Lecture 8 - Species, Speciation, Phylogenies
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Sexual dimorphism
the systematic differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species
EX:
birds of paradise
gorillas
beetles
Can individuals vary within a colony or population?
Yes

Ecophenotypic variation
when morphology changes in different habitats
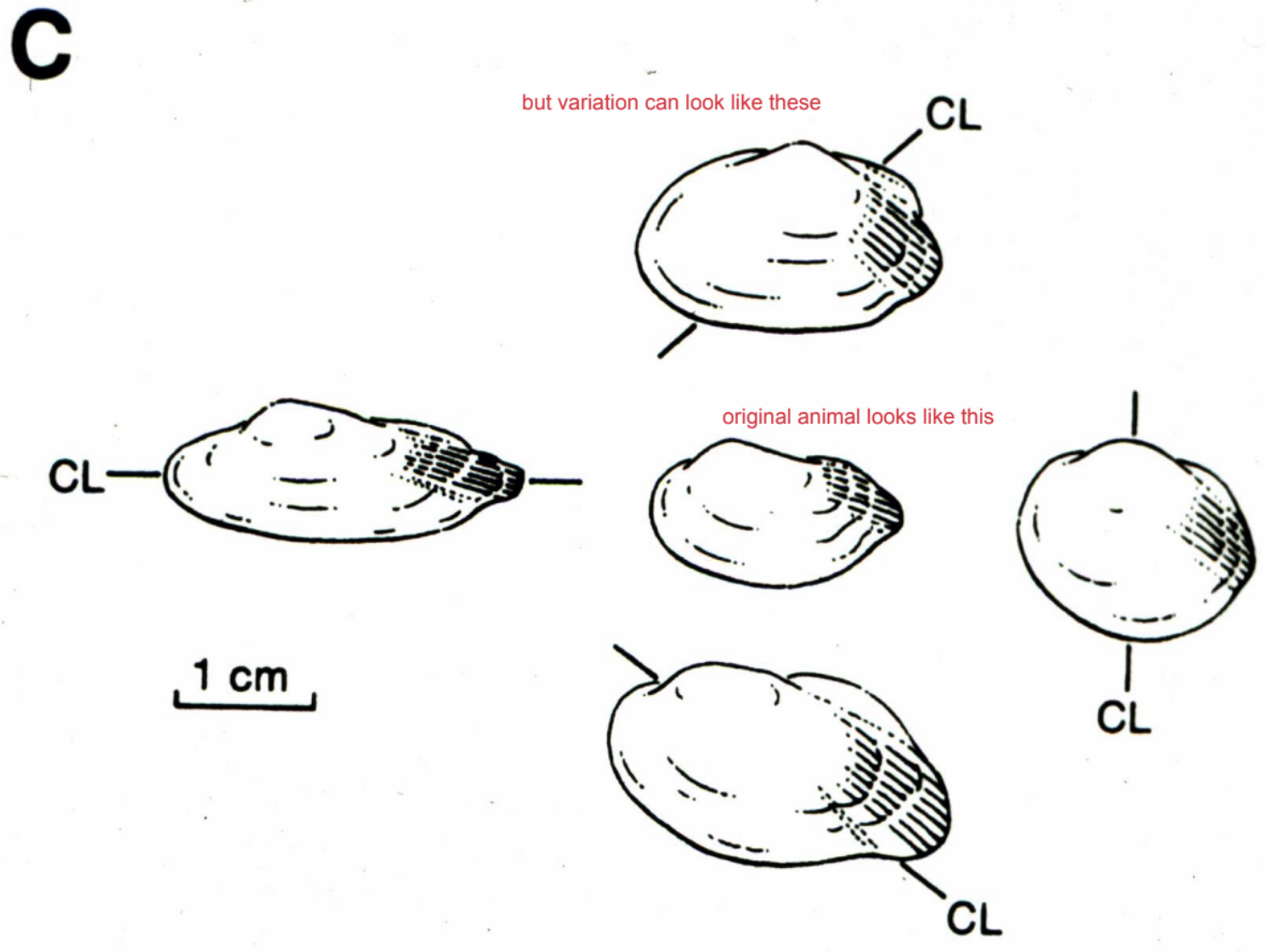
Taphonomic distortion
the ways that geological and biological processes after an organism's death can alter its remains, potentially leading to misinterpretations of its original form and features
Genetic habitat
the sequence of nucleotides in a gene, acting as a template for replication
can change through recombination, mutation
Somatic habitat
the physical entity or phenotype
immediate conditions within which the genes act
can change through growth and development
Environmental habitat
everything external to the body
supplies resources to an organism
can change as external conditions change
Population
