Ultrasound physics ch 9
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
shape of a sound beam is based on
-single disc-shaped
-unfocused PZT crystal
-operating in a CW mode
sound beam width changes as
it travels
-progressively narrows until it reaches its smallest diameter, then begins to diverge
beam diameter initially=
PZT diameter
focus also called
focus point
Focus/point
location where sound beam reaches its minimum diameter
-beam most narrow
Focus=
1/2 width of beam at origin
near zone also called
fresnel zone
near zone
space or region between transducer and focus
focal length also called
-focal depth
-near zone length
-fresnel zone
focal length
distance from transducer face to focus
far zone also called
far field or Fraunhofer zone
far zone
region beyond near field
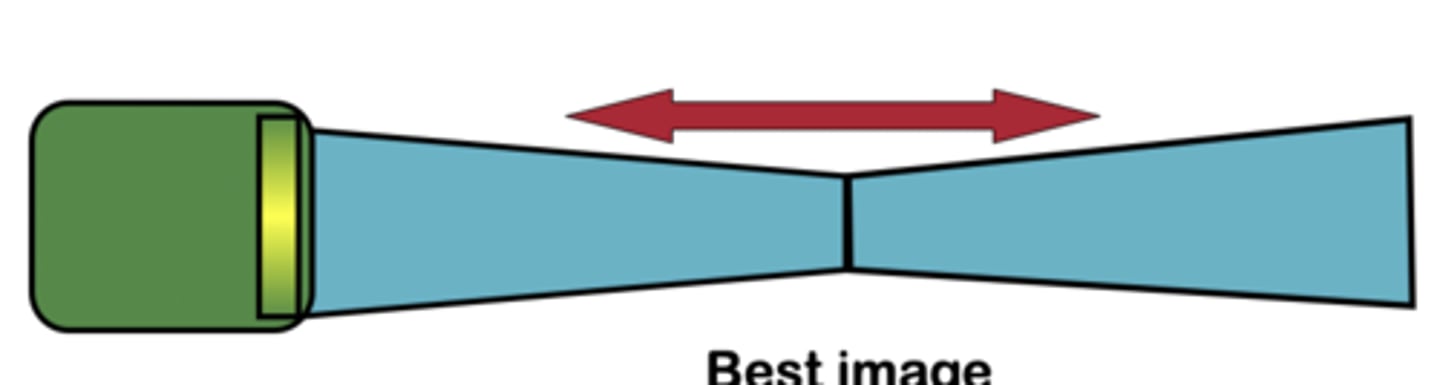
focal zone
area around focus
-1/2 in near field, 1/2 in far field
-best image quality
beam diameter is 1/2 transducer diameter at ________
focus
at 2 near zone lengths, beam diameter is equal to
transducer diameter
Focal depth, or near zone length in a fixed focus transducer is determined by:
transducer diameter
F of US
adjustable focus systems
phased array
larger diameter=
longer focal length
Higher F=
longer focal depth or near zone length
F and depth have a ___________ relationship
direct
focus determined by
diameter and F
high F sound wave with a shallow focus can be achieved with
a small diameter
what probed would create a beam with the shallowest focus
smallest diameter and lowest F
F and focal depth relationship
direct
crystal diameter and focal depth relationship
direct
divergence
spread of sound wave in far field
divergence affected by
F and crystal diameter
larger diameter crystal improves
lateral resolution
smaller diameter crystals _________ more readily than large
diverge
relationship between diameter and divergence
inverse
F and divergence relationship
inverse
lesser divergence=
greater diameter, higher F
greater divergence=
smaller diameter, lower F
crystal diameter and divergence relationship
inverse
spherical waves each created a wallet with V-shape, also known as
-spherical waves
-diffraction patterns
-huygen's wavelets
Huygen's principal
Constructive and destructive interference of sound wavelets. Cumulative sound wave is shaped like an hourglass.
Which transducer will provide the longest near zone length?
greater diameter and higher F
Name the properties of a pulsed wave transducer that will provide the highest emitted sound wave frequency.
thin, fast prop speed of crystal
What happens when pressure is applied to a piezoelectric crystal?
emits electrical signal
Why does a coin shaped crystal create an hour glass sound beam?
Constructive and deconstructive interference (Huygen's)
A shorter focal length is associated with a _______f transducer and a _______crystal diameter.
Low, small
Active element diameter and beam divergence have this relationship:
inverse
The ceramic has a diameter of 9 mm. What is the beam diameter at the focus?
