Science & resistance training (Exam 1-study guide)
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
What are the THREE main principles of specificity?
Principle of Specificity
Principle of Overload
Principle of Progression
Name TWO things on what the Principle of Specificity is.
The adaptation of the body or change in physical fitness is specific to the type of training undertaken.
Train at what you want to improve in
In other words, if you want to improve in something for example: sprinting, you need to sprint. Or if you want to build leg strength you will need to train your legs directly
Give TWO EXAMPLES of the Principle of Specificity?
squat machine vs leg press machine
Both make your legs stronger, but they target different because they do not share the same squat movement. therefore, their results are specific to the exercise you choose.
What does the acronym SAID stand for?
Specific Adaptation to Imposed Demand
Principle of Specificty:
What are the TWO types of fibers of skeletal muscle?
Type I fibers (Type I Slow Twitch)
Type II fibers (Type II Fast Twitch)
How many Myosin ATPase does type I slow twitch fibers and type II fast twitch fibers have? (ex: low or high)
Myosin ATPase:
Type I slow twitch: LOW
Type II fast twitch: HIGH
How many Energy Utilization does type I slow twitch fibers and type II fast twitch fibers have? (ex: low or high)
Energy Utilization:
Type I slow twitch: LOW
Type II fast twitch: HIGH
How many Mitochondria does type I slow twitch fibers and type II fast twitch fibers have? (ex: many or few)
Mitochondria:
Type I slow twitch: MANY
Type II fast twitch: FEW
What COLOR is type I slow twitch fibers and type II fast twitch fibers have? (ex: two different colors)
Type I slow twitch: RED
Type II fast twitch: WHITE
What kind/type of fibers does Myoglobin have? (ex: many or low)
It has type I slow twitch fibers
Type I Slow Twitch fibers: YES
Type II Fast Twitch fibers: NO
What is the Contraction Rate in type I slow twitch fibers and type II fast twitch fibers? (Options: Slow and Fast)
Contraction Rate:
Type I slow twitch: SLOW
Type II fast twitch: FAST
What is the Duration in type I slow twitch fibers and type II fast twitch fibers (Options: Prolonged and short)
Duration:
Type I slow twitch: Prolonged
Type II fast twitch: Short
Name TWO things on what the Principle of Overload is.
To improve any aspect of physical fitness the individual must increase the demands placed on the appropriate body systems.
“Adaptation to a stimulus”
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Muscular strength, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
muscular strength makes the skeletal muscle:
INCREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Muscular endurance, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
muscular endurance makes the skeletal muscle:
Increases for high power output
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Aerobic Power, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Aerobic power makes the skeletal muscle:
No change or increases slightly
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Anaerobic Power, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Anaerobic power makes the skeletal muscle:
INCREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Rate of Force Production, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Rate of Force Production makes the skeletal muscle:
INCREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Fiber cross-sectional area, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Fiber cross-sectional area makes the skeletal muscle:
INCREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Capillary Density, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Capillary Density makes the skeletal muscle:
No change or decreases
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Mitochondrial Density, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Mitochondrial Density makes the skeletal muscle:
DECREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Stored ATP, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Stored ATP makes the skeletal muscle:
INCREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Stored Creatine Phosphate, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Stores Creatine Phosphate makes the skeletal muscle:
INCREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Stored Glycogen, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Stored Glycogen makes the skeletal muscle:
INCREASES
Principle of Overload
Effects of Types of Training on Skeletal Muscle:
The variable is Stored triglycerides, what are the strength training adaptations to this training?
Options: Increase, increases for high power output, decrease, no change or increases slightly, may increase, or no change or decreases
Stored Triglycerides makes the skeletal muscle:
MAY INCREASE
Give one example of Principle of Overload?
If you start bench pressing 100 Ibs (10 reps) and starts to feel easy. To challenge your body, you should progress to 110 Ibs (12 reps). The extra challenge forces your muscles to adapt and get stronger.
Name TWO things on what the Principle of Progression.
• To improve any aspect of physical fitness the individual must continually increase the demands placed on the appropriate body systems.
• “Progressive overload”
Name an example of the principle of progression.
Ex: Milo of Croton (class example)
He carried a calf as it grew older and heavier every day. This is an example of principle of progression because he did not carry all the weight at once, instead he gradually increased the weight little by little every day and his body adapted and got stronger
Real life ex (made up): To get better at pushups you can increase the amount you do every week (e.g., wk 1: 5 push-ups and wk 2: 7 push-ups) this allows the muscle time to adapt and get stronger
Define Motor Unit
a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates (controls)
How many muscle fibers are in a single motor unit?
There are several hundred
Name the FOUR main FUNCTIONS of the SARCOLEMMA
Protects muscle fiber (acts as the skin around muscle cell)
Transmit electrical signal (carries action potential across muscle fiber so it knows when to contract)
helps with nutrients and waste exchange (works with capillaries to let O2 and nutrients in & waste out)
connects to tendons (transfers force produced inside muscle to the tendons and then to bone
Name the FOUR main FUNCTIONS of the SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM?
