Biology DNA & RNA
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
The genetic blueprint for each cell that determines every characteristic of a living organism.

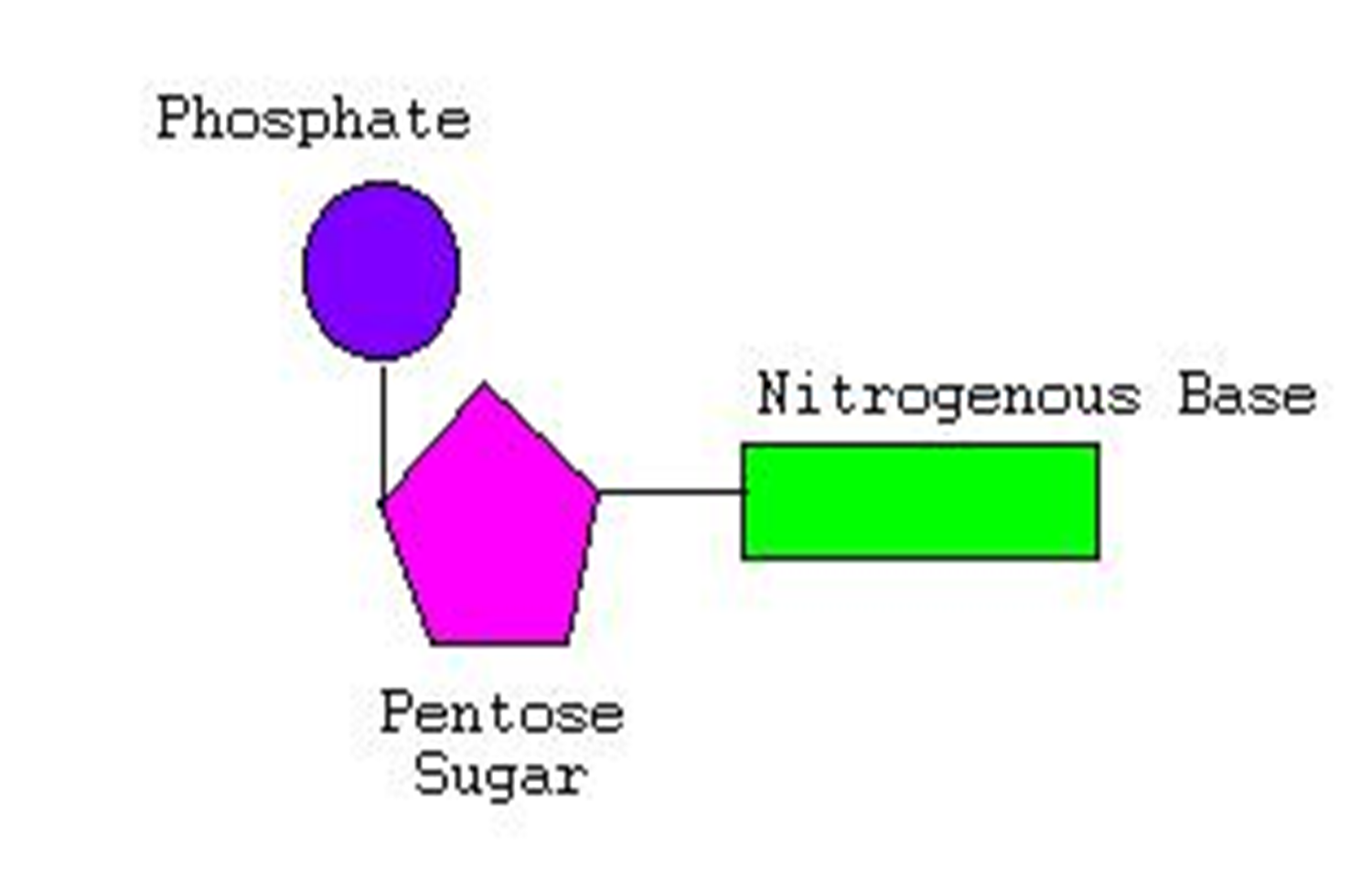
A DNA nucleotide is made up of three main parts:
Deoxyribose (simple sugar or pentose sugar)
Phosphate group
Nitrogen base
How to draw DNA
Nitrogen Base Pairing
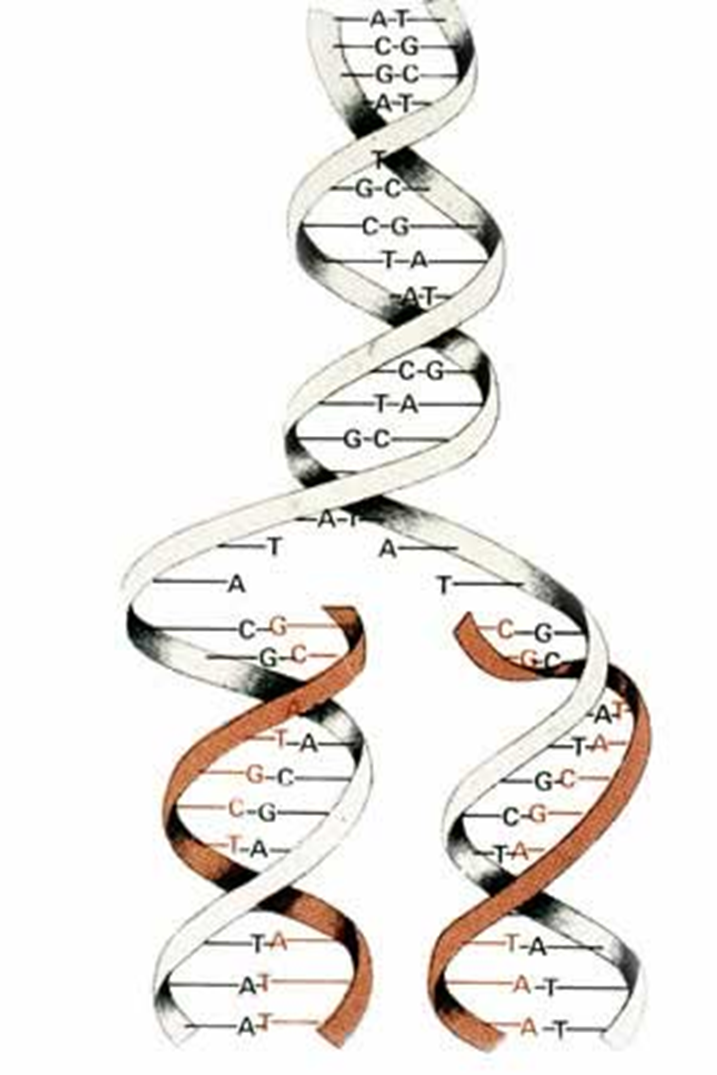
Adenine bonds with Thymine
Cytosine bonds with Guanine
What do nucleotides do
They combine to form two long chains (making one molecule).
