4. MCQS Muscle Physiology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
The tetanic muscle contraction is:
a) as strong as the single muscle contraction;
b) 7-8 times stronger than the single muscle contraction;
c) 3-4 times weaker than the single muscle contraction;
d) 3-4 times stronger than the single muscle contraction;
e) the weakest type of muscle contraction.
The tetanic muscle contraction is:
a) as strong as the single muscle contraction;
b) 7-8 times stronger than the single muscle contraction;
c) 3-4 times weaker than the single muscle contraction;
d) 3-4 times stronger than the single muscle contraction;
e) the weakest type of muscle contraction.
The duration of a single muscle contraction is:
a) equal to the duration of the action potential;
b) is shorter than the duration of the action potential;
c) depends on the latency period;
d) depends on the refractory period;
e) is longer than the duration of the action potential.
The duration of a single muscle contraction is:
a) equal to the duration of the action potential;
b) is shorter than the duration of the action potential;
c) depends on the latency period;
d) depends on the refractory period;
e) is longer than the duration of the action potential.
During isotonic contraction of a skeletal muscle fibre:
a) the sarcomere length changes;
b) both length and tension change;
c) tension increases;
d) fibres relax;
e) tension decreases.
During isotonic contraction of a skeletal muscle fibre:
a) the sarcomere length changes;
b) both length and tension change;
c) tension increases;
d) fibres relax;
e) tension decreases.
Every two bones flexibly connected by a joint form:
a) a kinematic chain;
b) a motor unit;
c) a statokinetic system;
d) a triad;
e) a kinematic pair.
Every two bones flexibly connected by a joint form:
a) a kinematic chain;
b) a motor unit;
c) a statokinetic system;
d) a triad;
e) a kinematic pair.
What is the function of the protein titin?
a) causes calcium to be released into the cytoplasm of the cell;
b) increases the amount of ATP produced;
c) aids in the orientation of myosin to actin;
d) leads to stronger contractions;
e) provides nutrition to the muscle cell.
What is the function of the protein titin?
a) causes calcium to be released into the cytoplasm of the cell;
b) increases the amount of ATP produced;
c) aids in the orientation of myosin to actin;
d) leads to stronger contractions;
e) provides nutrition to the muscle cell.
In which type of muscle contraction is there a change in both the length and the tension at the same time?
a) isotonic;
b) auxotonic.
c) isometric;
d) eccentric;
e) concentric;
In which type of muscle contraction is there a change in both the length and the tension at the same time?
a) isotonic;
b) auxotonic.
c) isometric;
d) eccentric;
e) concentric;
'Motor unit' refers to:
a) a single motor neuron plus all the muscle fibres it innervates;
b) a single muscle fibre plus all the motor neurons that innervate it;
c) all of the motor neurons supplying a single muscle;
d) a pair of antagonistic muscles;
e) all of the muscles that affect the movement of any given joint.
'Motor unit' refers to:
a) a single motor neuron plus all the muscle fibres it innervates;
b) a single muscle fibre plus all the motor neurons that innervate it;
c) all of the motor neurons supplying a single muscle;
d) a pair of antagonistic muscles;
e) all of the muscles that affect the movement of any given joint.
What method is used to record skeletal muscle bioelectrical activity?
a) electromyography (EMG);
b) electrocardiography (ECG);
c) electroneurogram (ENG);
d) electroencephalography (EEG);
e) echography.
What method is used to record skeletal muscle bioelectrical activity?
a) electromyography (EMG);
b) electrocardiography (ECG);
c) electroneurogram (ENG);
d) electroencephalography (EEG);
e) echography.
Thick filaments in skeletal muscle are composed of:
a) actin;
b) troponin;
c) myosin;
d) calmodulin;
e) tropomyosin.
Thick filaments in skeletal muscle are composed of:
a) actin;
b) troponin;
c) myosin;
d) calmodulin;
e) tropomyosin.
In skeletal muscle calcium facilitates contraction by binding to:
a) tropomyosin;
b) actin;
c) troponin;
d) myosin;
e) the thick filament.
In skeletal muscle calcium facilitates contraction by binding to:
a) tropomyosin;
b) actin;
c) troponin;
d) myosin;
e) the thick filament.
With regard to knee jerk:
a) it is a monosynaptic reflex;
b) the impulse travels via type Ca afferent fibres;
c) the Golgi body is an important component;
d) the stimulus begins in the tendon;
e) it is a visceral reflex.