Stores Calcium when muscle is resting
Releases calcium when it receives a signal (nerve impulse); then calcium floods into muscle fiber
Triggers contraction - Calcium binds to troponin, which starts the sliding if actin and myosin filaments
Reabsorbs calcium when contractions done! Helps muscle relax
Name the THREE main FUNCTIONS of the Transverse Tubules (T-tubules)
Carry electrical signals inside muscle, brings the action potential from sarcolemma deep into the muscle fiber
Coordination contraction - ensures that the signal reaches all parts of the muscle fiber evenly so the whole muscle contracts at the same time.
Works with Sarcoplasmic reticulum - when signals travels through t-tubules then triggers SR then releases calcium, and results in a muscle contraction
Name the FIVE main FUNCTIONS of the Mitochondria
Produce ATP through aerobic (O2 using) metabolism
Breaks down carbs, fats, and sometimes protein to release energy
Supports endurance - the more mitochondria in a muscle fiber the better it can keep working for a long time
Regulates metabolism - controls how fast or slow muscle uses energy
Helps removes byproduct (e.g., lactate) after exercise
Name the FOUR main FUNCTIONS of the ACTIN
Forms the thin filament- structure interacts with myosin during contraction
Binding site for myosin - myosin heads attach to form cross-bridges
enables muscle contraction
Helps maintain structure - actin filaments anchor at the Z-line
Name the FIVE main FUNCTIONS of the Myosin
Forms thick filament
cross ridge formation - myosin heads attach to actin at binding sites
Power stroke - Myosin head on actin, slides filaments past each other and shortens the muscle
ATP usage - Breaks down ATP to release the energy needed for contraction
Generate force - moves bones and produces movement due to the pulling of myosin heads
Name the FOUR main FUNCTIONS of the Troponin
Binds Calcium - when released from SR it attaches to troponin
moves tropomyosin - Troponin shifts tropomyosin off actin binding sites
Allows cross-bridge formation - myosin heads attach to actin, leading to contraction.
Helps regulate contraction & relaxation
Name the FOUR main FUNCTIONS of the Tropomyosin
Covers actins binding sites - at rest tropomyosin blocks spots on actin where myosin would attach which prevents contraction
Controls contraction - Calcium binds to troponin, tropomyosin shifts position, uncovering the binding sites on actin
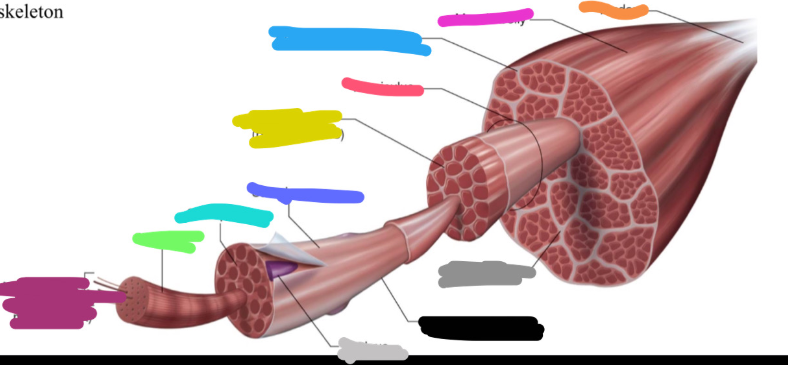
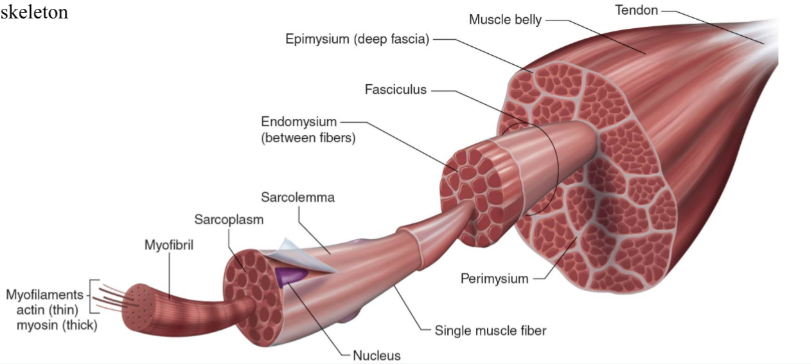
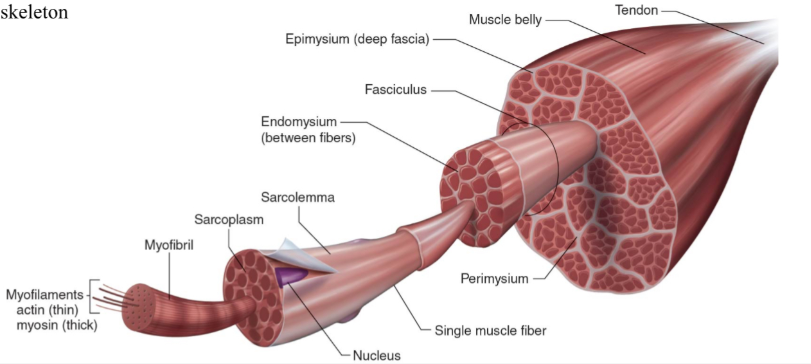
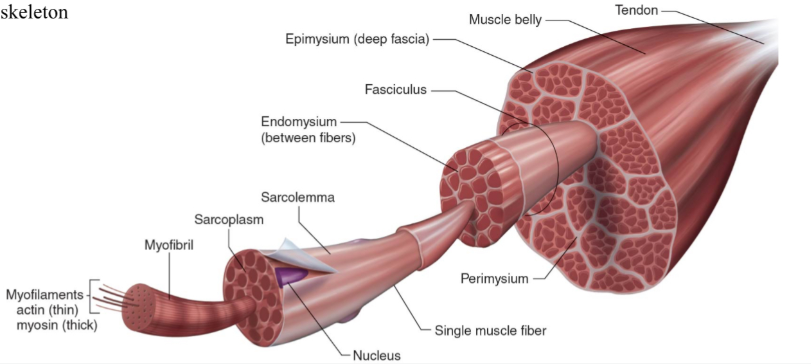
Structure of skeletal muscle
What is the dark purple mark called on the skeletal muscle?