The importance of replication in DNA
DNA must replicate so that each cell has a complete set of chromosomes
Without replication: Species could not survive
Individuals could not grow, heal or reproduce
Where does replication begin
Replication begins at specific locations called origins of replication, where the DNA strands are separated to allow for copying.
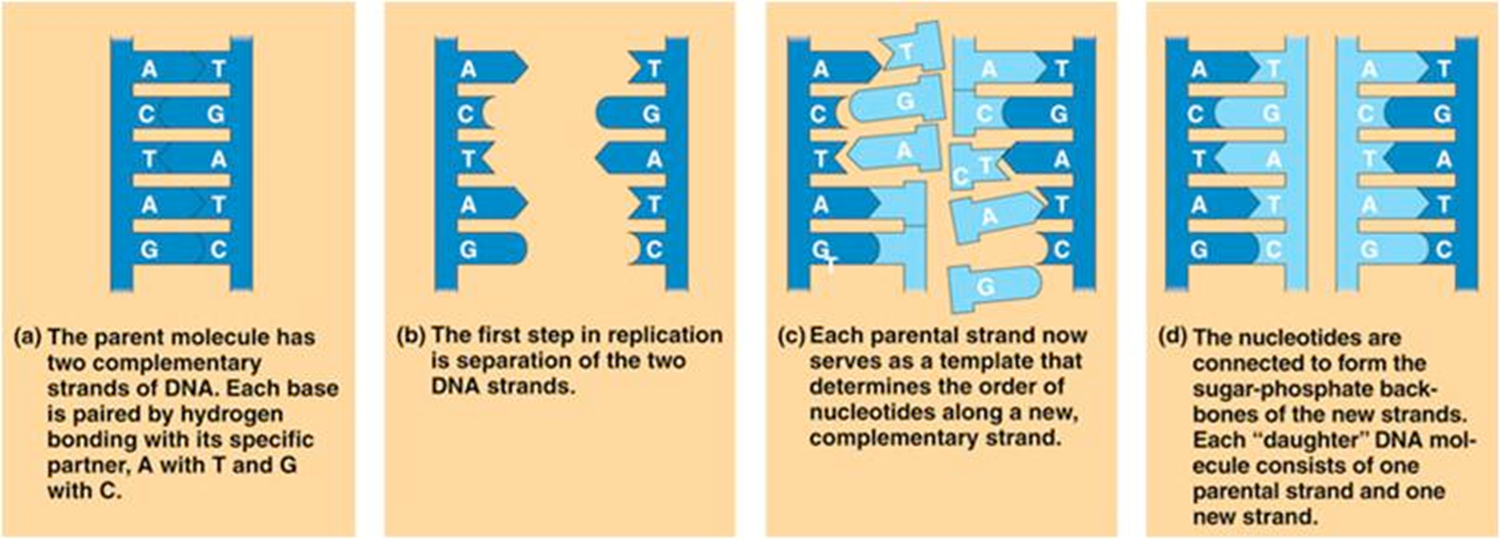
Step 1 of replication:
The enzyme, helicase, untwists the double helix at the replication fork, separating the two old strands and breaking the Hydrogen bond.
