1.4 - Malignant Bone Tumors
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Tumor
_____ = neoplasm = erratic growth
Benign
Will not kill the patient
Malignant
Will kill the patient if untreated
- Malignancy
- Carcinoma
- Sarcoma
- Aggressive
Primary malignant
Primary site in bone
Metastasis
Primary spreads to other location
Skeletal metastasis
Spreads to bone
- Osteoid osteoma
- Osteochondroma
- Osteoblastoma
State the benign osseous tumors
Osteosarcoma
State the malignant osseous tumors
- Chondroblastoma
- Enchondroma
- Osteochondroma
State the benign cartilaginous tumors
Chondrosarcoma
State the malignant cartilaginous tumors
- Fibroma
- Non-ossifying fibroma
State the benign fibrous tumors
Fibrosarcoma
State the malignant fibrous tumors
Lipoma
State the benign fat tumors
Liposarcoma
State the malignant fat tumors
Skeletal metastasis
_____ is the most common malignant tumor
Extraskeletal sites
Skeletal metastasis arises from primary _____
- Breast
- Lung
- Prostate
- Kidney
- Thyroid
- Bowel
20-35%
_____ of all patients with malignancy will get skeletal metastasis
- Often the cause of death
- Lesions tend to be multiple
- Solitary lesions in only 10% of cases
- Age 50-75
- Bone pain (nocturnal)
- Pathologic fracture
- History of cancer
- Unexplained weight loss
- Anemia
- Fever
- Soft tissue mass
- Deformity
State the clinical findings of skeletal metastasis
15
Metastases may occur _____ years later
- Pain is persistent
- Symptoms may be minimal
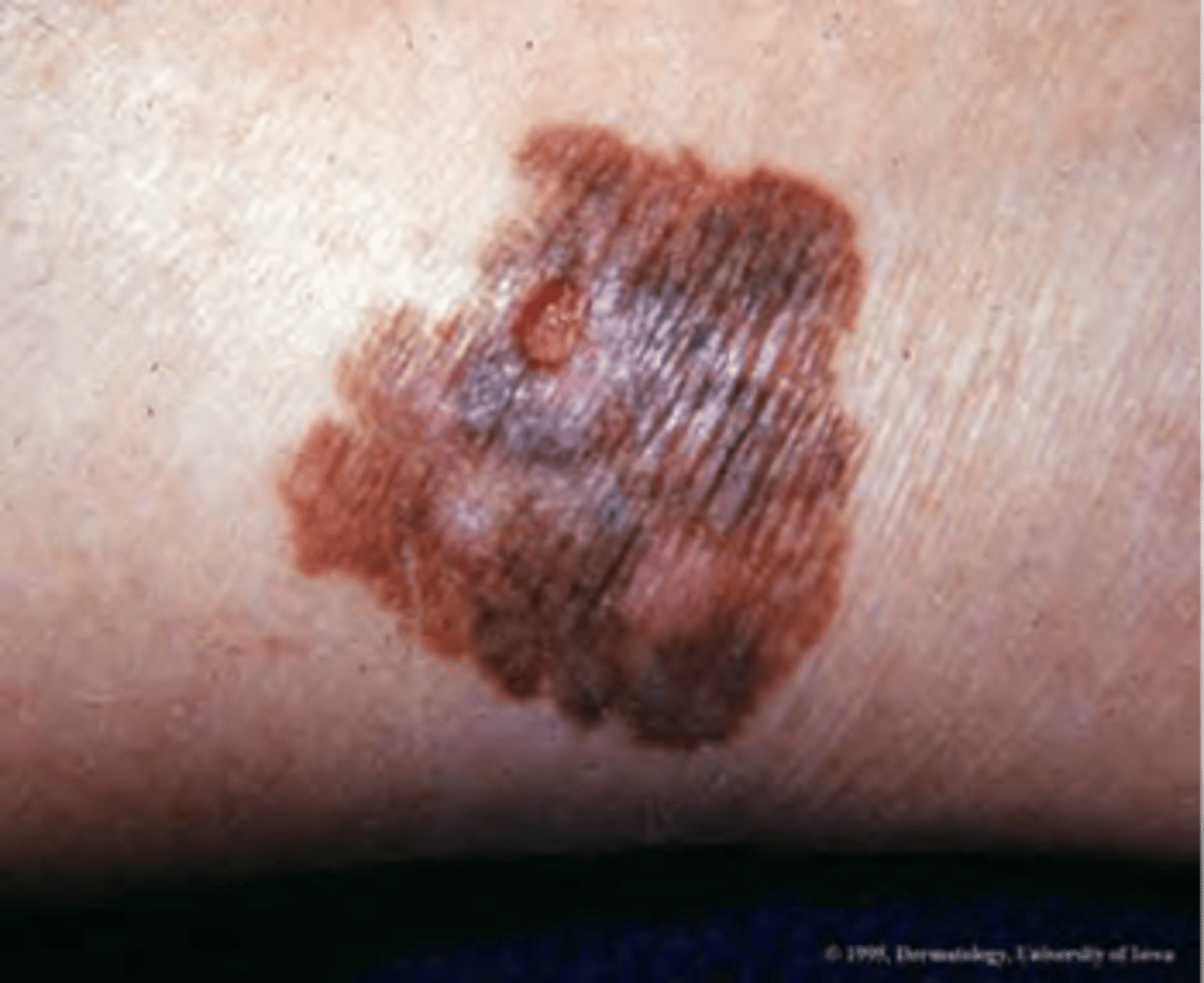
Malignant melanoma
ID skin cancer
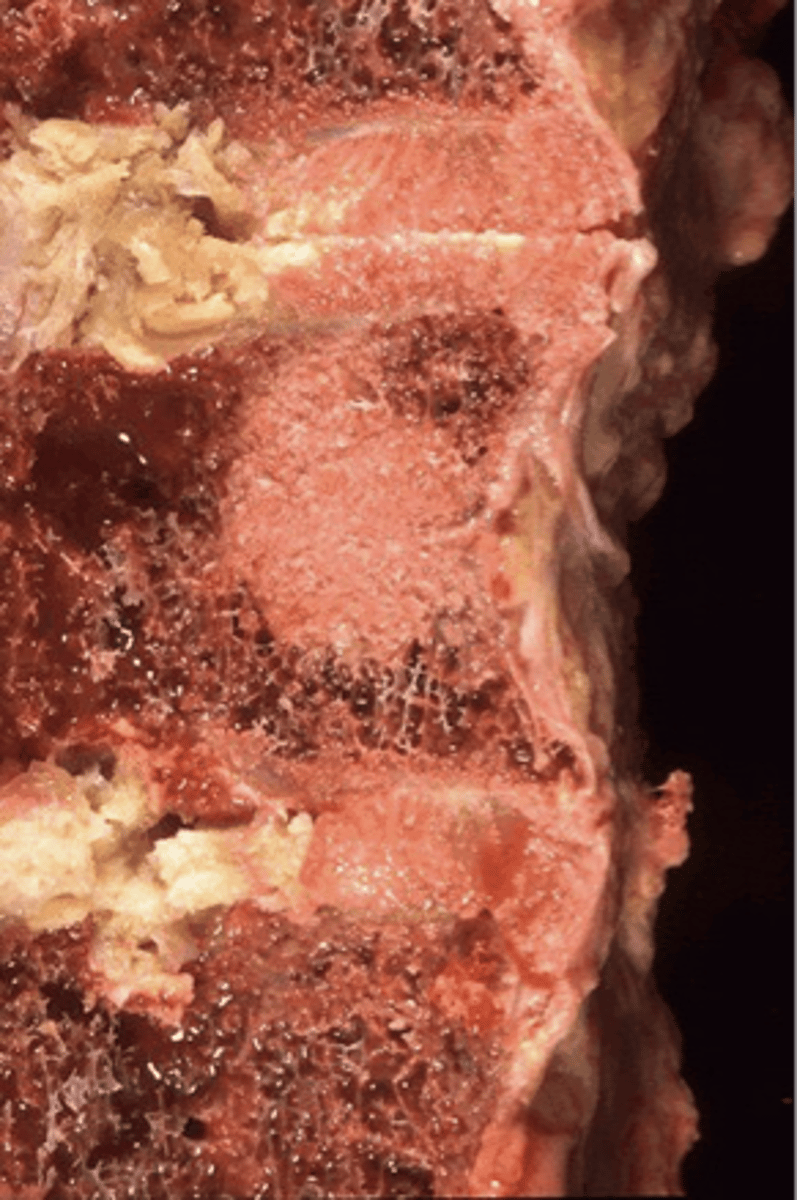
Osteolytic destruction
ID skeletal metastasis
Osteoblastic deposition
ID skeletal metastasis
Elevation of:
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Serum Calcium (lytic) (often normal)
- Alkaline Phosphatase (blastic)
- Acid Phosphatase (prostate)
- Prostate Specific Antigen (prostate)
State the laboratory findings of skeletal metastasis
- Hematogenous
- Direct
- Lymphatic
State the pathways of extension of skeletal metastasis
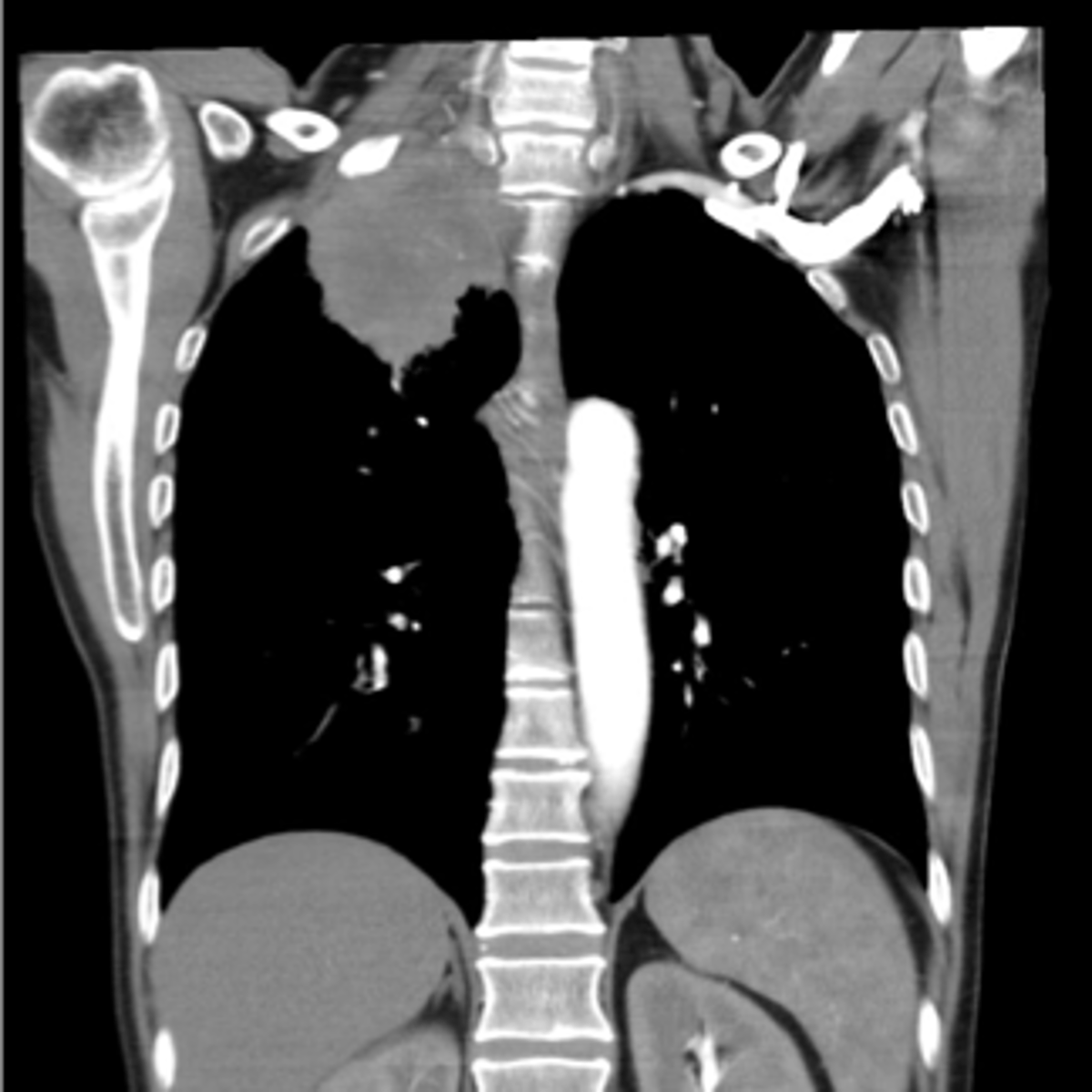
Hematogenous
What is the most common pathway of extension of skeletal metastasis?