Myofilaments
actin (thin)
Myosin (thick)
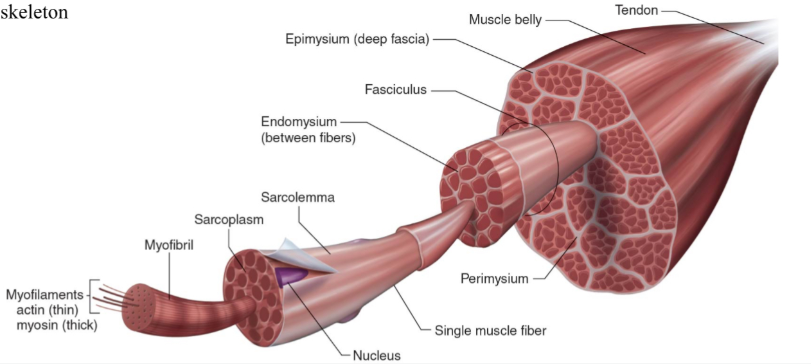
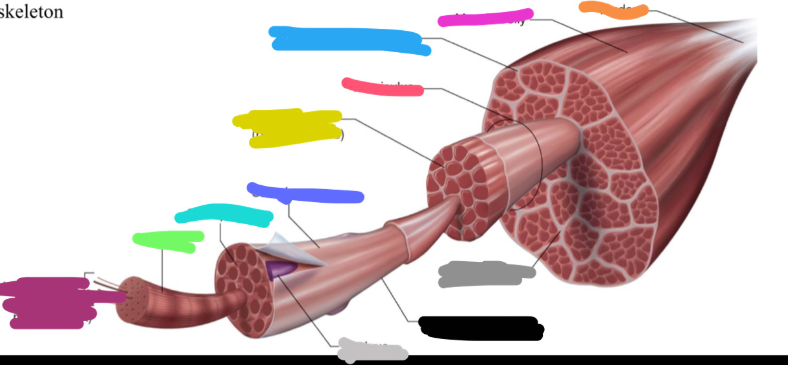
What is this neon green mark called on the skeletal muscle?
Myofibril
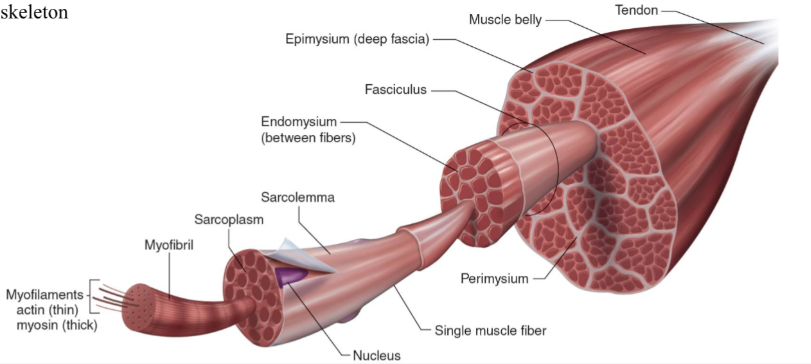
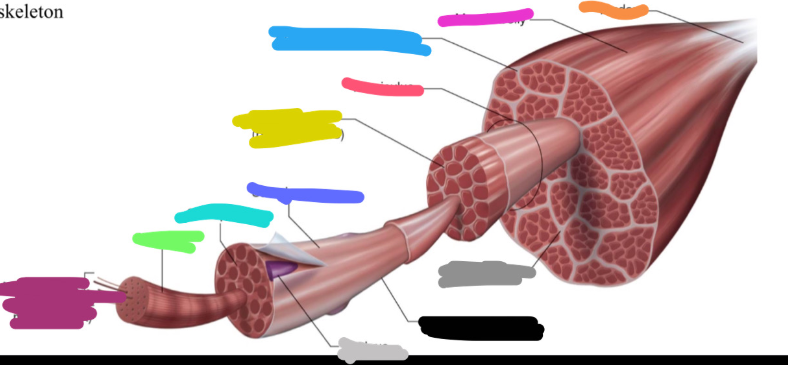
What is the turquoise mark called labeled on the skeletal muscle?
