Topic 4.1 Networks
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Network
An arrangement of two or more computing devices connected together in order to communicate with each other and share resources.
Stand-alone
A computer or device that is not connected to a network.
Reasons for connecting computers in a network
Share data(files)and software
Share hardware peripherals(such as printers)
Allow communication(such as using email)
Deploy/Update applications
What are the two types of Network?
LAN(Local Area Network)
WAN(Wide Area Network)
LAN(Local Area Network)
A network that connects individual devices together over a small geographic area, usually a single building or site.
Infrastructure is typically owned by one company (for example a school owns the hardware for its own network, a home network work is owned by the household…)
WAN(Wide Area Network)
A network that connects multiple LANs together over a large geographic area, usually several buildings or sites.
Infrastructure is often third party.
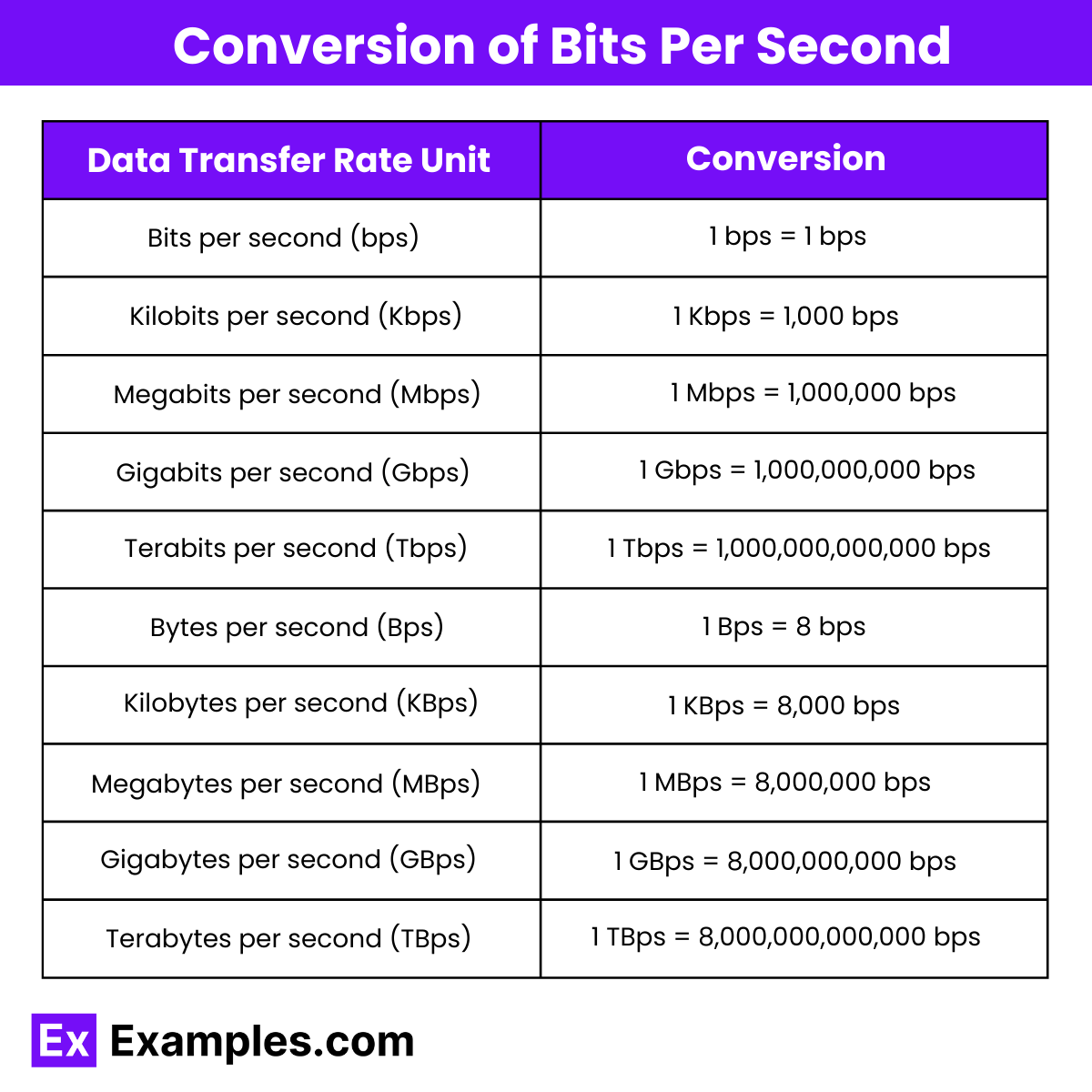
Bandwidth
The maximum volume of data that can be transmitted in one second. It is typically measured in bits per second (bps).
