1- Early Human Development Part 1: Germ cells, fertilization, and implantation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
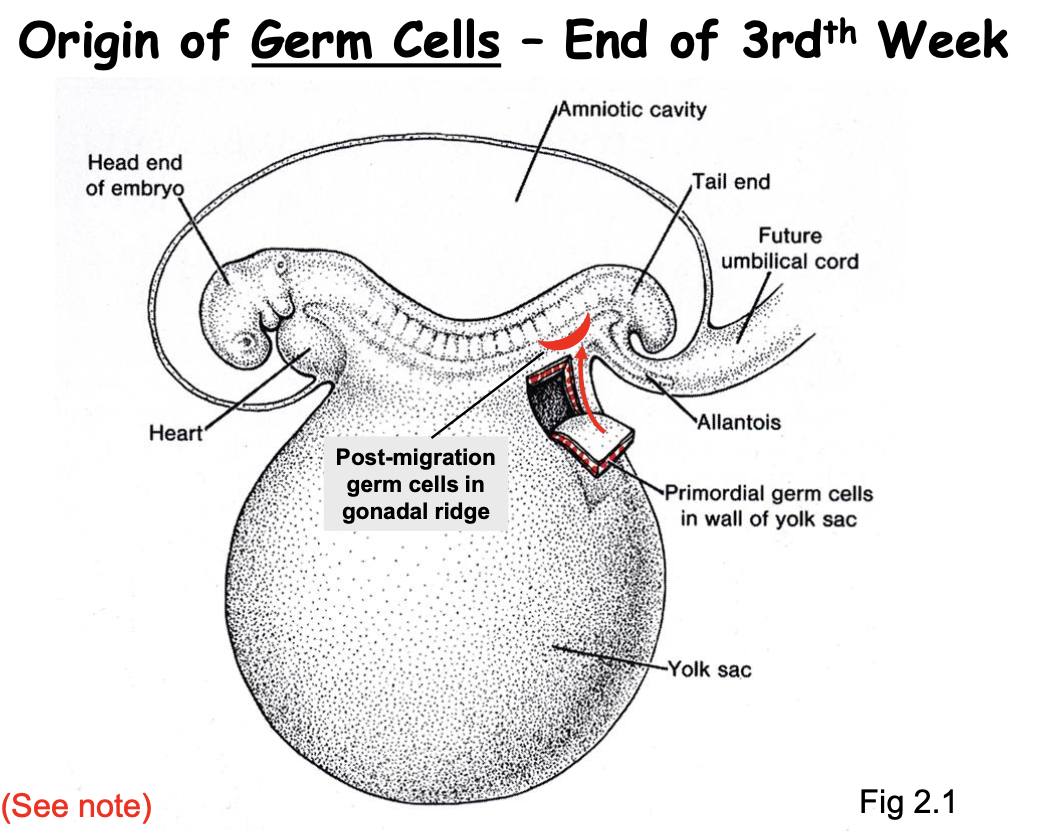
Origin and migration of primordial germ cells.
Germ Cells originate in the yolk sac &
Migrate into the gonadal ridge where differentiate into ovaries or testes where they form (post migration)
By end of 3rd Week
Head region gets an early start of development
The differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis
Somatic cells
No reduction in chromosome number
Start & Ends Diploid
(1 division occurs)
Meiosis
Germ cells
Reduction in chromosome number
Starts Diploid & Ends in Haploid
(2 divisions occur)
Pairing & Crossover occurs to allow for variation
Primordial germ cells ____
& form 1 oocytes arrested in ____ in the developing ovaryAt puberty when the menstrual cycles begin, ____ primary oocytes remain, and fewer than 500 will be ____.