Batson's venous plexus
Prostate cancer can metastasize to the lumbar spine via ____
- 75%
- 15%
- 10%
Skeletal metastasis radiologic patterns of disease
- Osteolytic = _____
- Osteoblastic = _____
- Mixed = _____
Osteolytic
ID radiologic pattern of disease
Osteoblastic
ID radiologic pattern of disease
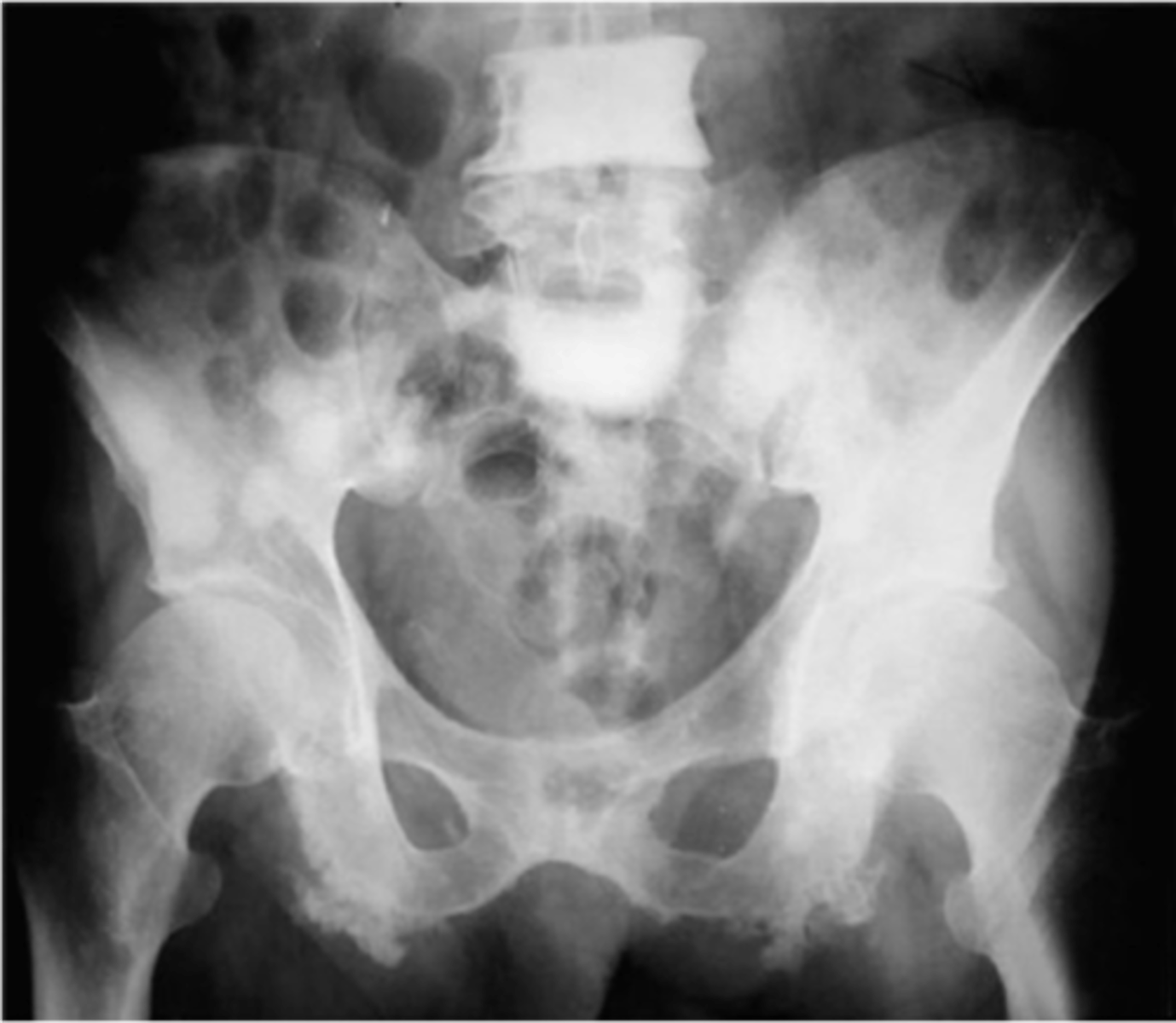
Mixed
ID radiologic pattern of disease
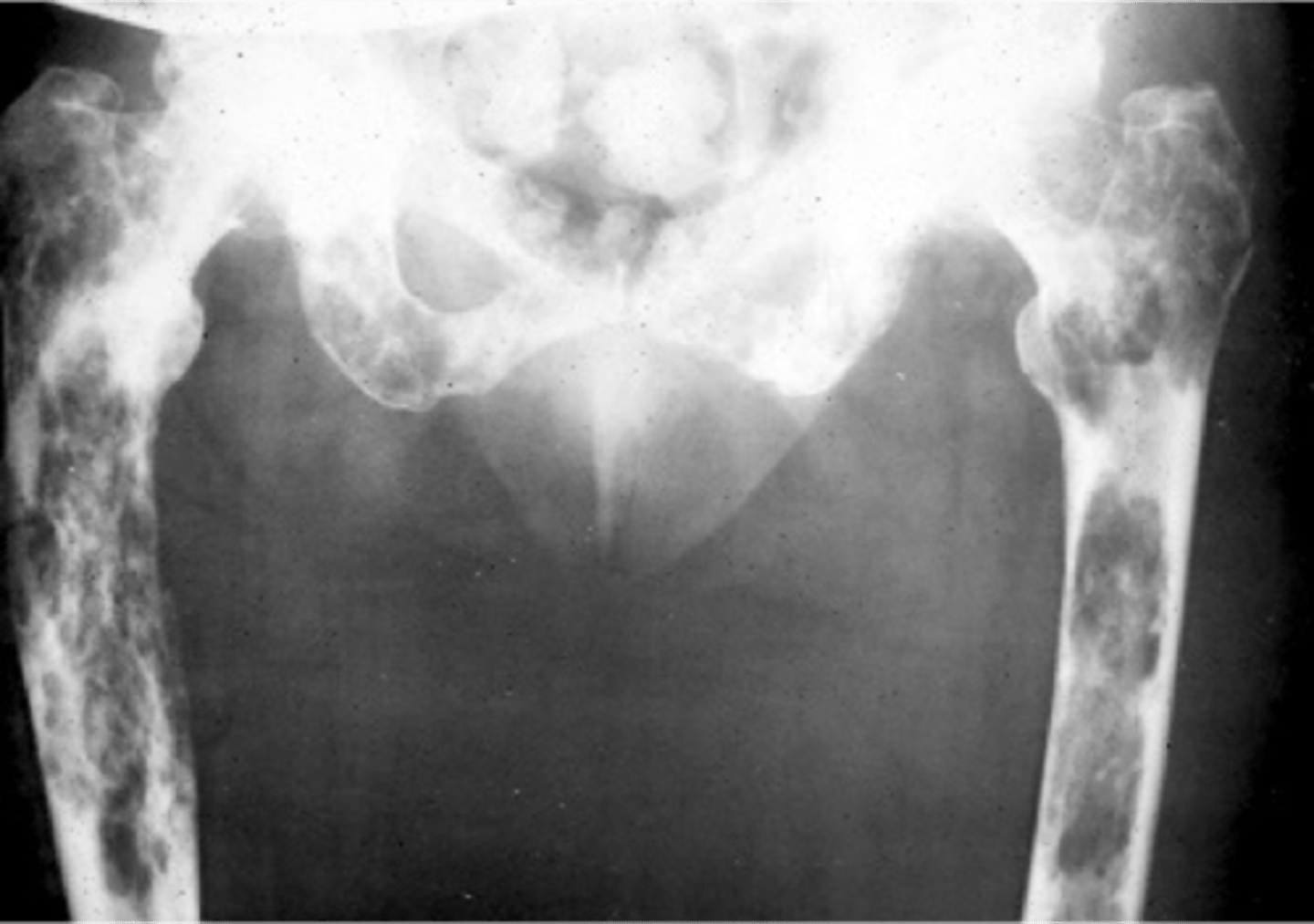
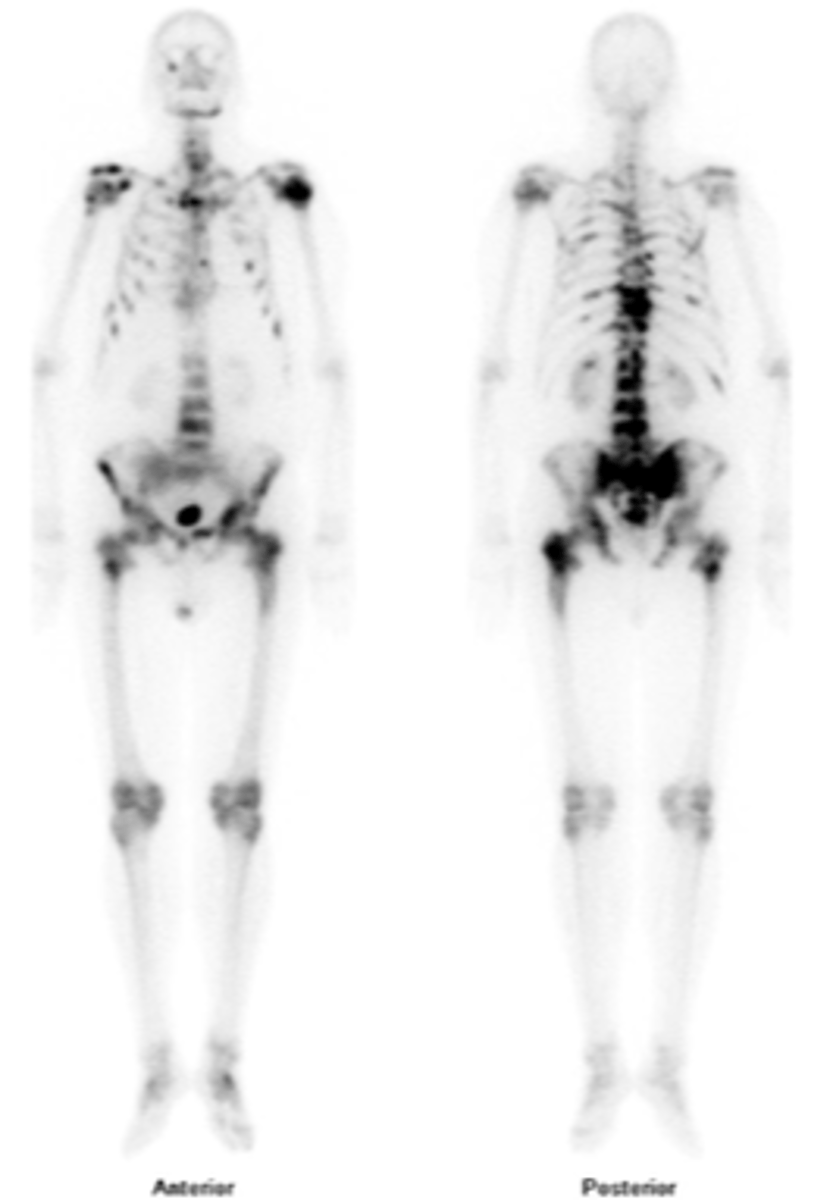
- Bone scan
- Radiography
- CT
- MR
State the imaging techniques for skeletal metastasis
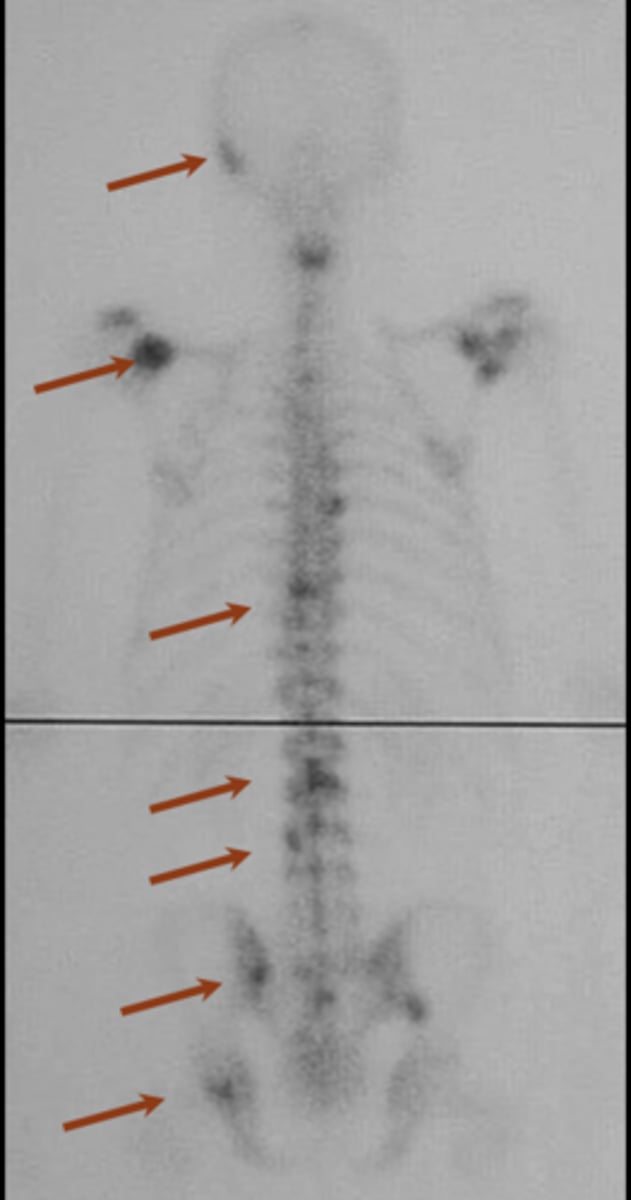
Bone scan
ID imaging technique
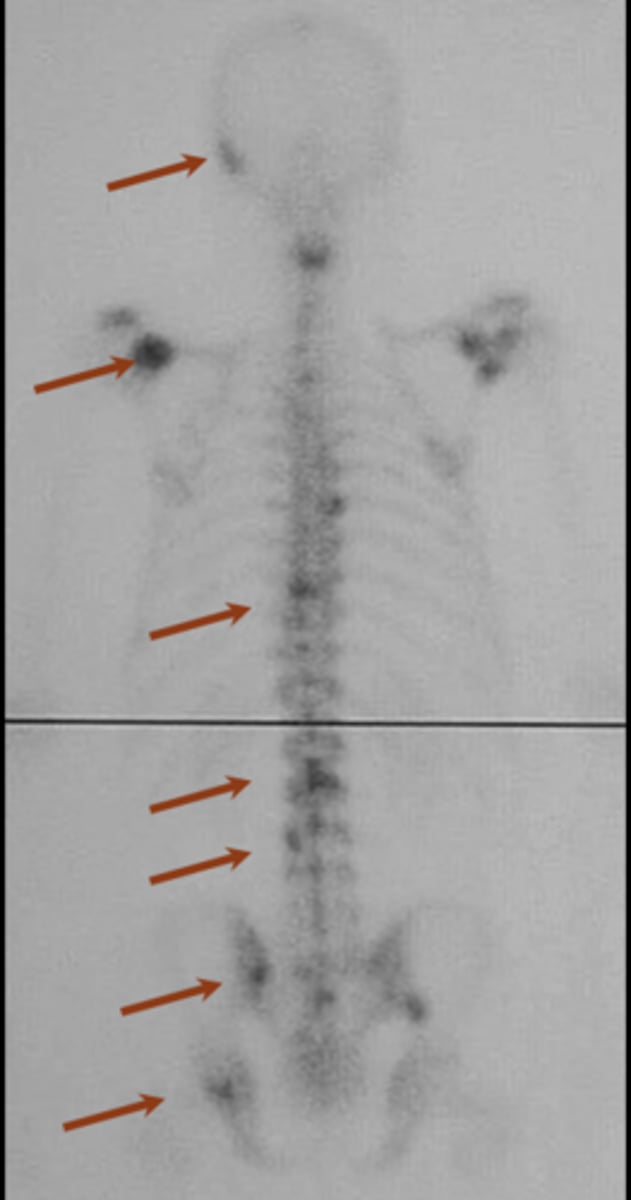
3-5%
Bone scans require _____ of destruction (highly sensitive)
Radiography
ID imaging technique
30-50%
Radiography requires _____ of destruction (insensitive)
CT
Used for sensitive/specific bone detail
MR
Used for sensitive/specific soft tissue and marrow
10%
_____ of skull lesions are blastic
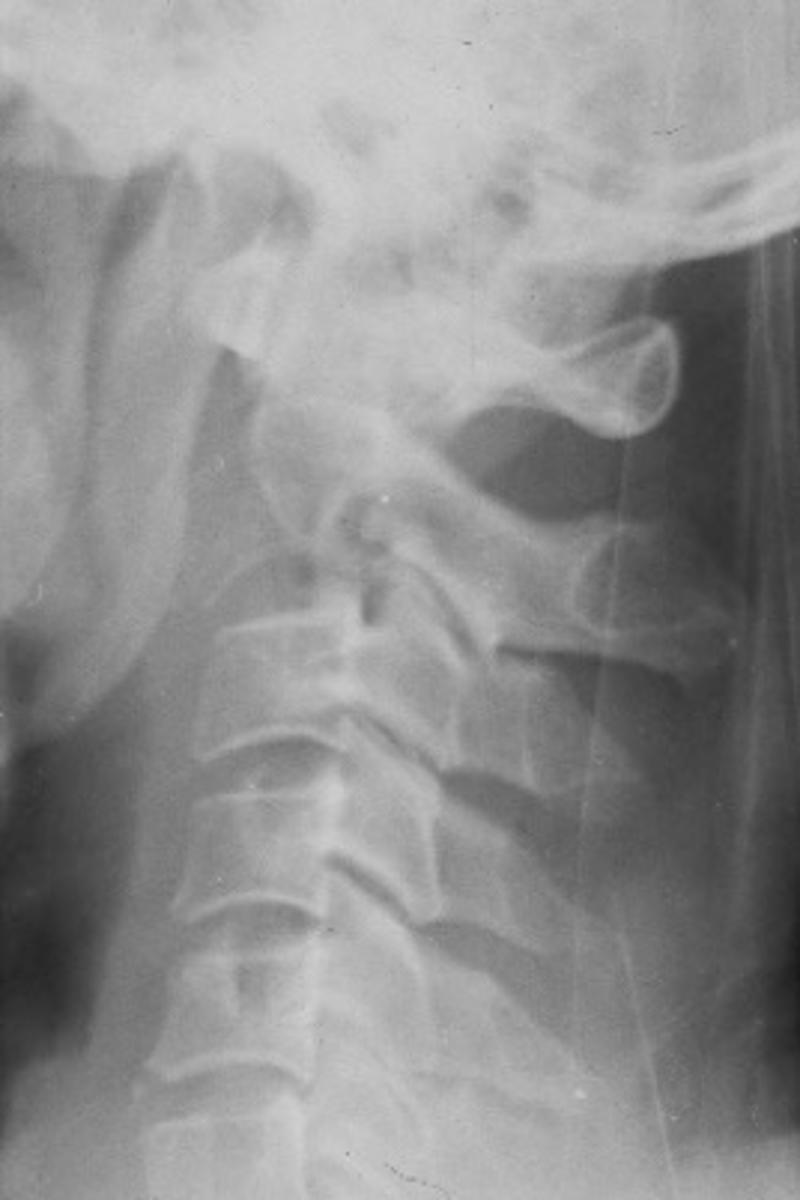
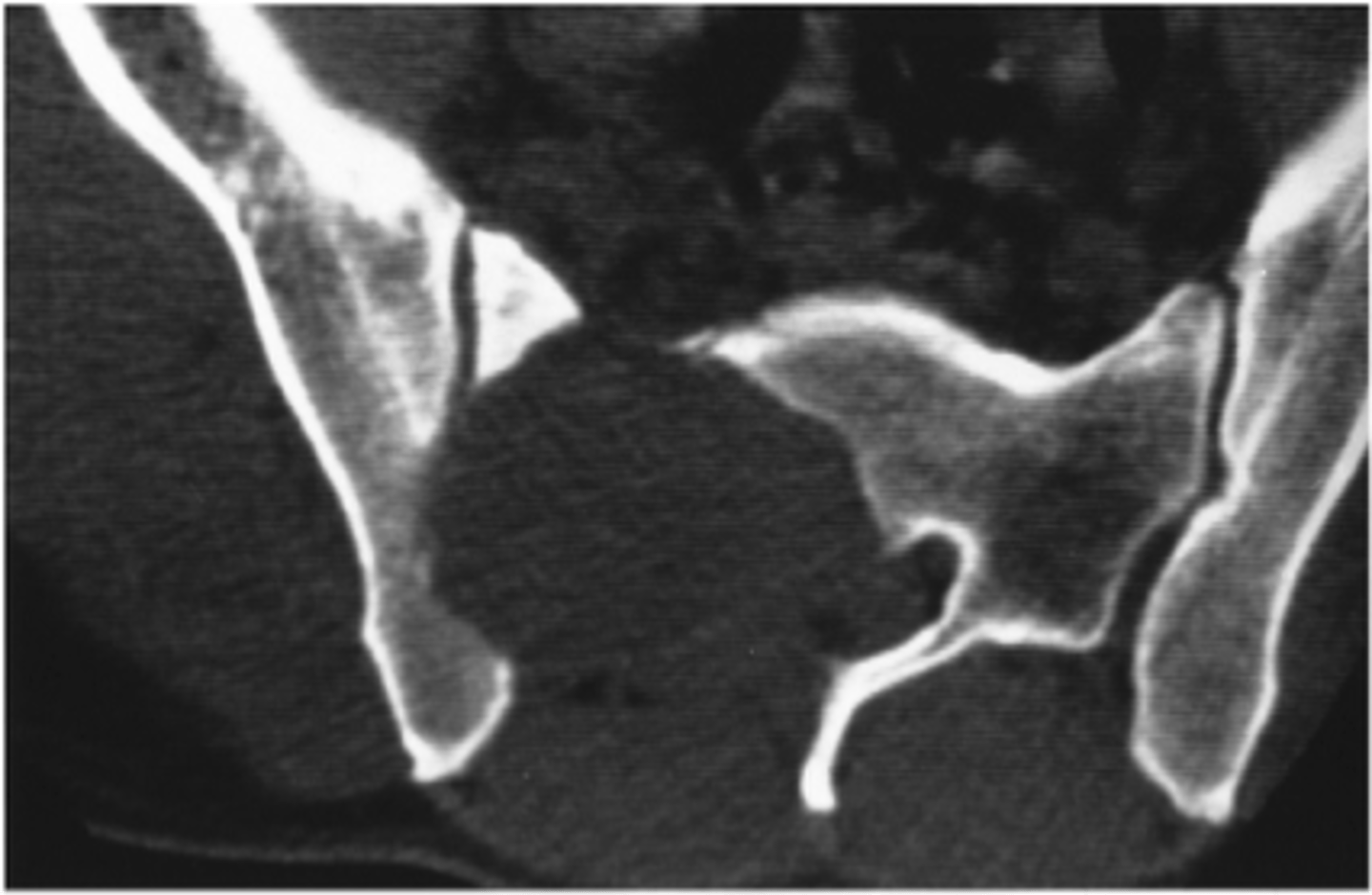
