1.04 Medical Sciences
1/333
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
334 Terms
what are the 3 main stages of atherosclerosis formation?
1) endothelial damage
2) uptake of LDLs and macrophage adhesion
3) smooth muscle proliferation to form fibrous cap
what causes endothelial damage?
- shear stress (increased by hypertension)
- toxic damage (cigarette smoke)
- exposure to high concs of LDLs
- glycosylation of proteins
how are LDLs and macrophages taken up? (4)
- LDLs enter the artery wall through damaged endothelium
- LDL gets modified by oxidation
- this causes endothelial cells to attract inflammatory cells
- monocytes cross endothelium and become macrophages
what do the macrophages do? (3)
- phagocytose modified LDLs unrestrictedly
- accumulated in large droplets called foam cells
- lipids released from foam cells and accumulate in subendothelial space
how does smooth muscle proliferation occur? (3)
- damaged endothelial cells release growth factors
- growth factors cause proliferation of smooth muscles cells and collagen which cover the plaque
- increases the size and forms a fibrous cap
what happens in plaque rupturing? (2)
- the fibrous cap can fissure, erode or rupture, exposing the lipid core
- triggers coagulation cascade
- blood clot is formed
what could happen to the thrombus?
- could completely occlude artery (lead to death)
- could embolise (small parts break off) and block off smaller distal arterial branches
what are the two types of risk factors for atherosclerosis?