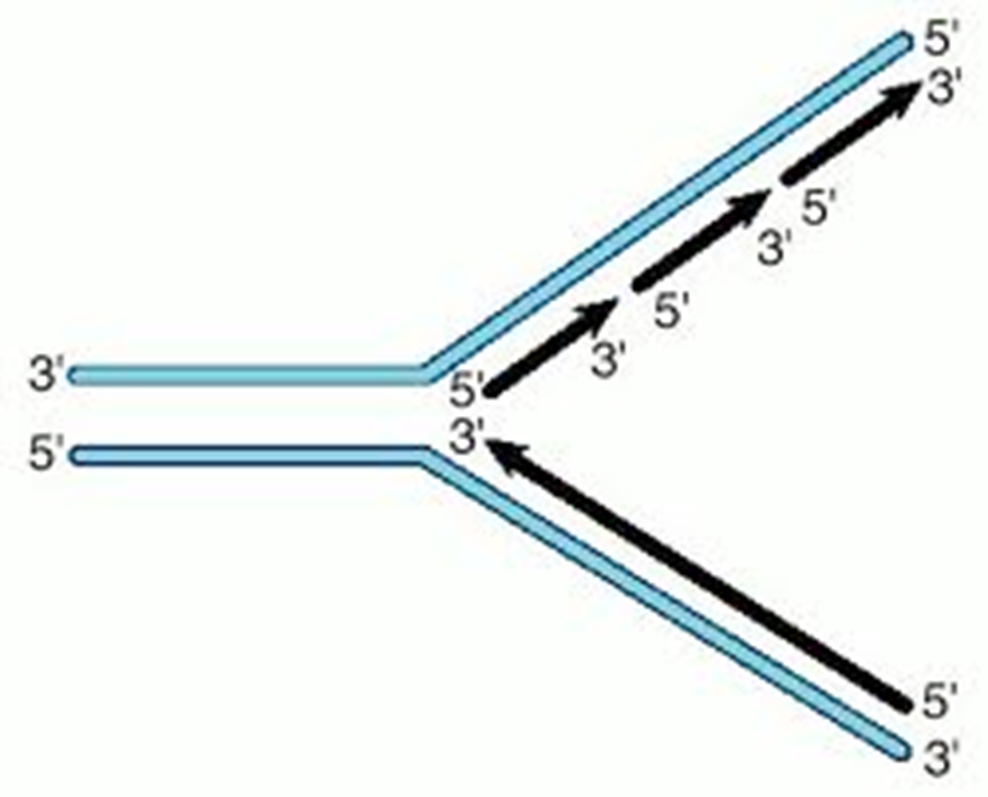
What is the replication fork?
The Y-shaped region where the new strands of DNA are elongated.
Step 2 of replication
Each strand then builds its opposite strand by pairing its bases with free nucleotides.