Sarcoplasm
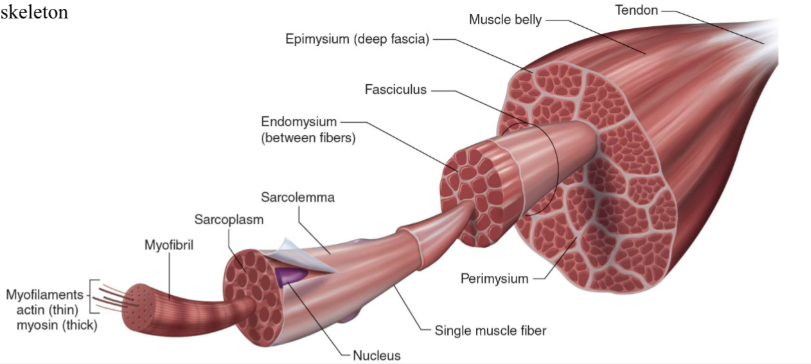
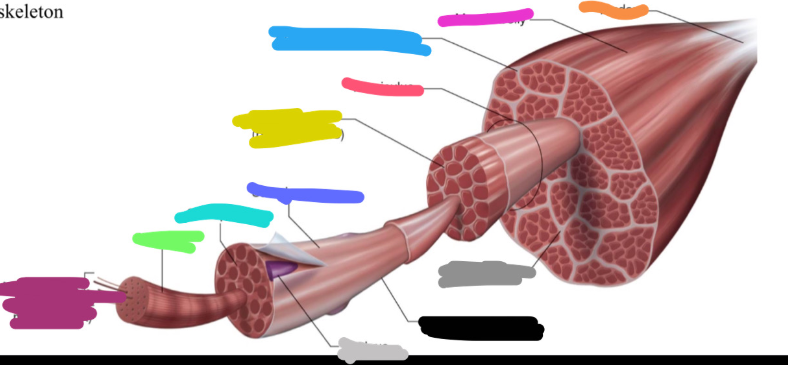
What is the dark violent mark called labeled on the skeletal muscle?
Sarcolemma
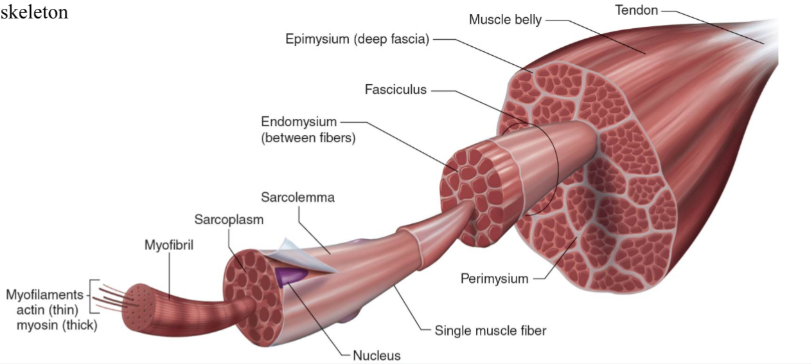
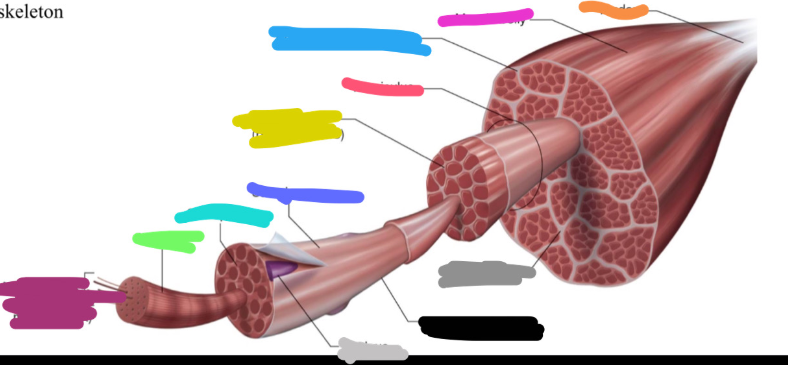
What is the light grey mark called labeled on the skeletal muscle?