- non-modifiable
- modifiable
what are some non-modifiable risk factors? (4)
- age
- gender
- family history
- race
what are some modifiable risk factors? (6)
- lipid intake
- smoking
- hypertension
- diabetes mellitus
- obesity
- lack of exercise
what can happen as a response to an occlusion of an artery?
reactive hyperaemia
what is reactive hyperaemia?
tissue ischaemia causes vasodilation, to try and increase the blood flow to the area
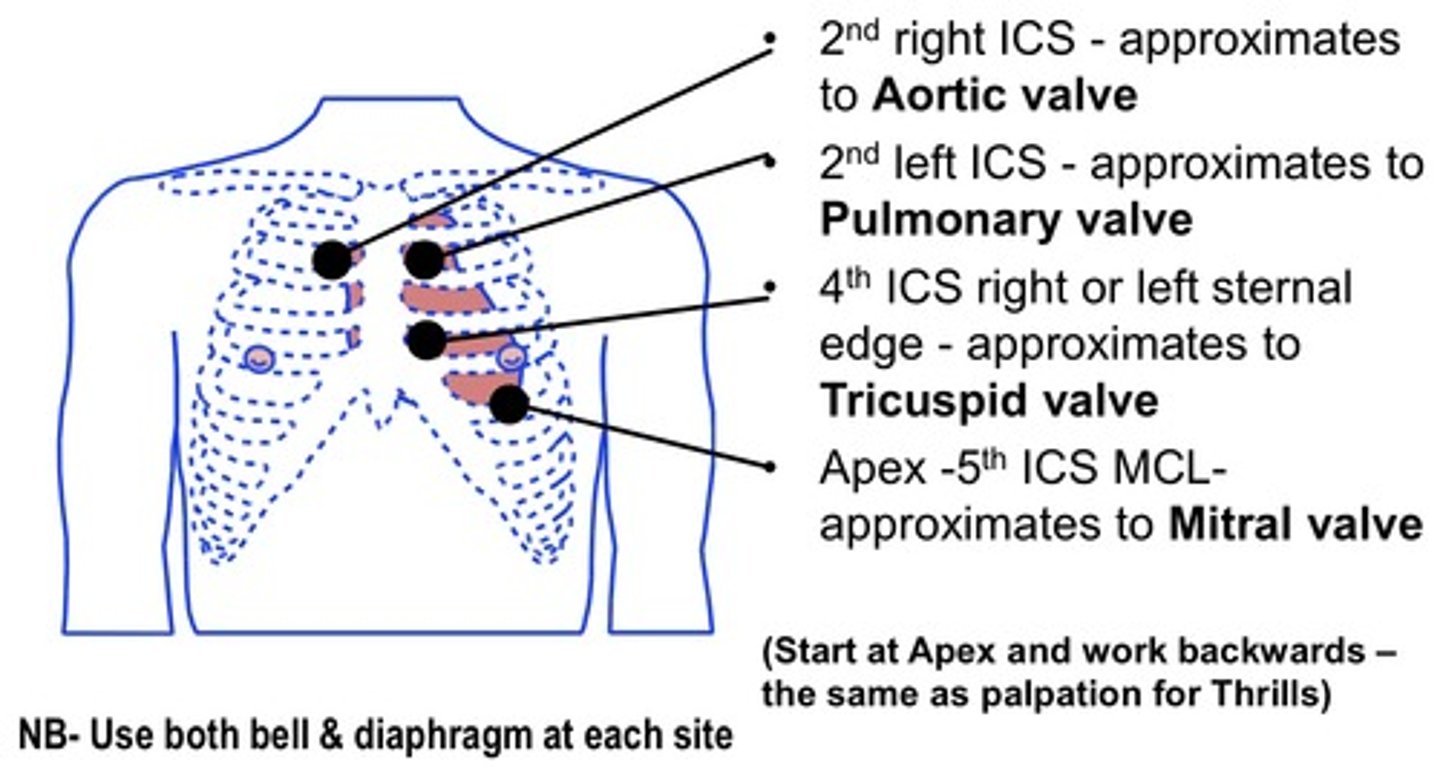
where can you auscultate the aortic valve?
2nd intercostal space - right of sternum
where can you auscultate the pulmonary valve?
2nd intercostal space - left of sternum
where can you auscultate the tricuspid valve?
4th intercostal space - on the right or left of sternum
where can you auscultate the mitral valve?
5th intercostal space - left midclavicular line
draw a diagram of the different auscultation sites of the heart
what is the first heart sound (S1)?
lub
what causes the lub sound?
closing of av valves
where can you hear the lub sound the best?
same as mitral valve:
- 5th intercostal space - left midlavicular line
what is the second heart sound (S2)?
dub
what causes the dub sound?
closing of the semilunar valves
where can you hear the dub sound the best?
same as pulmonary valve:
- 2nd intercostal space - left of sternum
where is erb's point?
third left intercostal space mid clavicular
what is the point of erb's point?
aortic regurgitation can be heard as a murmur here
what causes a positive deflection in an ecg?
