode was used to record the neural discharge of each neuron
-recorded interspike interval histograms
What did the vertical axis of the histogram show in the Rose et al study?
the number of interspike intervals that occurred
If an interval histogram had its largest peak at 1 ms in the Rose et al study, then...
the time between successive discharges was most often 1 ms
Each neuron does not fire to the peak of each sound wave, but rather...
fires to some percentage of the peaks
-this is related to the absolute refractory phase of the neuron
What was one of the neuron's responses?
412 Hz tone
-sine wave
Sine Wave
happens many times and measures the action potential
Period
time required to complete one cycle of a given frequency
How often does the neuron fire during the rarefaction pahse?
Period = 1000ms/Frequency (cycles/s)
= 1000ms/412 Hz
= 2.43ms
At 1200 Hz...
Period = 1000ms/Frequency (cycles/s)
= 1000ms/1200 Hz
= 0.83ms
Kiang et al. (1965)
Post Stimulus Time (PST) Histogram
for 18 auditory nerve fibers of a single cat in response to click stimuli (broadband frequency content)
-Kiang et al (1965)
Rarefaction
away from ear drum (air pressure, TM, and stapes footplate goes down, BM goes up)
-excitatory phase (stereocilia move away from the modiolus)
Condensation
inhibitory phase (BM goes down)
On PST histograms, the time interval between spikes...
approximates one period of the CF of the fiber
A compound histogram is formed by...
inverting the histogram to condensation clicks under that to rarefaction clicks
-the distance in time from the rarefaction to condensation peak approximates 1/2 the period of the CF
In the Kiang et al. study, they used...
a click and recorded the neural activity for several nerve fibers
Low frequency encoded the...
low frequency sounds
High frequency encoded the...
high frequency sounds
Why does the neuron respond later to a condensation click, rather than a rarefaction click?
during a rarefaction click, the basilar membrane goes up towards the scala vestibuli
-excitatory phase
Since at high click levels the earliest peak always occurs for rarefaction clicks...
it is likely to be the rarefaction phase (in which the stapes is pulled out of the oval window) of the cochlear motion that corresponds to increased neural activity
Why does the neuron fire earlier in response to a rarefaction click, rather than a condensation click?
the neural activity from a single neuron is earlier in response to a rarefaction click than a condensation click
During rarefaction...
-Diaphragm is moving away from the ear drum
-Air molecules move away from the ear drum in the ear canal (separated)
-Tympanic membrane is moving out
-Stapes footplate moves out (away from the oval window)
-Basilar membrane goes up (excitatory phase)
-Stereocilia move away from the modiolus (making microchannels open)
-The microchannels within the stereocilia allows potassium to enter due to the greater amount of potassium outside (reach equilibrium)
-Voltage in the hair cell is positive (depolarization)
-Outer hair cell shrinks due to prestin protein narrowing
-Active process allows the BM to move further up due to the shrinking of the OHC
During condensation...
-Diaphragm is moving towards the ear drum
-Air molecules move towards the ear drum in the ear canal (molecules are pushed together)
-TM goes in
-Stapes footplate goes in
-Basilar membrane goes down (inhibitory phase)
-Stereocilia move toward the modiolus
-Voltage goes down
-OHC expands (prestin protein expand) - hyperpolarization
Durrant and Feth (2013)
neurons are not, in and of themselves, frequency selective in their excitability
-there is an upper limit of frequency response imposed on the rate of discharge by the absolute refractory period
-this places serious constraints on a mechanism of simple translation of frequency to the timing of a neural spike potentials
The Volley Theory
even though one nerve cell might be incapable of carrying hih-frequency information above 6000 Hz, (due to the limitations of the absolute refractory period) a group of neurons could do so
The single unit tuning function of a primary auditory neuron reflects...
optimal sensitivity for only one frequency of stimulation
What is this point demonstrated by?
neural tuning curves from auditory neurons of multiple frequencies
It is evident that what makes a given primary auditory neuron frequency selective is...