With regard to knee jerk:
a) it is a monosynaptic reflex;
b) the impulse travels via type Ca afferent fibres;
c) the Golgi body is an important component;
d) the stimulus begins in the tendon;
e) it is a visceral reflex.
What role do Ca2+ ions play in the muscle contraction?
a) excitation-contraction coupling;
b) prevent the contraction;
c) form cross bridges;
d) release energy for the contraction;
e) excite the myofiber.
What role do Ca2+ ions play in the muscle contraction?
a) excitation-contraction coupling;
b) prevent the contraction;
c) form cross bridges;
d) release energy for the contraction;
e) excite the myofiber.
Smooth muscle is not cross striated because:
a) of myosin and actin in the myofibril;
b) myofibrils are in register with each other;
c) myofibrils are not in register with each other;
d) it has gap junctions;
e) it is surrounded by a basal lamina.
Smooth muscle is not cross striated because:
a) of myosin and actin in the myofibril;
b) myofibrils are in register with each other;
c) myofibrils are not in register with each other;
d) it has gap junctions;
e) it is surrounded by a basal lamina.
Intercalated discs are most likely to be observed in:
a) longitudinal section of skeletal muscle;
b) transverse section of skeletal muscle;
c) transverse section of cardiac muscle;
d) longitudinal section of cardiac muscle;
e) transverse section of smooth muscle.
Intercalated discs are most likely to be observed in:
a) longitudinal section of skeletal muscle;
b) transverse section of skeletal muscle;
c) transverse section of cardiac muscle;
d) longitudinal section of cardiac muscle;
e) transverse section of smooth muscle.
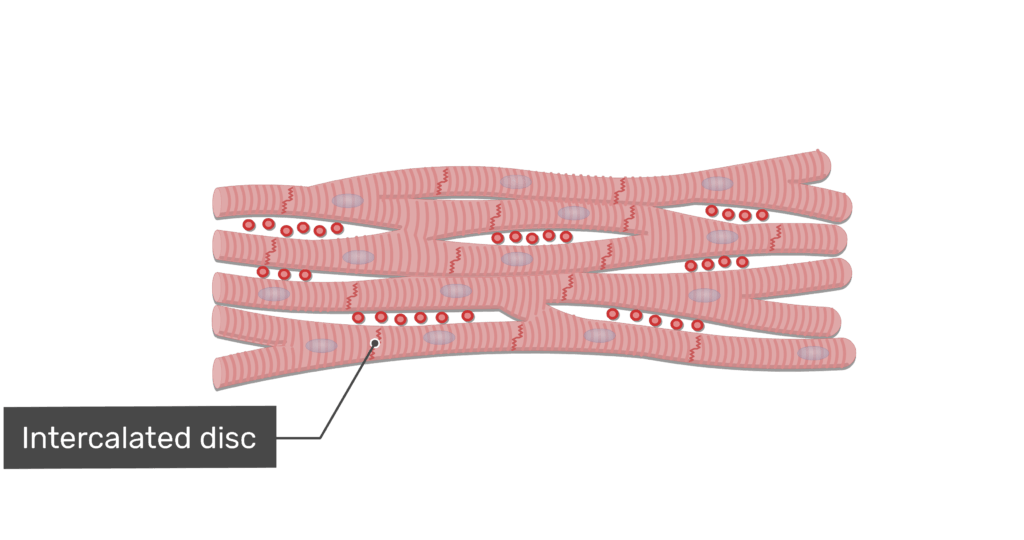
Cardiac muscle is:
a) voluntary and spindle shaped;
b) voluntary and striated;
c) involuntary and spindle shaped;
d) involuntary and striated;
e) innervated by the somatic nervous system.
Cardiac muscle is:
a) voluntary and spindle shaped;
b) voluntary and striated;
c) involuntary and spindle shaped;
d) involuntary and striated;
e) innervated by the somatic nervous system.
During an isometric contraction of a skeletal muscle:
a) the I-bands shorten and the A-bands stay the same length;
b) the thick and thin filaments slide past each other;
c) sarcomere length does not change;
d) tension does not change;
e) the sarcomere shortens.
During an isometric contraction of a skeletal muscle:
a) the I-bands shorten and the A-bands stay the same length;
b) the thick and thin filaments slide past each other;
c) sarcomere length does not change;
d) tension does not change;
e) the sarcomere shortens.
The cross bridges in the sarcomere of skeletal muscle are made of:
a) actin;
b) myosin;
c) troponin;
d) tropomyosin;
e) myelin.