depolarisation towards lead OR repolarisation away from lead
what causes a negative deflection in an ecg?
repolarisation towards the lead OR depolarisation away from lead
what does a normal ecg look like?
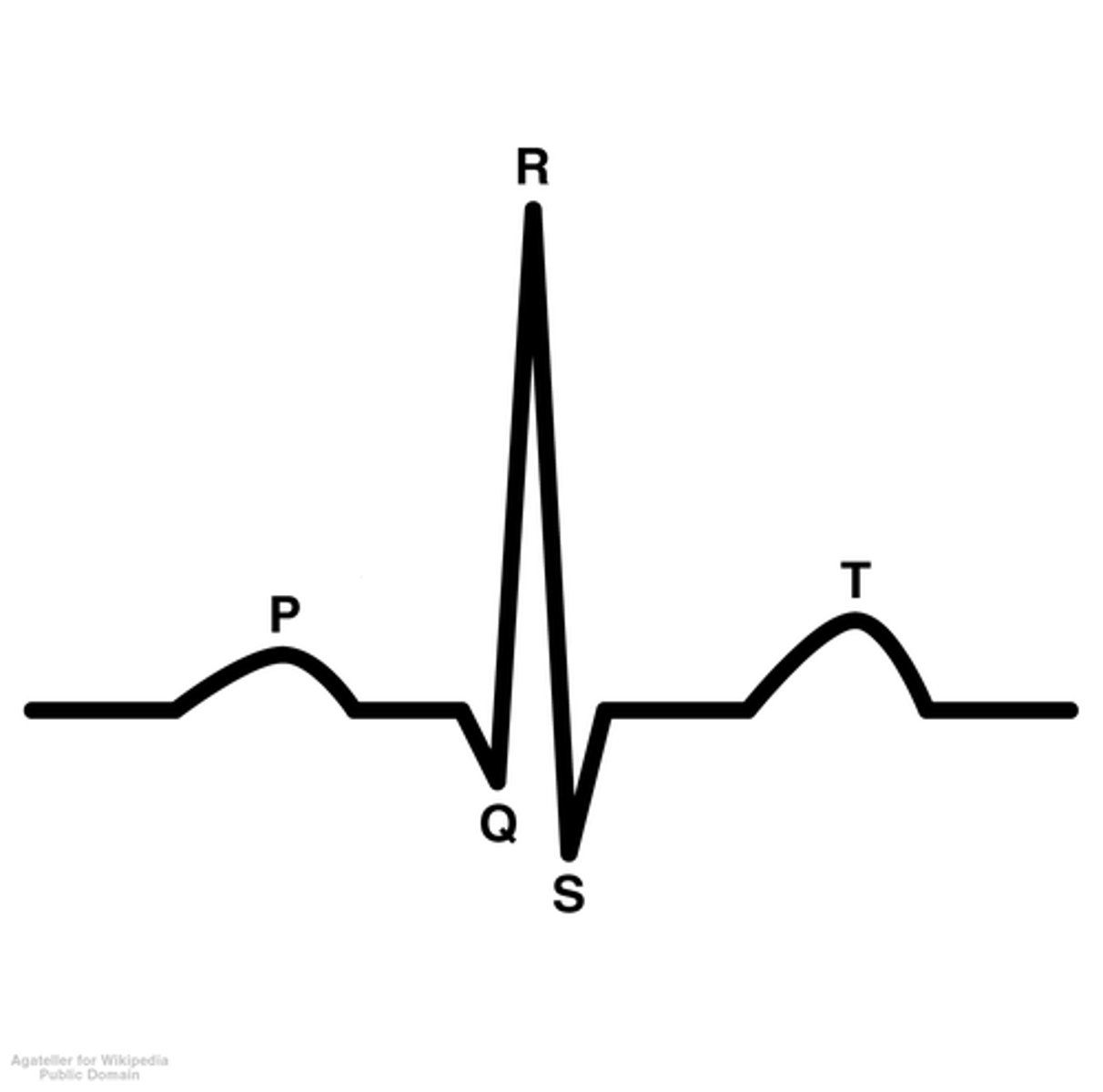
what causes the p wave?
atrial depolarisation
why does atrial depolarisation form a positive deflection?
depolarisation of atria towards the lead
what causes the flat line between the p wave and qrs complex?
the artioventricular septum temporarily blocking the depolarisation
what causes the qrs complex?
ventricular depolarisation
why does ventricular depolarisation have 3 parts?
1st part - depolarisation of interventricular septum - bundle of his
2nd part - depolarisation at apex
3rd part - depolarisation moving up lateral walls
what does the qrs complex hide?
atrial repolarisation
what causes the t wave?
ventricular repolarisation
why does ventricular repolarisation form a positive deflection?
repolarisation away from lead
what are the electrodes surrounding the heart called?
pre-cordial
how many pre-cordial electrodes are there?
6
where do you place v1?
4th intercostal space to the right of the sternum
where do you place v2?
4th intercostal space to the left of the sternum
where do you place v4?
5th intercostal space - midclavicular line
where do you place v3?
between v2 and v4
where do you place v6?
5th intercostal space - midaxillary
where do you place v5?
5th intercostal space - between v4 and v6 - anterior axillary line
where do you place the other 4 leads?