where it comes from within the cochlea
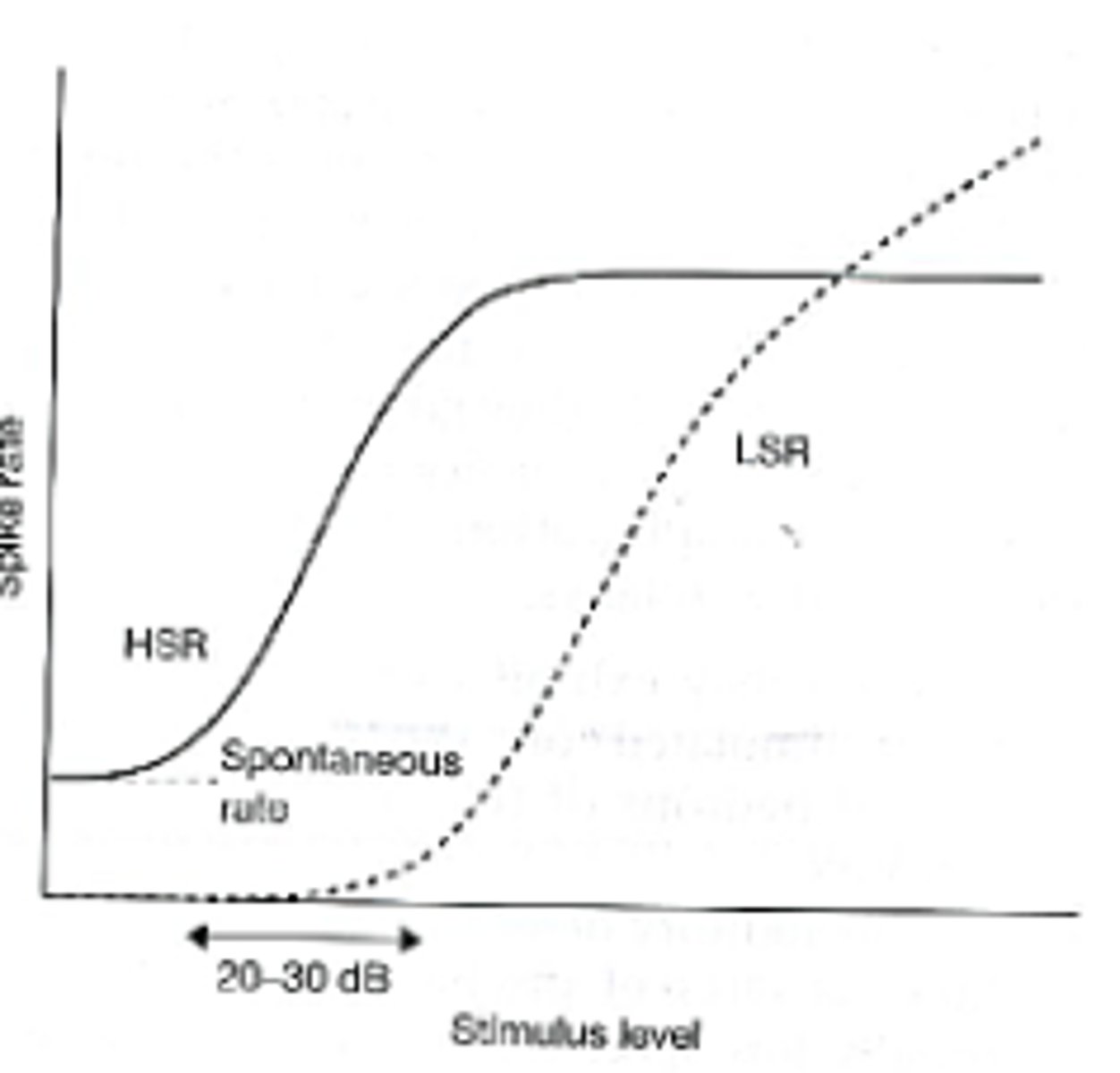
The most basic neural signal by which to represent stimulus intensity/level is...