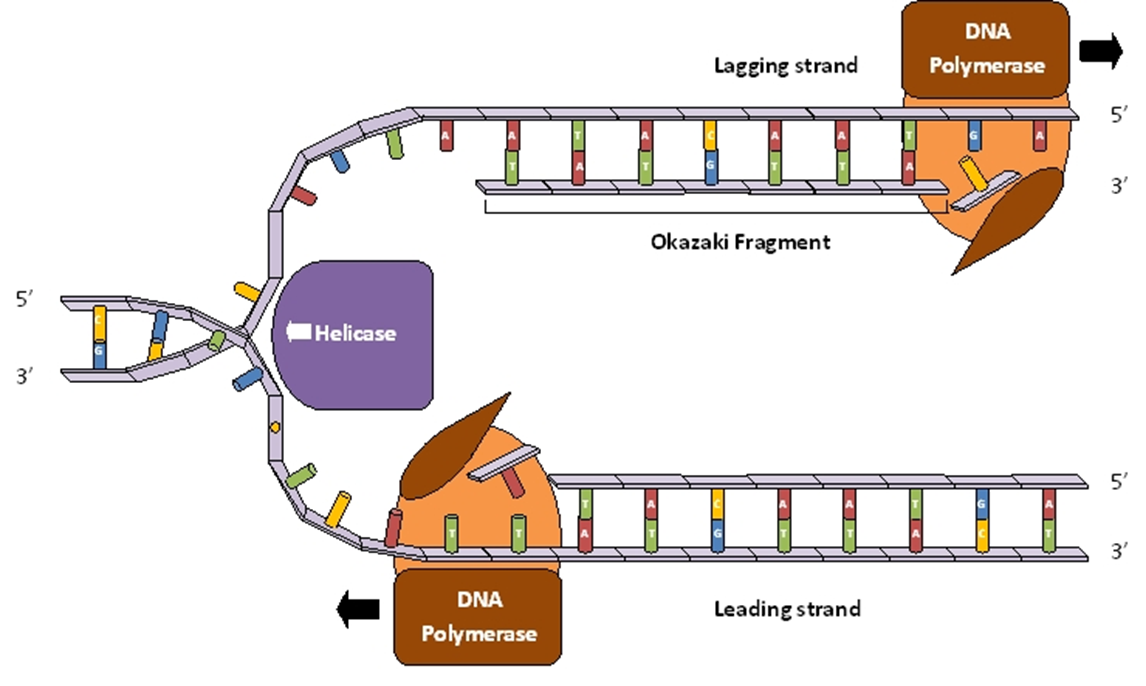
What does the DNA polymerase do in the 2nd step of replication
Adds complementary nucleotides to the growing DNA strand. Responsible for the elongation of new DNA at a replication fork.
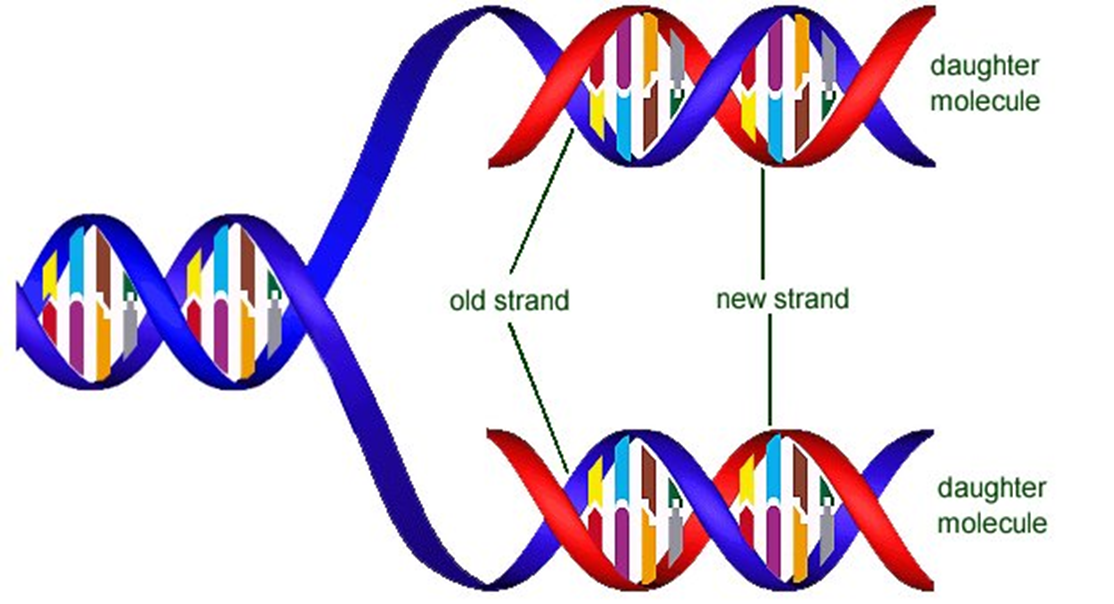
Step 3 of replication
Each new DNA molecule has one nucleotide strand from the original DNA molecule and one nucleotide strand that has been newly synthesized from free nucleotides in the cell.
