02 - Tree of life pt 2
1/61
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
when did bryophytes originate
somewhere after green algae, exact time unsure
why dont we know exactly when bryophyte orginate
bryophytes are tiny and hard to fossilize cuz they have any strong tissue
when did first lychophyte orginate
begining of paleozoic and silurian
how did vascular plants conquer dry land
presence of cuticles → seals wateer
stomata → gas exchange
vascular tissue → transports nutrienst
phloem
transports nutrients
xylem
water transport
guard cells
Guard cells are specialized plant cells that control gas exchange and water transpiration by opening and closing the stomata based on cells need
types of lycophytes
clubmosses
spikemosses
quillworts
lycophytes - order from most species to least
most - spike mosses
clubmosses
quilllworts
which species of lycophytes grow in water
quillworts
when did fern orginate
after lycophytes
in carboniferous era
what did the carboniferous look like
mix of lycophytes and ferns
carboniferous era
it is a coal bearing era
this era gives alot of fossilized and slight decomposed lycophytes and ferns
types of ferns
whisk ferns
horse tail
true ferns
least to most species of each type of ferns
whisk ferns
horse tail
true ferns
where do true ferns grow
Today 75% of fern species are found in tropics
how tall are true ferns
can be tiny and or short
which cycle is more dominant in ferns
sporophytic generation
diploid
sori

sporangia
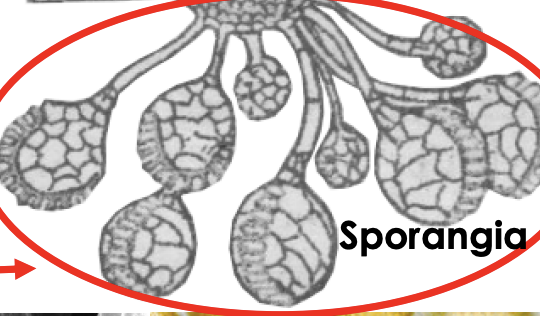
what releases spores in fern
sporangium
Prothallium
a small, heart-shaped structure that's part of the life cycle of ferns
The prothallium is the gametophyte stage of a fern's life cycle, where it produces both male and female sex cells (gametes)
diploid part of the fern life cycle
mature leaf sporophyte
mature root sporophyte
sori
mature sporangium
embryo
developing sporophyte
developing frond sporophyte
developing root sporophyte
haploid part of the fern life cycle
haploid spores
germinating spore
prothallium
gametophye
egg - archegonium
antheridium
spermatozoid
which generation is photosynthetic in fern life cycle
both generation
photosynthetic componet fern life cycle
mature leaf sporophyte
mature root sporophyte
mature sporangium
developing frond sporophyte
prothallium
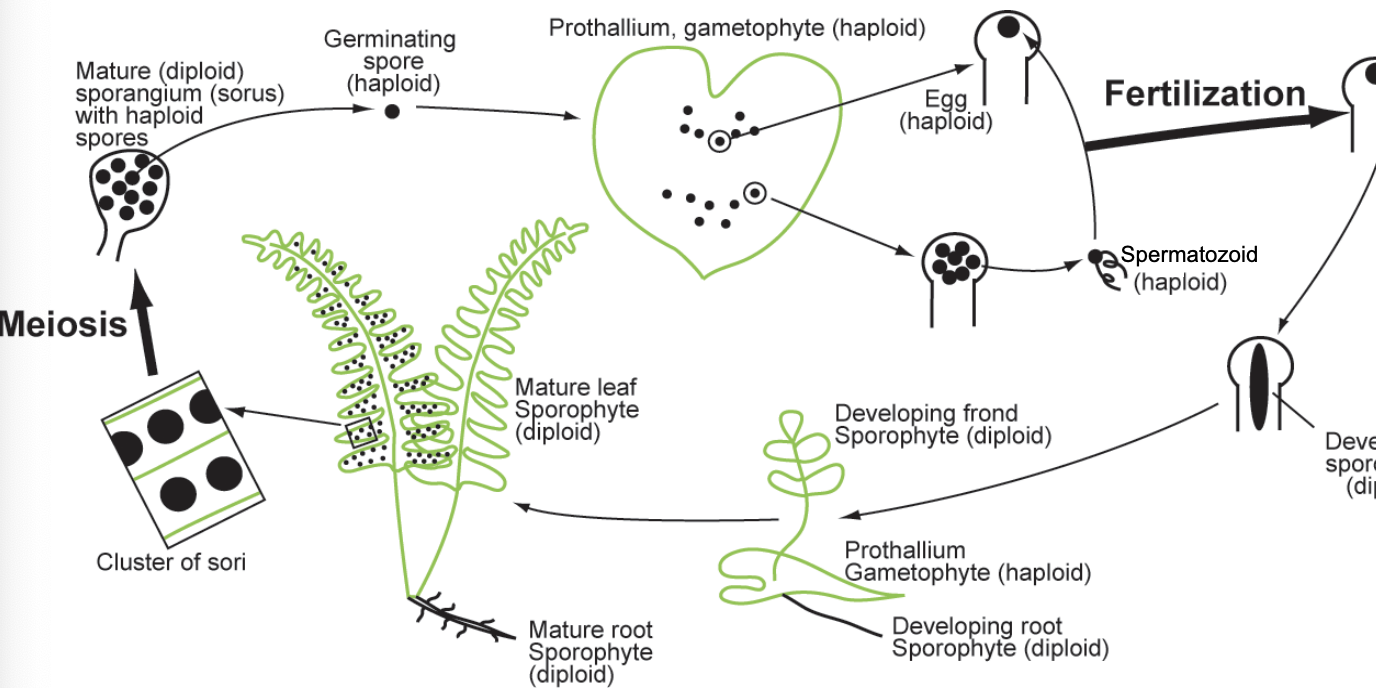
which phase of fern life cycle is wind dependant
is it short. or long distance
spores - long distance dispersal
which phase of fern life cycle is water dependant
is it short. or long distance
spermatozoid - short distance dispersal
fern life cycle - who feeds who
The two generations are “ food-wise independent” (PS)