Winking owl sign
- Missing pedicle
- Soft tissue mass
- Vertebral body destruction
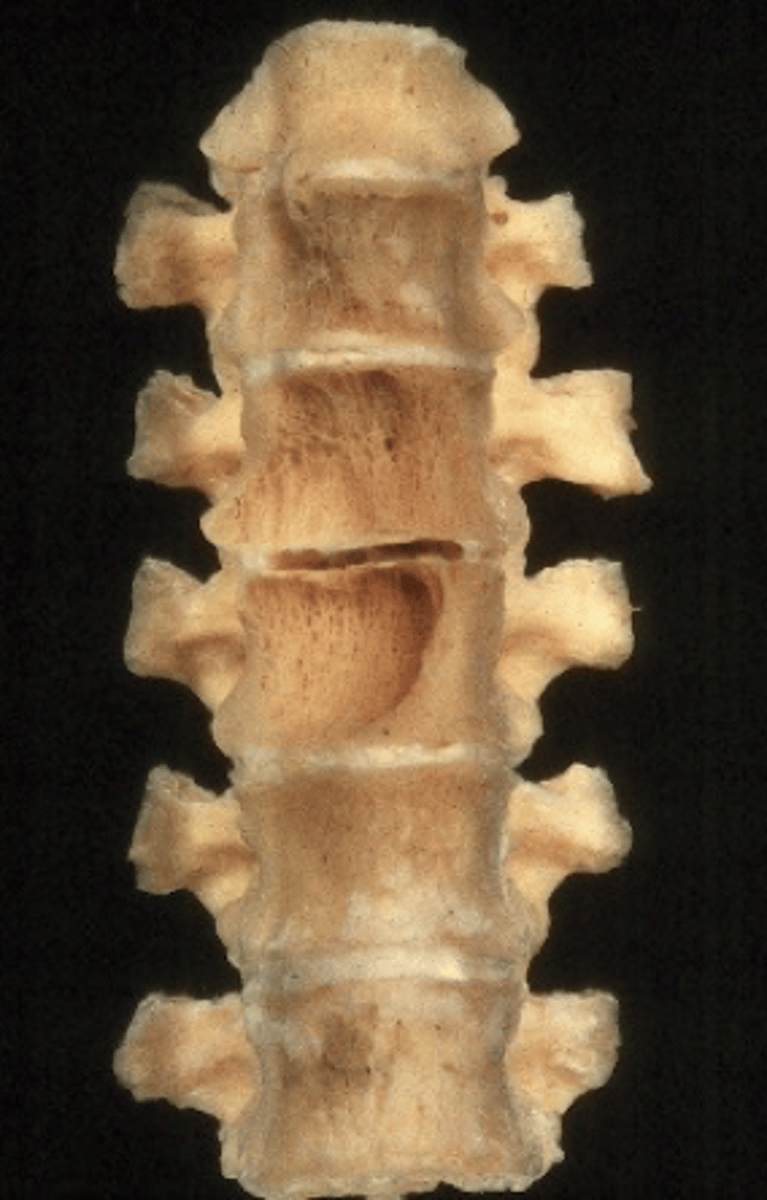
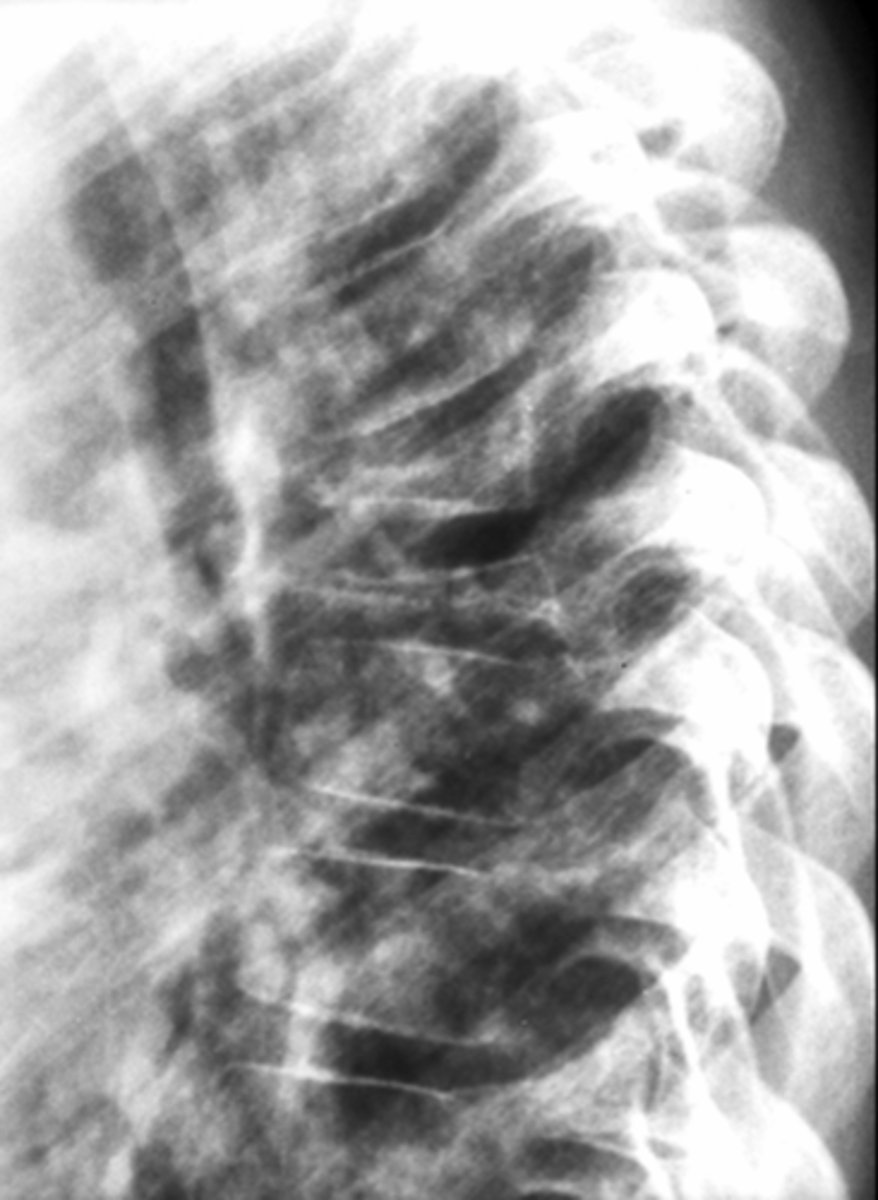
Vertebra plana
Pathologic vertebral body collapse
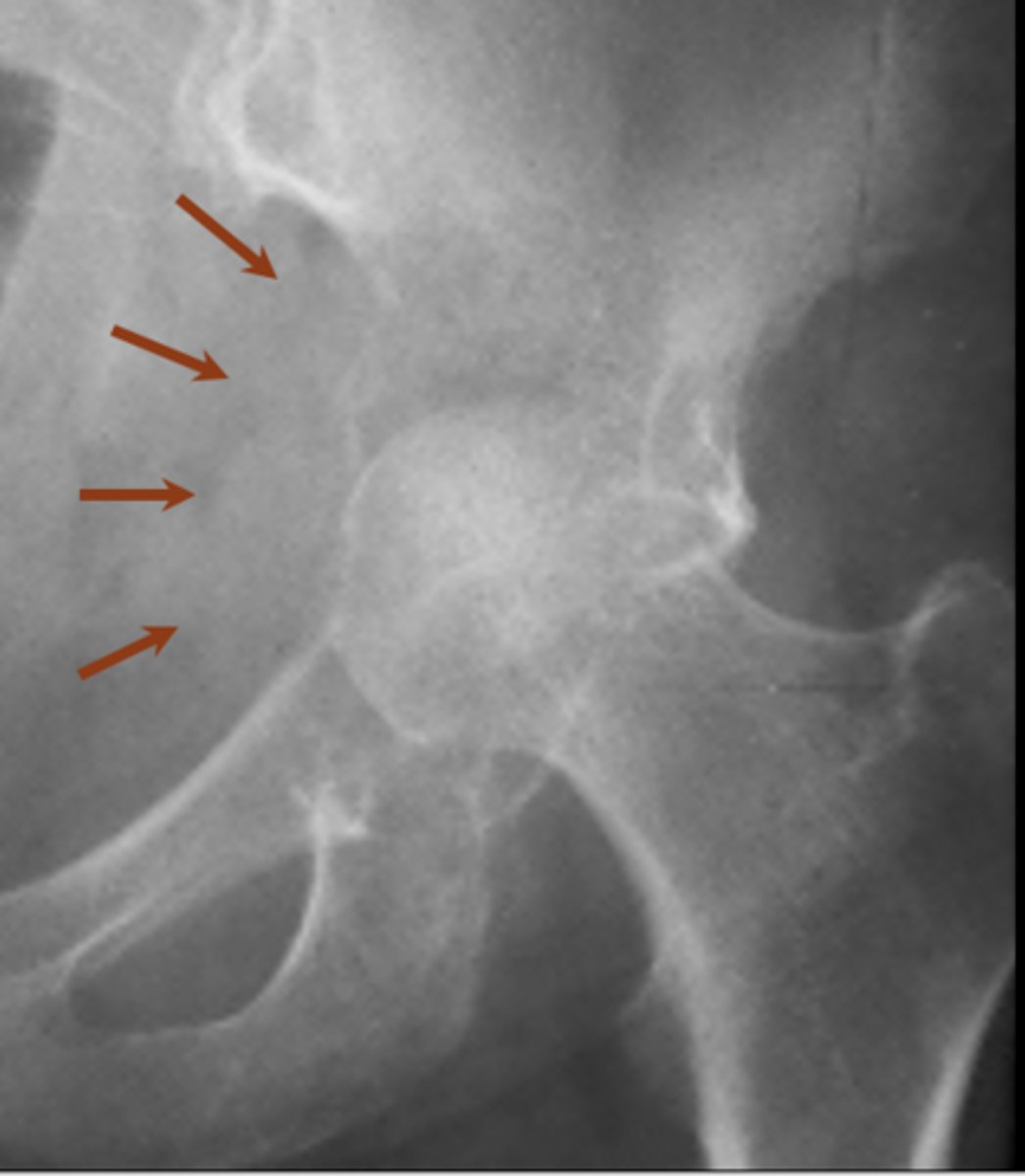
Renal cell carcinoma
Diagnosis?
- Missing inferior articular process
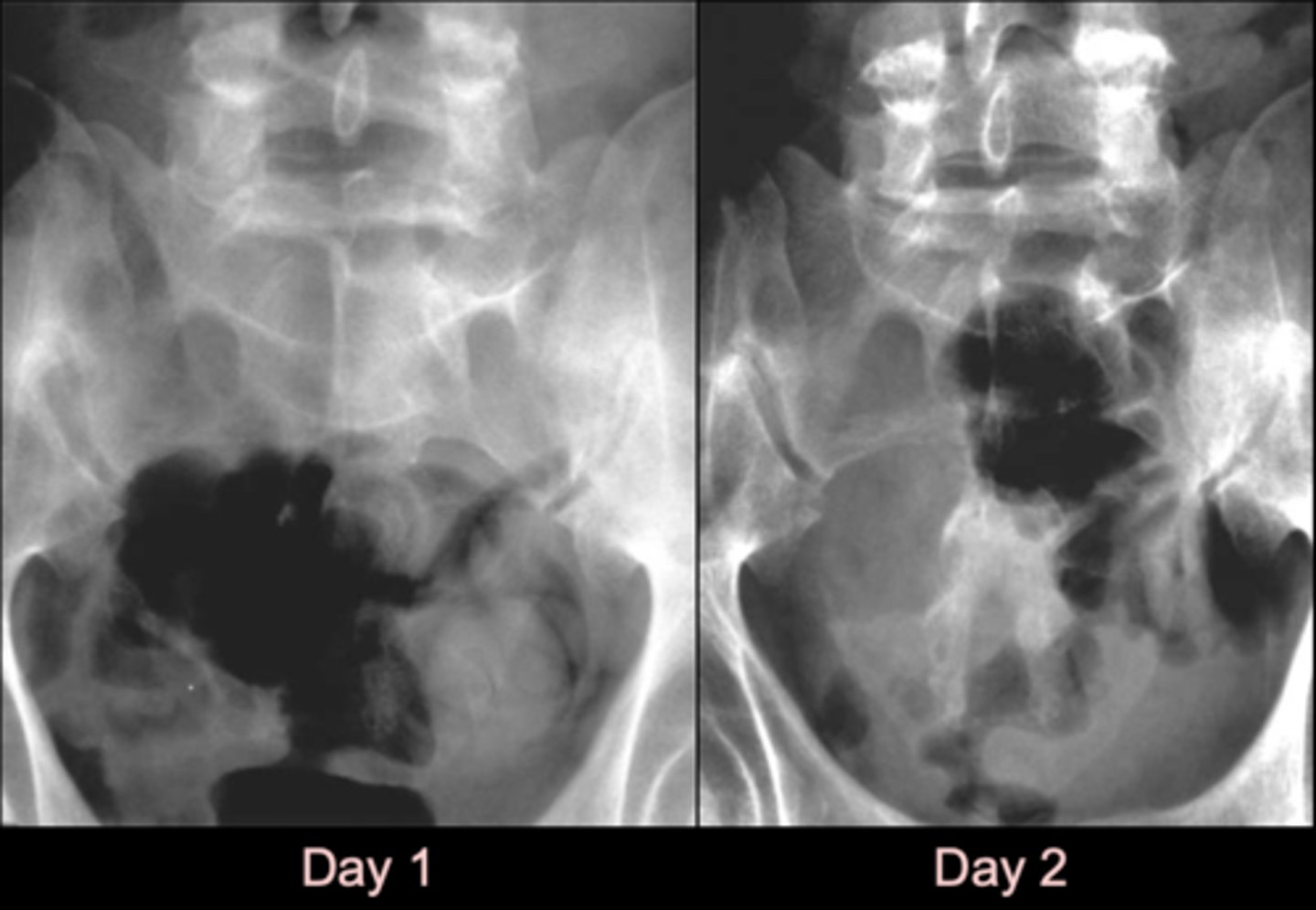
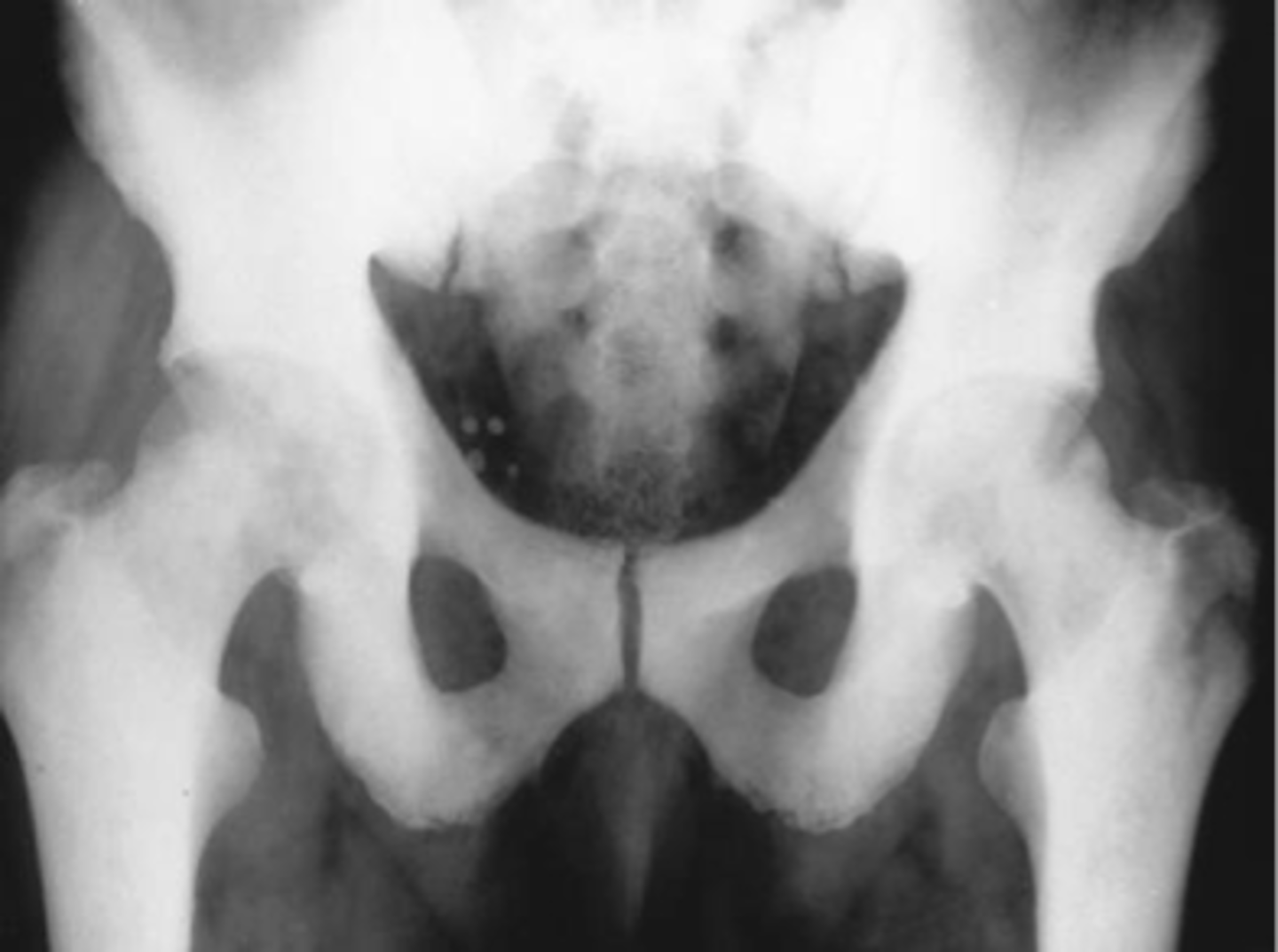
Diffuse
ID pelvic osteoblastic pattern
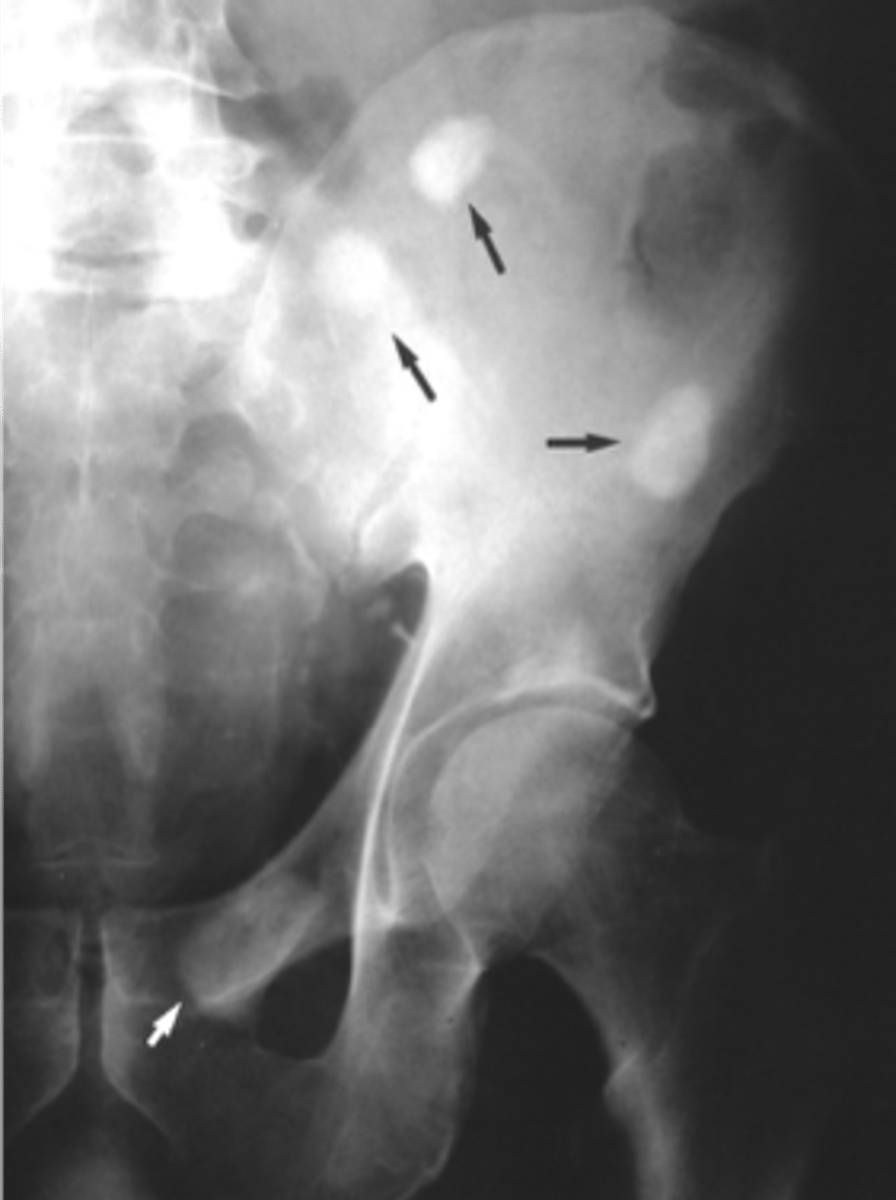
Punctate
ID pelvis osteoblastic pattern
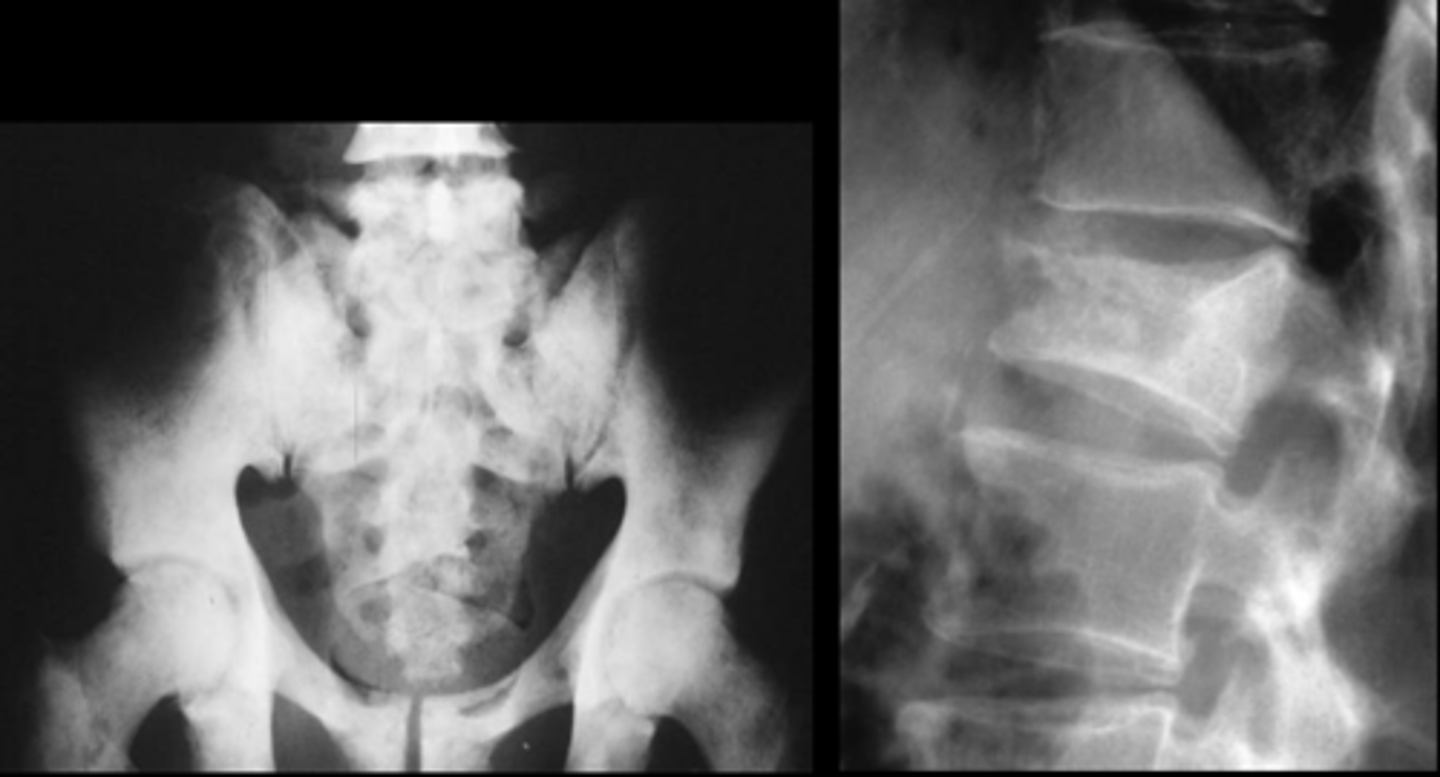
Prostate carcinoma
Diagnosis?
>45
Blastic metastasis age
+++
Blastic metastasis increased density
-
Blastic metastasis enlargement
-
Blastic metastasis anterior scalloping
+++
Blastic metastasis alkaline phosphatase
+++
Blastic metastasis PSA
>50
Paget Disease age
+++
Paget Disease increased density
+++
Paget Disease enlargement
-
Paget Disease anterior scalloping
+++
Paget Disease alkaline phosphatase
-
Paget Disease PSA
20-40
Hodgkin Lymphoma age