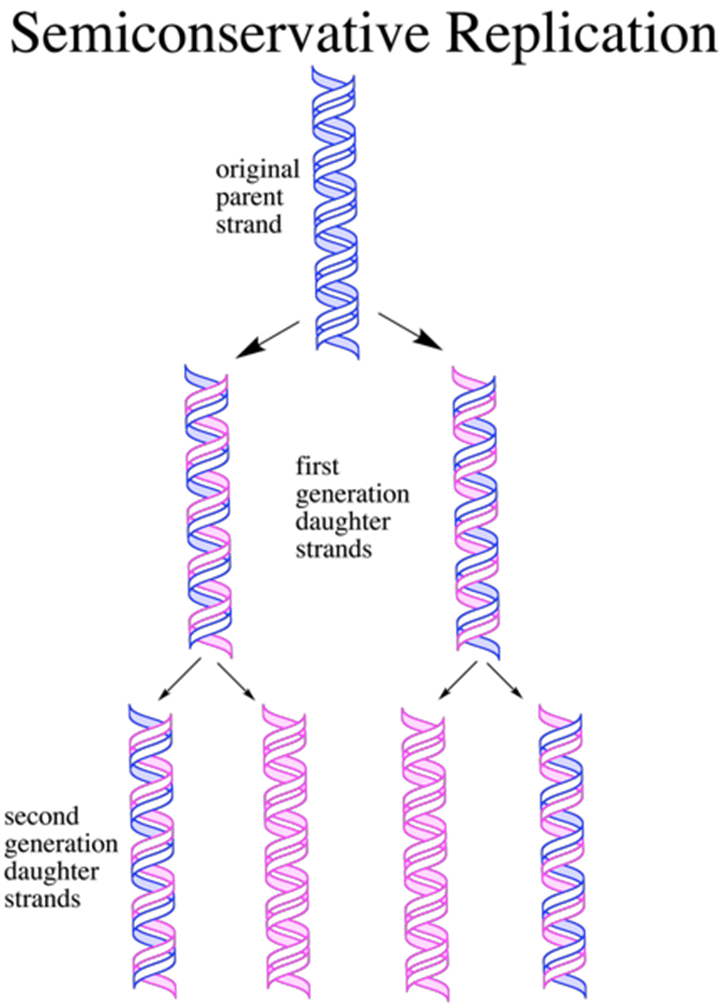
Semi-Conservative Replication
Half old DNA , half new DNA
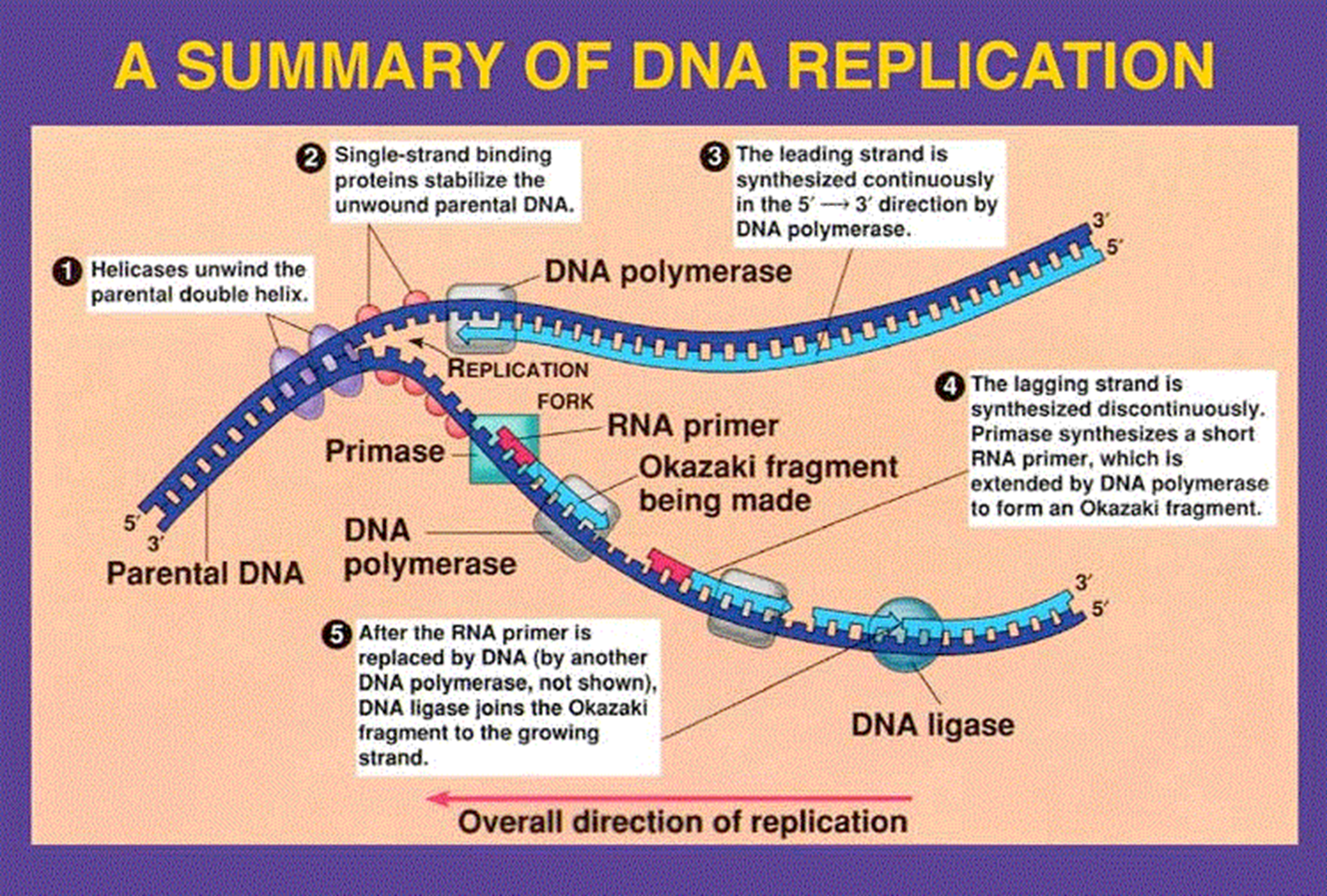
The replication process goes on until..
This process goes on until the entire molecule has been unzipped and replicated.
Each new strand is a complementary strand from the original strand.
The two strands of DNA are…