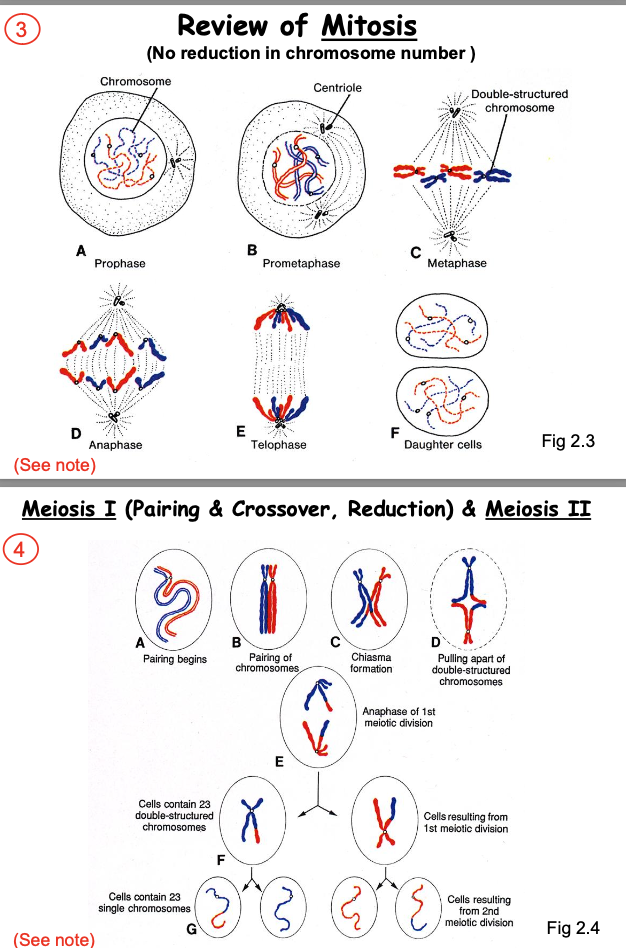
Proliferation of primordial germ cells & Arrest of primary oocytes at meiosis 1 prophase. (LEC OBJ)
replicate
prophase of meiosis I
only ~40,000 from 7mil
ovulated
By 5th month, 7 million primordial germs cells form from mitosis.
Start differentiating and become Oogonium
All Oogonium that survive go into meiosis and reside in ovary and stay in prophase of Meiosis 1 for years until sperm comes.
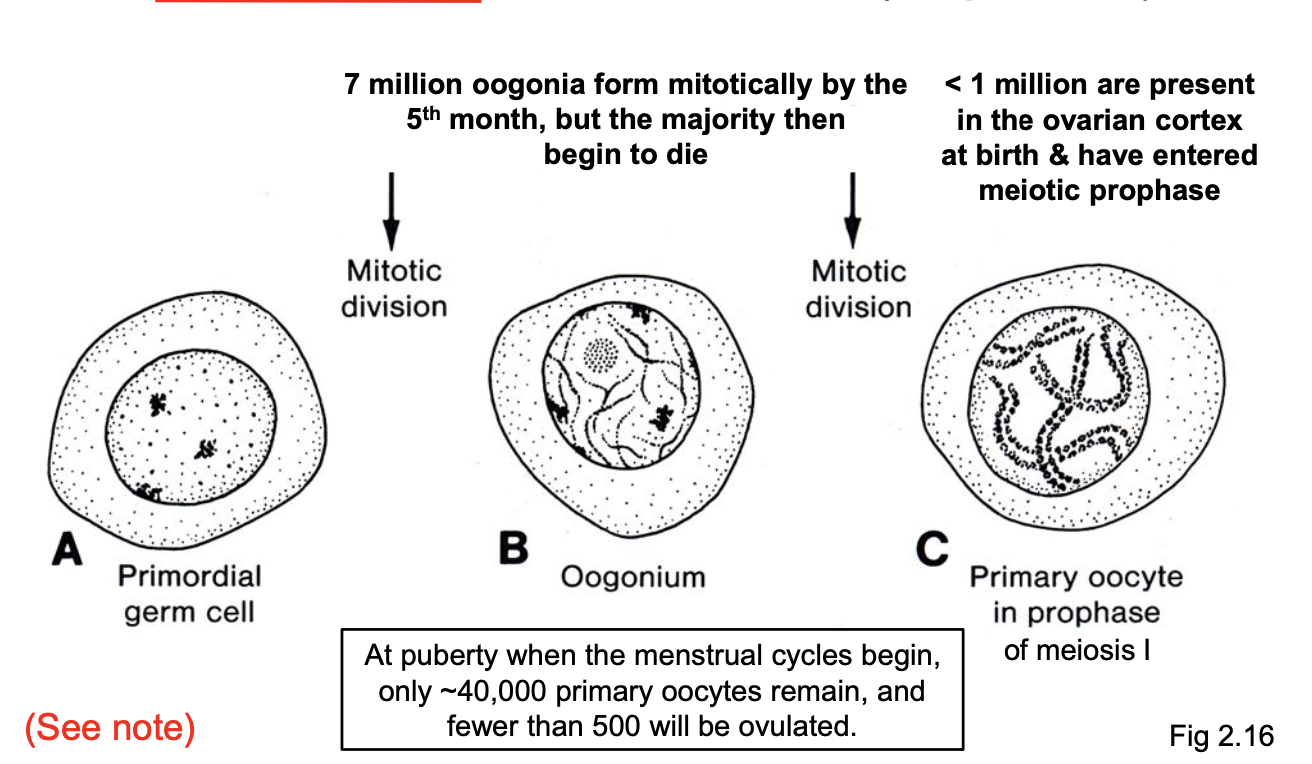
Primordial follicles (1 oocytes) form ____ in the mature ovary under the influence of _____.
