4- Alkenes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is E and Z isomerism?
E = priority group (highest atomic number) on diagonal side
Z = Priority group (highest atomic number) on same side
Compare either side of the double bond highest atomic number to find the priority group
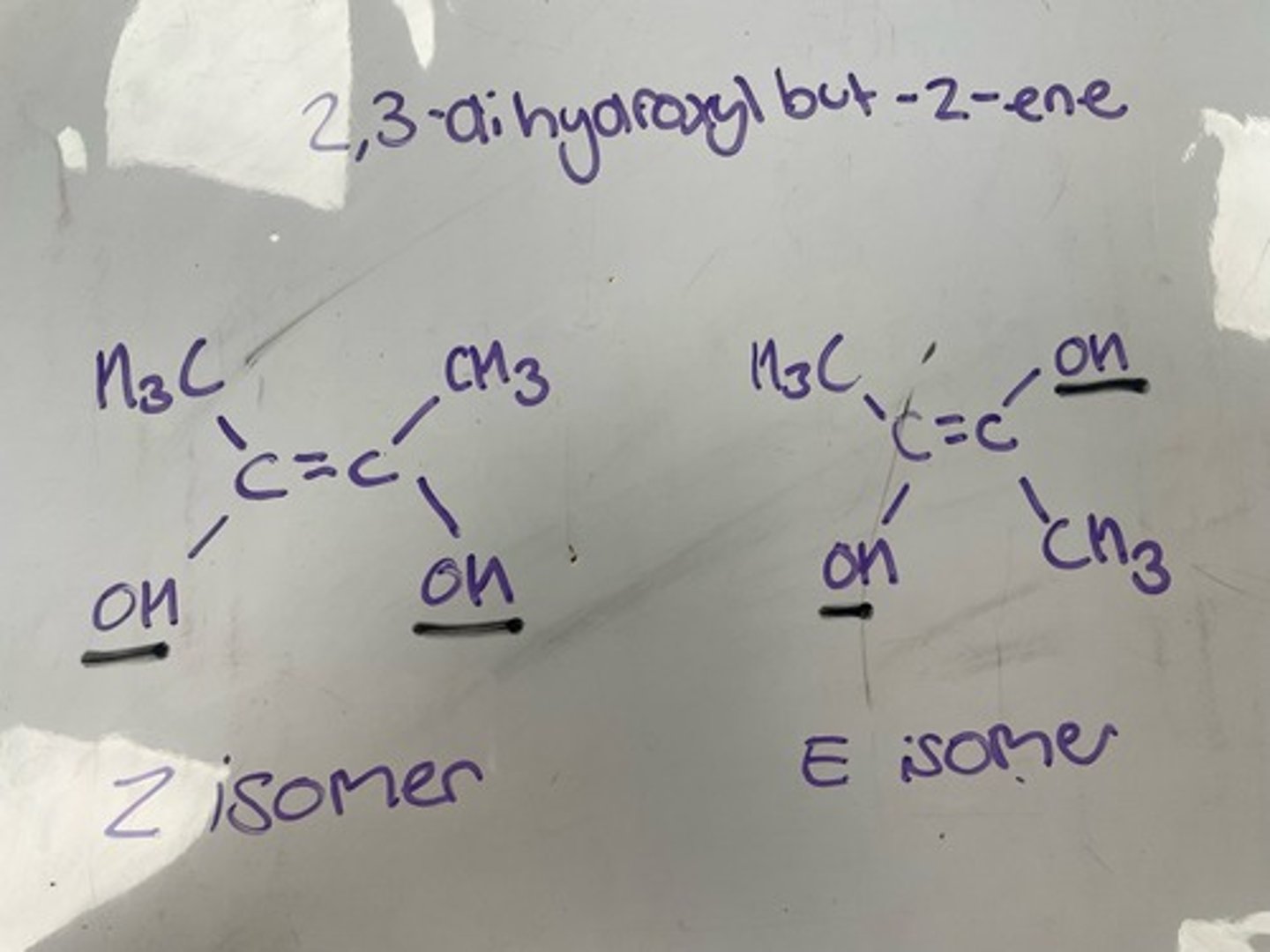
But-2-ene E and Z isomerism
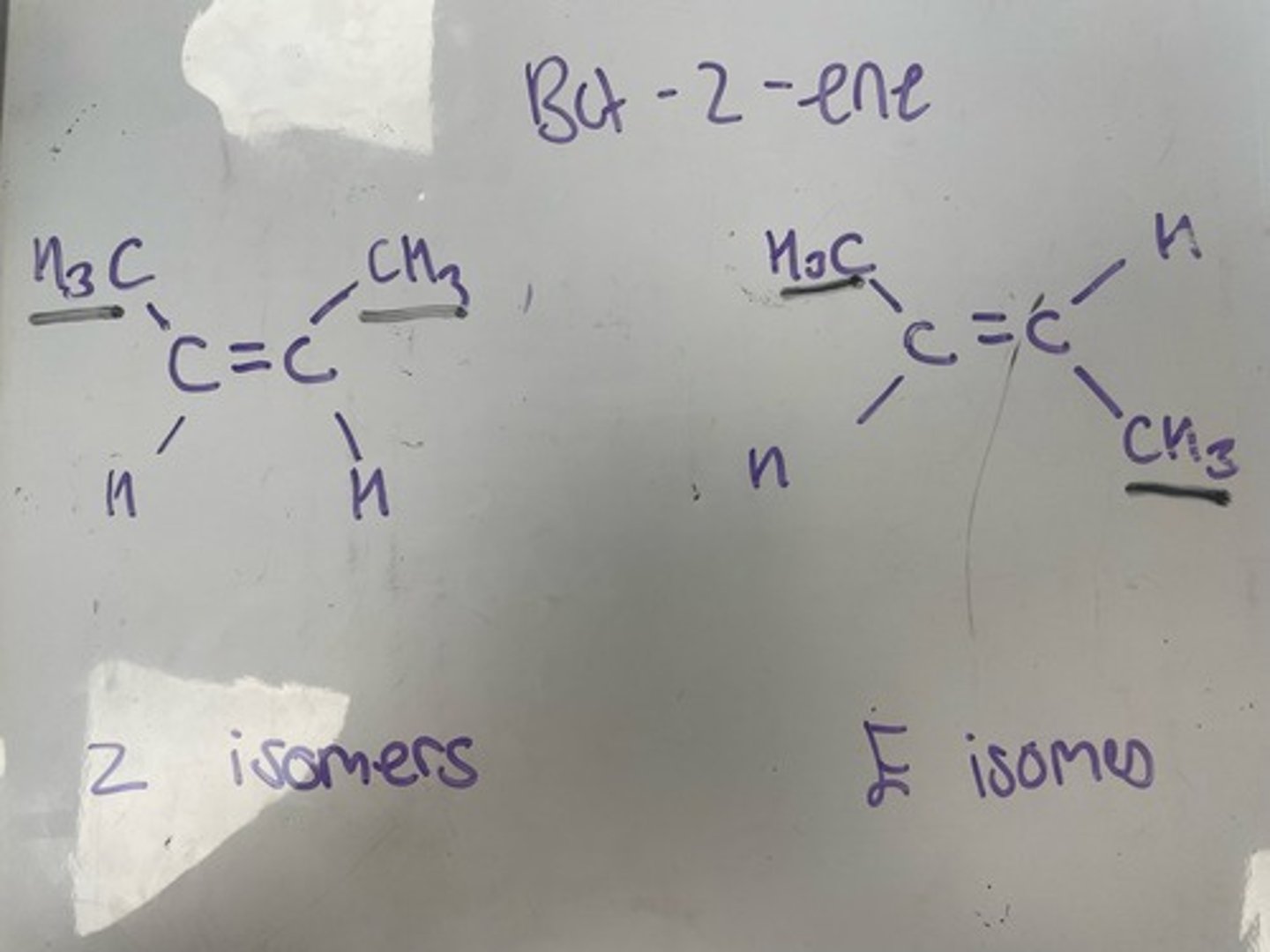
1,2-dibromo-1iodoethene E and Z isomerism