Latency
The amount of time(delay) between the data being sent and it being received.
Network Speed
= Data transfer rate. Measured in base 10 units.
Formula to calculate the length of time it would take to transmit a file
Time = File size (in bits) / Network Speed (in bps)
Method for constructing an expression to calculate the length of time it would take to transmit a file
1) Covert the file size to bits.
2) Divide file size by data transfer rate(draw fraction stroke)
3) Convert data transfer rate into bits per second
Wired transmission of data
Devices are physically connected , e.g., using a USB or Ethernet cable.
Wireless transmission of data
It uses no physical connection. Instead, it used radio waves to transmit data through air, e.g. Bluetooth, AirDrop, NFC.
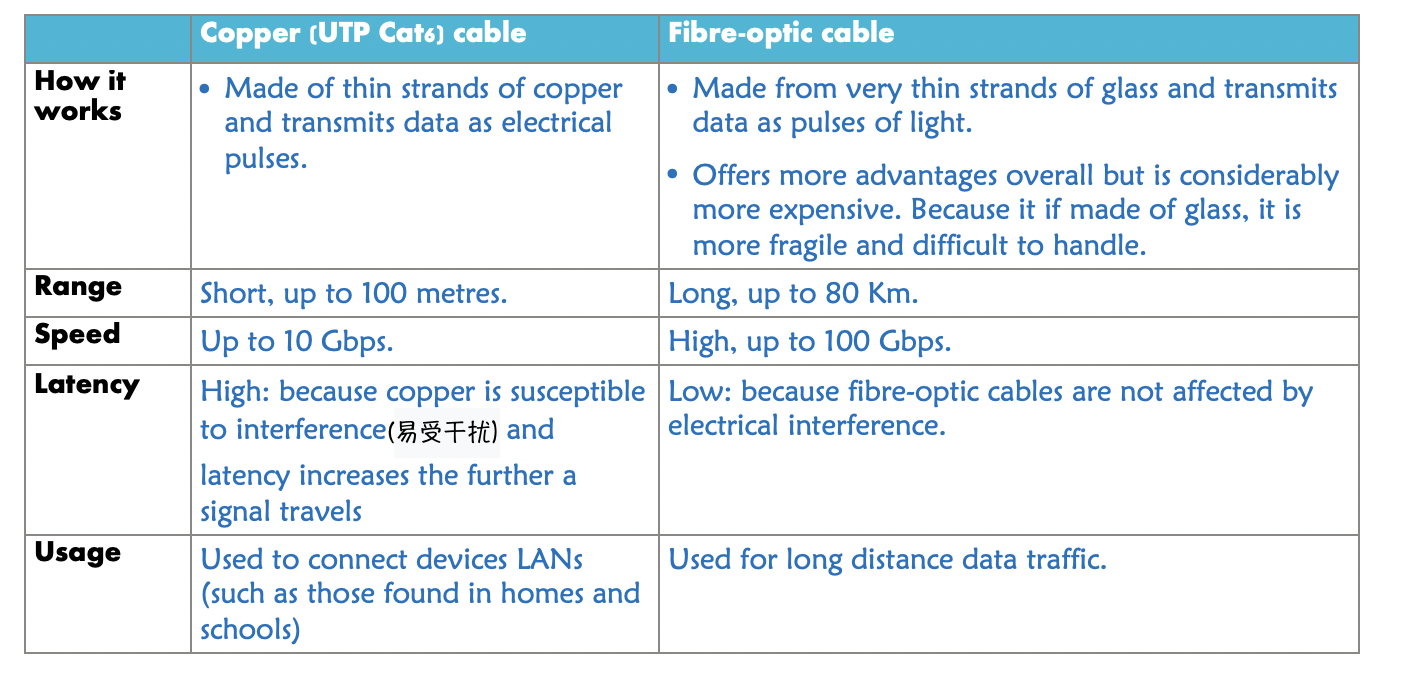
What are the 2 cables that wired transmission commonly uses?
