Inelastic Impression Materials
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 3. Chapter 46
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Dental impression
Negative imprint of hard and soft tissue (teeth and gingiva)
Thermoplastic
A material that reversibly softens upon heating and hardens upon cooling.
Registration
A thin impression of the biting surfaces of the teeth used to set gypsum casts in the correct occlusal relationship when casts are mounted on articulators.
Dental impression makes
A positive reproduction (cast or model) can be made
Gypsum
Used to make model
Positive reproduction
What is an impression material
Fluid substances
That changes from gel form to rigid form
Impression definition
Negative replica
Model or cast
Positive reproduction
Die
Model of a single tooth or several teeth
The positive reproduction of a single tooth is described as a
Die
When several teeth or whole arch is reproduced it is called
Cast or model
Flexibility
Measure material thickness
Wetting
How well the material will “spread out”
More wetting = good
Less wetting = poor
Contact angle
angle formed when drop of liquid placed on surface
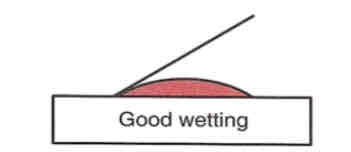
Low contact angle
less than 90 degrees, spreads easily, good wetting
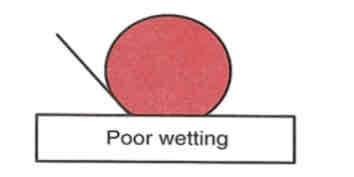
High contact angle
more than 90 degrees, resists spreading &
“beads”, poor wet
Accelerators
QUICKENS the hardening process
Retarders
SLOWS the hardening process
Inelastic
Impression Compound, ZOE
Elastic
Elastomers
∗ Polysulfide, Polyether, Polyvinyl
Hydrocolloids
Irreversible Hydrocolloid
∗ Alginate
Reversible Hydrocolloid
∗ Agar-Agar
Inelastic Impression Material Characteristics
∗ Not flexible, very rigid
∗ Easily deforms
∗ Can only be used in applications where no undercuts exist
What Is an Undercut?
An area that curves under and has a tendency to lock a material within it, making the material difficult to remove.
What is ZOE?
Zinc Oxide- Eugenol
Inelastic-Impression Compound Uses:
∗ Final Impression of single crown prepped tooth with no
undercuts
∗ Spacer impressions
Inelastic-Impression Compound Properties:
∗ Thermoplastic material
∗ Material that reversibly softens upon heating & hardens
upon cooling
∗ No flexibility when in a solid state
∗ Cracks and breaks easily
Inelastic-Impression Compound Packaging
∗ Plates and Sticks
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Uses
Impressions of edentulous arches
∗ Used to be very common for this but not so much now
Bite registrations
∗ Thin impression of the biting surfaces of the teeth to capture bite
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Properties
∗ No flexibility once set
∗ Fractures easily
∗ Poor detail
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Packaging
Two Paste System
∗ Catalyst
-Paste, eugenol, green
Base
∗ Zinc oxide powder, and oils, white
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Mixing Time
30-60 seconds
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Working Time
30-60 seconds
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Setting Time
30-60 seconds in the mouth
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Accelerators
∗ Too much catalyst, too little base
∗ Warm room temperature
∗ High humidity
∗ Presence of water
Inelastic- Zinc Oxide Eugenol Retarders
∗ Too much base, too little catalyst
∗ Cool room temperature