~ ____ maturing follicles/month)
Pituitary FSH stimulates follicular development. (LEC OBJ)
vesicular follicles
pituitary FSH
15-20
1 oocyte develops into vesticular follicles when stimulated by FSH.
Zona pellucida is a membrane that forms around and encapsules oocyte as granulosa cells prolliforate around it.
As granulosa cells prolliforate, a cavity forms (antrum).
________ stimulates follicle maturation, release of an oocyte at ______, and development of the _____ in the ruptured follicle
Granulosa cells secrete—> ____
Theca interna secrete—> _____
Pituitary LH triggers ovulation, resumption of meiosis until re-arrest at metaphase of meiosis 2, and corpus luteum formation.
Pituitary LH
metaphase of meiosis II into the cavity
corpus luteum in ovary
progesterone
estrogen precursors & progesterone
Corpus luteum now secretes lots of progesterone
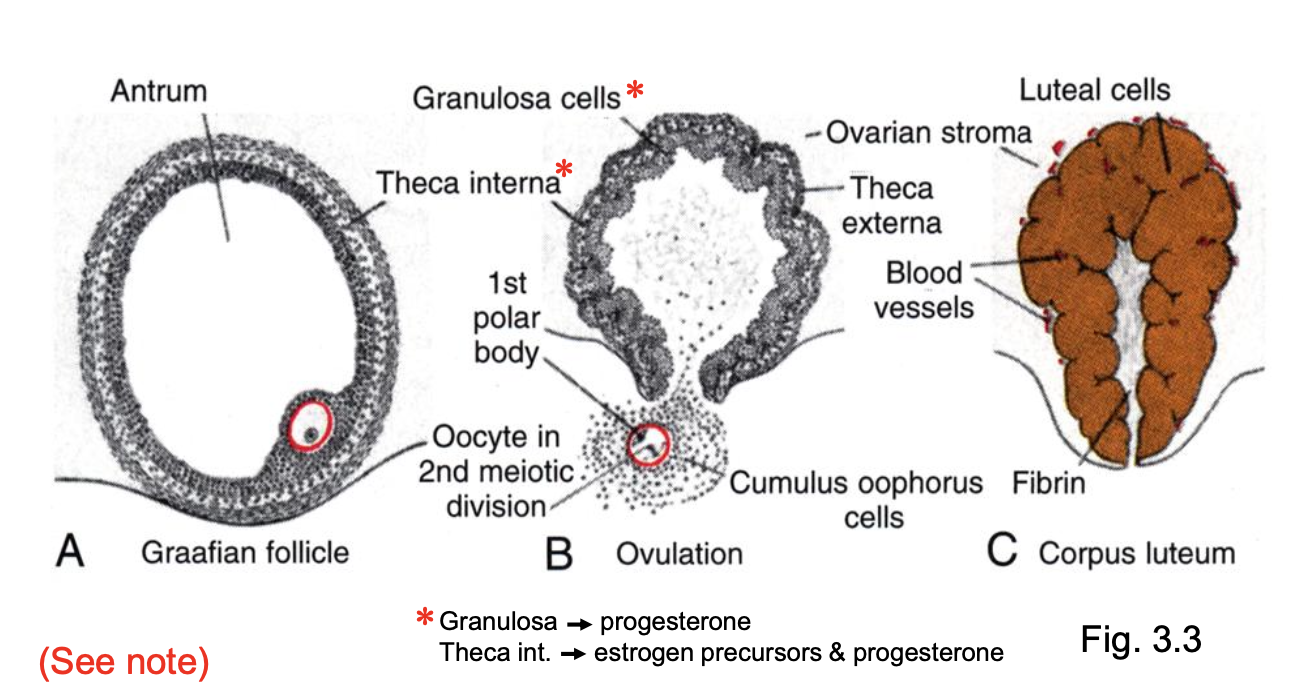
At the same time, the rupturing follicle sheds the oocyte into the _____.