the average rate of neural discharges as a function of intensity
-HSR = high spontaneous rate fiber
-LSR = low spontaneous rate fiber
-graph shows two different neurons
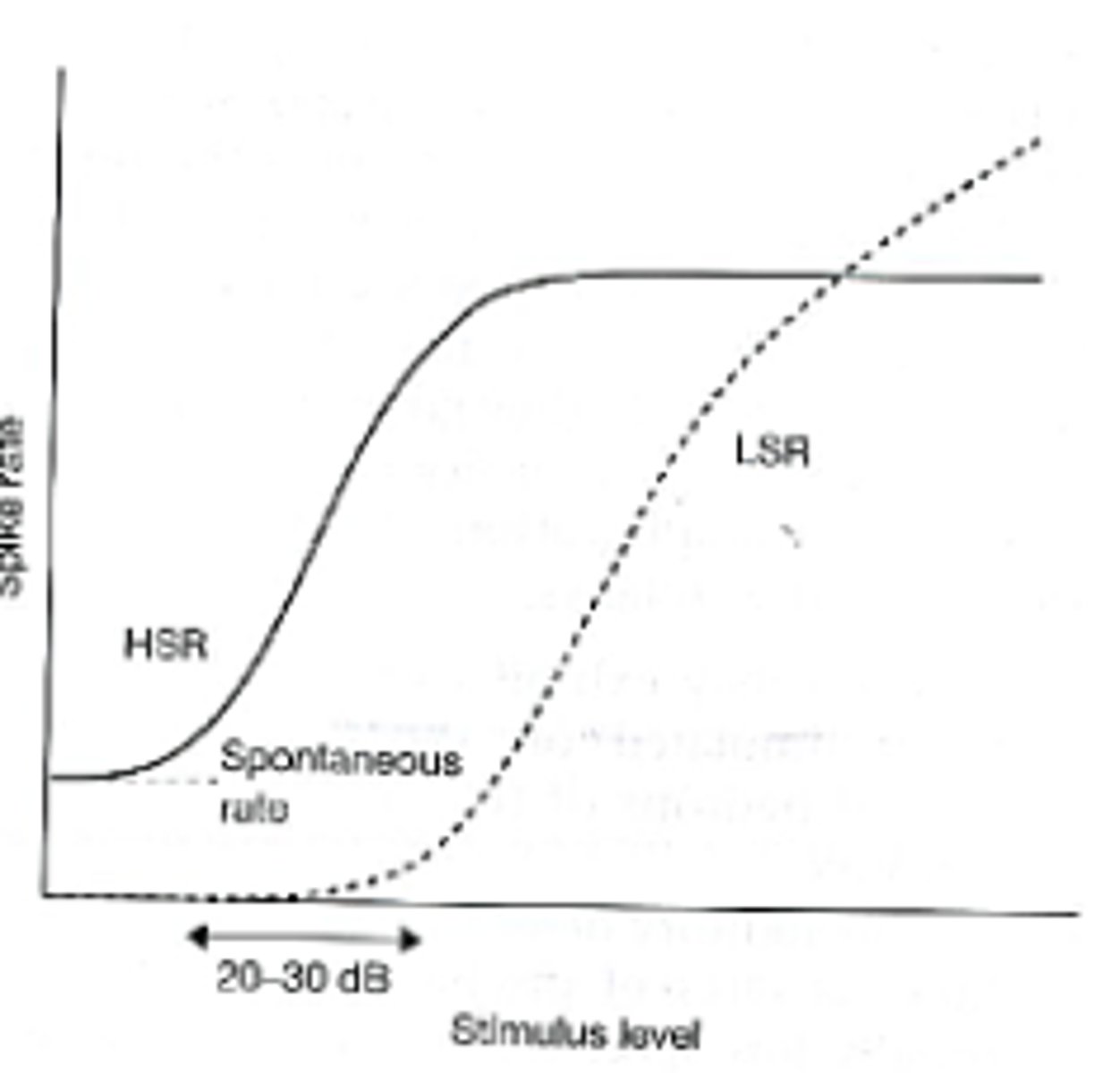
The dynamic range of most primary auditory neurons is rather limited at their...
characteristic frequency (CF)
The maximal spike rate is reached at...