+++
Hodgkin Lymphoma increased density
-
Hodgkin Lymphoma enlargement
+++
Hodgkin Lymphoma anterior scalloping
++
Hodgkin Lymphoma alkaline phosphatase
-
Hodgkin Lymphoma PSA
- Renal
- Adrenal
- Thyroid
- Skin (melanoma)
Blow-out metastasis (RATS)
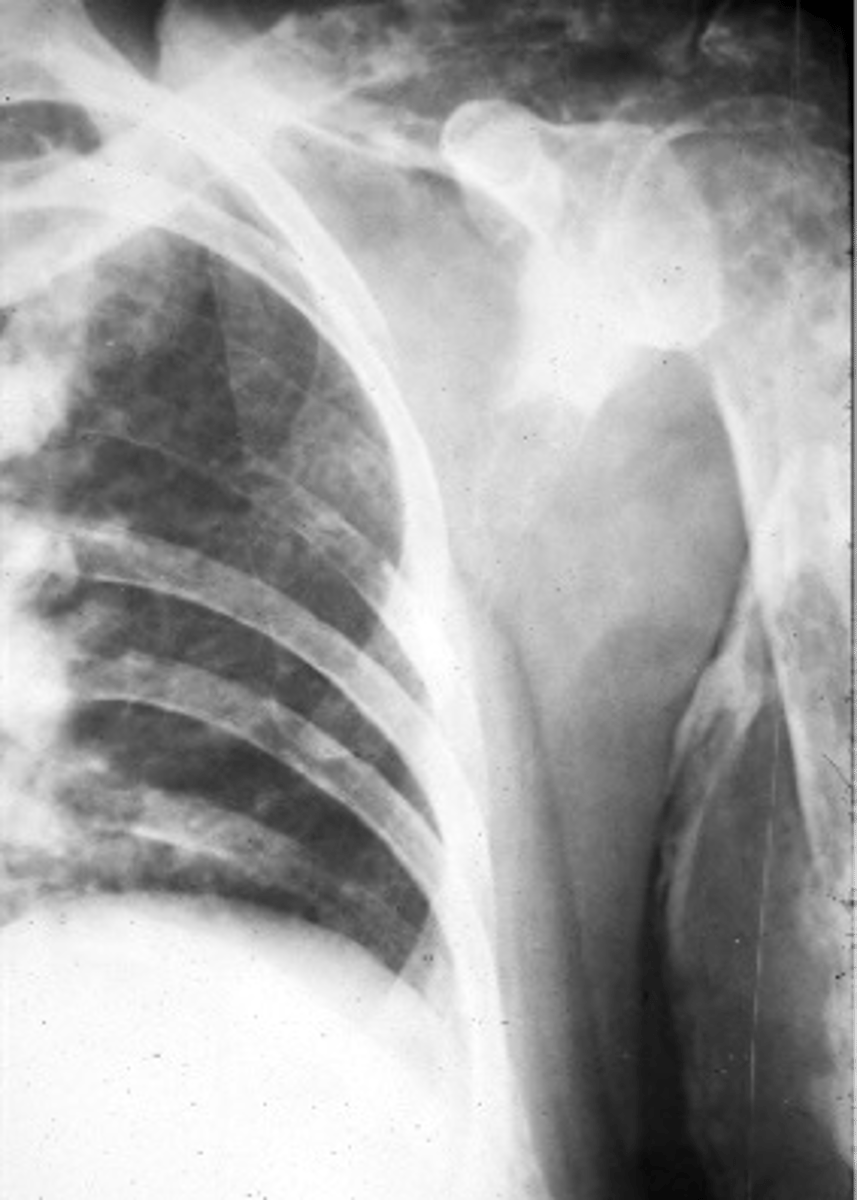
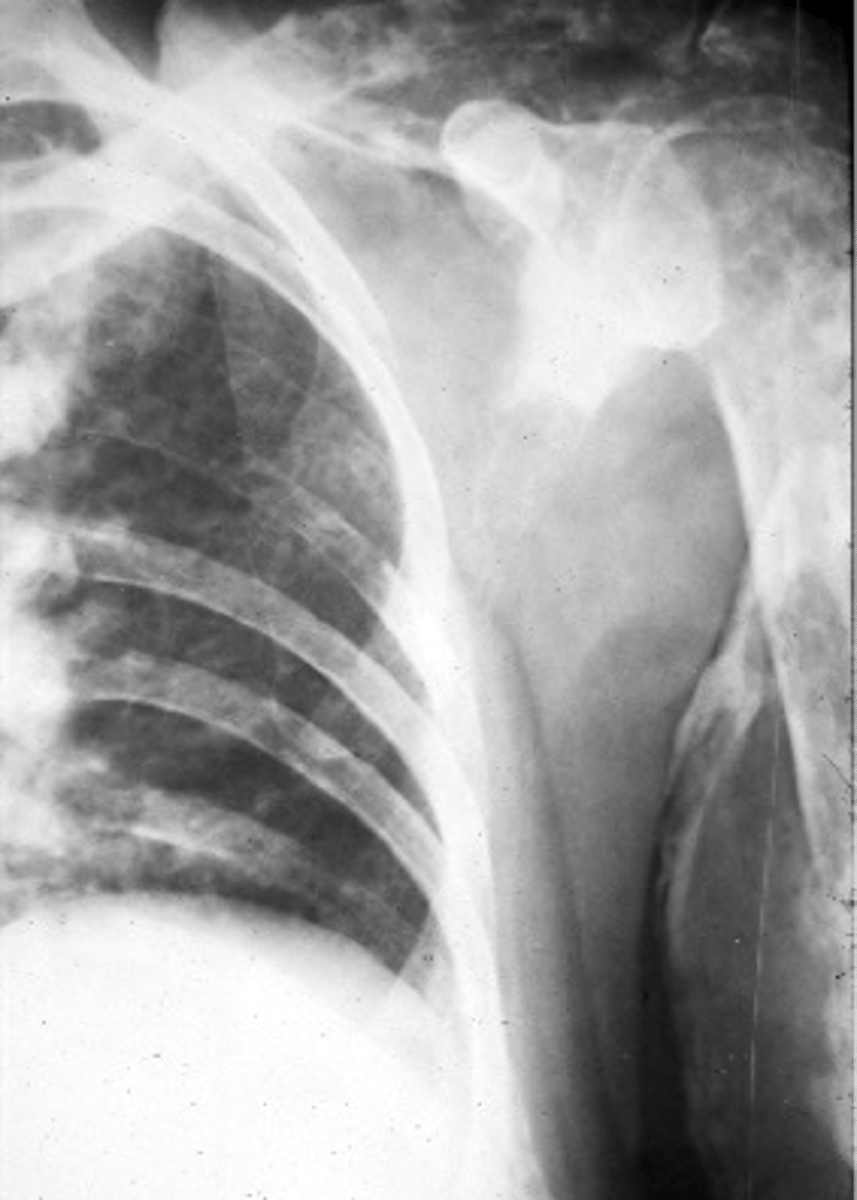
Pancoast tumor
- Lung cancer that occurs in the superior sulcus
- Bronchogenic carcinoma
- Rib and spine destruction
- Horner's syndrome
Multiple myeloma
Most common primary malignant tumor of bone
27%
Multiple myeloma accounts for _____ of biopsied bone tumors
10%
Multiple myeloma accounts for _____ of hematologic malignancies
- Age 50-70 (75%)
- M:F, 2:1
- Common in the black population
- Pathologic fractures
- Bone pain
- Weakness and fatigue
- Anemia
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Bleeding
State the clinical findings of multiple myeloma
Red
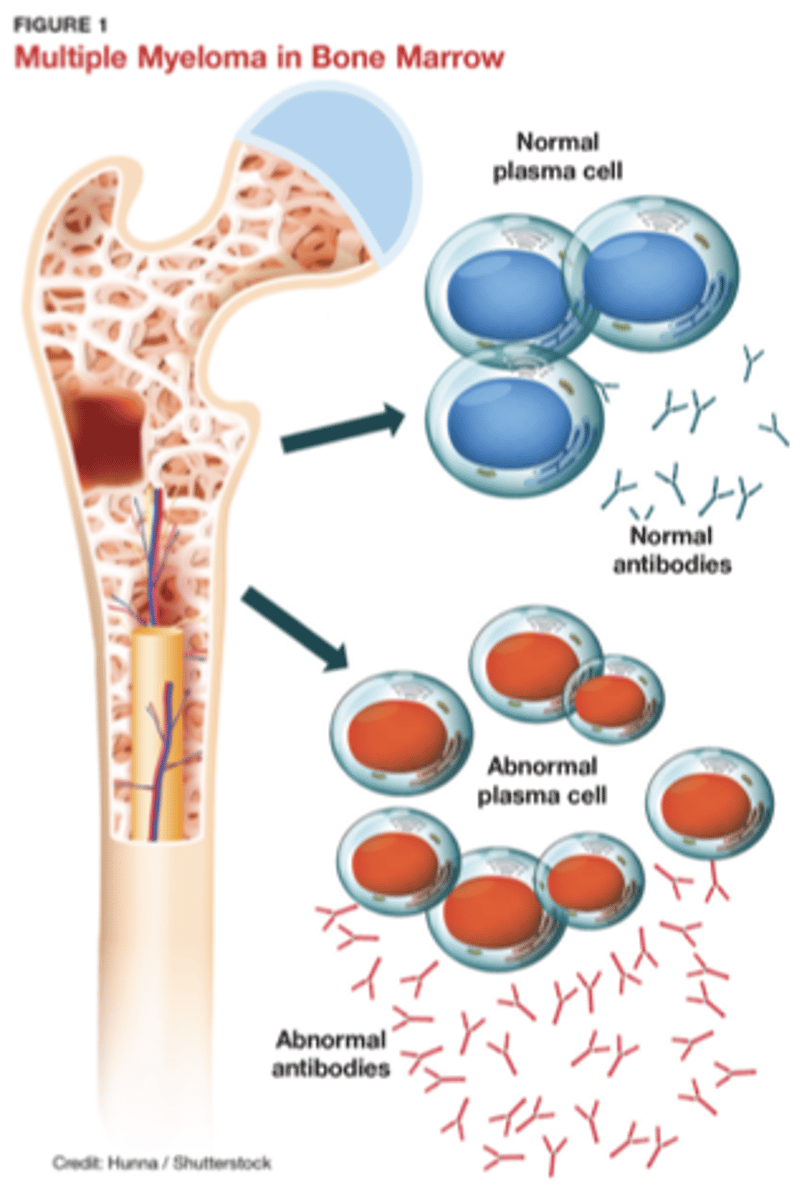
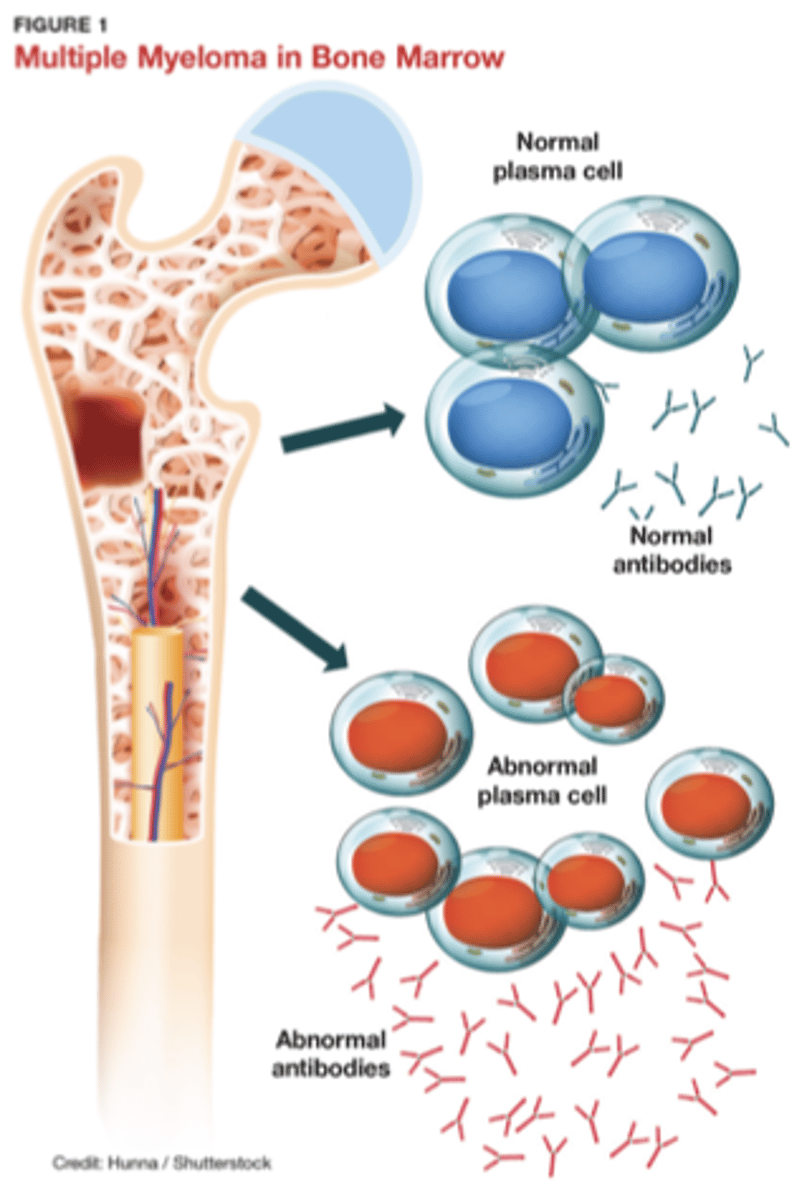
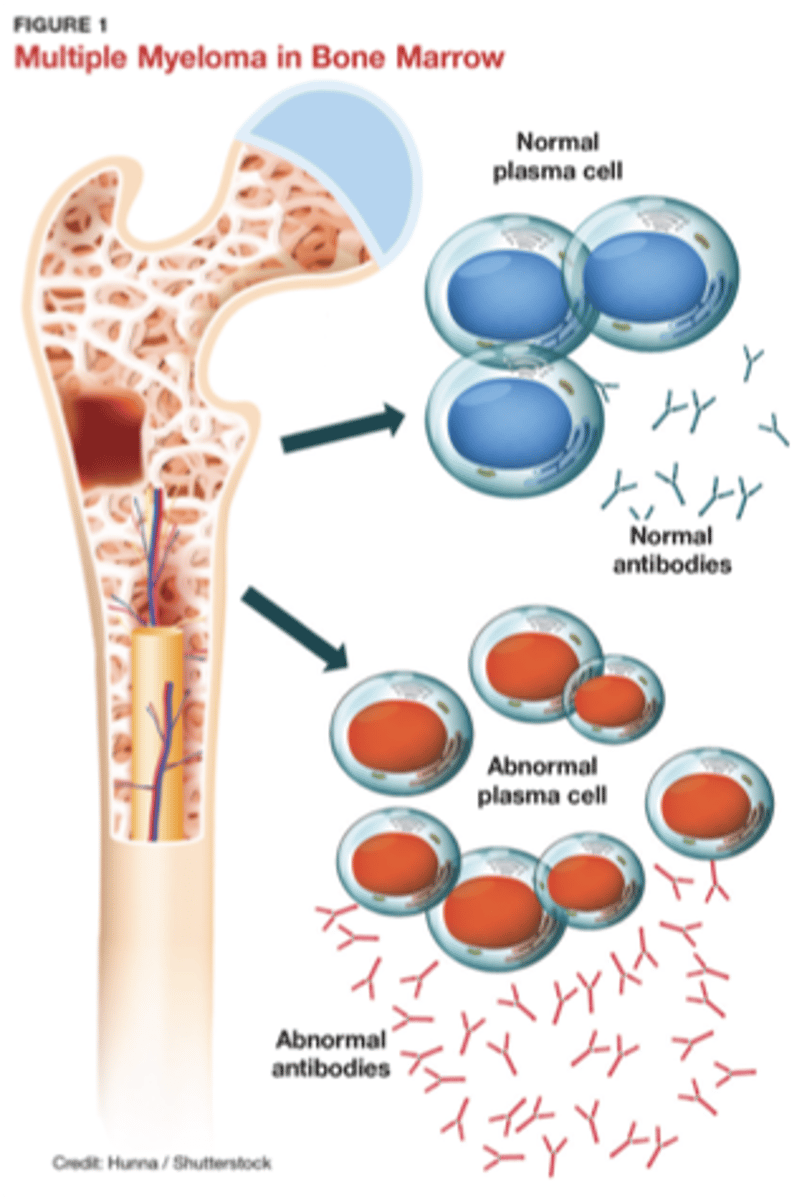
