toxins quick flashcards
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what are toxins
substances created by plants and animals that are poisonous to humans
produced for predation and defence
what are cyanotoxins
produced by cyanobacteria
(cyclic peptides, alkaloids and lipopolysaccharides)
what are hemotoxins
target and destroy red blood cells
transmitted through the blood stream
what are necrotoxins
cause necrosis (ie death) in the cells they encounter
destroy all types of tissues
what are neurotoxins
primarily affect the nervous systems of animals
what are cytotoxins
are toxic at the level of individual cells, either in a non-specific fashion or only in certain types of living cells
what is apitoxin
honey bee vneom
what are mycotoxins
toxins produced by fungi
what does alpha-amanitin target
targets RNA polymerase II (essential for transcription)
alpha-amanitin binds near the bridge helix of the the enzyme (hydrogen bonds)
hydrogen bonding plays crucical role (e.g hydroxyproline 2 & glu-A822)
what does the binding of alpha-amanitin do
disruption of helix bridge movement
slows down translocation (mvmt along DNA), halting gene expression
what is proamanullin
lacks the key hydroxyl groups involved in hydrogen bonding to bridge helix residue
is ~20,000 times less effective than alpha-amanitin
what is batrachotoxin
member of steroidal alkaloids called batrachotoxins
first discovered in frogs
how does batrachotoxin work
binds and irreversibly opens voltage-gated sodium channels
may bind within the pore of the channel
activity depends on temperature, max 37 degrees
where does batrachotoxin’s electrostatic interactin tkae place
electrostatic interaction between BTX’s protonated tertiary amine and aromatic phenylalanine residues on the sodium channel
what is aromatic-aromatic interactions
attractive, non covalent interactions between aromatic rings
partially pos charged hydrogen atoms on edge of one ring interacts with pi face of another ring
what are the different geometrys of aromatic-aromatic interactions
Sandwich config maximizes overlap of pi system and is LEAST STABLE
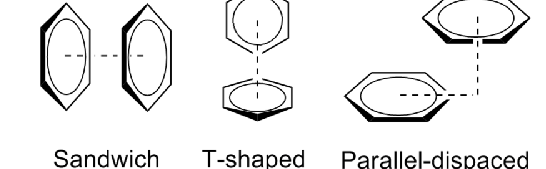
what are cation pi interactions
pos charged species bind to pi electron rich regions of aromatics
key in enzyme-substrate or toxin-protein interactions

in proteins, phenylalanine, tyrosine and trptophan are very effective at stabilizing pos charged reaction substrates or intermediates. the aromatic side chains are hydrophobic and cation stabilizing
what are van der waals forces
transient dipoles from fluctuation electron clouds create weak attractions
attraction between two oppositely oreineted dipoles
what are hydrophpobic interactions
non polar molecules cluster together, esp in aqueous environments (eg protein folding)
hydrophobic interactions in proteins
as protein folds, amino acid with a hydrophobic side chain are packed inside the structure, away from the surrounding water molecules
eg ALANINE, LEUCINE, PHENYLALANINE
what is a possible treatment for batrachotoxin
using tetrodotoxin (non competitive inhibitor) or saxitotoxin
both have antagonistic effects to batrachotoxin on sodium flux