copper wire(UTC)
fibre-optic
Compare copper wire with fibre-optic cable (Characteristics: Description, Range, Speed/Bandwidth, Latency, Usage)
Examples of wireless transmission media
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, RFID, NFC
Wi-Fi
A wireless technology that allows devices to connect to a network or the internet without using cables.
long range of up to 100 metres indoors
high data transfer speed/bandwidth (often over 100 Mbps), which makes it suitable for streaming, downloading, and online gaming
(comparatively)high power consumption, needs own power supply
commonly used to provide internet access in homes, schools, offices, and public places
Bluetooth
A short-range wireless technology used for connecting two or more nearby devices.
works within 10 metres (because it uses low-power signals meant for close connections).
medium speed (around 2–3 Mbps, which is enough for audio streaming and file sharing.
low power consumption, devices need their own power supply to stay connected
used for connecting wireless devices(fixed and mobile devices) like headphones, speakers, keyboards, and phones over short distances
Zigbee
A low-power wireless technology designed for communication between smart home devices.
range of up to 100 metres
low data speed of about 250 Kbps, which is enough for simple control signals and sensor data.
uses very little power, allowing devices like sensors to run for years on small batteries.
used in Home automation, medical device data collection, personal area networks, and Internet of Things
RFID
Uses radio waves to read information stored on tags attached to objects
range of up to 1m
very low data speed because it only transfers small amounts of data like ID numbers