Plasma cells originate in _____ bone marrow
Antibodies
Plasma cells produce _____ (gammaglobulins - IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD)
Dyscrasia
Multiple myeloma is considered a plasma cell "_____"
Multiple myeloma
- Uncontrolled plasma cell and antibody production
- Local environment rich in inflammatory biochemistry
• Increased bone lysis
• Decreased bone production
- Normal radiographs
- Diffuse osteopenia
State the early imaging findings of multiple myeloma
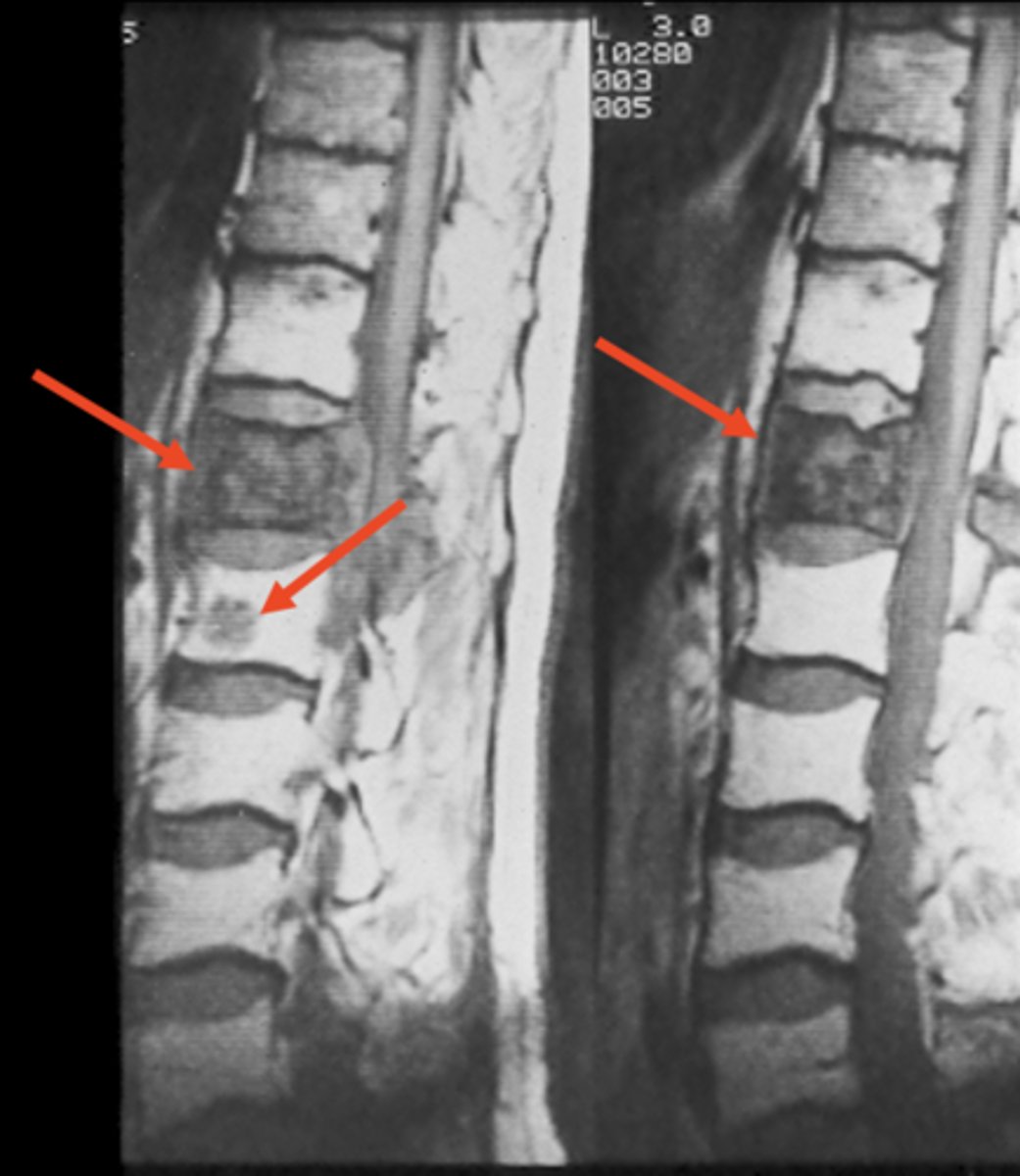
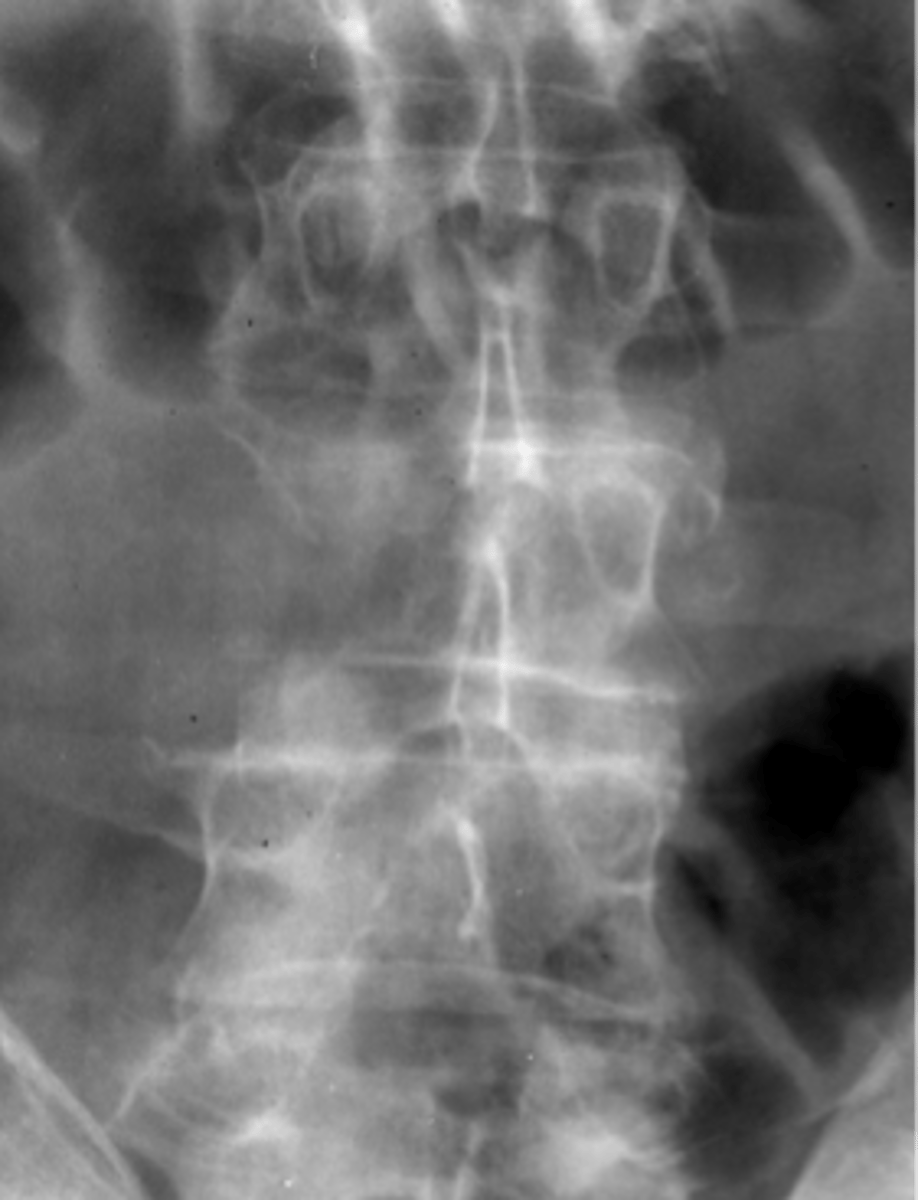
- Punched-out lucencies
- Vertebral collapse
- Diaphyseal osteolytic lesions
- Pedicles may be spared
- Bone scan often normal
State the late imaging findings of multiple myeloma
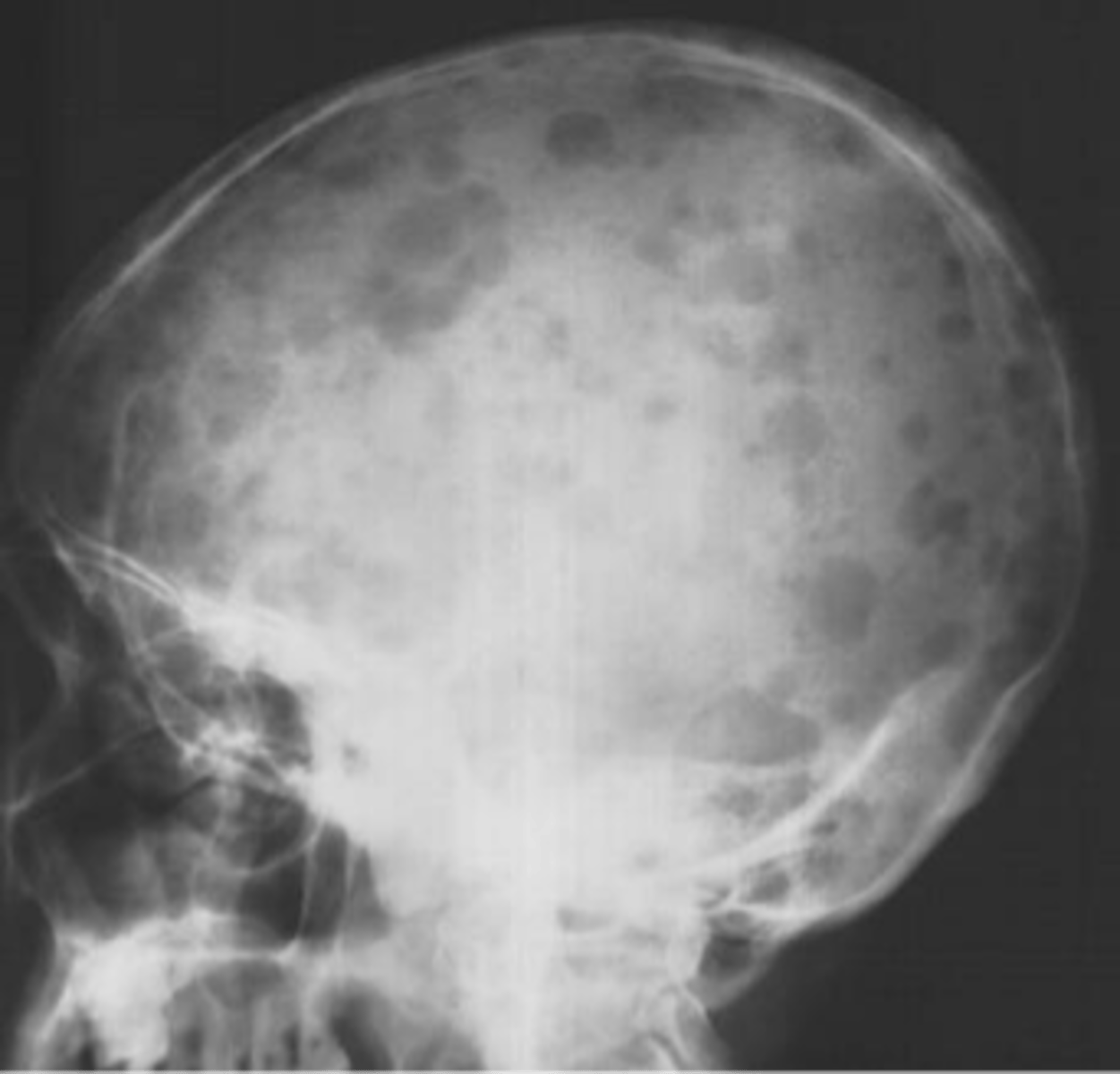
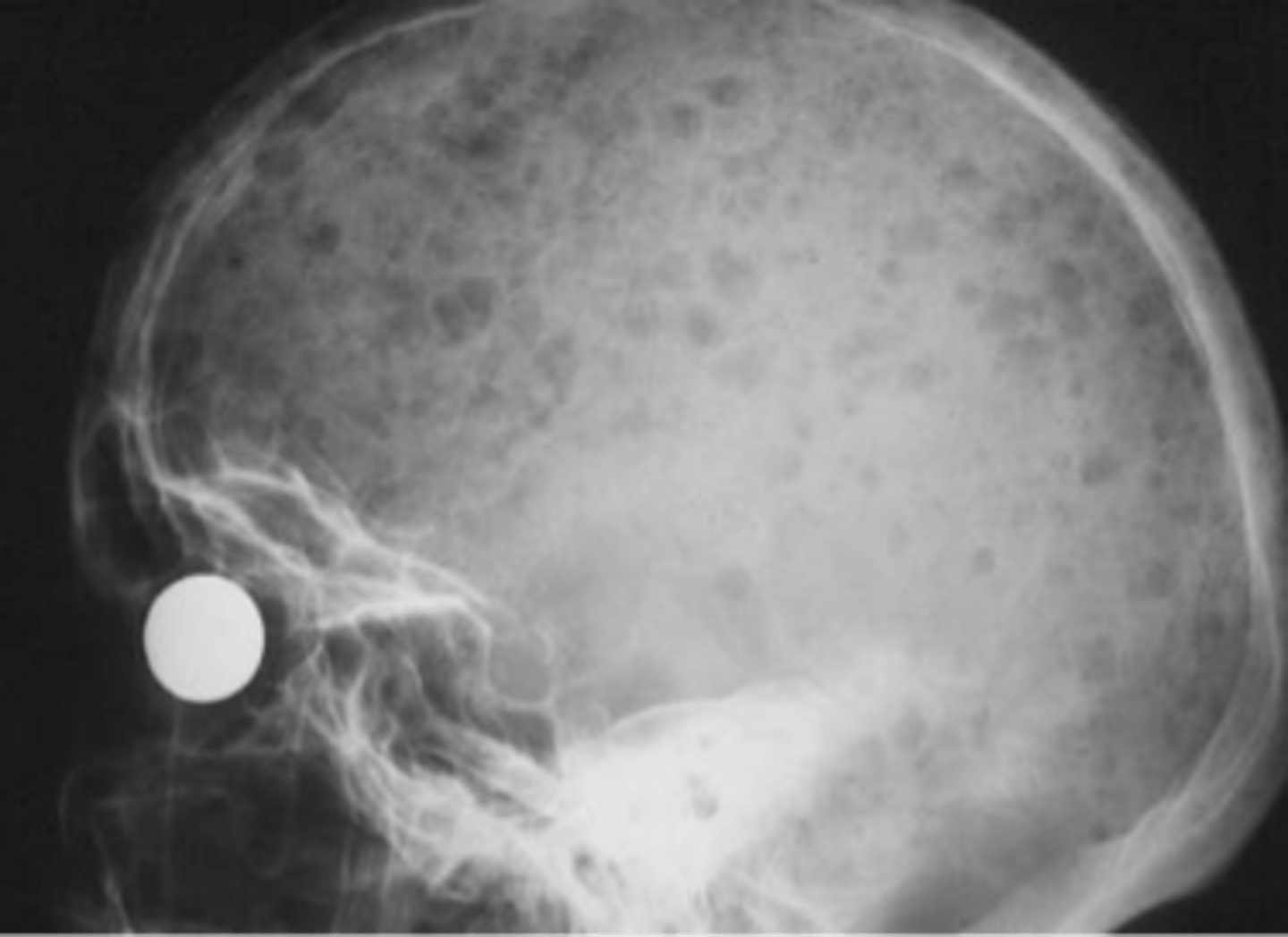
Raindrop skull
ID imaging finding of multiple myeloma
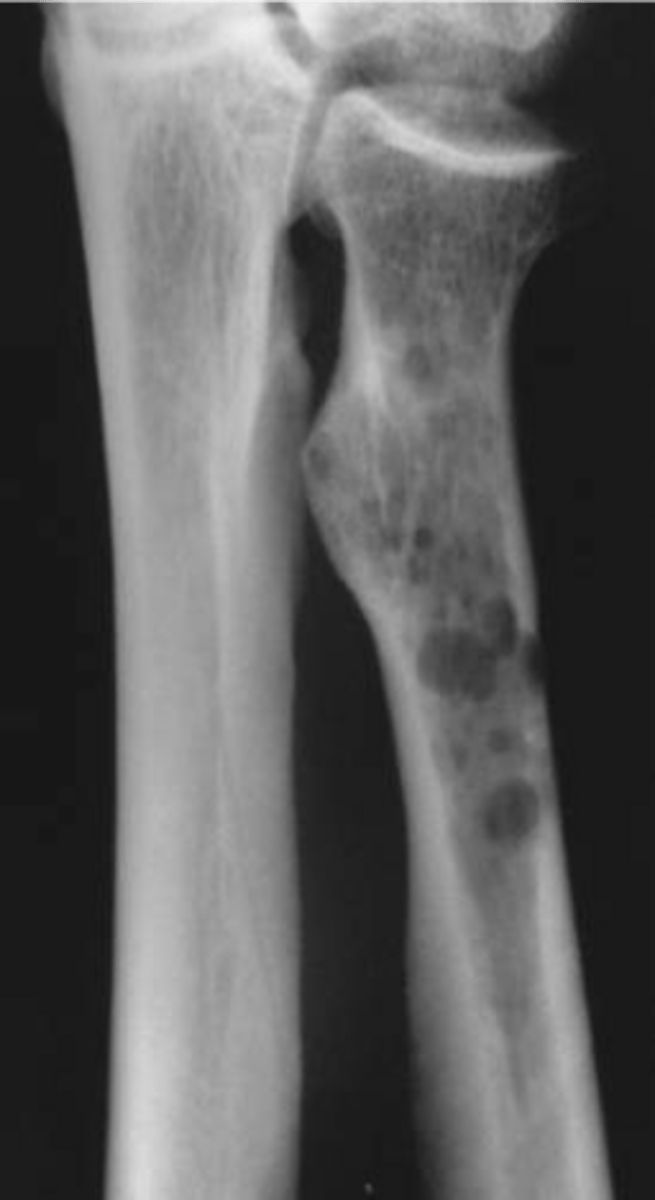
Hand involvement
ID imaging finding of multiple myeloma
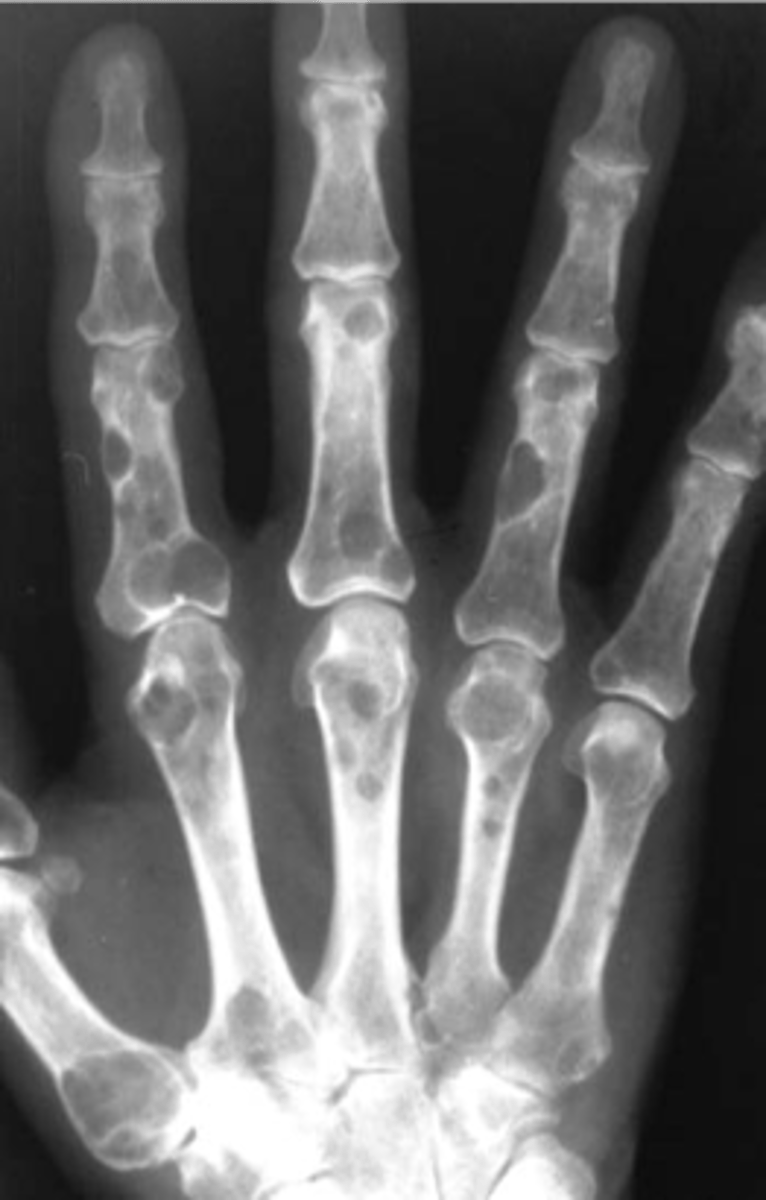
