Anatomy and Physiology (Chemistry) Flash Cards
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms related to atoms, bonding, isotopes, pH, and macromolecules from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Atom
The basic unit of matter that everything is composed of.
Protons
Positively charged subatomic particles located in the nucleus.
Neutrons
Neutral subatomic particles located in the nucleus.
Electrons
Negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus and participate in bonding.
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom; unique to each element and defines the element.
Atomic Mass
Measured in Daltons/AMU; essentially protons plus neutrons (electrons not counted).
Isotopes
Atoms with an unusual number of neutrons compared to the typical element.
Ions
Atoms with an unusual number of electrons, resulting in a net charge.
Cations
Positive ions with more protons than electrons.
Anions
Negative ions with more electrons than protons.
Electron Configuration
Arrangement of electrons in energy levels and orbitals around the nucleus.
Energy Levels
The main regions around the nucleus where electrons are found
Orbitals
Subdivisions within energy levels (s, p, d, f) that hold electrons.
First Energy Level Capacity
1st level holds 2 electrons (s orbital).
Second Energy Level Capacity
2nd level holds 8 electrons (2 in s, 6 in p).
Third Energy Level Capacity
3rd level holds 18 electrons (s, p, d).
Fourth Energy Level Capacity
4th level holds up to 32 electrons (includes f orbitals).
Covalent Bond
Bond formed by sharing electrons to satisfy orbitals.
Polar Covalent Bond
Uneven sharing of electrons, creating partial charges.
Ionic Bond
Bond between a positively charged ion (cation) and a negatively charged ion (anion).
Hydrogen Bond
Bond between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom (O or N), often involving water.
Hydrophilic
Molecules that are water-loving and form hydrogen bonds with water.
Hydrophobic
Molecules that are water-fearing and generally nonpolar (avoid water).
Nonpolar
Molecules with no significant partial charges; evenly shared electrons.
Polar
Molecules with uneven electron distribution and partial charges.
pH Scale
A scale from 1 to 14; 7 is neutral; acids donate protons, bases accept protons.
Acid
Substance that donates protons (H+ procedures).
Base
Substance that accepts protons.
Isomer
Molecules with the same formula but different connectivity.
Enantiomer
Molecules that have carbon with four different groups bond to it and have a mirror image.
Phospholipid
Lipid with a phosphate group; major component of cell membranes.
Triglyceride
is a storage of lipid in animals
Cholesterol
Stored lipid; precursor for fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones.
Carbohydrates
Macromolecules that provide energy; include glucose and glycogen; form glycosidic bonds.
Glucose
A simple sugar used for energy; metabolized via glycolysis.
Glycolysis
breaks down glucose to produce energy.
Glycosidic Bond
Covalent bond between carbohydrate units; alpha vs beta linkages.
Alpha Linkage
Glycosidic bond oriented downward; digestible by humans. (covalent bond)
Beta Linkage
Glycosidic bond oriented upward; generally not digestible by humans.
Glycogen
long chains of glucose ; these molecules are ring structures with OH groups.
Amine Group
nitrogen-based molecules
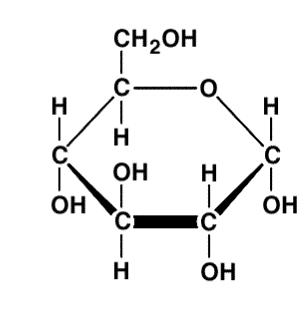
Carbohydrate(Glucose)
I identify this structure
Phospholipid(Lipid)
I identify this structure
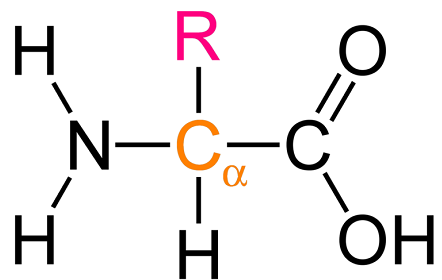
Amino Acid
I identify this structure
Hydrophilic head and Hydrophobic tail
Phospholipids are composed of what two parts
Unsaturated lipids have double bonds between carbons.