Nucleus
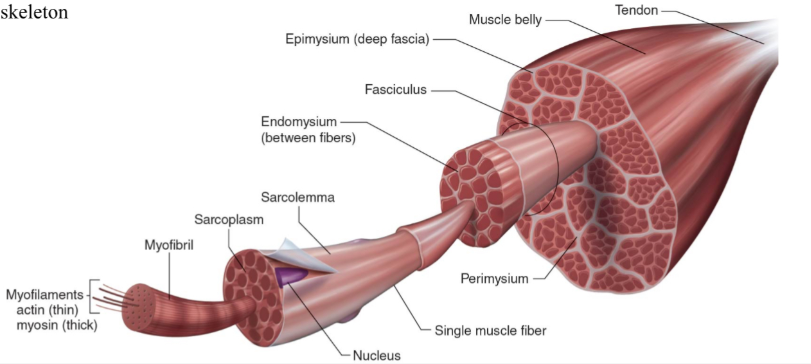
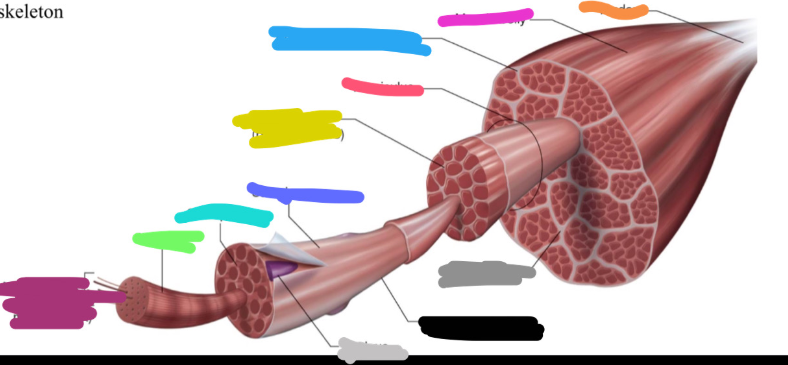
What is the black mark labeled on the skeletal muscle called? Is it a covering or bundles?
Single muscle fiber
BUNDLES
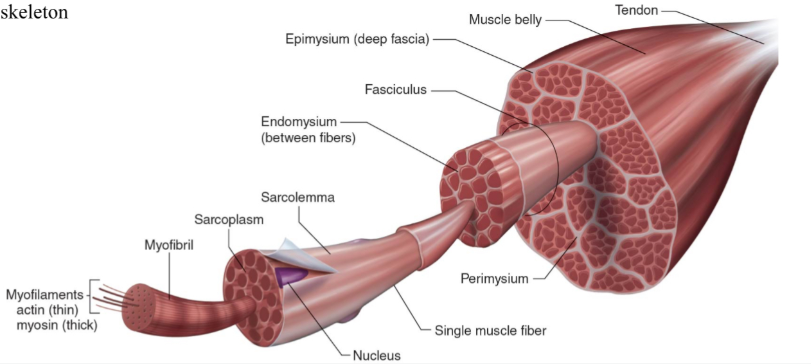
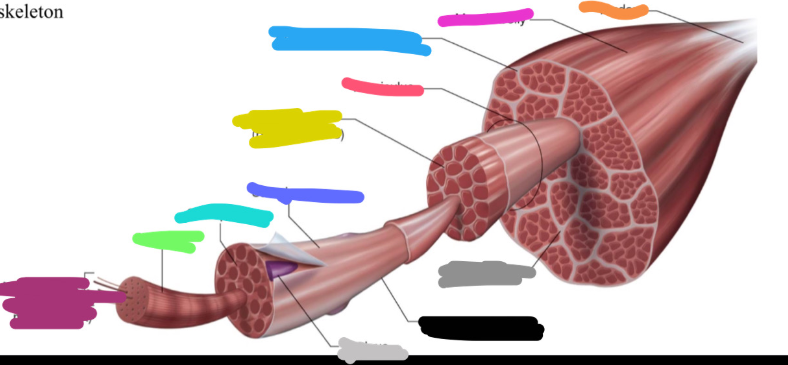
What is the dark grey mark labeled on the skeletal muscle called? Is it a covering or bundles?
Perimysium
COVERING
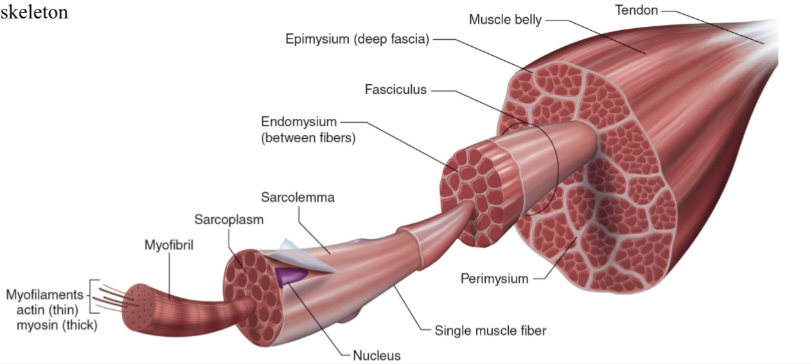
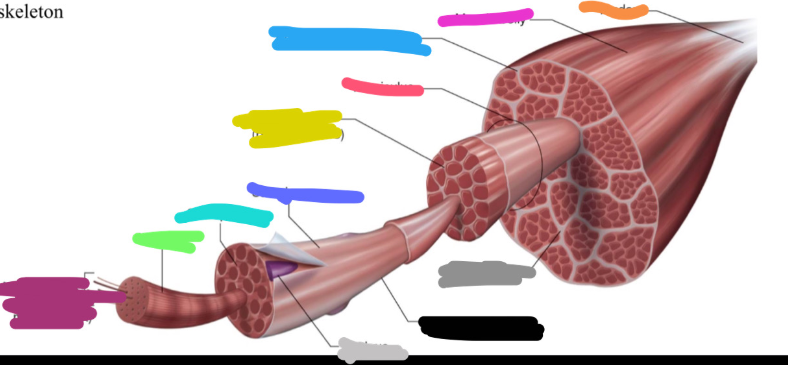
What is the yucky yellow mark labeled on the skeletal muscle called? Is it a covering or bundles?