- Anemia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Hypercalcemia
- Elevated plasma proteins (reversed A:G ratio)
- Bence Jones proteinuria
- Hyperuricemia
State the lab findings of multiple myeloma
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Bone marrow transplant
- Thalidomide
State the treatments for multiple myeloma
90%
_____ of patients with multiple myeloma die within 3 years
Osteosarcoma
_____ is the 2nd most common primary malignant bone tumor
Kids
Osteosarcoma is the most common primary malignant bone tumor in _____
20%
Osteosarcoma accounts for _____ of all primary malignant bone tumors
- Age 10-25 (75%)
- M:F, 2:1
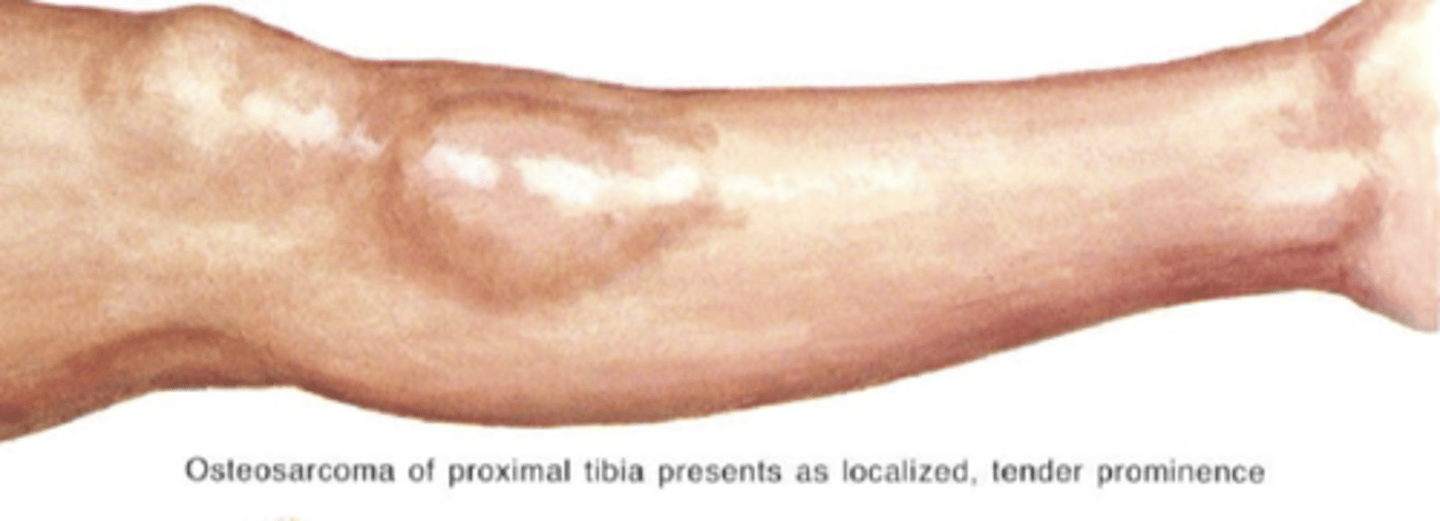
- Painful swelling of involved limb
- Metaphysis
- 3.5-7% occur in spine
- Elevated serum alkaline phosphatase
State the clinical findings of osteosarcoma
- 50%
- 25%
- 25%
Osteosarcoma pathology:
- Sclerotic: _____
- Lytic: _____
- Mixed: _____
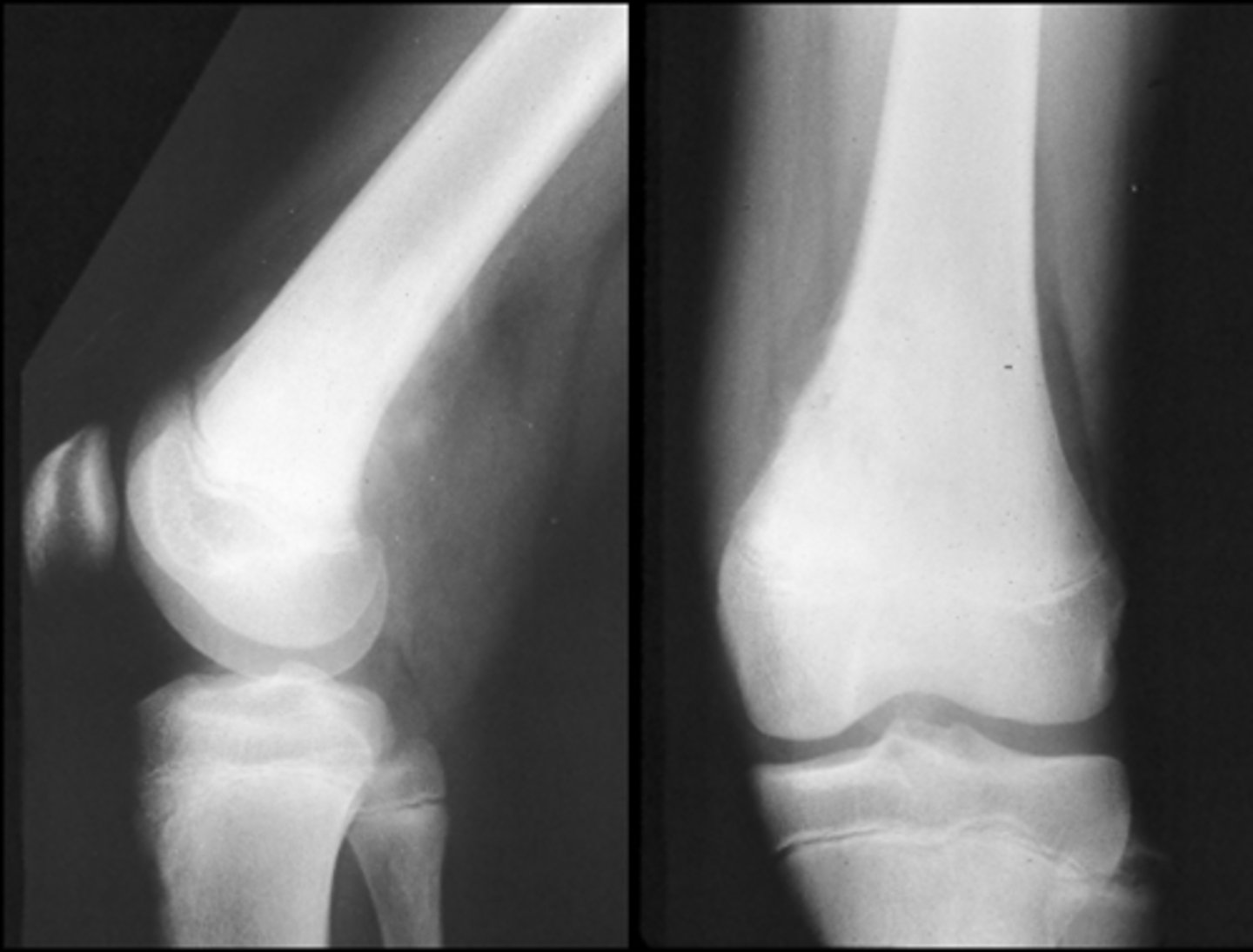
Osteosclerotic
ID type of osteosarcoma