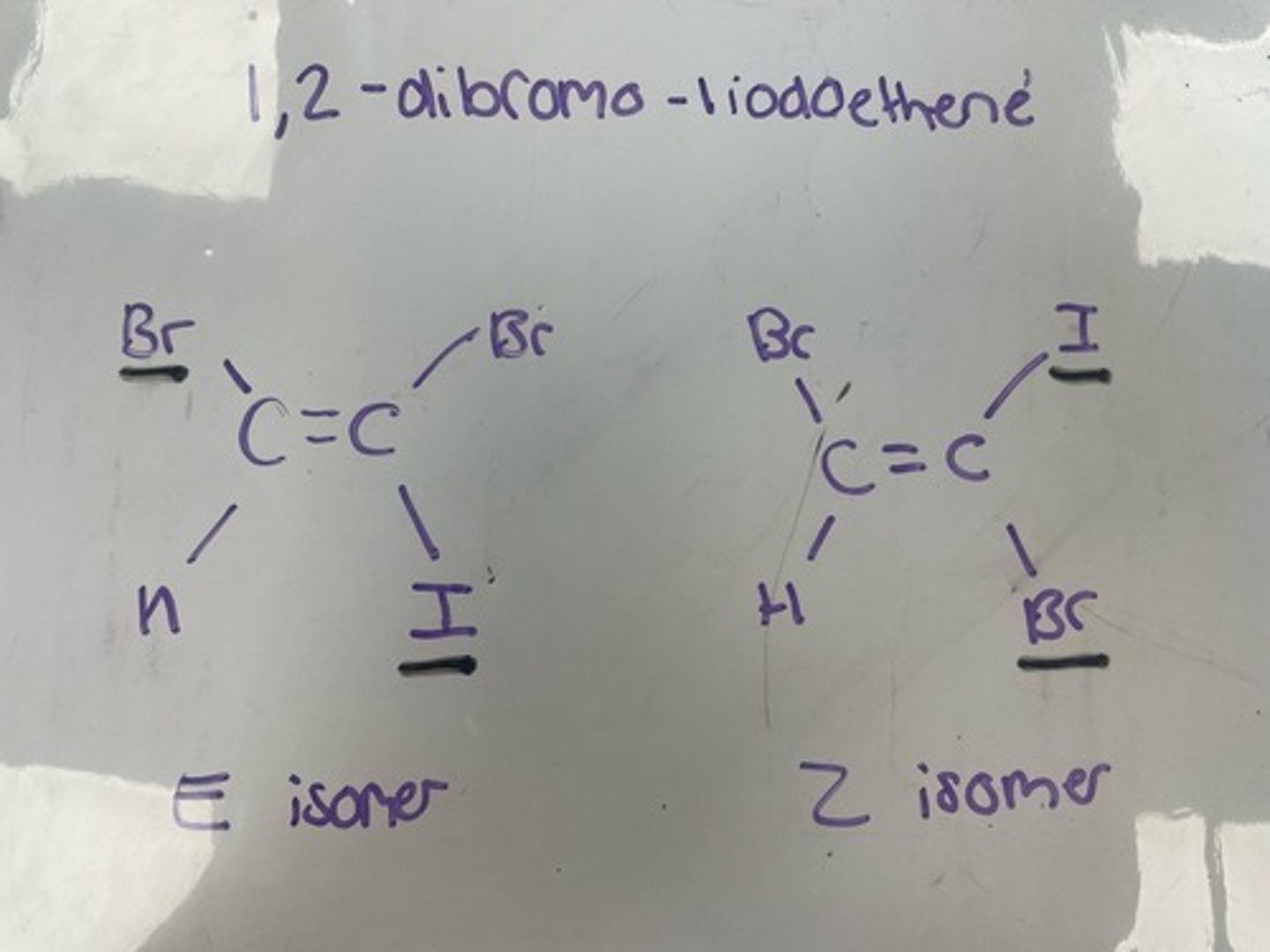
2,3-dihydroxylbut-2-ene E and Z isomerism
Draw the structure of (Z)-pent-3-en-2-ol
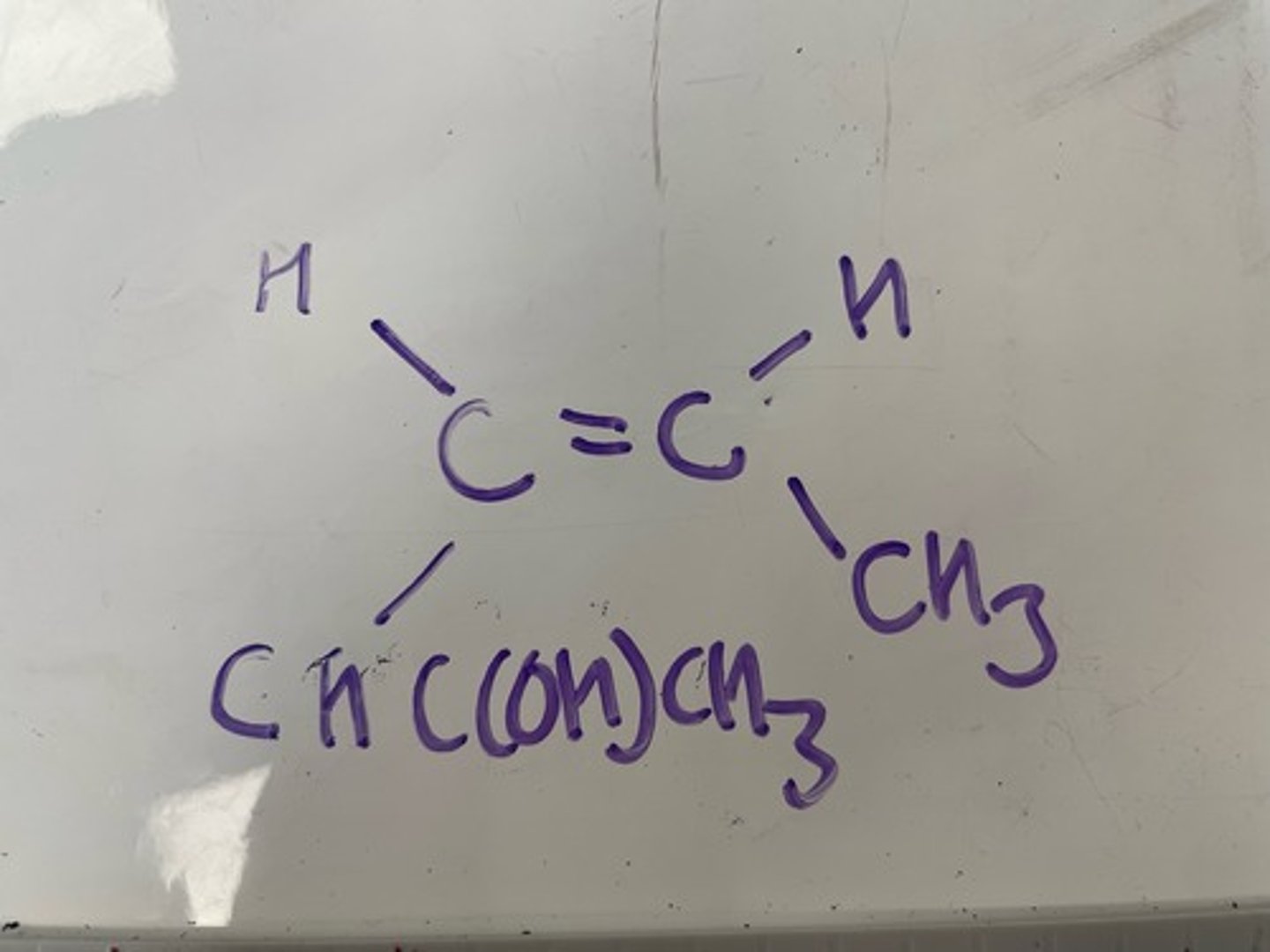
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes?
