biology chapter 24 populations and sustainability
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
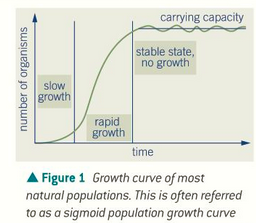
phase 1 - period of slow growth
phase 2 - rapid growth
phase 3 - stable state (happens due to limiting factors where BR = DR)
what does a population growth curve look like?
limiting factors prevent further growth and can cause decline
can be abiotic or biotic
what are limiting factors?
factors that have an effect on the whole population regardless of size
earthquakes, fires, volcanic reuptions and storms
what are density independent factors?
interspecific - between species
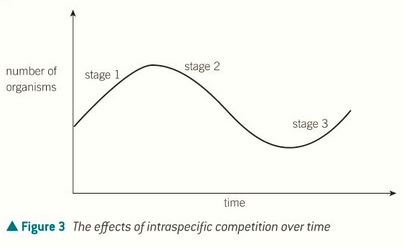
intraspecific - within the same species
what are the two types of competition?
when two or more different species compete for the same resource
for food or habitats
less well adapted species will be outcompeted and the less adapted species will decline in number and no longer exist
this is the competitive exclusion principle
how does interspecific competition happen?
for resources such as food or mates
not always stable as resources can vary
how does intraspecific competition happen?
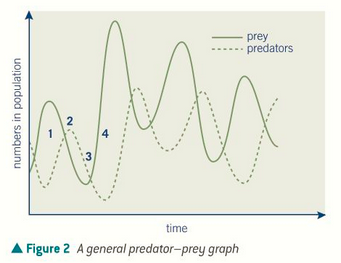
predator and prey population sizes fluctuate and are dependent on each other
as prey increases, more food for predators so predators also rise
more predators means more prey are eaten so prey deacreases
reduced prey population can’t support predators so they decrease
less predators so prey population rises
predator prey relationships graph
explain each main stage
maintenance of biodiversity through human intervention
to maintain biodiversity for sustainable development
also includes reclamation, restoring damaged ecosystems
what does conservation mean?
Protection of an area by restricting or banning human interference
Aim to protect sensitive ecosystems
what is preservation?
Economic - provide resources for human survival like emdicine and clothes
Social - people enjoy natural beauty
Ethical - moral responsibility to future generations
importance of conservation?
a renewable resource that is being economically exploited so that it will not run out
what is a sustainable resource?
preserve environment
ensure resources for future generations
balance consumption of resources
what are the aims of sustainability?
coppicing: tree trunk is cut close to the ground and new shoots are cut
shoots make even more leading to a tree with multiple trunks
rotational coppicing is done so that newly coppiced trees have time to grow and maintain biodiversity
How is timber sustainably produced through coppicing?
selective cutting removing only large trees
replace by replanting
plant at optimal distance to reduce competition
manage pests
Major disadvantage is that habitats are destroyed and soil minerals reduced. Trees are needed for binding soil together.
how is large scale timber production done sustainably?
disadvantage?
overfishing has led to species of populations reducing drastically
fishing quotas to avoid overfishing
bigger net holes to allow younger fish to get through
restrict fishing at times year
fish farming prevent the loss of wild species
what is sustainable fishing?
limit grazing to edges of the reserve and grazing in different areas to allow plants to recover
ecotourism to support the local tribes and the environment
conservation and research in reserves
livestock can compete with wildebeest during migration
sustainable forest management and agriculture
how ecosystems can be managed to balance the conflict between conservation/ preservation and human needs?