Passive RFID tags do not need their own power, while active tags have batteries and use very little energy
used in retail to secure goods in outlets, in transportation to locate goods during movement, in passports to hold identification information and to identify ownership or medical needs of animals
NFC
very short-range wireless technology used for secure communication between devices close together
works only in close proximity, around 10cm which reduces the risk of interference
very low bandwidth because it is designed for fast, simple tasks like making payments
uses very little power, and passive devices like cards do not need own power supply
used for contactless payments
Exam style question: The UK uses RFID passports. The RFID chip contains biometric information used to authenticate the identity of the the passport user. Explain 3 reasons why RFID is suitable for this purpose:
no need for physical connection as data is transmitted wirelessly between the RFID chip and the reader
risk of interference by a third party is reduced because the chip and the reader must be within 1 m of each other to transfer data
RFID is suitable for embedding within physical objects because the chip does not need its own power supply
Broadband
A high-capacity transmission medium over long distances at high speeds
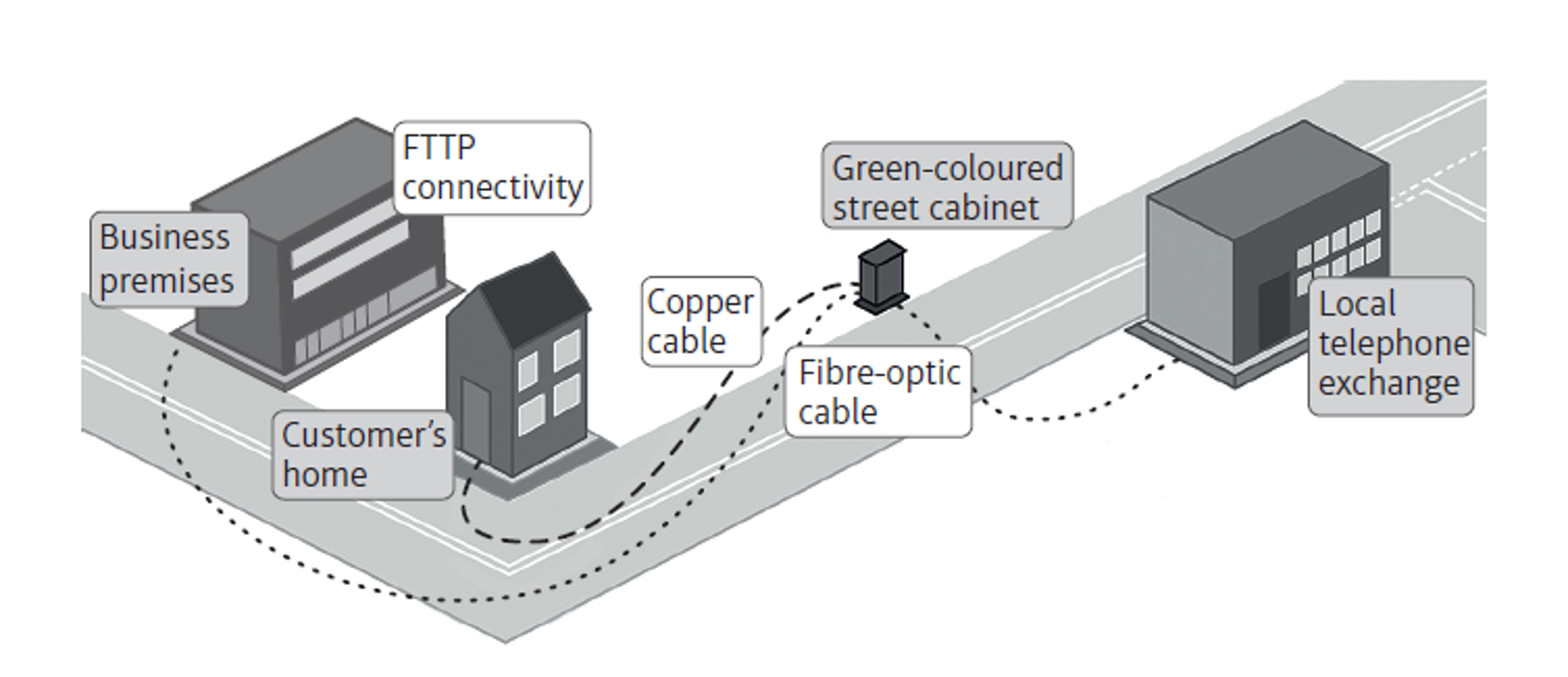
FTTC
Fibre to the cabinet
A way to provide broadband via a mix of fibre-optic and copper cables. Fibre-optic cabling runs from an ISP to a street cabinets and copper cabling runs from there to the premises.
FTTP
A high-speed way to provide broadband via fibre-optic cables that run from an ISP all the way to the premises.