4.5mm
T/F The Fraunhofer zone is the only region of the sound beam where the beam diameter is greater than the PZT diameter.
true
relationship between wavelength and near zone length
inverse
Two transducers are identical except for their frequencies. One TRX is operating at 8MHz and the other 4 MHz. The focal zone will be longer for TRX :
8MHz
Focus/focal point
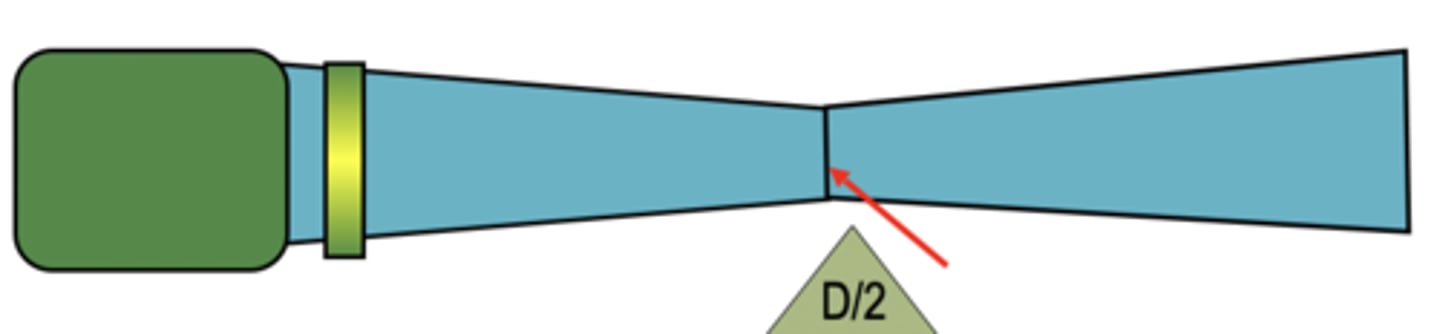
Near zone/nearfield/frensel zone
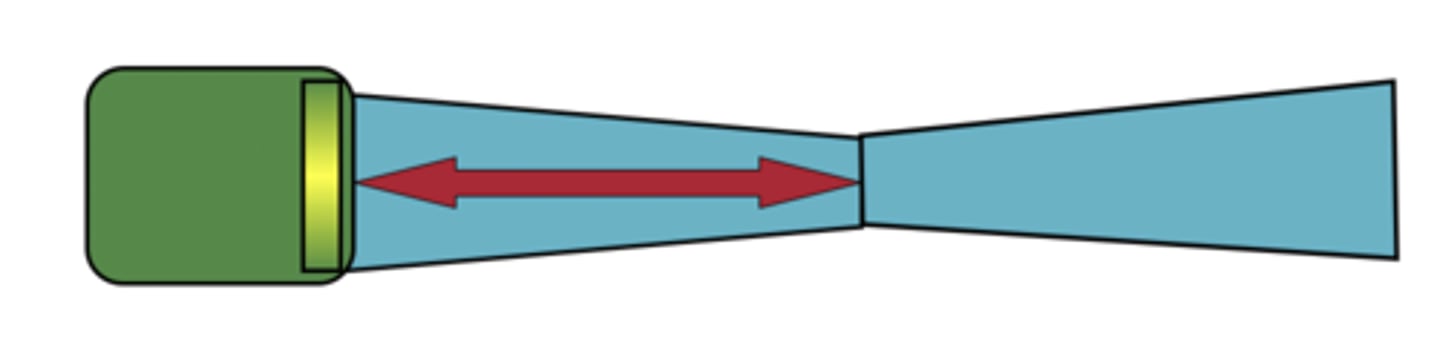
focal length/focal depth/near length
(distance)
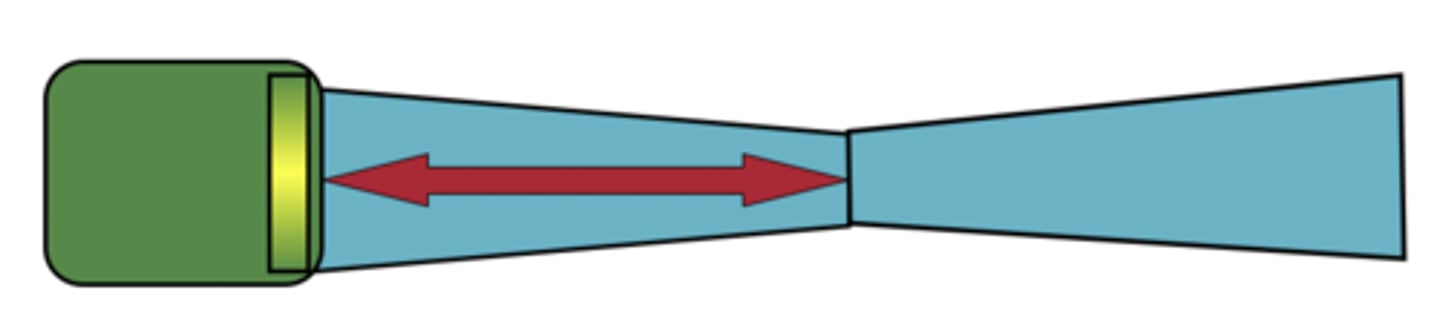
Far zone/far field/fraunhofer zone
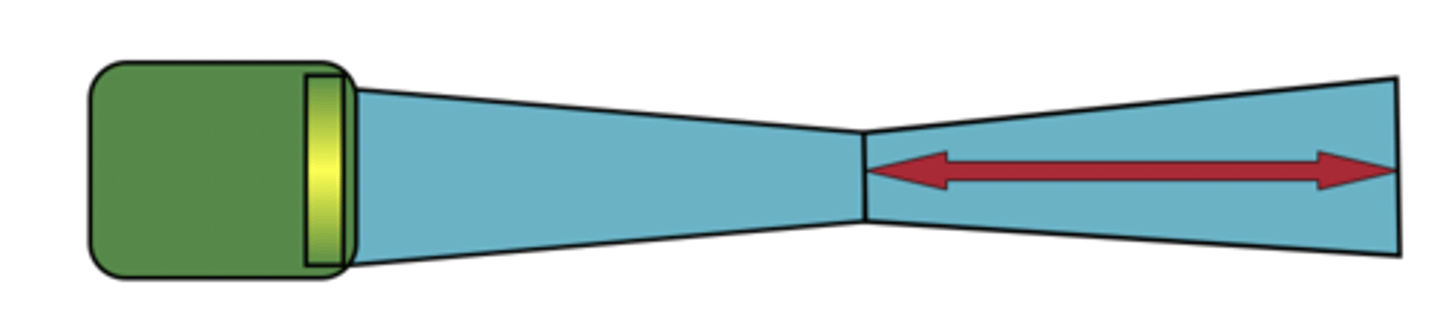
Focal zone
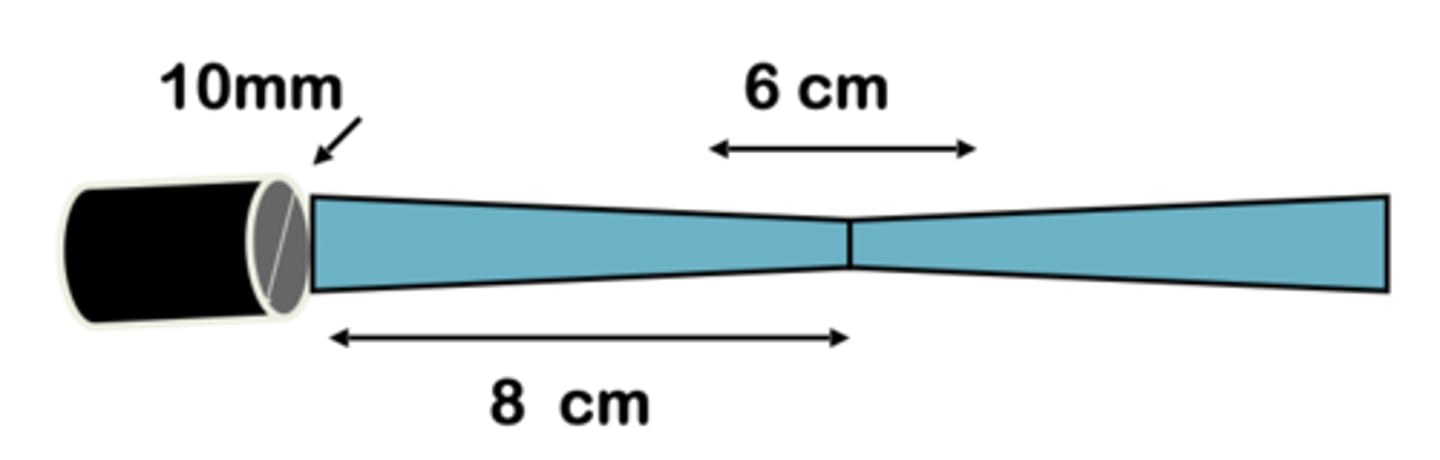