The cross bridges in the sarcomere of skeletal muscle are made of:
a) actin;
b) myosin;
c) troponin;
d) tropomyosin;
e) myelin.
Which area of the sarcomere consists only of myosin filaments?
a) I-bands;
b) H-zone;
c) A-bands;
d) M-line;
e) Z-disc.
Which area of the sarcomere consists only of myosin filaments?
a) I-bands;
b) H-zone;
c) A-bands;
d) M-line;
e) Z-disc.
Which muscle cell compound stores oxygen?
a) creatine phosphate;
b) glycogen;
c) hemoglobin;
d) myoglobin;
e) lipid droplets.
Which muscle cell compound stores oxygen?
a) creatine phosphate;
b) glycogen;
c) hemoglobin;
d) myoglobin;
e) lipid droplets.
Smooth muscle is:
a) voluntary and spindle shaped;
b) voluntary and striated;
c) involuntary and spindle shaped;
d) involuntary and striated;
e) innervated by the somatic nervous system.
Smooth muscle is:
a) voluntary and spindle shaped;
b) voluntary and striated;
c) involuntary and spindle shaped;
d) involuntary and striated;
e) innervated by the somatic nervous system.
Skeletal muscle is:
a) voluntary and spindle shaped;
b) voluntary and striated;
c) involuntary and spindle shaped;
d) involuntary and striated;
e) innervated by ANS.
Skeletal muscle is:
a) voluntary and spindle shaped;
b) voluntary and striated;
c) involuntary and spindle shaped;
d) involuntary and striated;
e) innervated by ANS.
Which type of muscle cell is multinucleated?
a) cardiac;
b) smooth muscles;
c) skeletal;
d) cardiac and smooth;
e) connective tissue.
Which type of muscle cell is multinucleated?
a) cardiac;
b) smooth muscles;
c) skeletal;
d) cardiac and smooth;
e) connective tissue.
What is an example of a smooth muscle?
a) masseter (face);
b) bladder;
c) heart;
d) pronator teres (forearm);
e) rectus abdominis (belly).
What is an example of a smooth muscle?
a) masseter (face);
b) bladder;
c) heart;
d) pronator teres (forearm);
e) rectus abdominis (belly).
How many actin filaments surround each myosin filament?
a) two;
b) four;
c) six;
d) eight;
e) seven.
How many actin filaments surround each myosin filament?
a) two;
b) four;
c) six;
d) eight;
e) seven.
The muscular system is controlled by which system?
a) the cardiovascular system;
b) the endocrine system;
c) the nervous system;
d) the respiratory system;
e) the urinary system.
The muscular system is controlled by which system?
a) the cardiovascular system;
b) the endocrine system;
c) the nervous system;
d) the respiratory system;
e) the urinary system.
Which protein is not involved in skeletal muscles contraction?
a) myosin;
b) troponin;
c) actin;
d) tropomyosin;
e) myoglobin.
Which protein is not involved in skeletal muscles contraction?
a) myosin;
b) troponin;
c) actin;
d) tropomyosin;
e) myoglobin.
The neuromuscular synapses are:
a) only excitatory;
b) only inhibitory;
c) neither excitatory nor inhibitory;
d) excitatory or inhibitory depending on the receptors;
e) excitatory or inhibitory depending on the neurotransmitter
The neuromuscular synapses are:
a) only excitatory;
b) only inhibitory;
c) neither excitatory nor inhibitory;
d) excitatory or inhibitory depending on the receptors;
e) excitatory or inhibitory depending on the neurotransmitter
The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores:
a) calcium ions;
b) chloride ions;
c) sodium ions;
d) potassium ions;
e) hydrogen ions.
The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores:
a) calcium ions;
b) chloride ions;
c) sodium ions;
d) potassium ions;
e) hydrogen ions.
Which of these is true of skeletal muscle:
a) spindle-shaped cells;
b) under involuntary control;
c) many peripherally located nuclei per muscle fiber;
d) forms the walls of hollow internal organs;
e) may be autorhythmic.
Which of these is true of skeletal muscle:
a) spindle-shaped cells;
b) under involuntary control;
c) many peripherally located nuclei per muscle fiber;
d) forms the walls of hollow internal organs;
e) may be autorhythmic.
Which of these is not a major property of muscle?
a) contractility;
b) elasticity;
c) excitability;
d) extensibility;
e) secretability.
Which of these is not a major property of muscle?
a) contractility;
b) elasticity;
c) excitability;
d) extensibility;
e) secretability.