Endomysium
- COVERING
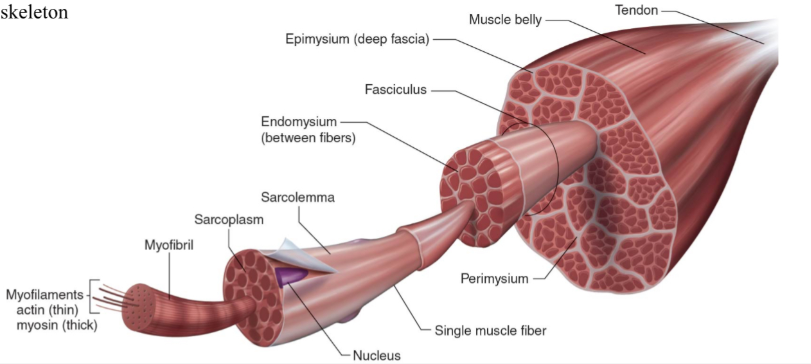
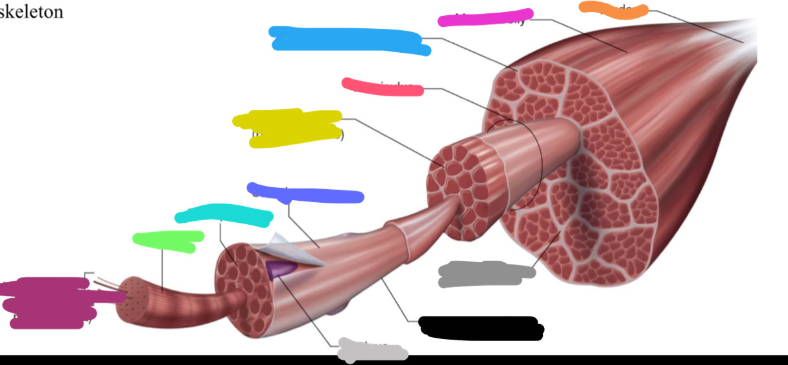
What is the ketchup red mark labeled on the skeletal muscle called? Is it a covering or bundles?
Fasciculus (fuh-sick-U-lus)
BUNDLES
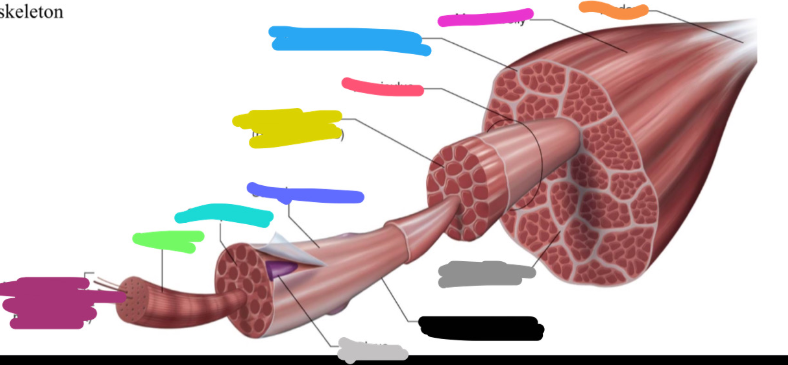
What is the sky blue mark labeled on the skeletal muscle called? Is it a covering or bundles?
Epimysium (deep fascia)
COVERING
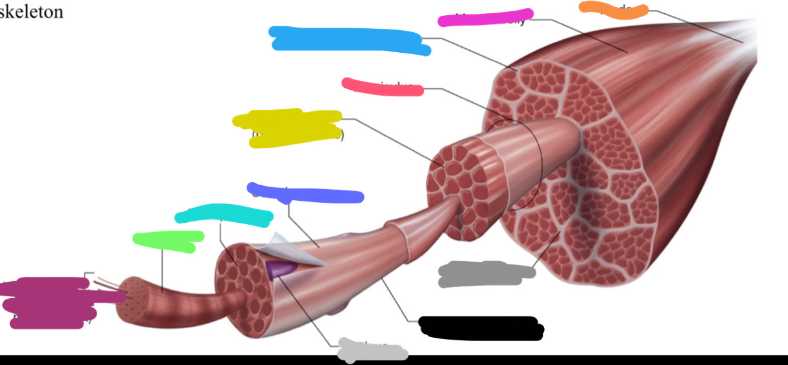
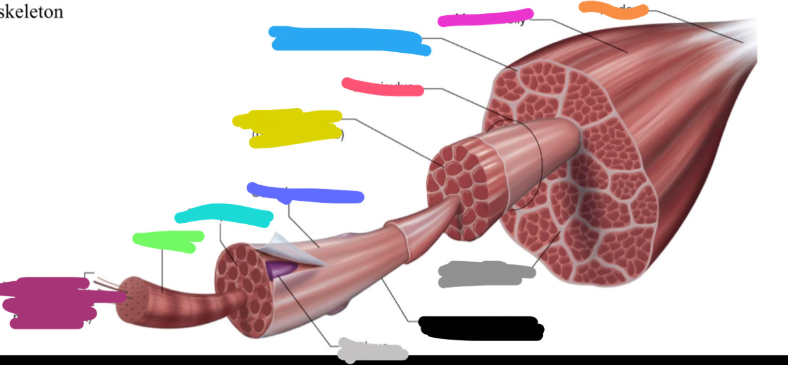
What is the fuchsia pink mark labeled on the skeletal muscle called? Is it a covering or bundles?