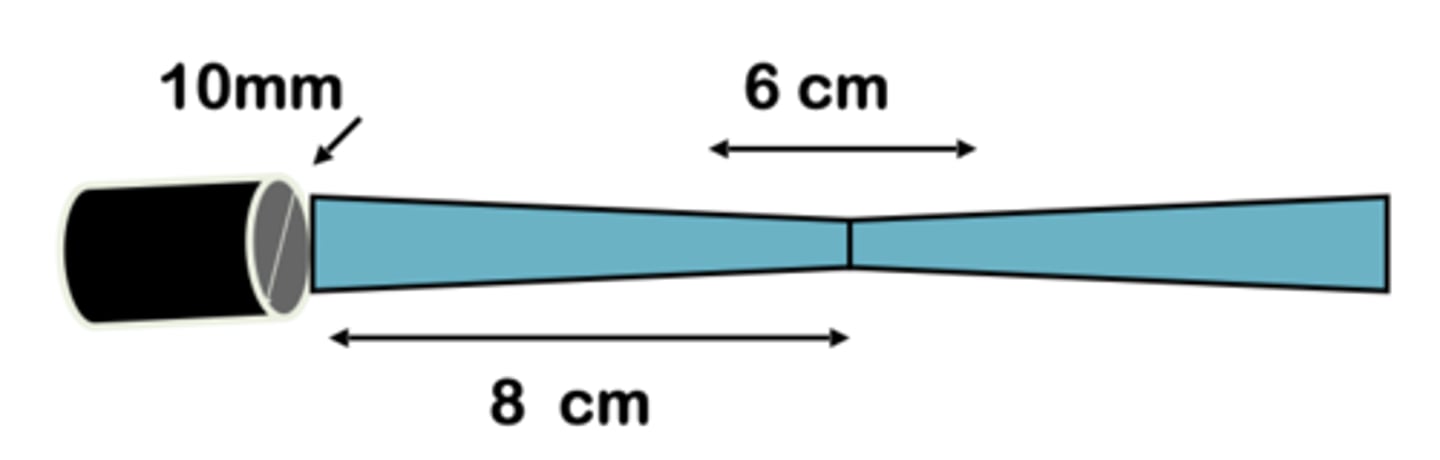
10mm
5mm
What is the diameter of sound beam at 16 cm? 8 cm?
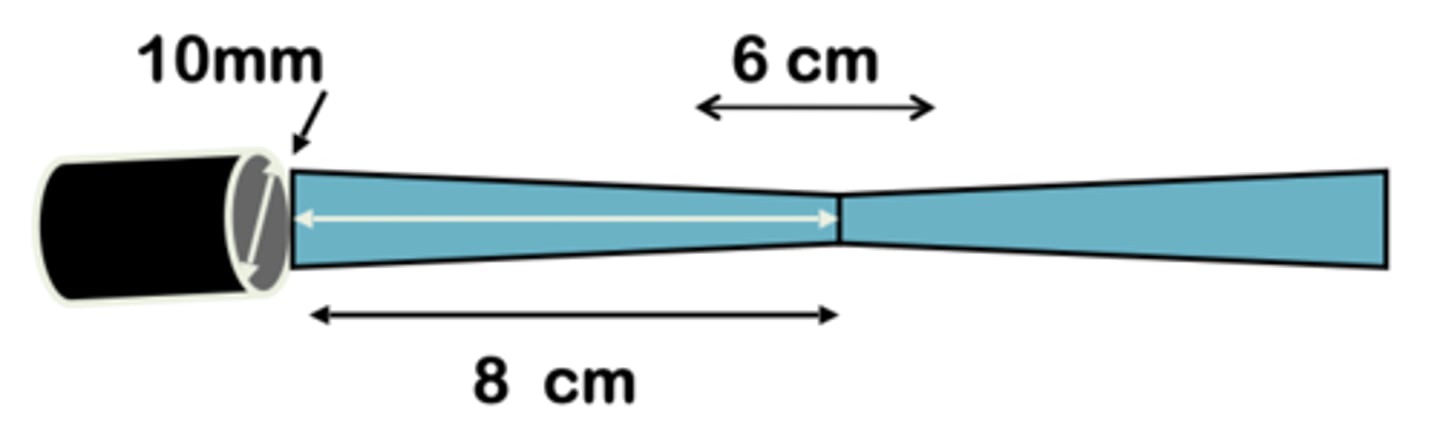
8cm
depth at focus?
5mm
at 8cm the beam's width is

3cm, 3cm
focal zone is ______ and ______ in the Fraunhofers zone
16cm
(8+8)
How deep is the beam when its diameter matches the PZT diameter?
