Physiology of the Kidneys: Exam 5
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
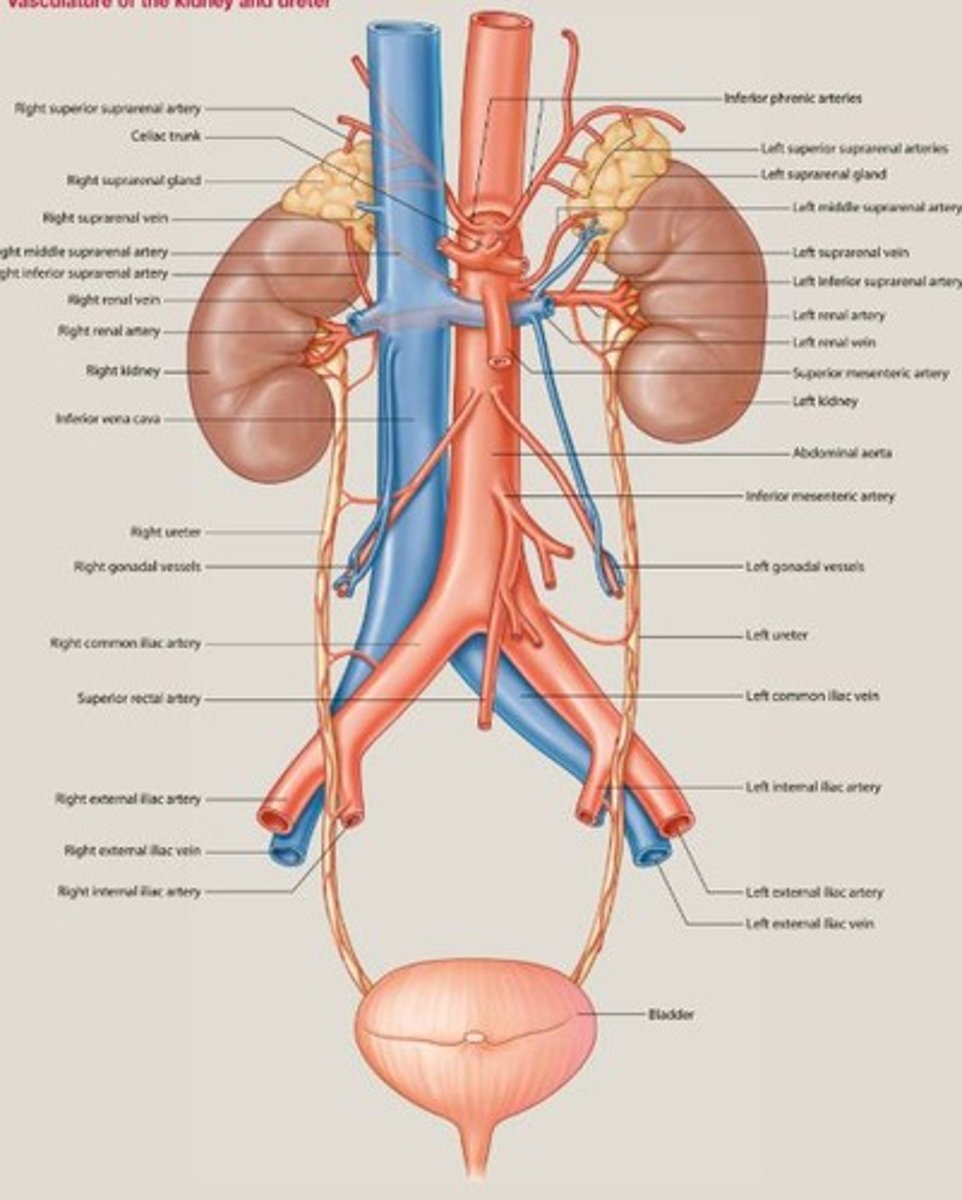
Vein draining blood from the kidneys.
Renal Vein
Smooth muscle area aiding ureter opening identification.
Trigone
Major vein returning blood to the heart.
Inferior Vena Cava
Capillaries involved in blood filtration.
Glomerular Capillaries
Structure surrounding glomerulus for filtration.
Bowman's Capsule
Functional unit of the kidney for filtration.
Nephron
What is GFR and what is the normal rate?
Glomerular Filtration Rate, 120 ml/min average.
Reabsorbs 60-70% of filtrate volume.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Section of nephron concentrating urine.