Groups of conspecific organisms that occupy a more or less well-defined geographic region and exhibit eproductive continuity from generation to generation
share a single gene pool
Natural selection
variation exisst among individuals where the advantageous variation is heritable
increase those gene frequencies that are more “fit” in environment
most powerful force in changing gene frequencies in LARGE POPULATIONS
Random genetic drift would
change fluctuation in gene frequency
Inbreeding would
reduce genetic variability
Migration would
cause mixing that prevents genetic divergence
Mutation would be
the ultimate source of genetic variation
Species
Groups of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations, which are reproductively isolated from other such groups
defined by genetic cohesion
Geographic isolation
individuals occupy different regions
Habitat isolation
live in different habitats, utilize different resources
Seasonal isolation
live in different times of year
Behavioral isolation
a type of reproductive isolation where differences in mating rituals or behaviors prevent different species from interbreeding
Mechanical isolation
no successful mating, different reproductive systems
Gametic mortality
sperm is transferred but no fertilization occurs
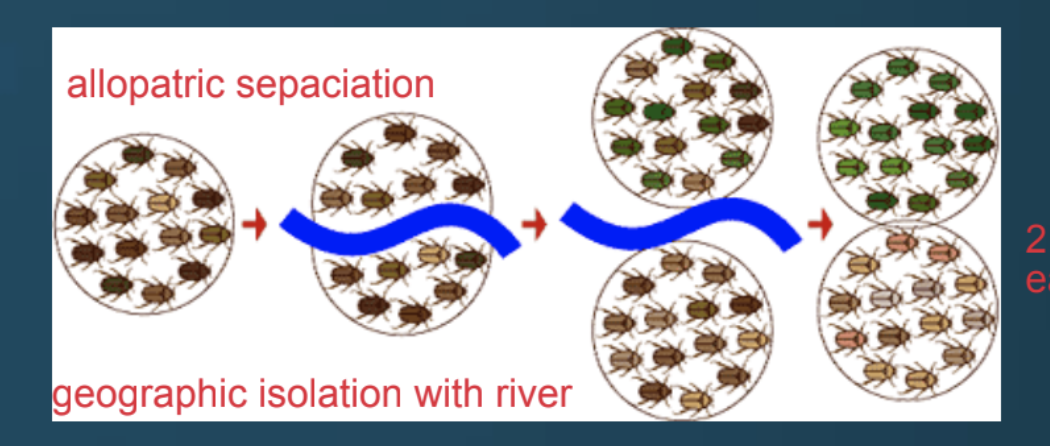
Allopatric speciation
geographic barrier introduces variation of species
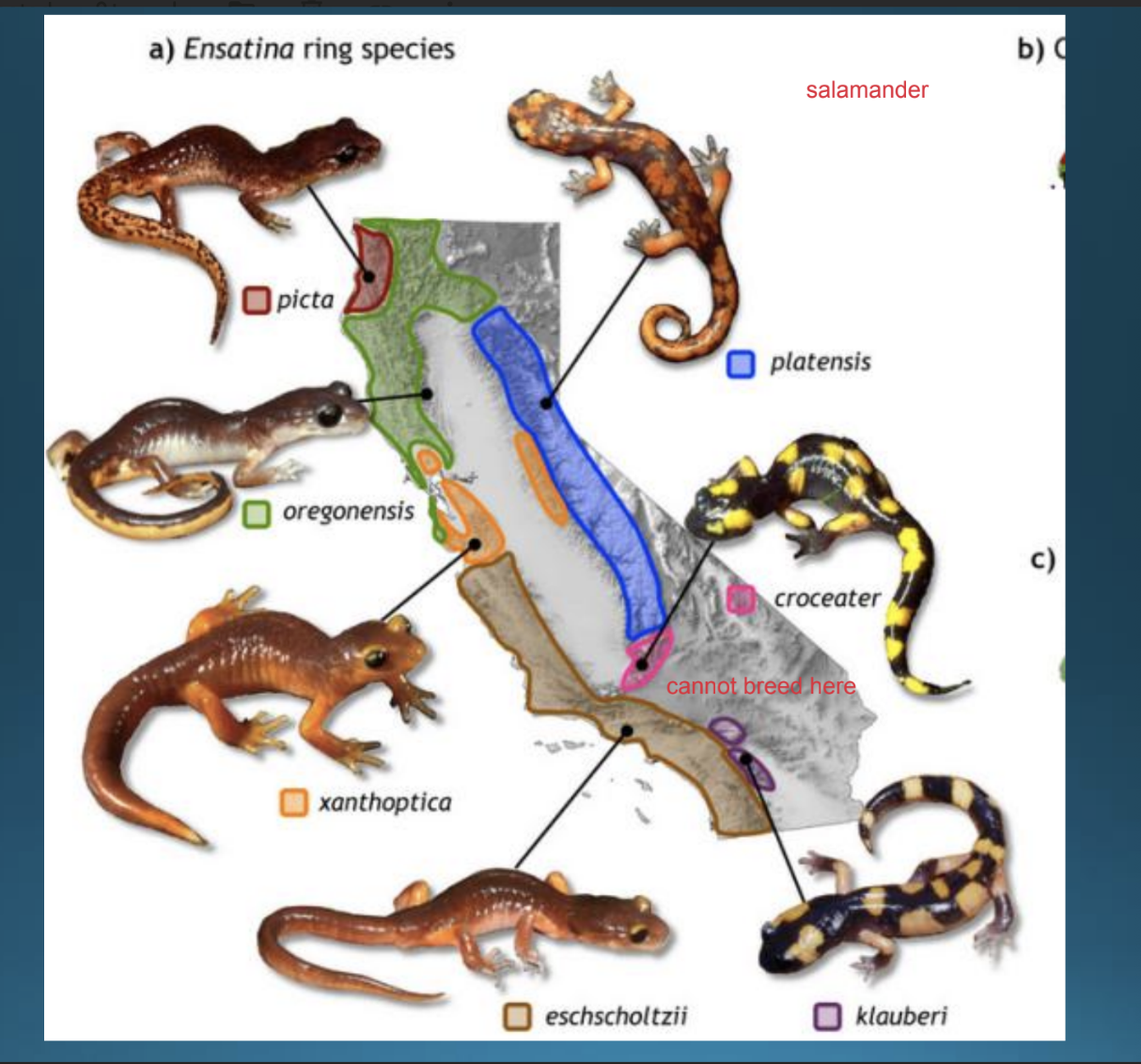
Parapatric speciation / ring species
speciation occurs in adjacent geographic areas
gene flow is reduced even thoug individuals are near each other
gradients form but the end populations are reproductively isolated
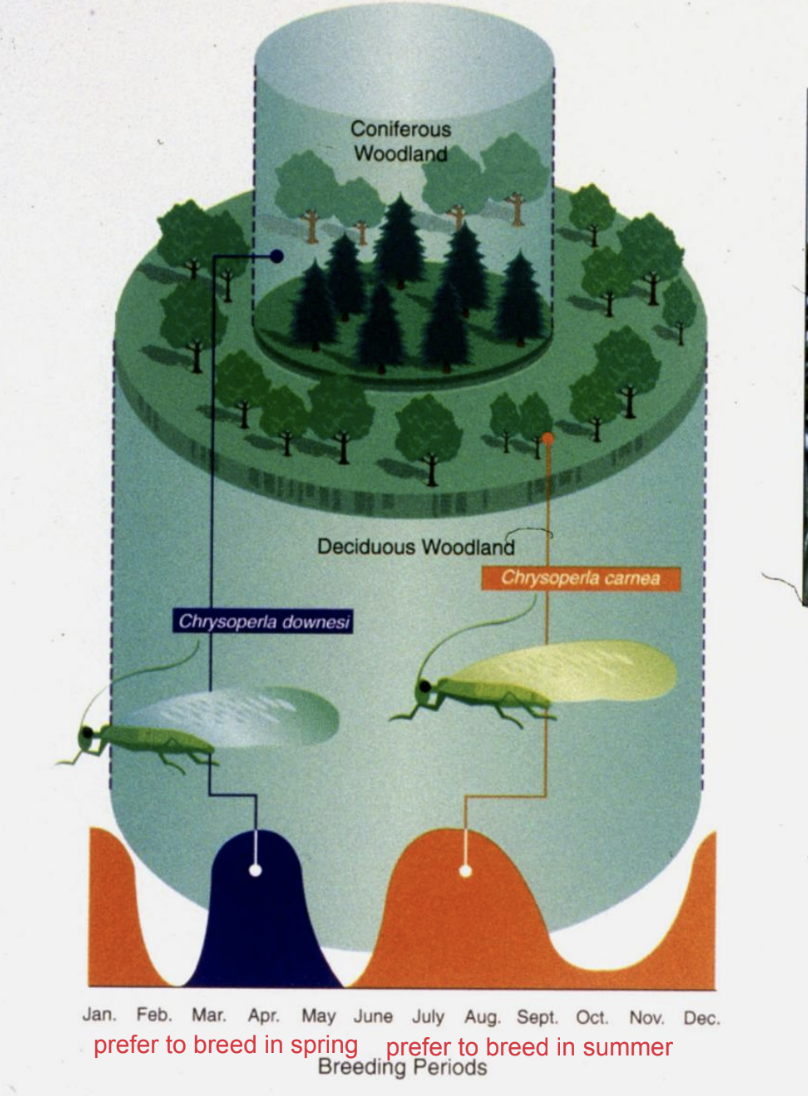
Sympatric speciation
Speciation occurs in one geographic area
EX: different mating seasons but both species can live in the same place still
Difficulties with the biological species concept that paleontologists have:
Reproductive isolation is difficult to identify or verify
Can’t test reproductive isolation directly in the fossil record
Reproductive isolation may not be expressed morphologically
This model ignores evolution (change over time) altogether
Speciation occurs over time!