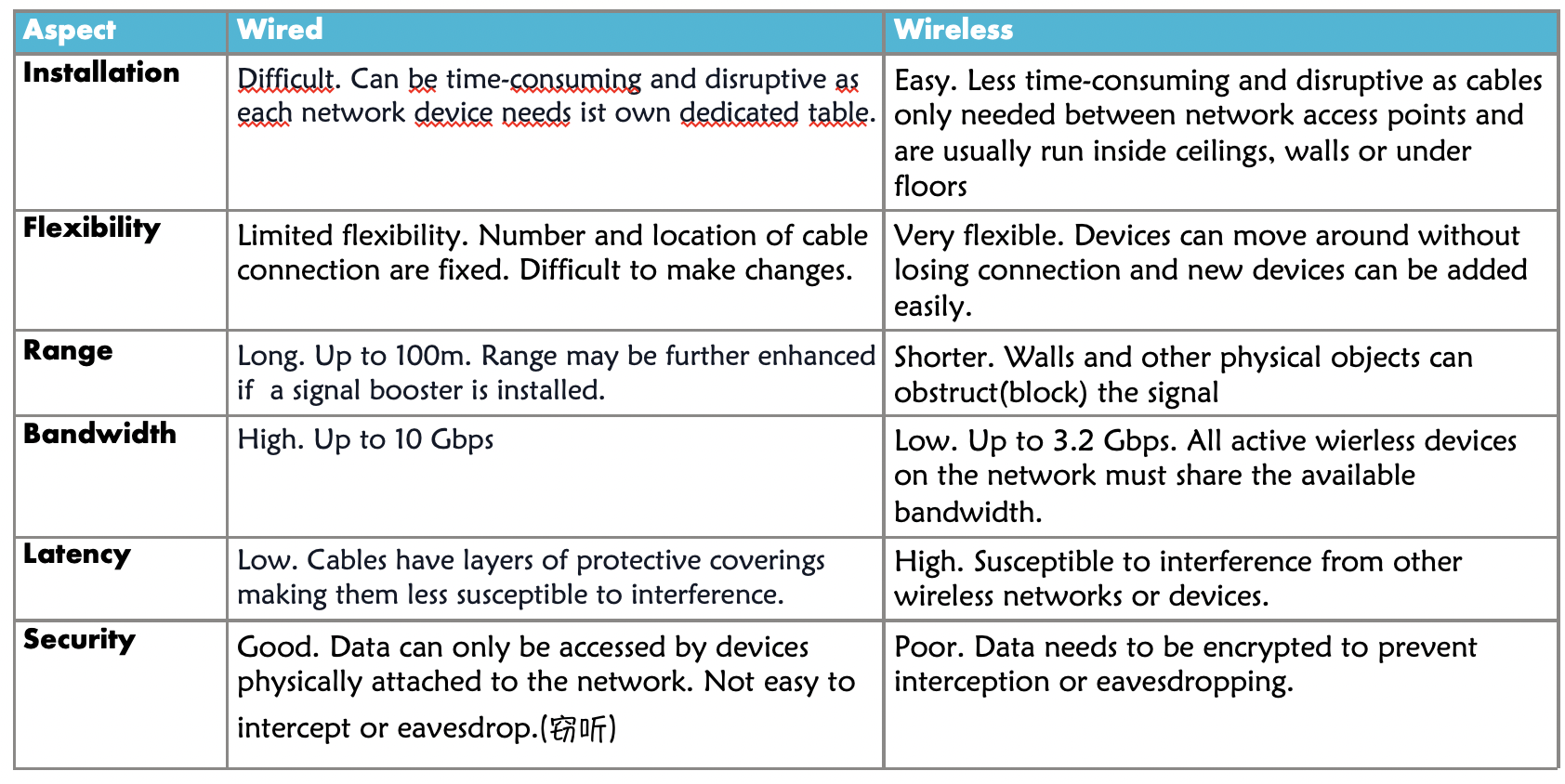
Wired vs Wireless LAN’s(Installation, Flexibility, Range, Bandwidth, Latency, Security)
Network topology
describes how devices are physically arranged and connected together
How does Bus topology work?
All the nodes are joined to one cable, called ‘the bu’.
A terminator is fitted at each end to stop signals reflecting back, causing interference.