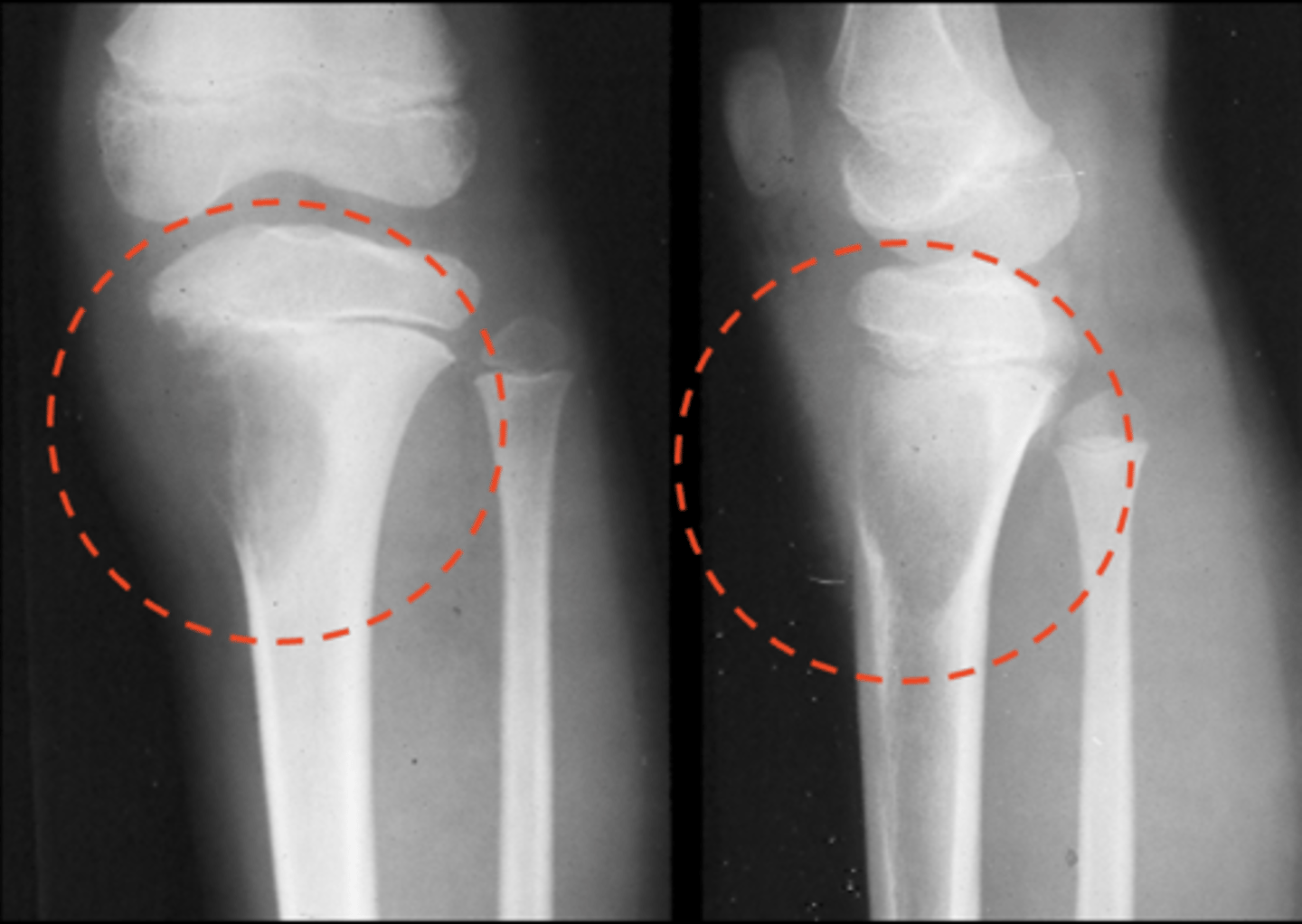
Osteolytic
ID type of osteosarcoma
80%
Osteosarcoma has an _____ survival rate
- Chemotherapy
- Amputation
- Limb salvage surgery
State osteosarcoma treatments
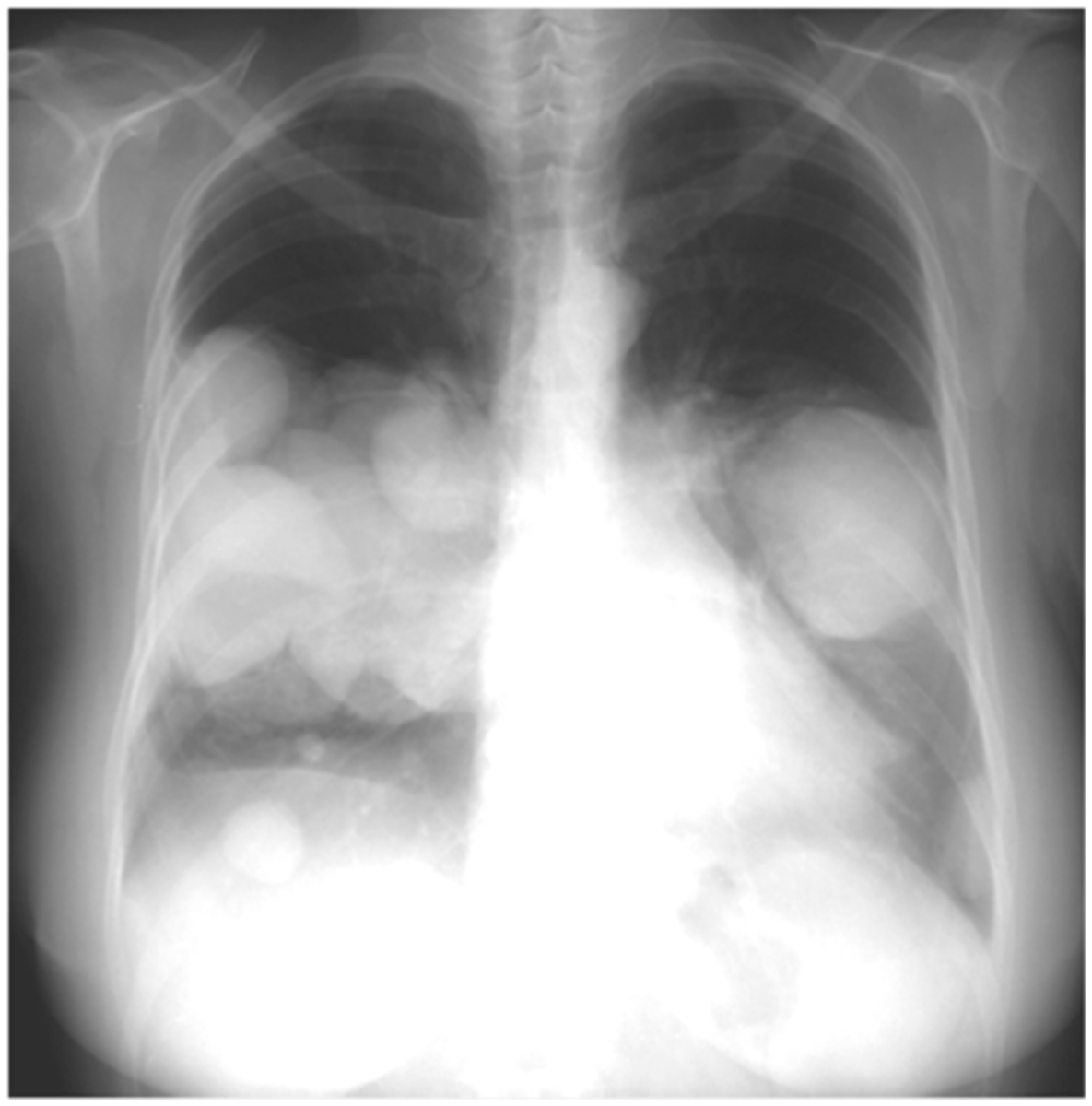
Cannonball metastasis
Osteosarcoma lung metastasis
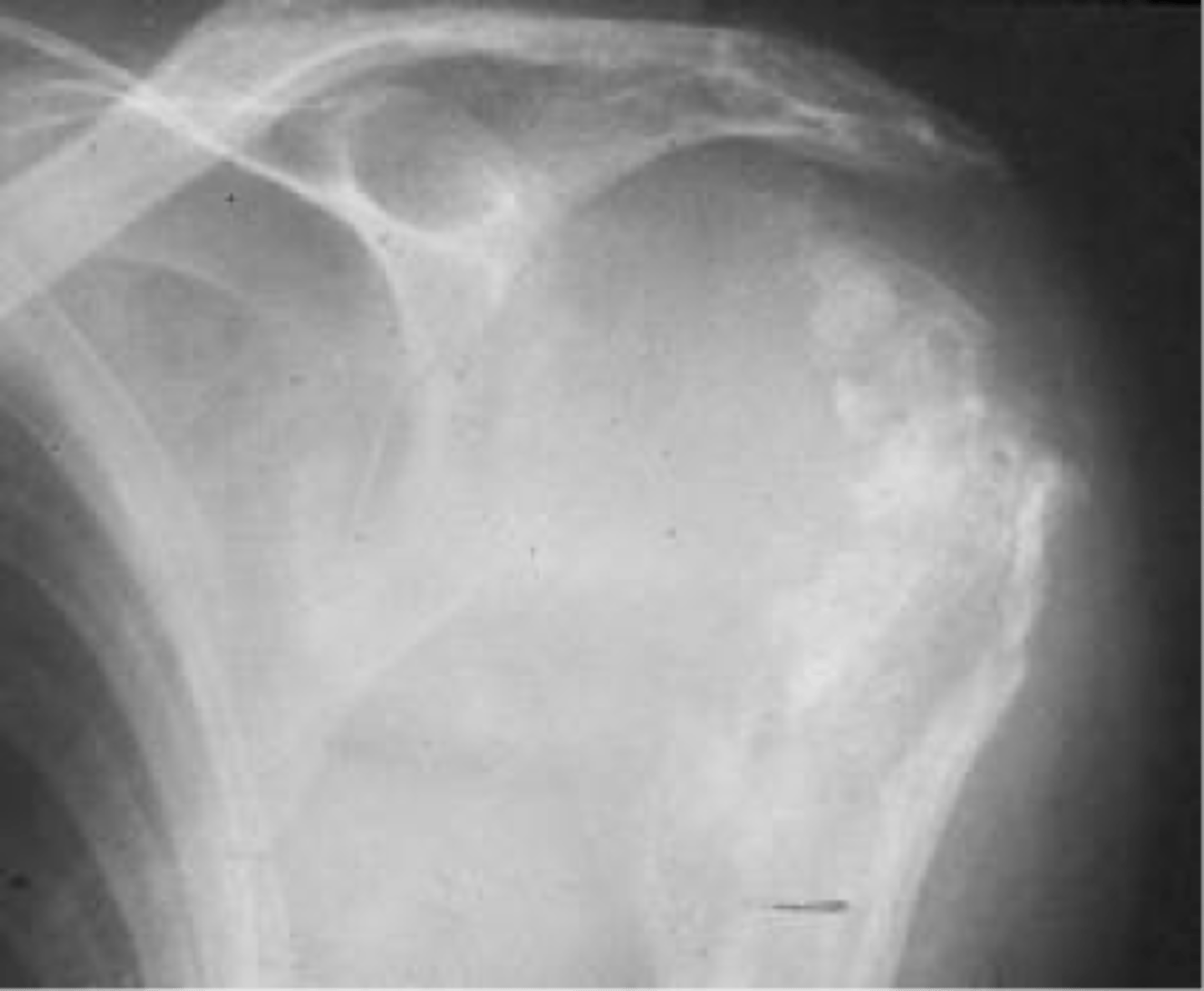
Secondary osteosarcoma
Malignant degeneration of benign process
- Paget disease
- Fibrous dysplasia
- Osteochondroma
Radiation therapy
State treatment for secondary osteosarcoma
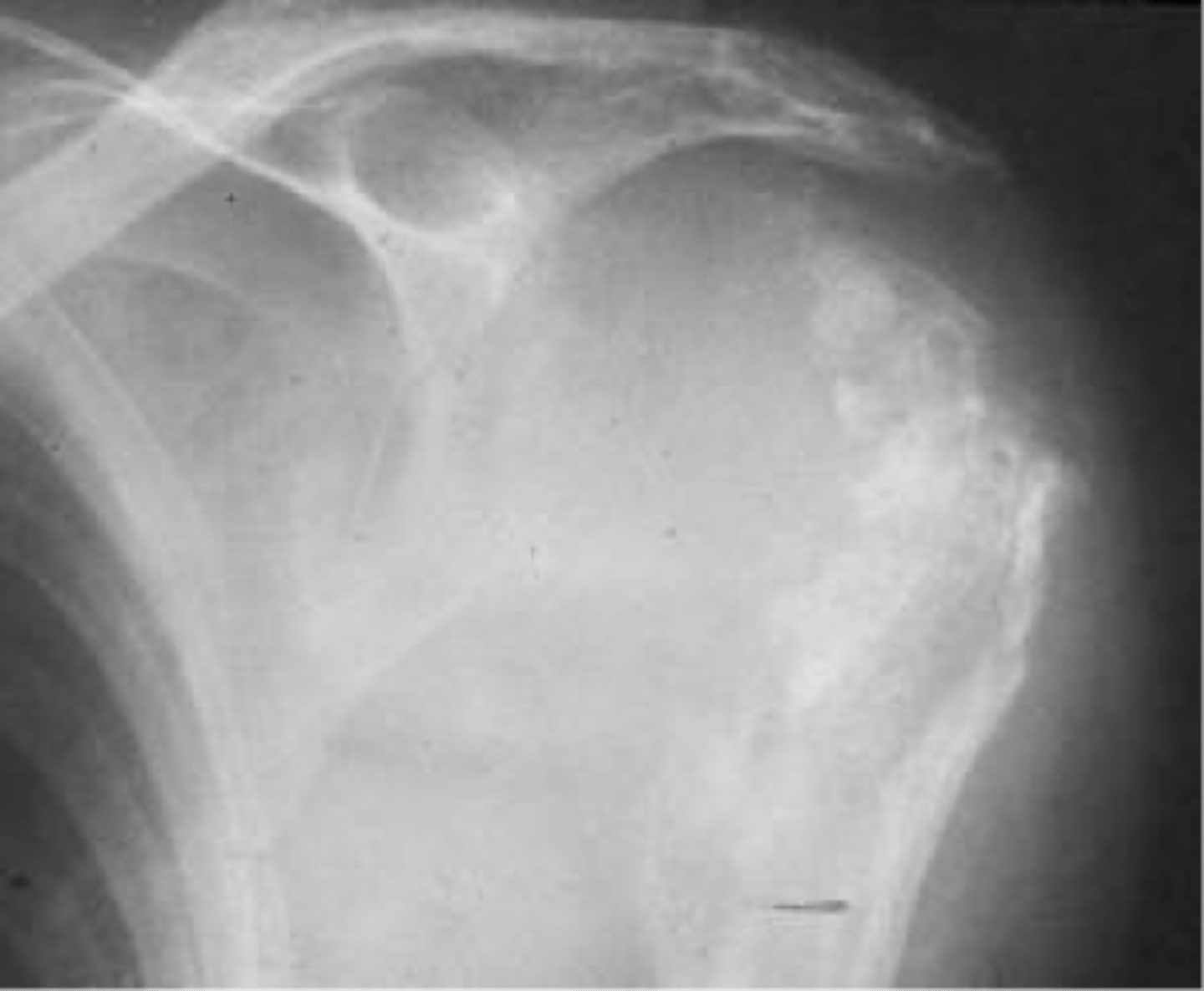
Chondrosarcoma
- 3rd most common primary malignant bone tumor
- 10% of all primary malignant bone tumors
- Primary or secondary forms
- Age 40-60
- M:F, 2:1
- Pain late in disease
- Large soft tissue mass
- Severe pain after pathologic fracture
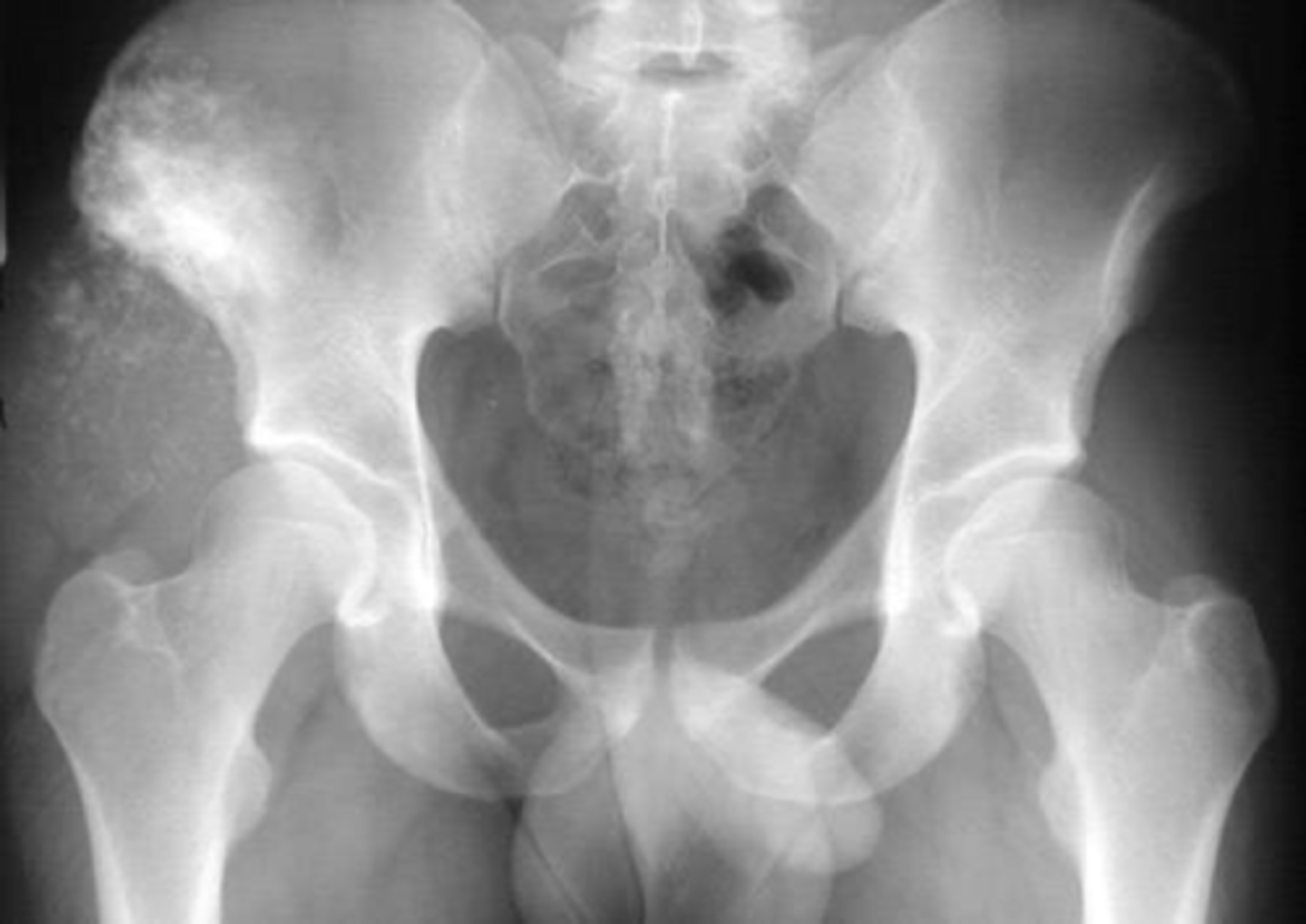
- Local excision
- Segmental resection
- Amputation
State treatment for chondrosarcoma
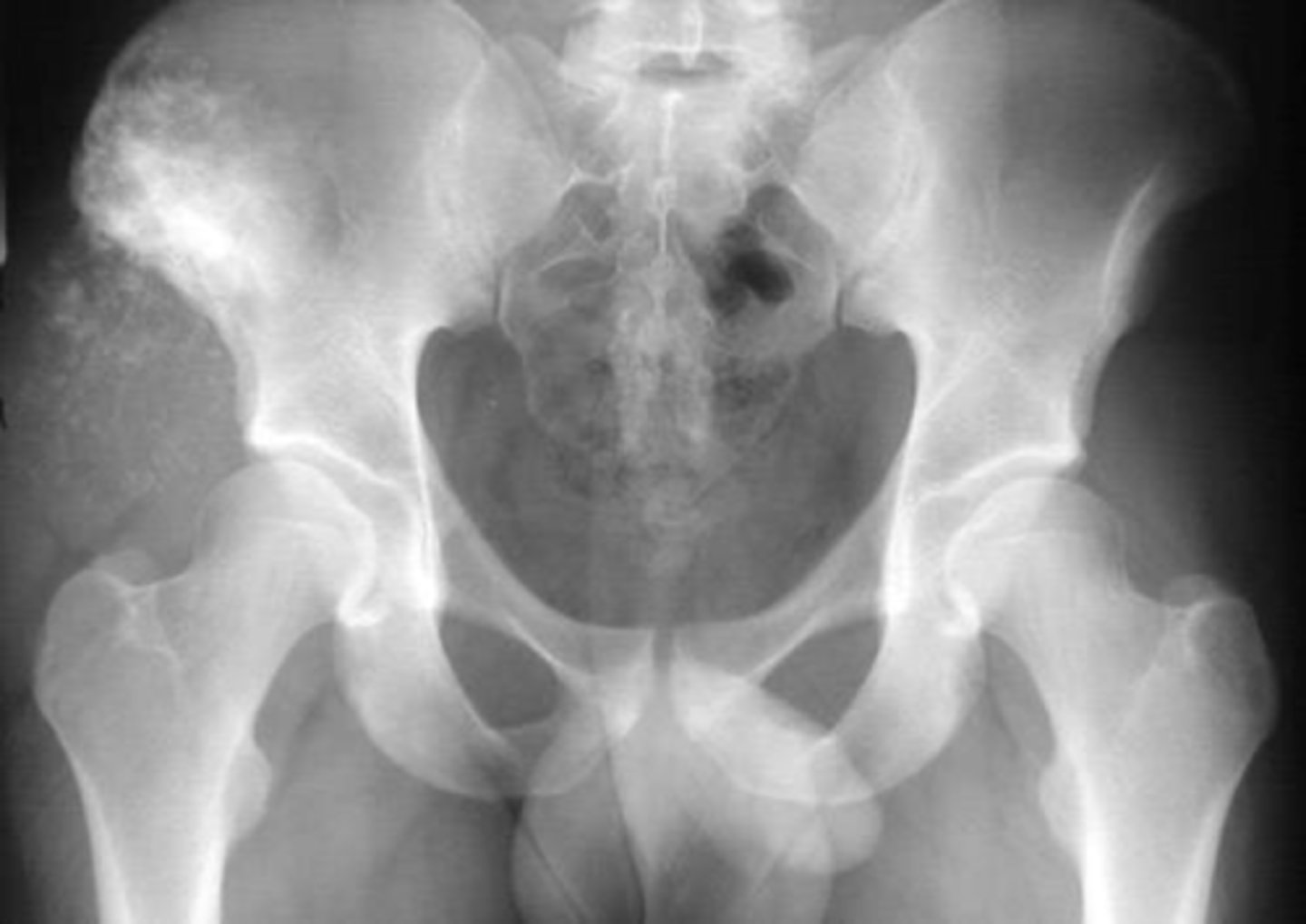
90%
Chondrosarcoma has a _____ 5-year survival after surgery