merely 20-30 dB above the level at which a just noticeable increase in the spontaneous rate is observed
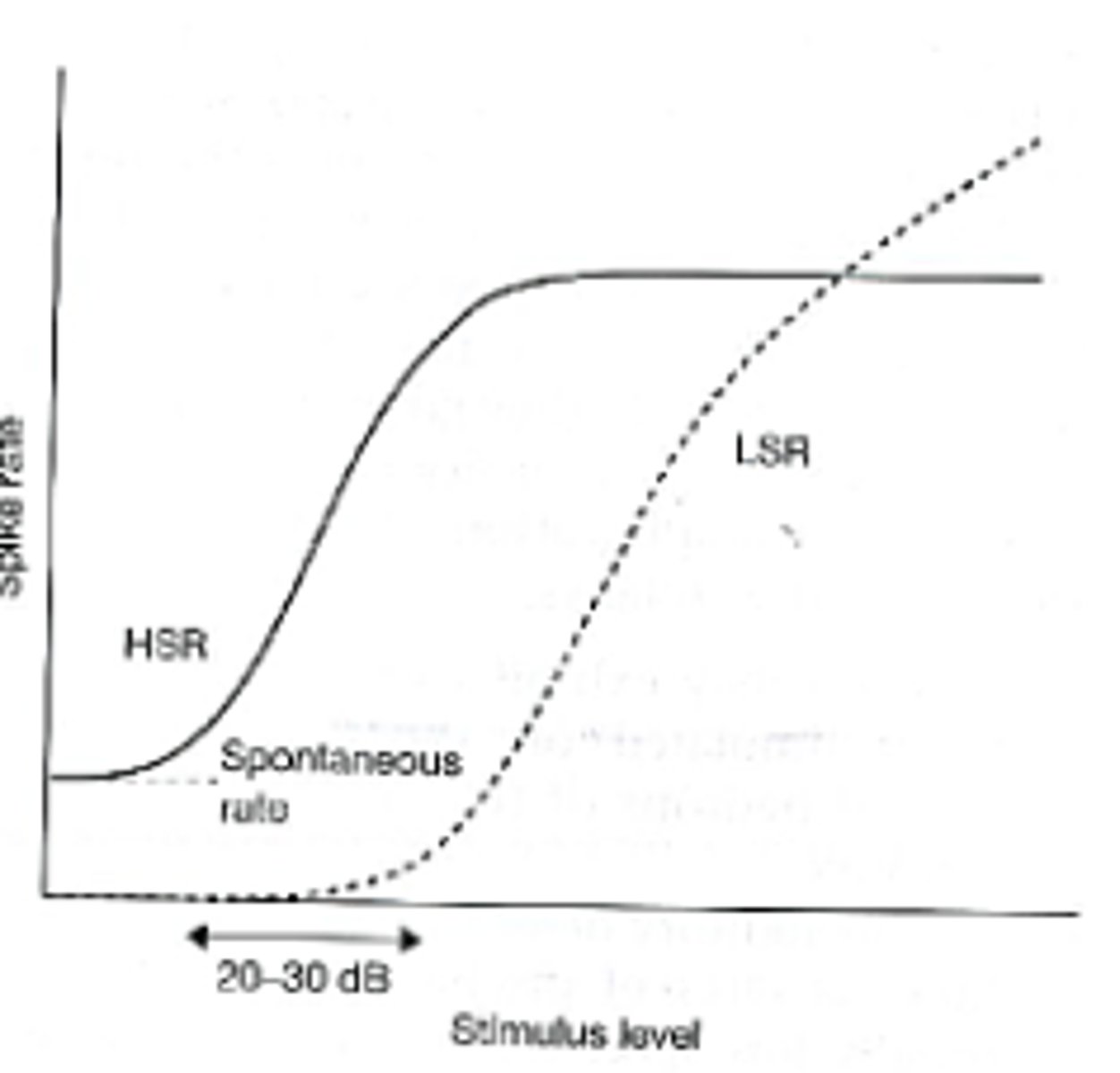
The dynamic range of hearing in humans is...