anti-Parallel- which means one runs from 5’->3’ and one runs from 3’->5’.
DNA vs RNA
DNA | RNA |
Double stranded Thymine Sugar= deoxyribose NEVER leaves the nucleus | Single stranded Uracil Sugar= ribose Leaves the nucleus |
What are the 3 types of RNA?
tRNA, mRNA, rRNA
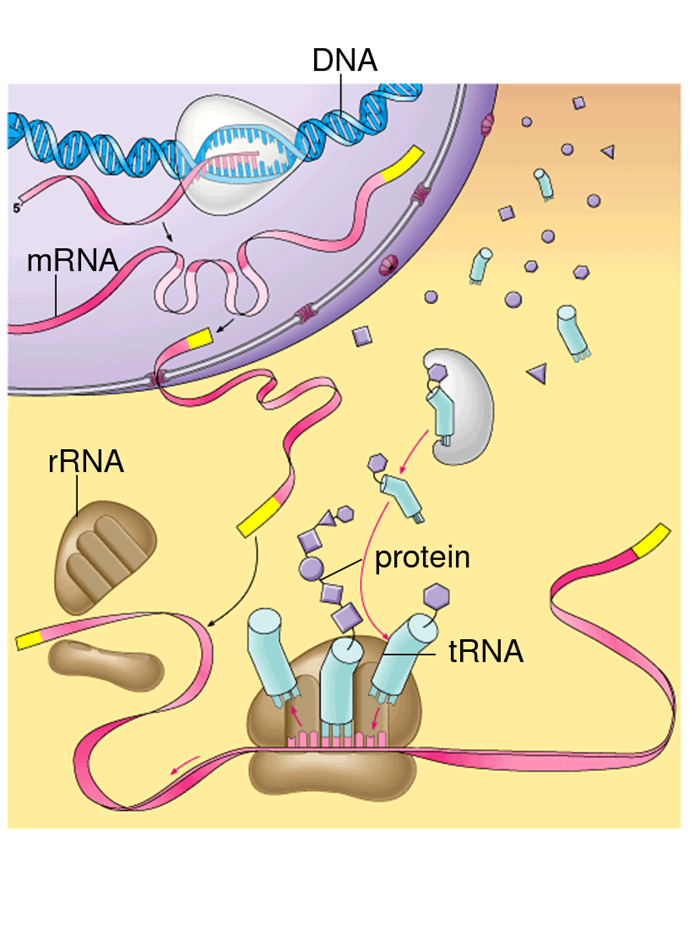
mRNA (messenger RNA)
RNA copy that carries information from the DNA in the nucleus out into the cytoplasm of the cell.

rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
The RNA that makes up the ribosome.
Helps produce enzymes needed to bond amino acids together during protein production.

tRNA (transfer RNA)
Brings amino acids to the ribosomes so they can assemble into proteins.
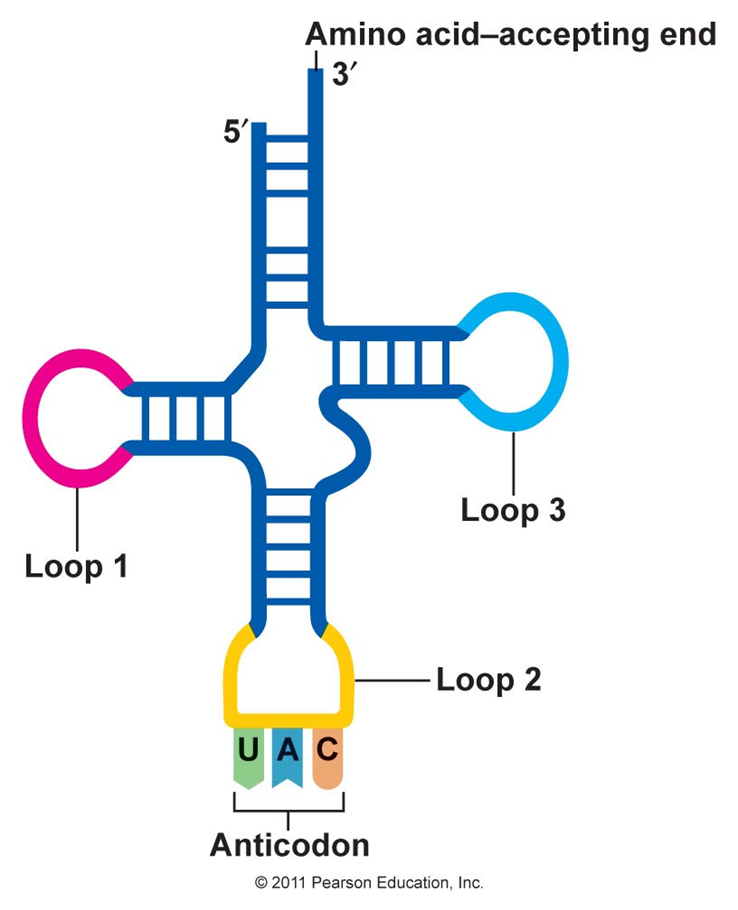
Anticodons
Three unpaired bases on a tRNA molecule. These bases are complementary to one mRNA codon.
Transcription
The creation of mRNA under the direction of DNA
Enzymes making an mRNA copy of a DNA strand
Takes place in the nucleus
Step 1 of transcription
An enzyme, helicase, unzips the molecules of DNA, just as it does during DNA replication.
Step 2 of transcription
Free RNA nucleotides pair with complementary DNA nucleotides on one of the DNA strands.
Assisted by RNA polymerase
RNA elongates
Step 3 of transcription
Transcription ends when the RNA polymerase molecule reaches the terminator region of the DNA
The mRNA molecules break away as the DNA strands rejoin
Translation
mRNA to protein
Where does translation occur
Ribosome
Translation is the process of…
Reading codons
Laying amino acids in chains
Making proteins
What does tRNA do in translation?
Brings amino acids to the ribosomes so they can assemble into proteins.