- right arm
- left arm
- right leg
- left leg
what is the lead going to the right arm called?
aVR
what does aVR stand for?
augmented vector/voltage right arm
what is the lead going to the left arm called?
aVL
what does aVL stand for?
augmented vector/voltage left arm
what is the lead going to the left leg called?
aVF
what does aVF stand for?
augmented vector/voltage foot
which lead is the ground lead?
right leg
what forms the 3 other views of the heart?
communication between:
- right arm and left arm (lead I)
- left leg and right arm (lead II)
- left arm and left leg (lead III)
(like a triangle)
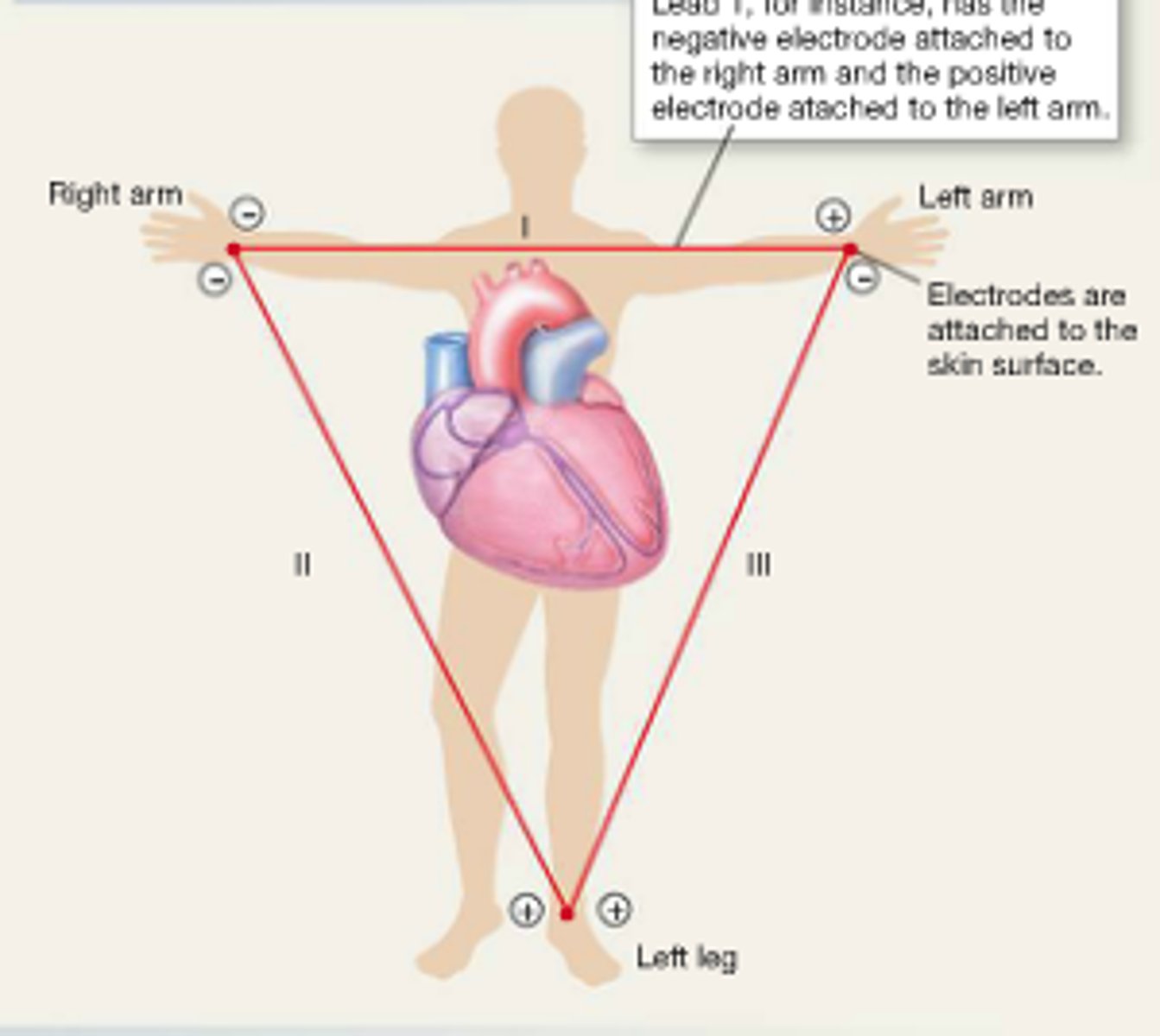
which are the bipolar leads?
leads I, II and III
which leads are inferior?