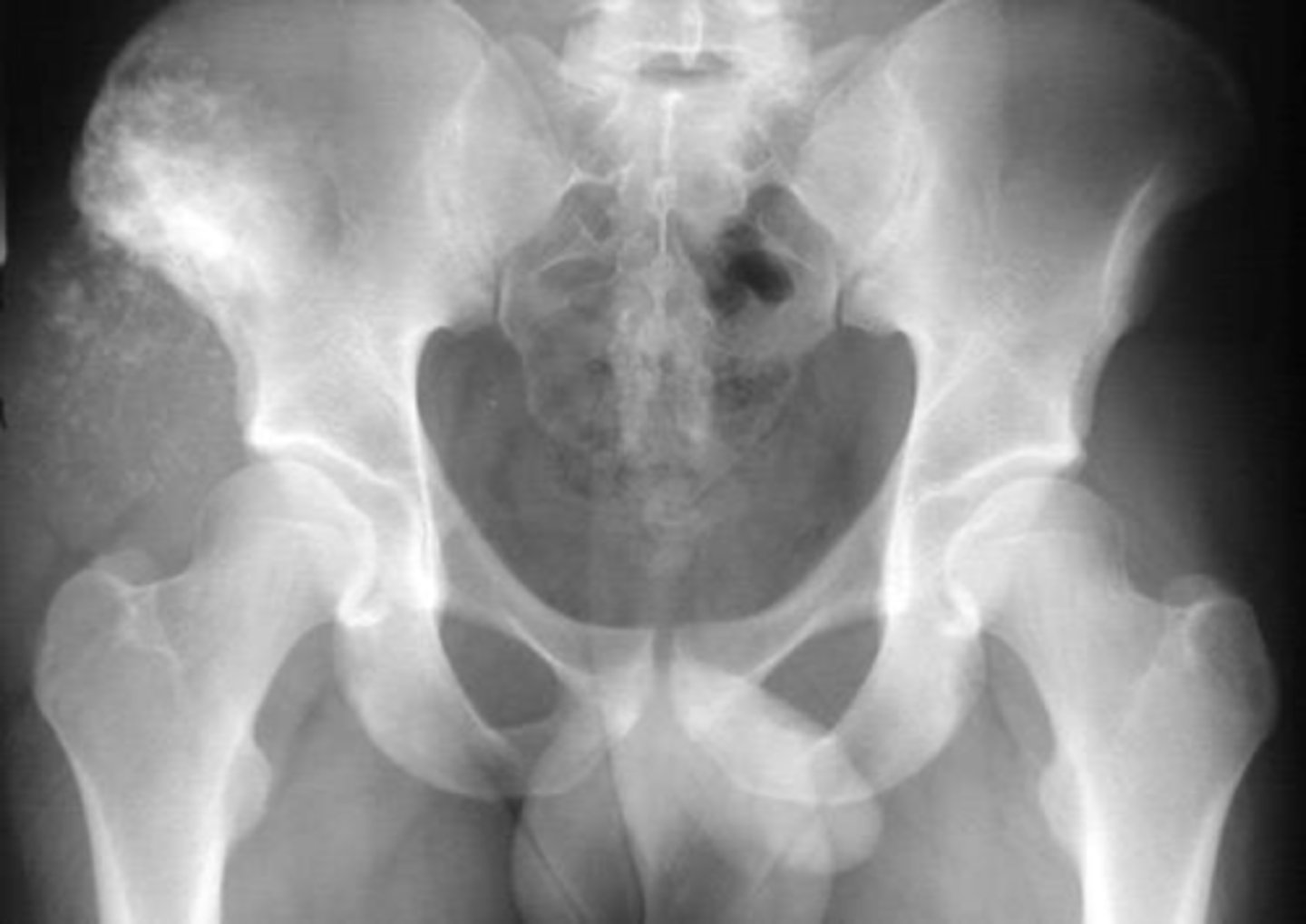
Ewing's Sarcoma
- 7% of all primary malignant bone tumors
- 4th most common primary malignant bone tumor
- Lower incidence among the black population in the US and Africa
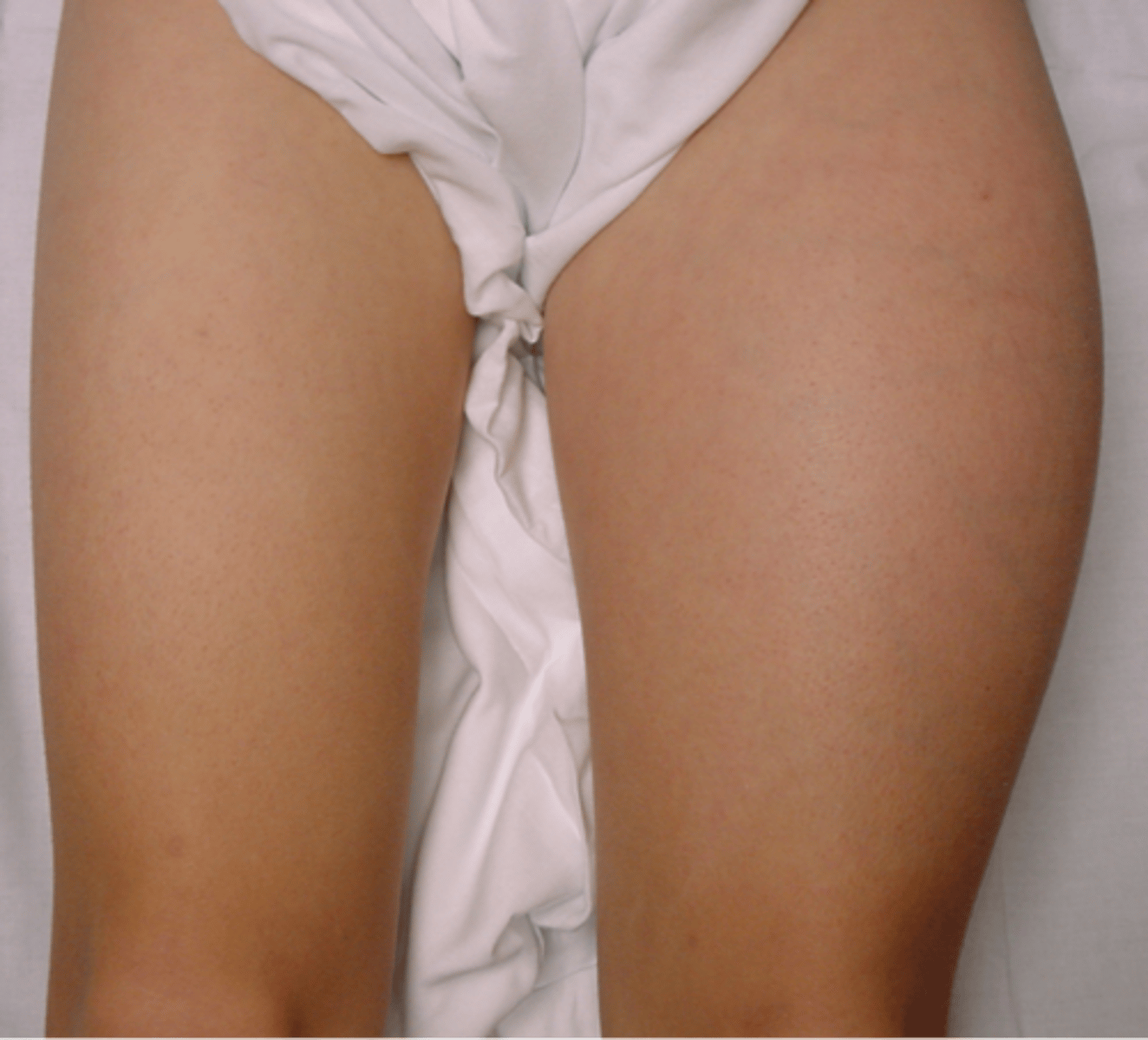

- Age 10-25
- M:F, 2:1
- Localized pain and swelling
- May mimic infection: fever, anemia, ESR
- Most common 1º malignant bone tumor to metastasize to bone
State clinical features of Ewing's Sarcoma

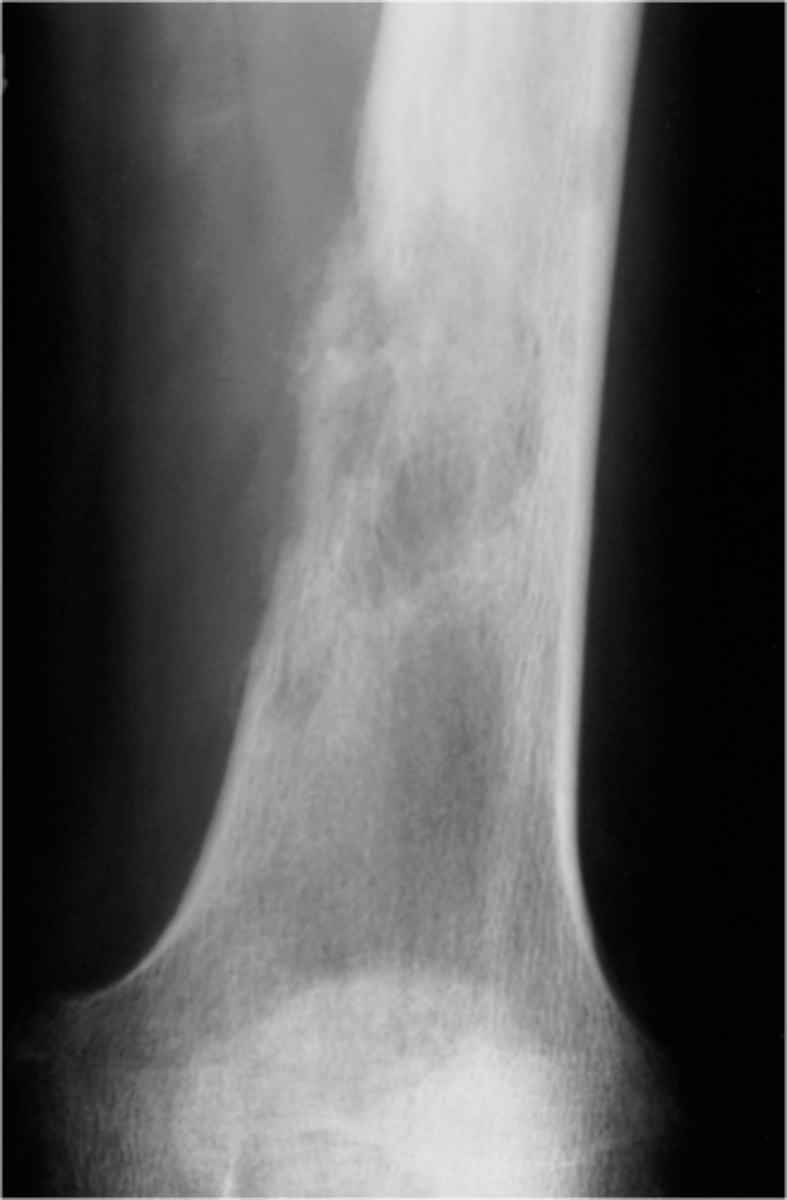
Diaphyseal permeative lesion
- Laminated periosteal reaction (25-50%)
- Lytic or mixed destruction
- Pathologic fracture (5%)
State imaging findings of Ewing's Sarcoma
- Amputation for lesions about knee
- Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in early lesions
State treatment for Ewing's Sarcoma
35%
Ewing's Sarcoma has a _____ 5-year survival
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- "Primary Lymphoma"
- Rare extranodal lymphoma
- Skeletal involvement in 30% of patients
- 3-4% of all primary malignant bone tumors