Muscle belly
BUNDLES
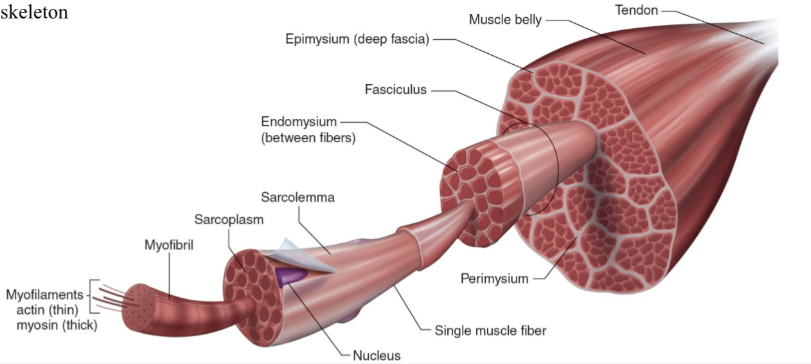
What is the orange mark labeled on the skeletal muscle called?
Tendon
Action potential travels in what order
Sarcolemma
Sarcoplasm
Transverse tubules (T tubules)
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)
Know the steps of an action potential and how it travels from the NMJ to actin and myosin filaments and the steps of a contraction (Excitation coupling contraction steps)
Name the first step of the EXCITATION STAGE of action potential
translate this: The discharge of an action potential from a motor nerve…..
Translation: This is the signal traveling down the motor neuron to the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). It’s the “go” signal that starts everything
Name the second step of the Excitation Stage - Contraction Coupling of action potential
translate this: Signals the release of calcium from the SR into the myofibril
Translation: Once the action potential spreads inside the muscle fiber, it triggers the SR to release calcium ions into the area around the myofibrils
Name the third step of the Excitation “Contraction” Stage of action potential
Translate this: Causing tension development in muscle
Translation: calcium binds to troponin, shifts tropomyosin, and allows actin and myosin to interact. This starts the cross-bridge cycle, which creates tension (force) in the muscle (causes contraction)
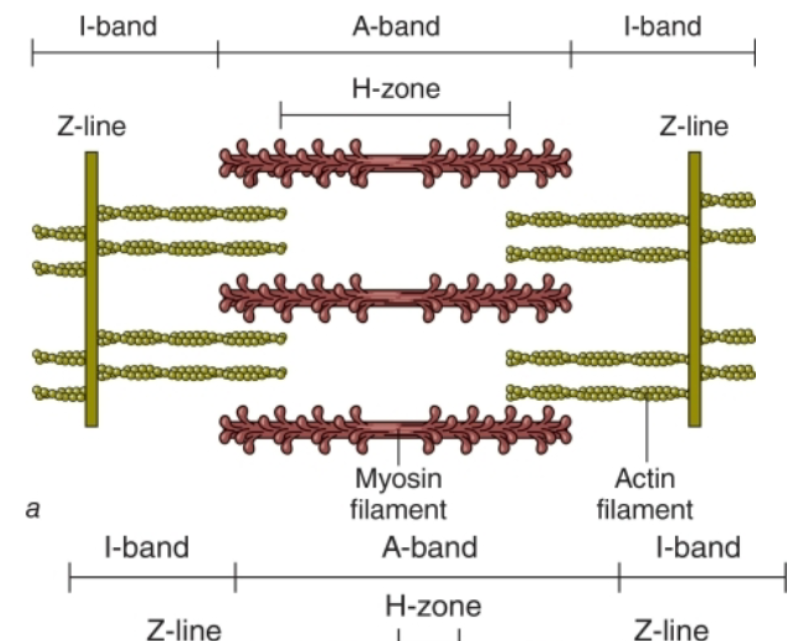
Explain the Sliding-Filament Theory of Muscular Contraction.
The actin filaments at each end of the sarcomere slide inward on myosin filaments, pulling the Z-lines toward the center of
the sarcomere and thus shortening the muscle fiber
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Depolarization of motor end plate(excitation) is coupled to muscular
Name the FOUR steps (not as much detail)
contraction
1. Action potential travels down transverse tubules and causes release of Ca++ from SR
2. Ca++ binds to troponin and causes position change in tropomyosin
• Exposing myosin binding sites on actin
Strong binding state formed between actin and myosin
Contraction occurs (i.e., power
stroke)
Excitation-Contraction Coupling
More detail (EXPLAIN THE 6 steps)!!