II, III, aVF
what do the inferior leads detect?
inferior border of heart - receiving blood from right coronary artery
which leads are lateral?
I, aVL, V5, V6
what do the lateral leads detect?
lateral wall - receiving blood from left circumflex artery
which leads are septal?
V1, V2
what do the septal leads detect?
along the anterior interventricular septum - receiving blood from left anterior descending/anterior interventricular artery
which leads are anterior?
V3, V4
what do the anterior leads detect?
along anterior wall of heart - receiving blood from the left anterior descending/anterior interventricular artery
which leads would lead to an anterolateral MI?
II, aVL, V3, V4, V5, V6
which vessel would II, aVL, V3-6 detect?
left coronary artery - LCA
what are the 6 layers of the heart?
- endocardium
- myocardium
- epidcardium/visceral layer of serous pericardium
- pericardial cavity
- parietal layer of serous pericardium
- fibrous pericardium
what is the endocardium also called?
tunica intima
what does the endocardium line?
atria, ventricles and valves
what is the endocardium made up of?
simple squamous epithelium
what is another name for the myocardium?
tunica media
what does the myocardium contain?
cardiac muscle fibres and endomysial connective tissue with capillaries
what is another name for the epicardium?
tuncia adventitia/visceral layer of the serous pericardium
what does the epicardium consist of?
simple squamous mesothelium
what does the parietal layer of serous pericardium consist of?
simple squamous mesothelium
what does the fibrous layer of pericardium consist of?
connective tissue
what is the fibrous layer of the pericardium continuous with?
central tendon of the diaphragm
what is the pathway of conductivity in the heart? (5)
- sinoatrial node
- atrioventricular node
- His bundle
- either right or left bundles
- Purkinje fibres
what is the effect of parasympathetic innervation of SA node? (3)
- acetylcholine acts of M2 muscarinic receptors at SA node
- lengthens the interval between pacemaker potentials
- slows heart rate
which nerve delivers the parasympathetic innervation of the heart?
vagus nerve (CNX)
what is the effect of sympathetic innervation of the SA node? (3)
- noradrenaline acts on B1 adrenoceptors
- shortens interval between pacemaker potentials by making it steeper
- increases heart rate
which nerve supplies sympathetic innervation to the heart?
sympathetic cardiac nerves
what is the intrinsic heart rate without autonomic inputs?
100bpm
what is the actual normal resting rate and why?
60bpm - parasympathetic system dominates at rest
what is initial increase in heart rate caused by?
decrease in parasympathetic outflow
what is further increase in heart rate caused by?
increase in sympathetic outflow
what are the 3 types of blood vessels?
- arteries
- veins
- capillaries
what are the 4 types of arteries?
- large elastic (conducting) arteries
- medium muscular (distributing) arteries
- arterioles
- metarterioles
what are the 3 layers of large and medium arteries?
- tunica intima
- tunica media
- tunica adventitia
what are the 3 components of the tunica intima?
- endothelium
- subendothelium
- internal elastic lamina
what are the 3 components of the tunica media?
- myocytes
- elastin
- collagen
what lies in between the tunica media and tunica adventitia?
external elastic lamina
what are the 3 components of the tunica adventitia?
- fibres
- fibroblasts
- vasa vasorum (neurovascular bundle)
which layers do arterioles not have?
- internal elastic lamina
- external elastic lamina
how is smooth muscle arranged in metarterioles?
rings called precapillary sphincters
what are the 2 layers of capillaries?
- endothelium
- basement membrane
what are 3 types of capillaries?
- continuous
- fenestrated
- sinusoidal
where are continuous capillaries found? (2)
muscles and skin
what can pass through continuous capillaries? (2)
- water
- some ions
where are fenestrated capillaries found? (2)
kidneys and small intestine
what can pass through fenestrated capillaries?
slightly larger molecules
where are sinusoid capillaries found? (3)
spleen, liver and bone marrow