Mysoin myofilaments are:
a) attached to the Z-disk;
b) found primarily in the I-band;
c) thinner than actin myofilaments;
d) absent from the H-zone;
e) attached to filaments that form the M-line.
Mysoin myofilaments are:
a) attached to the Z-disk;
b) found primarily in the I-band;
c) thinner than actin myofilaments;
d) absent from the H-zone;
e) attached to filaments that form the M-line.
The part of the sarcolemma that invaginates into the interior of skeletal muscle fibers is the:
a) T-tubule system;
b) sarcoplasmic reticulum;
c) myofibrils;
d) terminal cisternae;
e) mitochondria.
The part of the sarcolemma that invaginates into the interior of skeletal muscle fibers is the:
a) T-tubule system;
b) sarcoplasmic reticulum;
c) myofibrils;
d) terminal cisternae;
e) mitochondria.
Which of these events occurs during the lag (latent) phase of muscle contraction?
a) cross-bridge movement;
b) active transport of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum;
c) Ca2+ binding to troponin;
d) sarcomere shortening;
e) breakdown of ATP to ADP.
Which of these events occurs during the lag (latent) phase of muscle contraction?
a) cross-bridge movement;
b) active transport of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum;
c) Ca2+ binding to troponin;
d) sarcomere shortening;
e) breakdown of ATP to ADP.
Muscle contraction which cannot move weight because it is too heavy is:
a) isometric;
b) isotonic;
c) isokinetic;
d) concentric;
e) eccentric.
Muscle contraction which cannot move weight because it is too heavy is:
a) isometric;
b) isotonic;
c) isokinetic;
d) concentric;
e) eccentric.
A small motor unit would control which type of movement?
a) fast but brief;
b) intense and strong;
c) delicate and precise;
d) sprinting;
e) marathon running.
A small motor unit would control which type of movement?
a) fast but brief;
b) intense and strong;
c) delicate and precise;
d) sprinting;
e) marathon running.
Muscle fibers type I have only one of the following features:
a) slow onset of contraction
b) easily fatigued;
c) many enzymes for glycolysis;
d) a slow refractory period;
e) low mitochondrial content.
Muscle fibers type I have only one of the following features:
a) slow onset of contraction
b) easily fatigued;
c) many enzymes for glycolysis;
d) a slow refractory period;
e) low mitochondrial content.
Muscle fibers type IIa are:
a) slow-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable resistant;
b) fast-twitch, oxidative-glycolytic, relatively fatigue resistant;
c) fast-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable;
d) slow-twitch, oxidative, fatigue resistant;
e) fast-twitch, oxidative, fatigable.
Muscle fibers type IIa are:
a) slow-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable resistant;
b) fast-twitch, oxidative-glycolytic, relatively fatigue resistant;
c) fast-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable;
d) slow-twitch, oxidative, fatigue resistant;
e) fast-twitch, oxidative, fatigable.
Muscle fibers type IIb are:
a) slow-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable resistant;
b) fast-twitch, oxidative-glycolytic, relatively fatigue resistant;
c) fast-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable;
d) slow-twitch, oxidative, fatigue resistant;
e) fast-twitch, oxidative, fatigable.
Muscle fibers type IIb are:
a) slow-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable resistant;
b) fast-twitch, oxidative-glycolytic, relatively fatigue resistant;
c) fast-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable;
d) slow-twitch, oxidative, fatigue resistant;
e) fast-twitch, oxidative, fatigable.
Muscle fibers type I are:
a) slow-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable resistant;
b) fast-twitch, oxidative-glycolytic, relatively fatigue resistant;
c) fast-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable;
d) slow-twitch, oxidative, fatigue resistant;
e) fast-twitch, oxidative, fatigable.
Muscle fibers type I are:
a) slow-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable resistant;
b) fast-twitch, oxidative-glycolytic, relatively fatigue resistant;
c) fast-twitch, glycolytic, fatigable;
d) slow-twitch, oxidative, fatigue resistant;
e) fast-twitch, oxidative, fatigable.
These bands of the sarcomere do not shorten during contraction:
a) A-bands;
b) H-, I-, and M-bands;
c) Z-discs and A-bands;
d) I-bands;
e) Z-discs.
These bands of the sarcomere do not shorten during contraction:
a) A-bands;
b) H-, I-, and M-bands;
c) Z-discs and A-bands;
d) I-bands;
e) Z-discs.