Double bond has high electron density, easily attacked by electrophiles
Alkene shape
Trigonal planar, 120 degrees
There is no rotation about the double bond
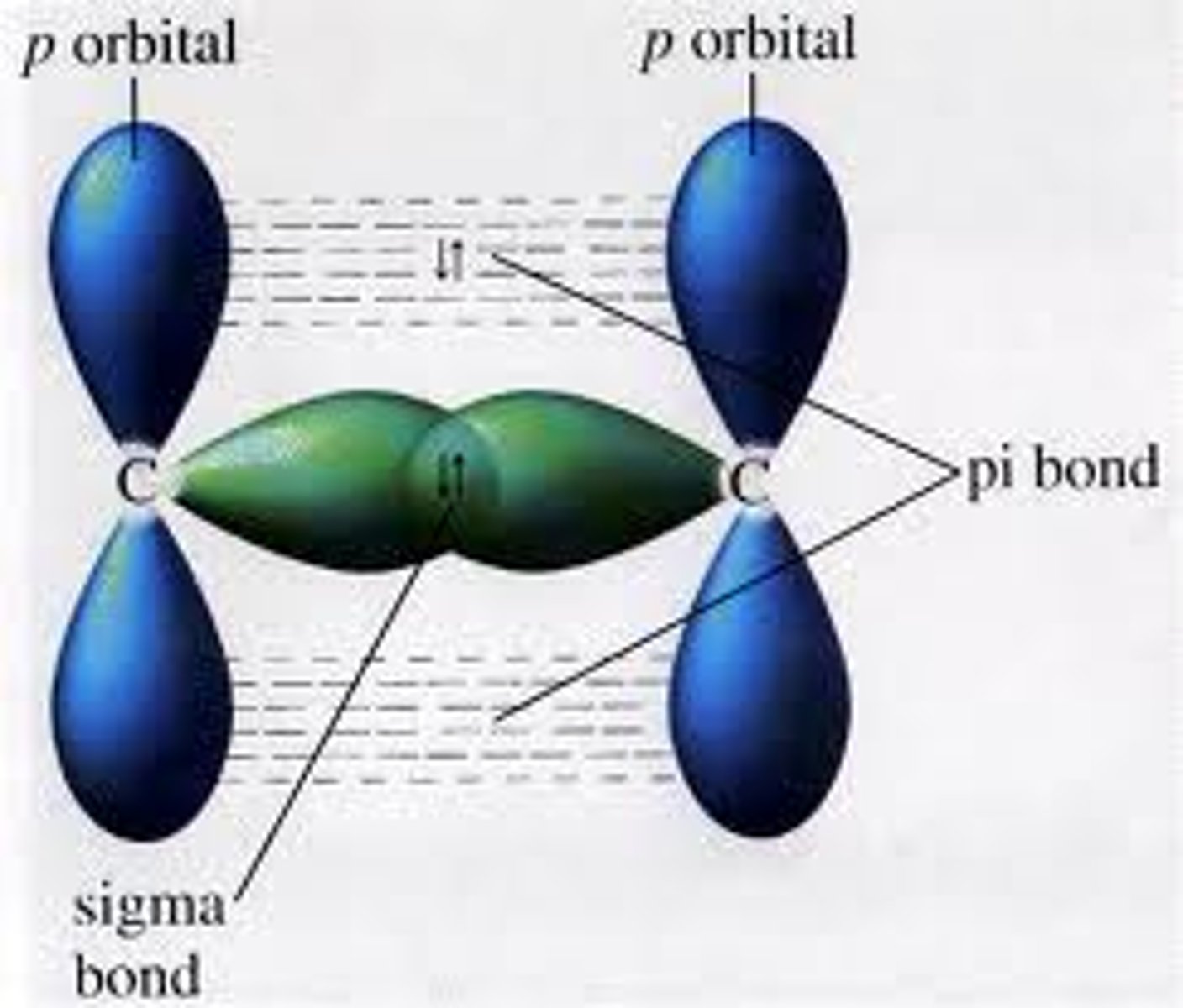
Explain why there is no rotation about the double bond in alkenes
As well as a normal C-C bond, alkenes have a P-orbital (contains single electron) on each carbon. The two orbitals overlap to form a pi orbital.