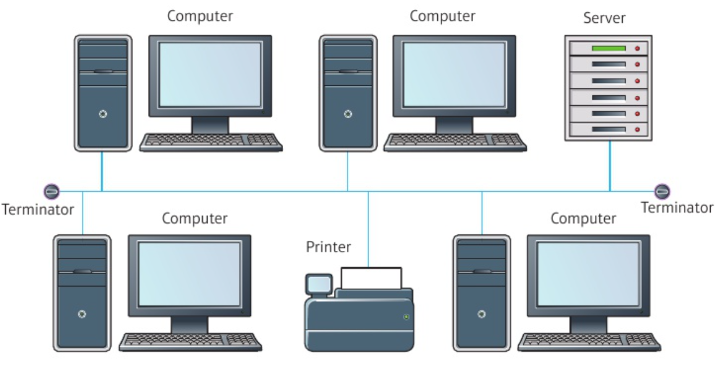
Advantages of Bus Network
easy and relatively cheap to set up because very little cabling is needed
easy to add extra devices
if one node fails, the others can still communicate with each other.
Disadvantages of Bus Network
if the main cable(bus) fails or gets damaged, the whole network will fail
Security risk - because every node on the bus receives every transmission
Since only one device at a time can transmit data along the cable, the more devices added, the more data collisions occur, slowing the network down.
How does Star topology work?
Each node is connected to a central device, either a ‘hub’ or a ‘switch’, which acts as a central point. All communications go through this central point.
A hub broadcasts messages across the whole network, whereas a switch sends the message to the intended receiver only.
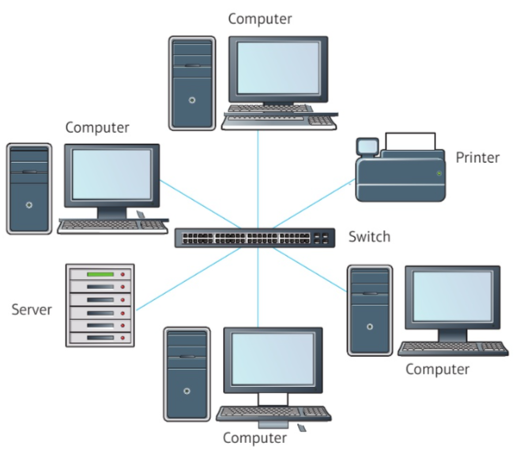
Advantages of Star Network
Each node is separately connected to the central device, so if one node fails, the others can still communicate with each other.
Easy to add new devices.
secure - Data is only sent to the intended recipient without passing through other nodes.
Network traffic is kept to a minimum.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
If the central node fails, the whole network stops functioning.
requires a lot of cables because each node is individually connected to the central device-difficult and expensive to set up
network performance depends on the central node, which also determines maximum number of nodes there can be
How does Mesh topology work?
Each node is connected to at least one other node either wired or wirelessly.
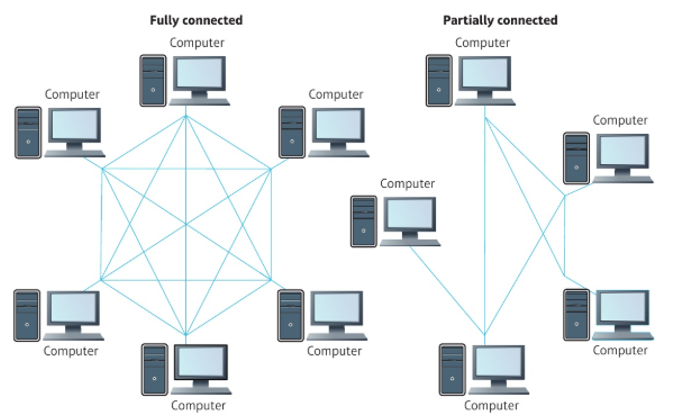
Advantages of Mesh Network
If one node fails, data can be rerouted
Data can be transmitted from different devices simultaneously
Adding more devices will not slow data transmission
Disadvantages of mesh network
Overall cost is high because more cabling is required unless a wireless network is used.
Difficult to install and manage, requires more maintenance and expert supervision.