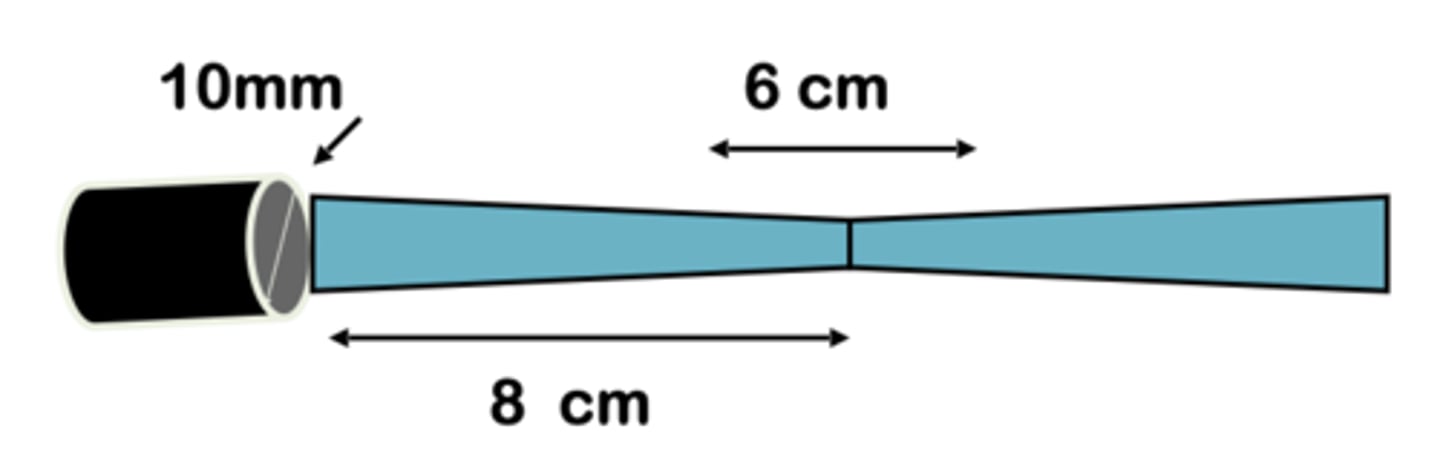
focal depth/near zone length
12mm
beam diameter at point C
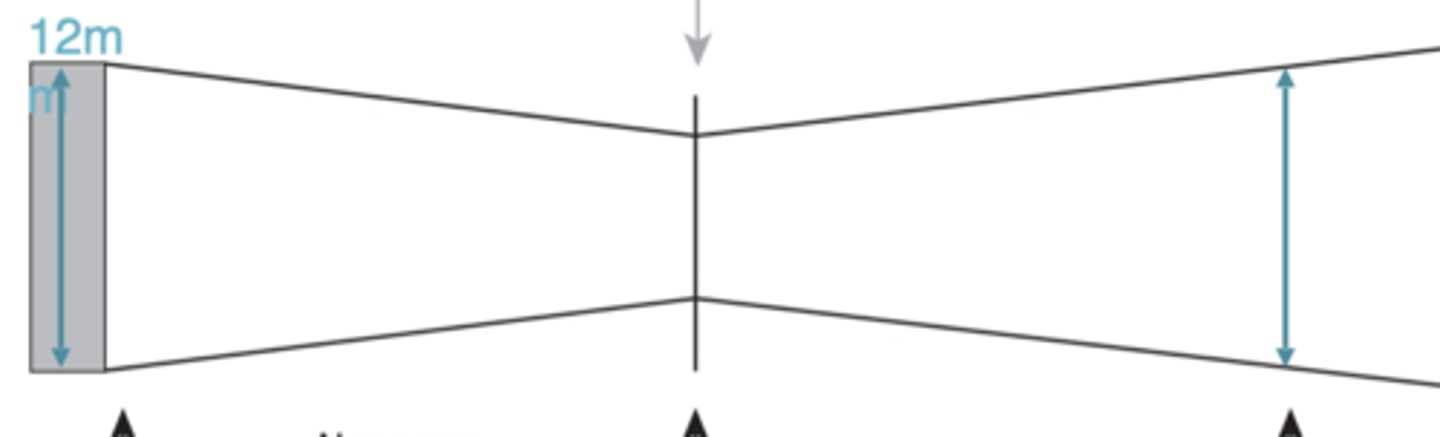
at 2 near zone lengths
beam diameter equals transducer diameter
deeper than 2 near zone lengths
beam diameter is wider than transducer diameter