If the Tails in Phospholipids are Unsaturated they have what kind of bond and what atom is it
Single bonds only with Hydrogen
What makes a lipid tail saturated?
introduce kinks in their hydrocarbon chains. These kinks prevent the fatty acid tails from packing tightly together.
Why do unsaturated fatty acid tails create movement?
glycosidic bond
What type of bond connects two carbohydrates?
Humans lack the enzymes to break them
Why can’t humans digest Beta glycosidic bonds?
Amino acids
What are proteins composed of?
the shape determines what the protein can do.
How is a protein's structure related to its function?
Structural support, enzymes, antibodies
Name three functions of proteins in the body.
What is unique about the R group in amino acids?
Determines amino acid properties (hydrophobic, hydrophilic, ionic, size)
What are the four levels of protein structure?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary
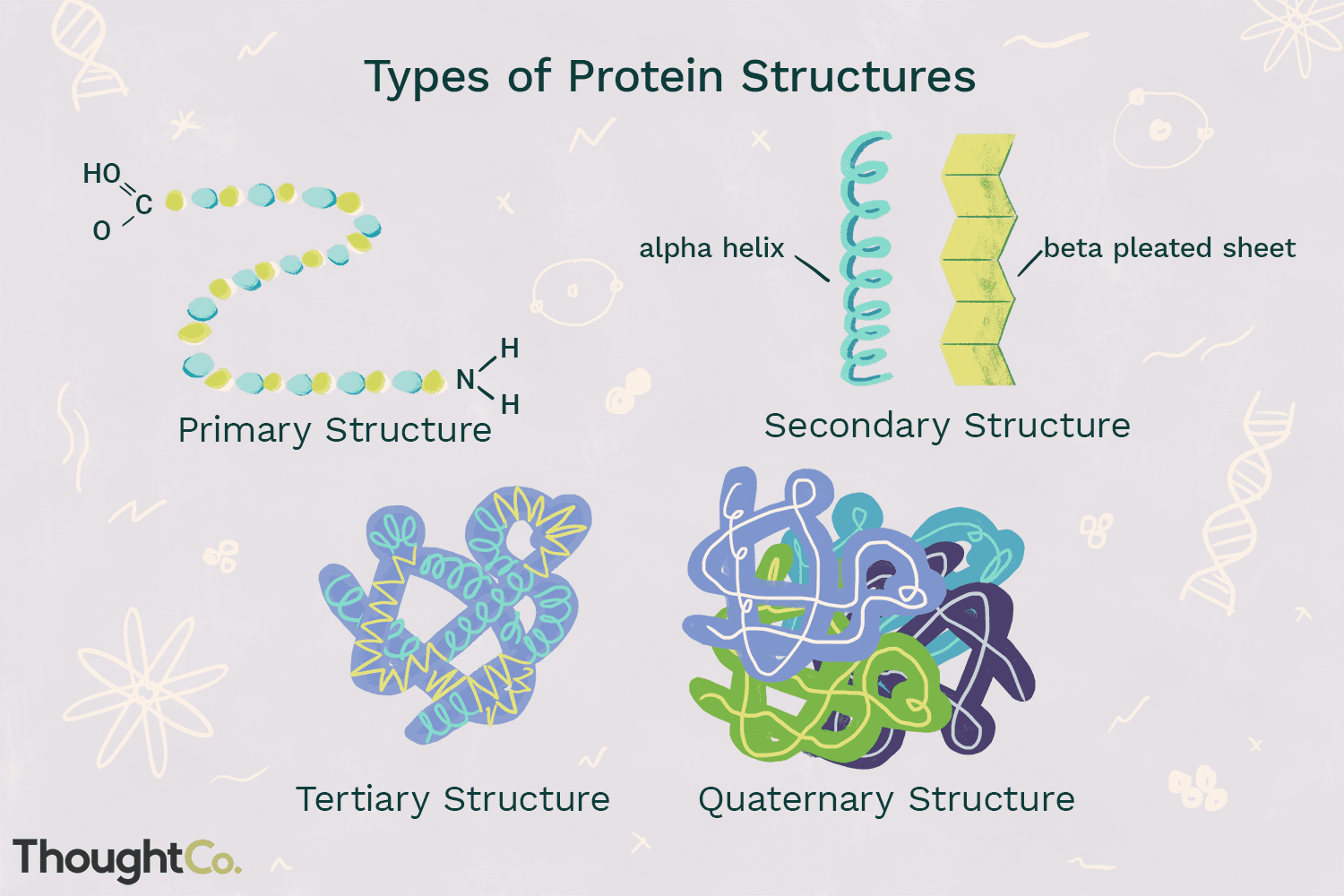
What is the primary structure of a protein?