Loop of Henle
Final segment for electrolyte reabsorption.
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Water channels regulating urine concentration located on the collecting ducts.
Aquaporin
Cells preventing protein filtration in kidneys that make up the Visceral Layer of Bowman’s Capsule.
Podocytes
Brings blood to the glomerulus.
Afferent Arteriole
Carries blood away from the glomerulus.
Efferent Arteriole
Process enhancing urine concentration in kidneys(happens in the loop of henle).
Counter Current Mechanism
Cells regulating blood pressure and filtration by dilating or contracting the smooth muscle on the arterioles.
Juxtaglomerular Cells
Cells located in the Distal convoluted tubule that sense sodium concentration in filtrate and signal the juxtaglomerular cells. They also sense low BP and release Renin to activate Aldosterone.
Macula Densa
Enzyme regulating blood pressure via angiotensin.
Renin
Hormone increasing sodium re-absorption in kidneys mostly in the distal convoluted tubules.
Aldosterone
Urine with low pH, often due to UTI.
Acidic Urine
Process of separating waste from blood.
Filtration
Process returning substances from filtrate to blood.
Reabsorption
Process moving waste from blood to filtrate.
Secretion
The urethra is shorter in ____ making it more prone to bacteria remaining and causing an UTI
Females
The urethra is longer in ____ but passes through the prostate gland that can become swollen in 50+ years and pinch the urethra messing up urine retention.
Males
What cells is the urinary bladder made of?
Transitional epithelium→Stratified cuboidal epi.
Describe the Juxtaglomerular apparatus system:
Macula Densa: Signal the arterioles to contract or dilate the smooth muscle through the juxtaglomerular cells to control BP in the arterioles. →Inside the DCT
Messengial Cells: Relay the signal from the macula densa cells to the juxtaglomerular cells on the smooth muscle.
→ Floating on the outer parts.
Juxtaglomerular Cells: Carry out the constriction or dilation. → Smooth muscle on arterioles
How much do the kidneys filter out per min(GFR) and per day:
GFR: 120 ml/min and 180 L/day
Every day how much should humans pee out?
0.5-2.5 L/day
When your kidneys reabsorb water and dissolved substances (like salts) together in a balanced way, the fluid concentration doesn’t change.
Isotonic reabsorption
Which of the following segments of the nephron reabsorb mostly water, about 80% of HCO3- ions and 100% of the glucose and amino acids in filtrate?
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
How does the Proximal Convoluted Tubules reabsorb water and electrolytes?
special pumps called Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase pumps on the basal side of the cells actively push sodium (Na⁺) out of the cell into the blood. This creates a low sodium level inside the cell, so sodium from the tubule (urine side) naturally flows into the cell to balance it out. As sodium flows in, it brings glucose and amino acids with it through special transport proteins (called co-transporters). Water follows by osmosis, moving through the cells or between them to keep balance.
How does the Proximal Convoluted Tubules reabsorb HCO3- ?
it reacts with H⁺ in the tubule to form CO₂ and H₂O, which can easily enter the cell. Inside the cell, they turn back into HCO₃⁻, which is then transported into the blood.
How does the Loop of Henle reabsorb water and electrolytes?
In the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle, there are Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase pumps on the basal side that actively move sodium out of the cell into the blood, keeping sodium levels low inside the cell. This allows sodium, potassium (K⁺), and chloride (Cl⁻) to be reabsorbed from the tubule into the cell through special transporters (like the NKCC transporter) on the tubule side. This part of the loop is impermeable to water, so only salt is reabsorbed here.
In contrast, the thin descending limb has no active pumps, it just passively allows water to leave the tubule because it's very permeable to water but not to salts. This helps concentrate the fluid inside the tubule as it moves down.
How does the Distal Convoluted Tubules reabsorb them?
the Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase pumps on the basal side keep pumping sodium out of the cell into the blood, making sodium flow in from the tubule. Here, sodium reabsorption continues, and calcium (Ca²⁺) is also reabsorbed under the influence of hormones like parathyroid hormone (PTH).
How does the Collecting ducts reabsorb them?
Water reabsorption is controlled by the hormone ADH (antidiuretic hormone). ADH tells the cells to add special water channels called aquaporins to their walls, allowing water to flow out of the tubule and back into the bloodstream.
Which nephron segment is the only one that can change the volume of urine?
Collecting Ducts because they only handle water retention changing the concentration or diluting the urine