Pi orbital makes rotation impossible
What is meant by addition polymerisation?
Method of alkenes joining together, double bonds are removed
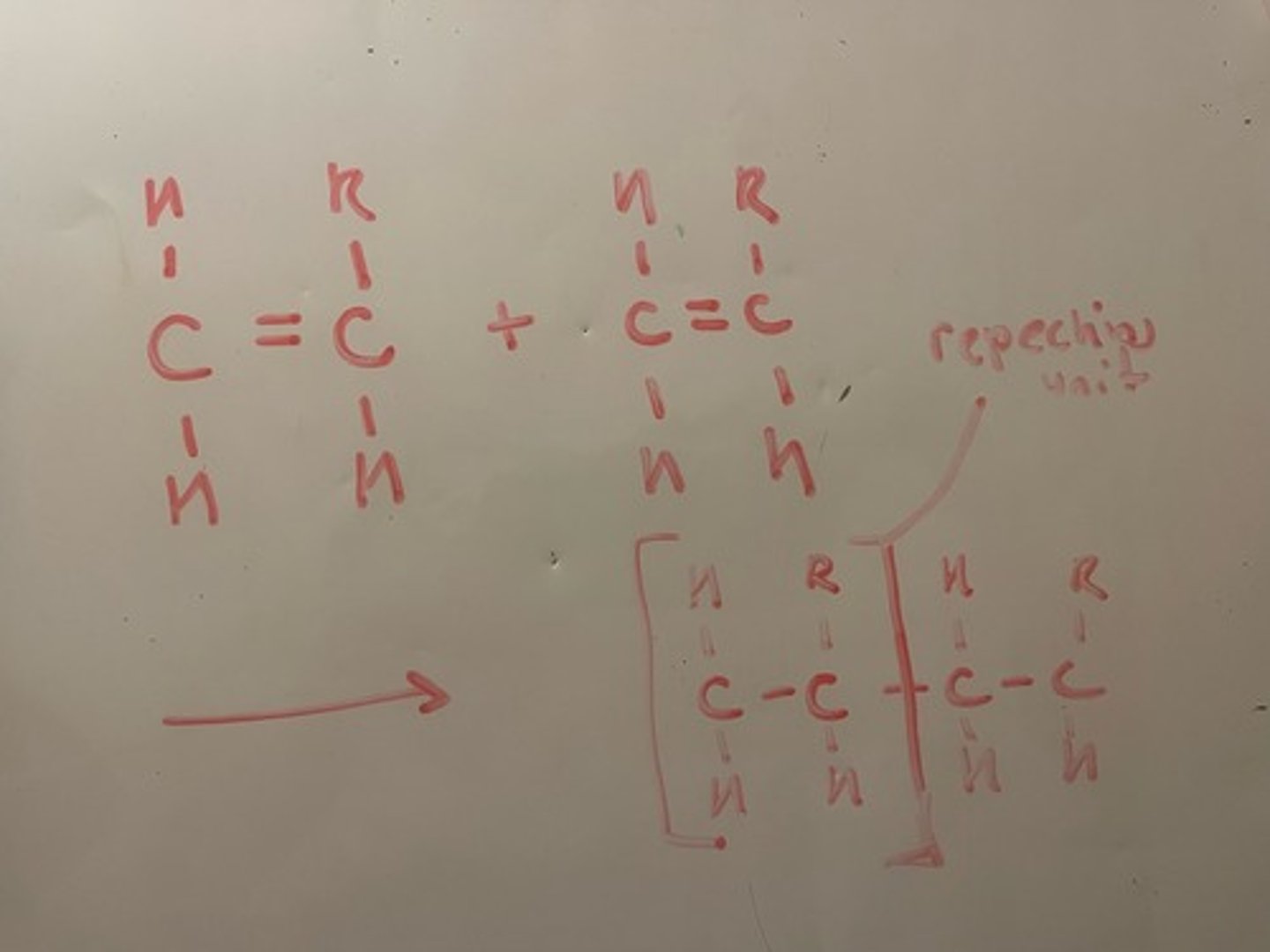
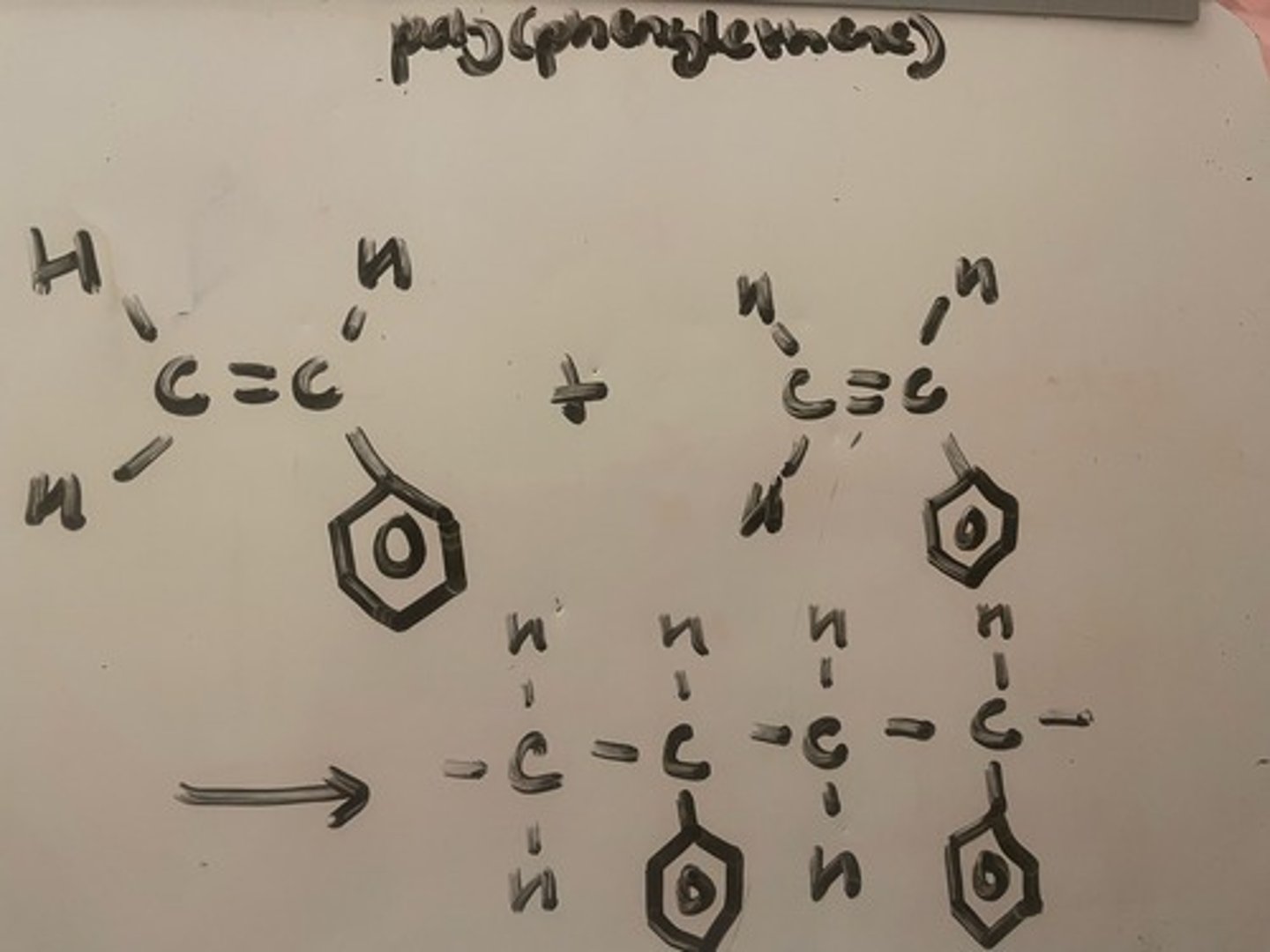
Addition polymerisation of poly(phenylethene). Name the monomer
Remove the poly ---> phenylethene
How and why are plastics modified?
Use of additives such as plasticisers, these are small molecules that get between the polymer chains and force them apart. The chains are now able to slide across each other and become flexible
Name the monomer of this polymer
But-2-ene. We know the double bond is at C2 due to the position of the C-C bond
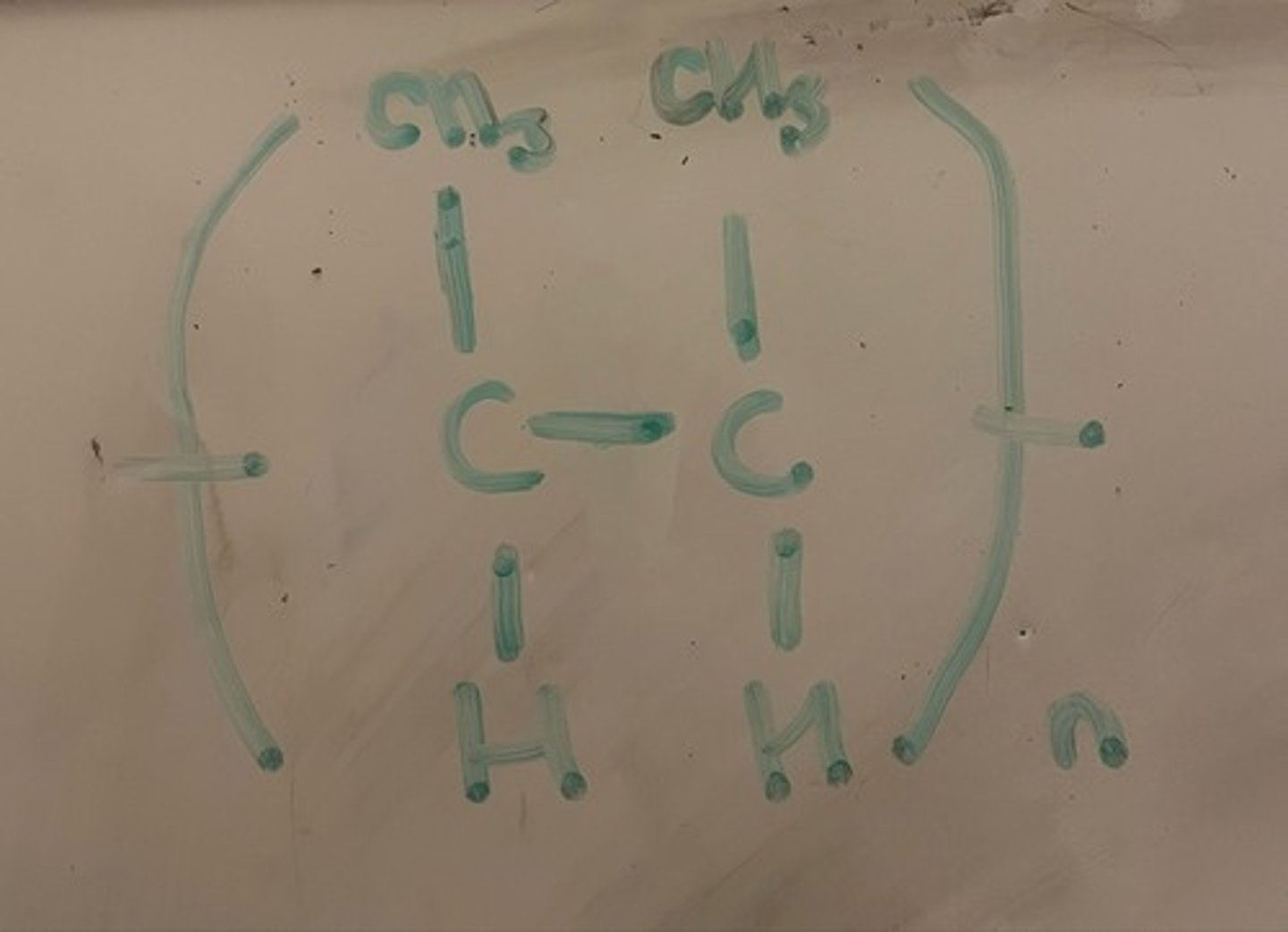
Why are alkenes not biodegradable?
Alkane backbone consists of strong non polar C-C and C-H bonds, so they are very unreactive molecules. They are hence not attacked by biological agents
Solutions to pollution by plastics