The smooth muscles are innervated by:
a) a-motor neurons in the spinal cord;
b) y-motor neurons;
c) pseudounipolar neurons in the spinal ganglia;
d) postganglionic neurons of the ANS;
e) preganglionic neurons of the ANS.
The smooth muscles are innervated by:
a) a-motor neurons in the spinal cord;
b) y-motor neurons;
c) pseudounipolar neurons in the spinal ganglia;
d) postganglionic neurons of the ANS;
e) preganglionic neurons of the ANS.
The function of tropomyosin in skeletal muscle is:
a) sliding on actin to produce shortening;
b) releasing Ca2+ after initiation of contraction;
c) binding to myosin during contraction;
d) covering up the active sites of actin at rest;
e) releasing Na+ after contraction.
The function of tropomyosin in skeletal muscle is:
a) sliding on actin to produce shortening;
b) releasing Ca2+ after initiation of contraction;
c) binding to myosin during contraction;
d) covering up the active sites of actin at rest;
e) releasing Na+ after contraction.
The cell membranes in skeletal muscle:
a) are impermeable to fat-soluble substances;
b) are more permeable to sodium than to potassium ions;
c) become more permeable to glucose in the presence of insulin;
d) become less permeable to potassium in the presence of insulin;
e) are ligand dependent.
The cell membranes in skeletal muscle:
a) are impermeable to fat-soluble substances;
b) are more permeable to sodium than to potassium ions;
c) become more permeable to glucose in the presence of insulin;
d) become less permeable to potassium in the presence of insulin;
e) are ligand dependent.
A skeletal muscle fibre at rest:
a) presents with a membrane which is positively charged on the inside with respect to the outside;
b) contains intracellular stores of calcium ions;
c) is normally innervated by more than one motor neurone;
d) becomes more excitable as its resting membrane potential increase in absolute value;
e) becomes less excitable as the extracellular ionized calcium levels fall.
A skeletal muscle fibre at rest:
a) presents with a membrane which is positively charged on the inside with respect to the outside;
b) contains intracellular stores of calcium ions;
c) is normally innervated by more than one motor neurone;
d) becomes more excitable as its resting membrane potential increase in absolute value;
e) becomes less excitable as the extracellular ionized calcium levels fall.
In skeletal muscle:
a) contraction occurs when its pacemaker cells depolarize sufficiently to reach the threshold for firing;
b) calcium is taken up by the sarcotubular system when it contracts;
c) actin and myosin filaments shorten when it contracts;
d) the sarcomeres shorten during contraction;
e) contraction strength is related to the influx of K+ ions.
In skeletal muscle:
a) contraction occurs when its pacemaker cells depolarize sufficiently to reach the threshold for firing;
b) calcium is taken up by the sarcotubular system when it contracts;
c) actin and myosin filaments shorten when it contracts;
d) the sarcomeres shorten during contraction;
e) contraction strength is related to the influx of K+ ions.
The action potential of skeletal muscle:
a) has a prolonged plateau phase;
b) spreads inwards to all parts of the muscle via T-tubules;
c) is longer than the action potential of cardiac muscle;
d) is not essential for muscle conduction:
e) has different amplitudes.
The action potential of skeletal muscle:
a) has a prolonged plateau phase;
b) spreads inwards to all parts of the muscle via T-tubules;
c) is longer than the action potential of cardiac muscle;
d) is not essential for muscle conduction:
e) has different amplitudes.
Smooth muscle need help of:
a) calmodulin for contraction;
b) acetylcholine for contraction;
c) K+ for contraction;
d) monoamine oxidase for contraction;
e) secondary messenger for contraction.
Smooth muscle need help of:
a) calmodulin for contraction;
b) acetylcholine for contraction;
c) K+ for contraction;
d) monoamine oxidase for contraction;
e) secondary messenger for contraction.
The sarcomere is:
a) the principal protein in the skeletal muscle;
b) the basic functional unit of the smooth muscle;
c) the main energy source of muscle contraction;
d) the basic functional unit of the skeletal muscle fibre;
e) the main proprioceptor.
The sarcomere is:
a) the principal protein in the skeletal muscle;
b) the basic functional unit of the smooth muscle;
c) the main energy source of muscle contraction;
d) the basic functional unit of the skeletal muscle fibre;
e) the main proprioceptor.
The types of muscles in the human body are:
a) skeletal, voluntary and smooth;
b) striated, smooth and cardiac;
c) involuntary, smooth and striated;
d) striated, smooth and skeletal;
e) cardiac and smooth.
