Reaction of 2,4-DNPH and melting point analysis
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What kind of reaction does 2,4-DNPH undergo with carbonyl compounds?
Condensation reaction
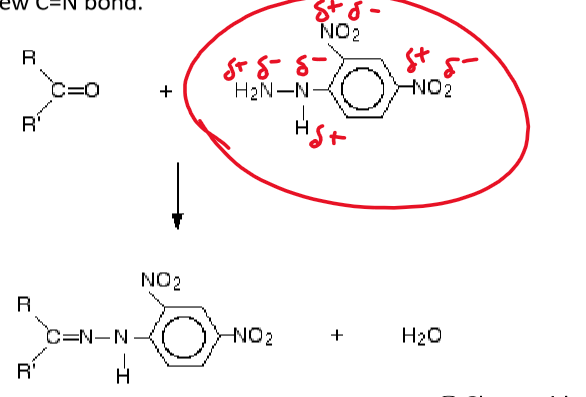
the C=O functional group on the carbonyl and the NH2 group on the hydrazine produce water and a new C=N bond
new product is known as a hydrazone and precipitates out as a solid
solid is yellow / orange if the carbonyl is aliphatic but more orange / red if the carbonyl is aromatic (contains a benzene ring) - result of extended conjugation
Method:

Account for any difference between measured and data book melting point
Significantly lower melting point + larger range - very impure e.g. still contained water
What is the benefit of doing vacuum filtration (as opposed to gravity filtration)?
faster
removes more water/ solvent therefore drier
What can you do if the hydrazone product is impure?
can be purified further by recrystallisation

Why must the minimum amount of hot solvent be used?
to get a saturated solution - so that crystals form when cooled down
Why should cold solvent be used in the rinsing stage?
to make sure the solvent can’t dissolve the crystals (but can wash off soluble impurities)
Ethanol is chosen as a solvent here. Explain why.
‘Universal solvent’ - dissolves both polar and non-polar substances
When measuring the melting point, what would indicate whether the derivative was pure?
Melts over a narrow range (1-2 degrees Celsius)
Which impurities (soluble or insoluble) are removed during the cooling and filtering stage?
soluble impurities (insoluble impurities already removed in step 2).