-Mechanical recycling: separate different types of plastics, wash plastics and grind down into small pellets. Pellets can be melted/remoulded
Pellets from PET (plastic bottles) used to make fleece clothes
DIASDV: energy to melt plastics, not all can be recycled
Feedstock recycling: heat plastics to high temps so that polymer bond breaks and coverts into monomers. These can be used to make new plastics
DISADV: continuous reheating polymers can only be done a limited number of times as some of the chains break and become shorter thus degrading plastics properties
HDPE vs LDPE
High density polyethene:
-Temps and conditions slightly greater than room
-Ziegler Natta catalyst
Results in a polymer with less chain branching, chains pack together well hence the density and mp of the polymers is higher
Used in buckets/crates
Low density polyethene:
-High temperatures and pressures
-Free radical mechanism
Results in polymer with some branching (due to random nature of free radical)
Branches do not pack well together, product is flexible. Uses involve packaging/insulation of electrical cables
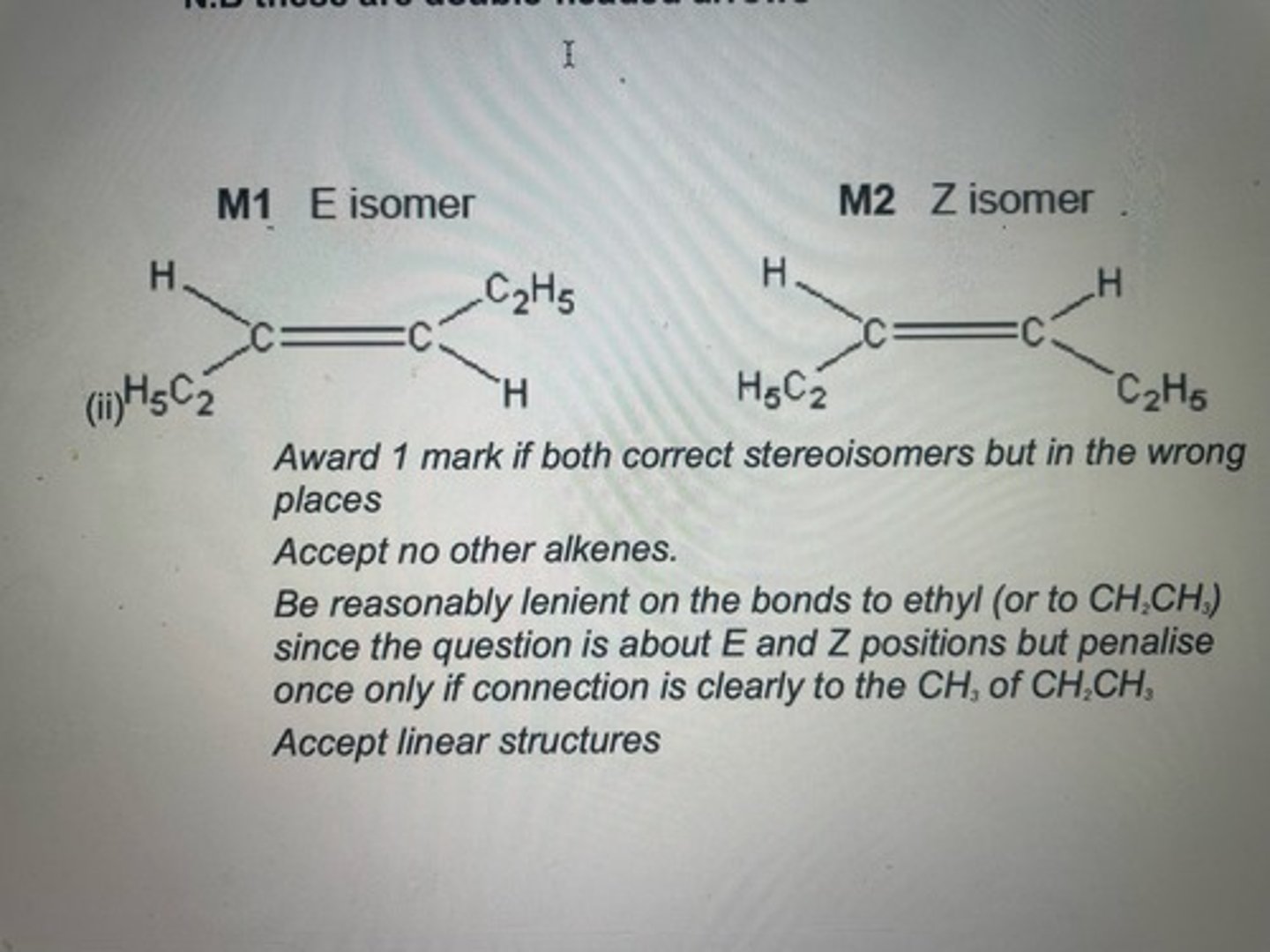
Draw structures for the E and Z stereoisomers of hex-3-ene
Draw poly(but2-ene)
Type of reaction that converts ethanol into ethene
Dehydration
Give a reagent and observation that would enable you to distinguish between butan-2-ol and 2-methyl-propan-2-ol, the reagent should be added separately
Reagant = potassium dichromate
Observation for butan-2-ol= Orange to green
Observation for 2-methyl-propan-2-ol = remains orange
Draw the structure of the alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O that is resistant to oxidation by acidified potassium dichromate(VI)