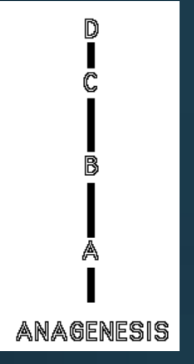
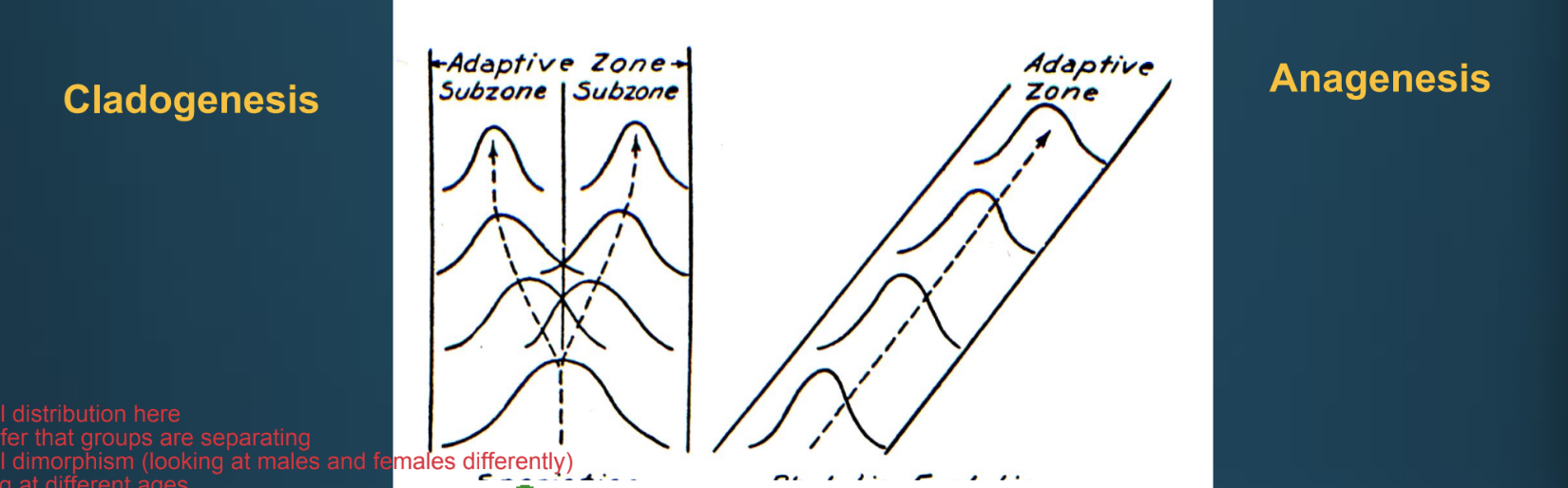
Anagenesis
gradual change in fossil populations over time
arbitrarily divided
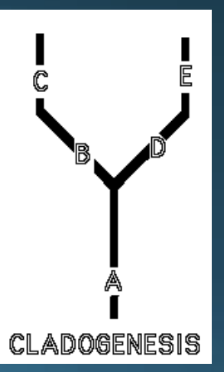
Cladogenesis
splitting of lineages
barrier to reproduction leads to divergence of each
Visualizing anagenesis versus cladogenesis