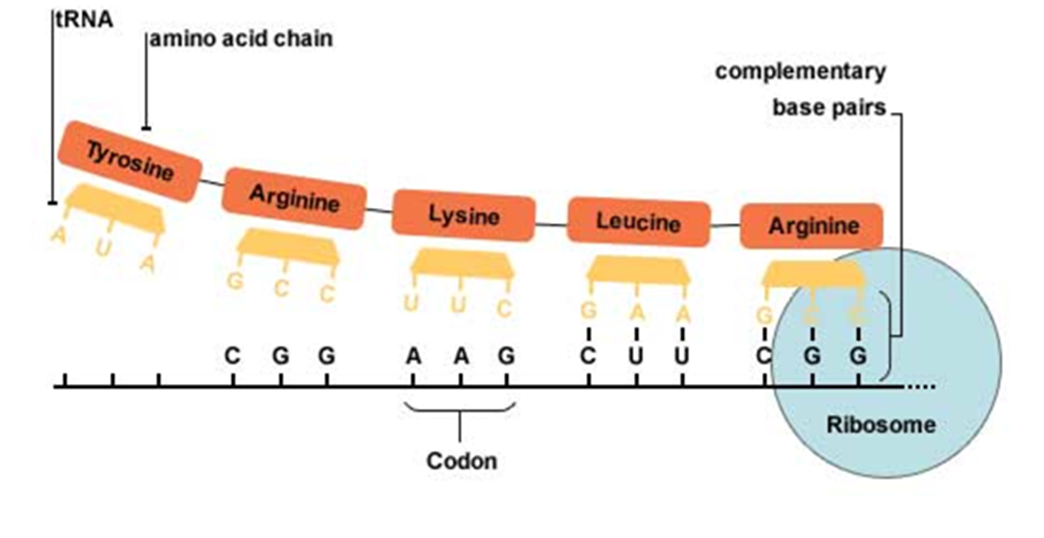
What is a codon
A sequence of three consecutive nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that codes for a specific amino acid.
Step 1 of translation
The first codon of the mRNA strand attaches to a ribosome
The tRNA molecule (carrying a specific amino acid) approaches the ribosome
When the tRNA anticodon pairs with the mRNA codon, the two molecules join and the tRNA molecule remains there
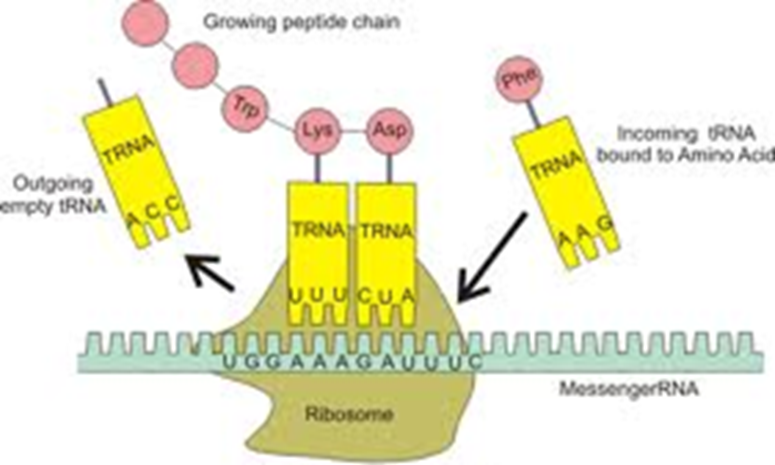
Step 2 of translation
Can’t start unless there is a start codon (AUG) on mRNA that signals the start. Once it starts, the ribosome slides to the next codon.
Step 3 of translation
A new tRNA molecule carrying an amino acid pairs with the mRNA codon.
Step 4 of translation
When the first and second amino acids are in place, a peptide bond is formed between them.
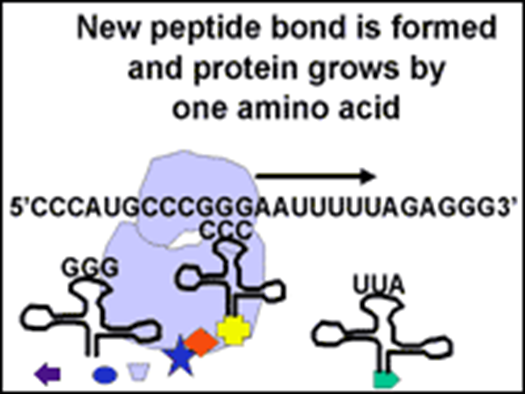
Step 5 of translation (last step)
As the process continues, a chain of amino acids is formed. This occurs until the mRNA reaches a stop codon.