1. Depolarization of t-tubules causes release of Ca++ from
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR).
2. Ca++ binds to troponin, causing shift in tropomyosin to uncover
myosin binding sites on actin.
3. Myosin binds to actin to form cross-bridge.
4. Pi released from myosin and “power stroke” movement
occurs.
5. New ATP attaches to myosin, breaking the cross-bridge. Then
ATP is broken down to ADP+Pi, which energizes myosin.
6. Muscular contraction occurs by multiple cycles of cross-bridge
activity. Shortening will continue as long as energy is available
and Ca+2 is free to bind to troponin. Ca+2 and ATP are
required.
What is the importance of CA (calcium) & ATP for a muscle contraction?
Calcium & ATP are two essential requirements for skeletal muscle contractions
Calcium and ATP are necessary for crossbridge cycling with actin and myosin filaments
What dictates the force production of a muscle?
The number of cross bridges that are formed between actin and myosin at any instant in time dictates the force production of a muscle
Define Hypertrophy
slide definition:
Muscular enlargement (size) from an increase in the cross-sectional area of the existing fibers
Easier definition:
An increase in muscle fiber SIZE
Define Hyperplasia
Slide definition:
Results in an increase in the number of muscle fibers via longitudinal fiber splitting
Easier defintion:
An increase in the NUMBER of muscle fibers
What is the difference between muscle hypertrophy & muscle hyperplasia?
Muscle Hypertrophy: Growth in muscle SIZE due to an increase in the SIZE existing muscle fibers
Muscle Hyperplasia: Growth in muscle size due to an increase in the number of muscle fibers
Mechanical loading/ deformation stimulates the ________ pathway to increase muscle synthesis
Atk/mTOR
muscle synthesis: the process your body uses to build new muscle proteins inside muscle fibers
Resistance training down regulates ______ activity, which inhibits growth factors.
inhibiting the inhibitor allows growth
inhibits: slow down, block, or prevent growth
Myostatin activity
Which of the following will result in an increase in skeletal muscle growth?
A) Decrease in Atk/mTOR and increase in Myostatin activity
B) Decrease in Atk/mTOR and decrease in Myostatin activity
C) Increase in Atk/mTOR and decrease in Myostatin activity
D) Increase in Atk/mTOR and increase in Myostatin activity
C) Increase in Atk/mTOR and decrease in Myostatin activity
Which of the following will result in an decrease in skeletal muscle growth?
A) Decrease in Atk/mTOR and increase in Myostatin activity
B) Decrease in Atk/mTOR and decrease in Myostatin activity
C) Increase in Atk/mTOR and decrease in Myostatin activity
D) Increase in Atk/mTOR and increase in Myostatin activity
A) Decrease in Atk/mTOR and increase in Myostatin activity
What is the angle of pennation?
The angle of pennation
How does it’s affects a muscles ability to produce force?
Resistance training increases the angle of pennation
The angle of pennation influenced force production; greater angles can lead to a higher force generation by allowing more fibers to be packed into a muscle
How does it change with training in a pennated muscle?
How does the activity in the cell signaling pathways change with muscle growth?
What are the basic differences of the muscle fiber types?
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the motor neuron size
Options: small and large
Type I (motor neuron size):
Small
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the motor neuron size
Options: small and large
Type IIa (motor neuron size):
Large
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the motor neuron size
Options: small and large
Type IIx (motor neuron size):
Large
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the recruitment threshold
Options: High, low, or intermediate/High
Type I (recruitment threshold):
Low
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the recruitment threshold
Options: High, low, or intermediate/High
Type IIa (recruitment threshold):
Intermediate/High
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the recruitment threshold
Options: High, low, or intermediate/High
HIGH
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Nerve Conduction Velocity
Options: fast, fast, slow
SLOW
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the Nerve Conduction Velocity
Options: fast, fast, slow
FAST
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the Nerve Conduction Velocity
Options: fast, fast, slow
FAST
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Contraction Speed
Options: fast, fast, slow
SLOW
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the Contraction Speed
Options: fast, fast, slow
FAST
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the Contraction Speed
Options: fast, fast, slow
FAST
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Relaxation Speed
Options: fast, fast, slow
SLOW
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the Relaxation Speed
Options: fast, fast, slow
FAST
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the Relaxation Speed
Options: fast, fast, slow
FAST
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Fatigue resistance
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/Low
HIGH
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the Fatigue resistance
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/Low
Intermediate/LOW
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the Fatigue resistance
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/Low
LOW
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Endurance
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/Low
HIGH
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the Endurance
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/Low
Intermediate/Low
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the Endurance
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/Low
LOW
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Force Production
Options: Low, high, Intermediate
LOW
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the Force Production
Options: Low, high, Intermediate
Intermediate
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the Force Production
Options: Low, high, Intermediate
High
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Power output
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/high
LOW
Characteristics:
For Type IIa what is the Power output
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/high
intermediate/high
Characteristics:
For Type IIx what is the Power output
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/high
HIGH
Characteristics:
For Type I what is the Aerobic enzyme content
Options: Low, high, Intermediate/low
HIGH