Sequence of amino acids
What forms the secondary structure of a protein?
hydrogen bonding of other primary structures
What characterizes the tertiary structure of a protein?
3D folding due to ionic, hydrophobic, and covalent interactions
What is quaternary structure in proteins?
Interaction of two or more tertiary structures
Which interactions stabilize tertiary and quaternary structures?
Ionic, hydrophobic, and covalent interactions
What type of macromolecule are enzymes?
Proteins
What does an enzyme's active site usually contain?
A metal ion (e.g., Fe, Zn, Cu, Mg)
What is an anabolic reaction?
Building macromolecules (produces water)
What is a catabolic reaction?
Breaking down macromolecules (uses water)
What is Gibbs free energy (G)?
The energy throughout a reaction
What does Delta G indicate in a reaction?
Whether a reaction is favorable or not (spontaneous vs. nonspontaneous)
How do you calculate Delta G (Gibbs free energy)?
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS (enthalpy minus temperature times entropy)
What is ATP composed of?
Adenine with 3 phosphates
What happens when the terminal phosphate of ATP is cleaved?
Energy is released
What is a gene?
A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein
What is gene expression?
The process where DNA is transcribed into mRNA and then translated into protein.
What is a codon?
A set of 3 nucleotides coding for an amino acid
What nucleotides make up DNA
A, T, C, G (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine)
What is a nucleotide composed of?
Sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base
How is DNA transcribed into mRNA?
A → U, T → A, C → G, G → C (thymine is replaced by uracil in RNA)
What sugar does RNA use?
Ribose
Which base does RNA use instead of thymine?
Uracil
How many hydrogen bonds he base pair adenine-thymine (A-T) and guanine-cytosine (C-G) DNA?
A-T: 2, C-G: 3
What are DNA and histones arranged into?
Chromosomes
What percentage of the genome codes for genes?
2%
What is the difference between transcription and translation?
Transcription: DNA → mRNA, Translation: mRNA → Protein
What is DNA made of?
Nucleotides
What is mRNA made of?
Nucleotides
What is protein made of?
Amino acids
How many pairs of chromosomes are in the human genome?
23 pairs
How many copies of each chromosome do humans have?
2
Approximately how many genes are estimated in the human genome?
50,000
What are telomeres?
Tips of chromosomes with repeat sequences
What happens to telomeres over time?
They shorten and coding regions may be lost
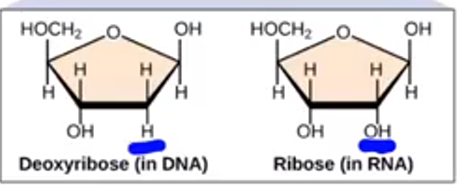
what is the difference between deoxyribose and Ribosome
There is a extra single Oxygen in the Ribosome
What makes each cell type unique?
Its structure and the genes it expresses.
Do all cells have the same organelles?
Yes, but their structures differ to suit unique functions.
In the cell membrane, what do hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails do?
Hydrophilic heads face water; hydrophobic tails hide inside the bilayer.
What do channel proteins do?
Move substances with the concentration gradient, no ATP needed.
What do pump proteins do?
Move substances against the concentration gradient, require ATP.
What do adhesion proteins do?
Link cells together and form organ/tissue structure.
What do receptor proteins do?
Allow cells to communicate (immune & endocrine signaling).
What is cytosol?
Jelly-like fluid that fills the cell, suspending organelles.
What is cytoplasm?
Cytosol + all organelles except the nucleus.
How many chromosomes are in the human nucleus?
23 pairs (46 total).