how water dependant are ferns
still strong water dependance as prothallium has no cuticle
even though sporophyte has cuticle & vascular system!
when was the peak diversity of seedless vascular plants
end of carboniferous to start of jurassic
what originated after ferns
gymnosperms
when did gymnosperms originate
outgoing carboniferous era
types of gymnosperms
conifers
ephedra
gnetum
gingko
welwitschia
gymnosperms - most to least species
conifers
ephedra
gnetum
gingko
welwitschia
what does conifer mean
cone bearers
how is pollen dispersed in gymnosperms
air
fertilizatoin in gymnosperms
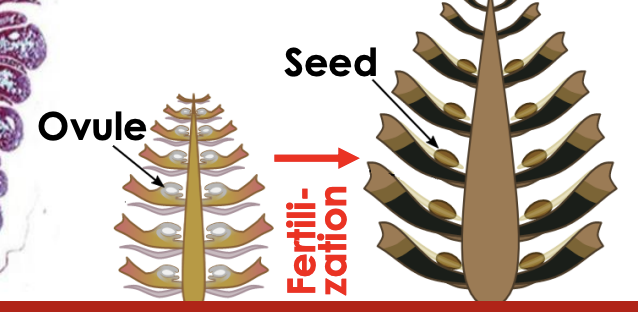
seed wings
rest on top of scales
seed end is protected in the centre
wind dispersed

how do cones look
very different shape and sizes
Key invention in gymnosperms:
wood
Continued desiccation proofing in gymnosperms
Desiccation-prone spore (bryophytes, lycophytes, ferns)
Seed: drought resistant (plus wing)
have vascular bundles - transports nutrients
cuticles - seals water
stoma - gas exchange
what came after gymnosperms
angiosperms
types of seed plants
angiosperms and gymnosperms
types of vascular plants
lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms, angiosperms
when did the first snagiosperm orginate
jurassic
when was the big angiosperm radiation
cretaceous
explosive diversity (most groups we find today)
Key invention of angiosperms:
flowers
development to pick up pollen and spread it = more diverse
dominant generation in Life cycle of flowering (seed) plants
sporophytic generation
diploid
hevailiy
diploid part of Life cycle of flowering (seed) plants
mature apple tree (sporophyte)
flower
anther
embryo
developing apple
seed
develping seedling
haploid part of Life cycle of flowering (seed) plants
stigma
ovary containing eggs (female gametophyte)
pollen (male gametophyte)
pollen tube
what is equavalent to flowers in gymnosperms
flowers
angiosperms seeds
covered seeds
Flowers - key innovation
pollination syndromes
which generation feeds what in angiosperm
Sporophyte feeds the gametophytes
angiosperm life cycle - photodynthetic part
mature apple tree
developing seedling
angiosperm life cycle - mobile life cycle
Male gametophyte (pollen) moved over mostly short distances (pollination syndrome) Seeds dispersed over pot. long distances (seed dispersal syndrome)
Flowering plants are also known as…?
angiosperms
Which organ produces the spermatozoids in ferns?
Antheridium
Within the vascular plants, which group is the oldest?
Lycophytes
Within the vascular plants, which is the most modern group?
Angiosperms
Which life-stage can found a new population?
seedling