In terms of the intermolecular forces between the polymer chains, explain why polyamides can be made into fibres suitable for use in sewing and weaving, whereas polyalkenes usually produce fibres that are too weak for this purpose. (3)
In polyamides there is hydrogen bonding, whereas in polyalkenes there is only van de Waals forces
Hydrogen bonds are stronger forces than van de Waals
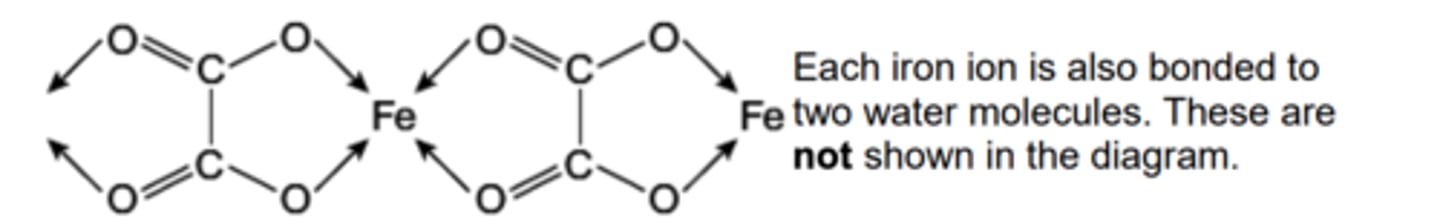
Solid iron(II) ethanedioate dihydrate (FeC2O4.2H2O) has a polymeric structure. Two repeating units in the polymer chain are shown
a) name the type of bond represented by the arrows
b) In terms of electrons explain how the water molecules, not shown in the diagram, form bonds to the iron.
c) Predict the value of the bond angle between the two bonds to iron that are formed by these two water molecules
a) co-ordinate bonding
b) lone pair from oxygen bonds to Fe
c) 180
Poly(propene) is not biodegradable because it is unreactive. Explain why poly(propene) is unreactive
No polar bonds