Ch 1- Telescopes and instruments
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What does wavelength coverage depend on?
The astrophysical source
The science question
The telescope
What factors contribute to effective throughput?
Atmospheric opacity
Optics throughput
Quantum efficiency of the CCD detector.
What is shot noise, and why does it occur?
Its an irreducible random variation in the number of photons counted
This is due to the random nature of photon emission.
What statistical distribution does shot noise follow?
Poisson statistics.
How is shot noise (N) calculated?

What is the formula for the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)?
S= the signal (number of photons collected).
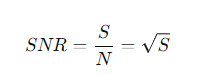
How is the SNR related to the flux of the source?
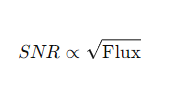
How is the SNR related to the telescope's collecting area?
D= the mirror diameter.
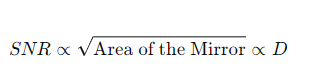
How is SNR related to the exposure time?
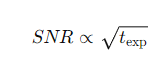
What is the combined formula for the SNR relation?
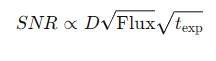
What is the full formula for the comparison of the SNRs of two observations?
F1,F2= the fluxes
D1,D2= mirror diameters
t1,t2= the exposure times.
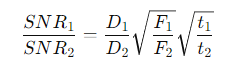
What factors increase the number of photons collected in an observation?
Higher flux of the source.
Larger telescope diameter.
Longer exposure time.
What does the parameter R represent in spectroscopy?
Spectral resolution
A dimensionless quantity that indicates a spectrograph's ability to resolve spectral features.
What is the formula for spectral resolution (R)?
λ =observed wavelength,
Δλ= the smallest wavelength difference that can be resolved.
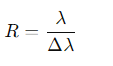
What is spatial resolution in astronomy?
The smallest angular separation at which two point sources on the sky can be distinguished as separate, θ.
What determines the smallest spatial resolution in the absence of atmospheric interference?
The diffraction limit of the telescope.
What is the formula for spatial resolution θ in diffraction-limited observations?
λ= Wavelength (in the same units as D)
D= Telescope mirror diameter
θ = Spatial resolution (in radians).
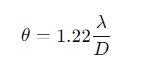
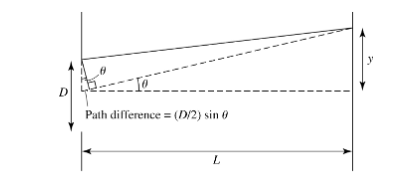
When does destructive interference occur in a 1D aperture scenario?
When the difference in path length equals λ/2
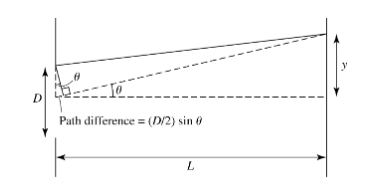
What is the formula for the small-angle approximation for angular resolution (spatial resolution) (θ) in a 1D aperture?
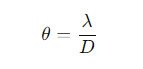
Under what conditions is diffraction-limited imaging achieved?
In space-based telescopes.
In ground-based telescopes using adaptive optics
What causes seeing-limited imaging in ground-based telescopes without adaptive optics?
Temperature variations in the atmosphere.
Variations in the index of refraction.
Distortion of the incoming flat wavefront.
What is the formula for angular resolution (spatial resolution) in seeing-limited imaging?
λ=Wavelength of light.
r0=Fried's coherence length.
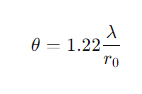
What is Fried’s coherence length (r0)?
The distance over which optical phase distortion is limited.
What is the formula for angular resolution (spatial resolution) in interferometry?
λ= Wavelength of light.
Dbaseline= Longest distance between telescopes/antennae in the array.
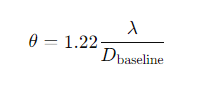
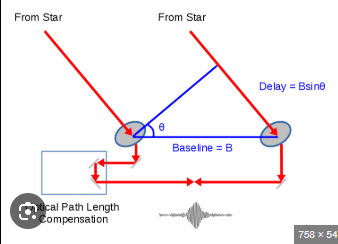
What factors affect the sensitivity of astronomical observations?
Observed wavelength
Observing conditions
Telescope design (e.g., collecting area)
Instrument specifications (e.g., optics and detector efficiency).
What is "throughput" in the context of astronomical observations?
The fraction of photons detected from a source compared to the number that would be detected if there were no losses.