on the order of 140 dB
-this suggests that the encoding of intensity must involve more than just the spike rate of any individual neuron stimulated at its CF
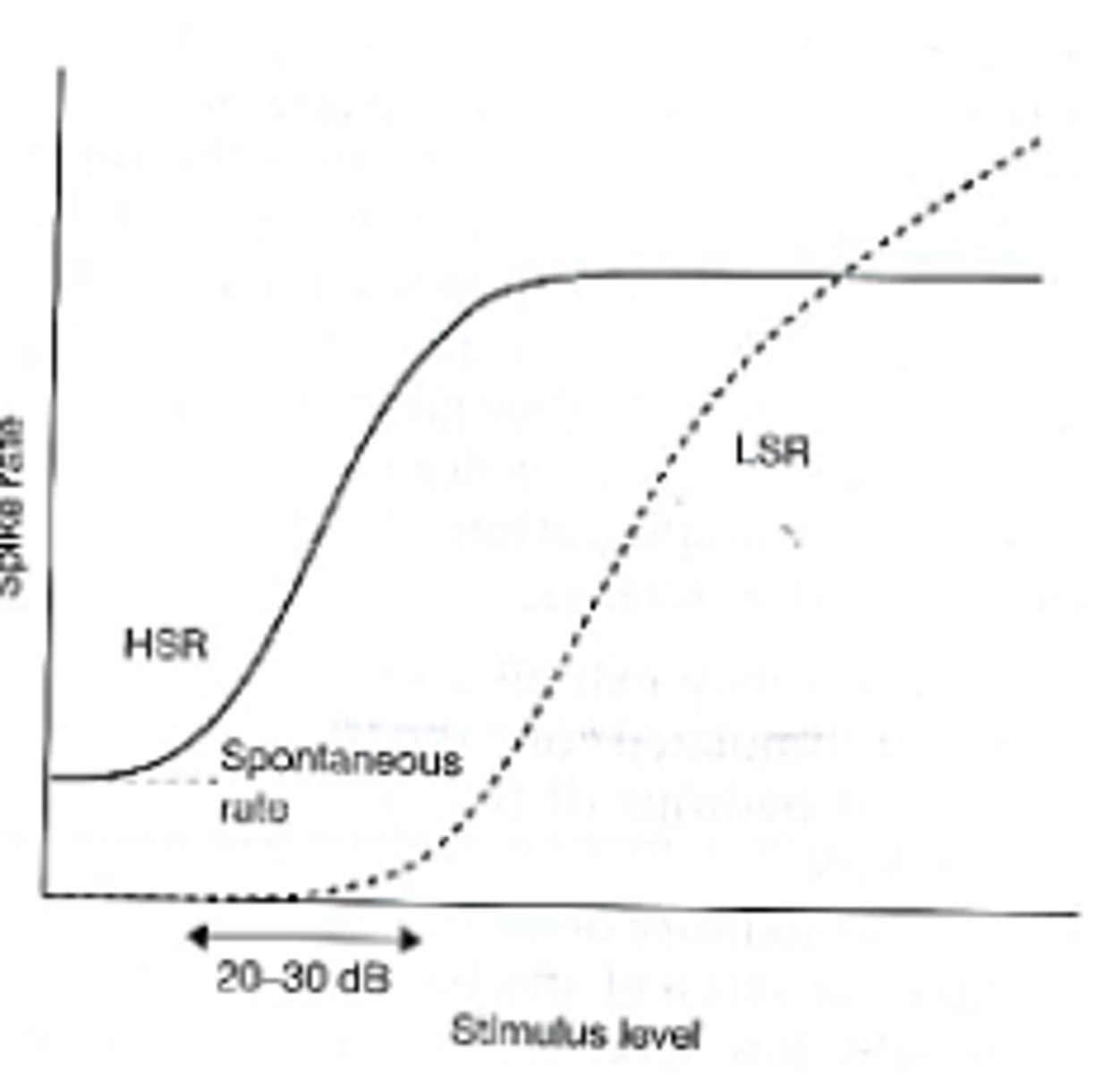
Saturation
where the spike rate cannot increase
Each inner hair cell is innervated by...
up to around 20 afferent neurons (Type I)
One hypothesis is that even at stimulus levels where a given neuron saturates...
the total discharges per unit time (or the density of discharges) will increase as more fibers are recruited into activity above their spontaneous rates
The auditory system is required to...
process complex sounds (such as speech)
What does the anatomy of the auditory brain stem pathways imply?
a complex processing system
The complex processing system...
process multiple "maps" of the cochlea simultaneously
The cochlear nucleus has...
nearly a half dozen different types of neurons
-we can infer from this that there are a variety of response patterns that are processed in the brain stem
Towards the upper levels of the brain stem...
increased specialization of neurons is found
Specialization of neurons permits the detection of...
specific features of the stimulus which most likely facilitates the processing of complex sounds like speech
The superior olivary complex and higher nuclei receive information from...
both ears
Two ears are better than one for...
sound localization and for the ability to recognize speech in the presence of background noise