The types of muscles in the human body are:
a) skeletal, voluntary and smooth;
b) striated, smooth and cardiac;
c) involuntary, smooth and striated;
d) striated, smooth and skeletal;
e) cardiac and smooth.
Adequate stimuli of the smooth muscle are:
a) mechanical overload/stretching, temperature changes and chemical substances;
b) electrical stimulation and slow stretching;
c) electrical and osmotic stimuli;
d) only electrical stimuli;
e) only stretching.
Adequate stimuli of the smooth muscle are:
a) mechanical overload/stretching, temperature changes and chemical substances;
b) electrical stimulation and slow stretching;
c) electrical and osmotic stimuli;
d) only electrical stimuli;
e) only stretching.
A lot of electrical synapses and autorhythmicity have:
a) skeletal muscles;
b) all smooth muscles;
c) visceral type of smooth muscles;
d) multi-unit smooth muscles;
e) all extensors.
A lot of electrical synapses and autorhythmicity have:
a) skeletal muscles;
b) all smooth muscles;
c) visceral type of smooth muscles;
d) multi-unit smooth muscles;
e) all extensors.
Red muscle fibers are:
a) only type I;
b) only IIa;
c) type I and IIa;
d) only IIb;
e) all muscle fiber types.
Red muscle fibers are:
a) only type I;
b) only IIa;
c) type I and IIa;
d) only IIb;
e) all muscle fiber types.
White muscle fibers are:
a) only type I;
b) only IIa;
c) type I and IIa;
d) only IIb;
e) all muscle fiber types.
White muscle fibers are:
a) only type I;
b) only IIa;
c) type I and IIa;
d) only IIb;
e) all muscle fiber types.
Muscle contraction in which the muscle lengthens is called:
a) concentric;
b) eccentric;
c) isotonic;
d) isometric;
e) auxotonic.
Muscle contraction in which the muscle lengthens is called:
a) concentric;
b) eccentric;
c) isotonic;
d) isometric;
e) auxotonic.
Muscle contraction in which the muscle shortens is called:
a) concentric;
b) eccentric;
c) isotonic;
d) isometric;
e) auxotonic.
Muscle contraction in which the muscle shortens is called:
a) concentric;
b) eccentric;
c) isotonic;
d) isometric;
e) auxotonic.
The neurotransmitter released from the final endings of the motoneurons innervating skeletal muscles is:
a) serotonin;
b) norepinephrine;
c) acetylcholine;
d) glycine;
e) adrenaline.
The neurotransmitter released from the final endings of the motoneurons innervating skeletal muscles is:
a) serotonin;
b) norepinephrine;
c) acetylcholine;
d) glycine;
e) adrenaline.
The number of muscle fibres in a motor unit determines:
a) its maximum contraction force;
b) the contraction speed;
c) whether or not the muscle contractions are 'concentric' or 'eccentric';
d) whether or not the muscle contactions are isometric or isotonic;
e) whether or not the muscle contractions are single or tetanic.
The number of muscle fibres in a motor unit determines:
a) its maximum contraction force;
b) the contraction speed;
c) whether or not the muscle contractions are 'concentric' or 'eccentric';
d) whether or not the muscle contactions are isometric or isotonic;
e) whether or not the muscle contractions are single or tetanic.
What is each myofibril made of?
a) many muscle fibers.
b) contains sarcoplasmic reticulum;
c) many sarcomeres;
d) contains T-tubules;
e) is the same thing as a muscle fiber.
What is each myofibril made of?
a) many muscle fibers.
b) contains sarcoplasmic reticulum;
c) many sarcomeres;
d) contains T-tubules;
e) is the same thing as a muscle fiber.
The motor units of the skeletal muscles are composed of:
a) fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibres;
b) type I and type II muscle fibres;
c) type I and type IIb (white) fibres;
d) uniform fibre type;
e) three different types of muscle fibres.
The motor units of the skeletal muscles are composed of:
a) fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibres;
b) type I and type II muscle fibres;
c) type I and type IIb (white) fibres;
d) uniform fibre type;
e) three different types of muscle fibres.
Muscle fibers type IIb have only one of the following features:
a) slow onset of contraction
b) easily fatigued;
c) many enzymes for oxidation;
d) a slow refractory period;
e) high mitochondrial content.
Muscle fibers type IIb have only one of the following features:
a) slow onset of contraction
b) easily fatigued;
c) many enzymes for oxidation;
d) a slow refractory period;
e) high mitochondrial content.