fimbriae of the uterine tube
to be ready and in place to be fertilized
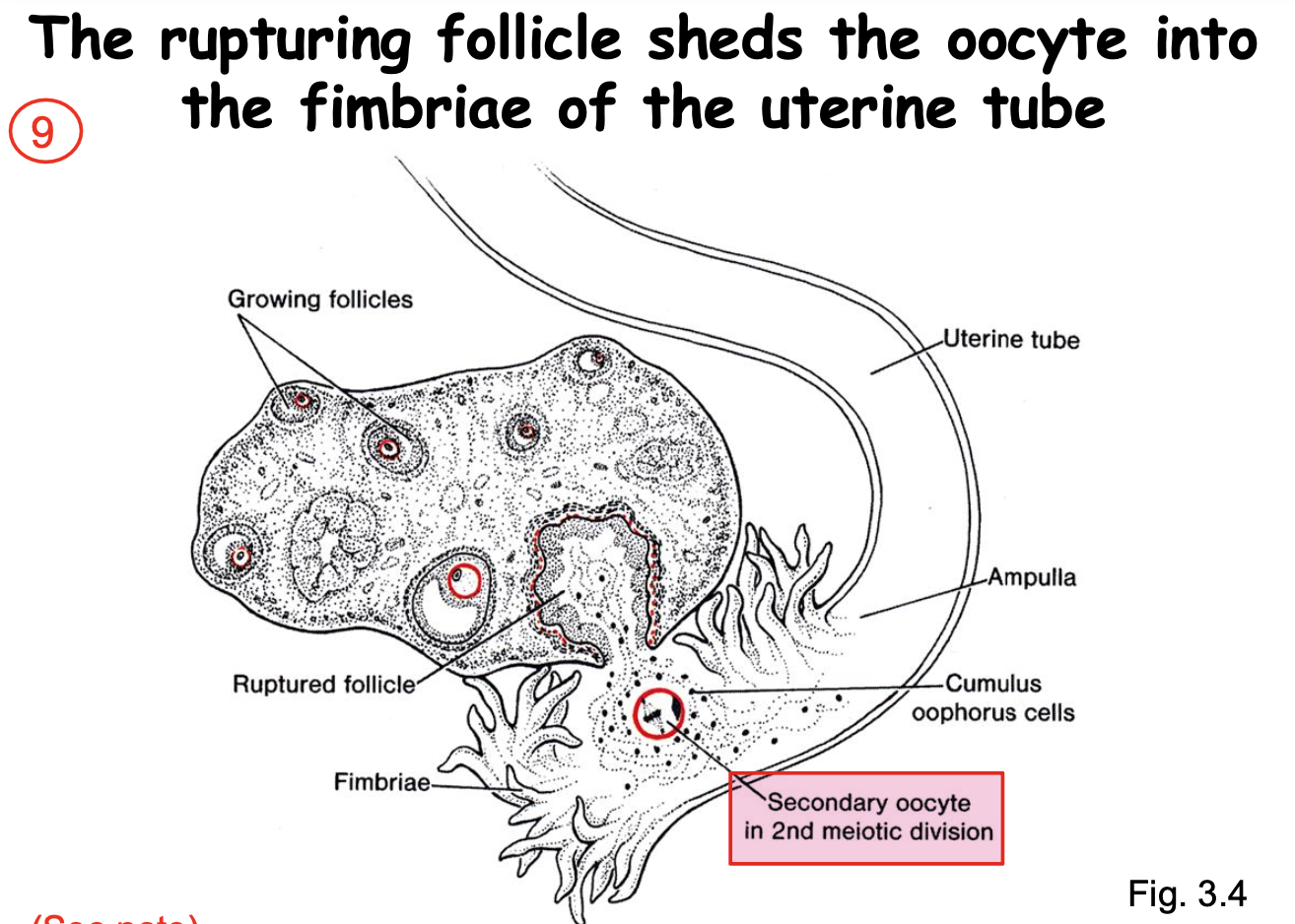
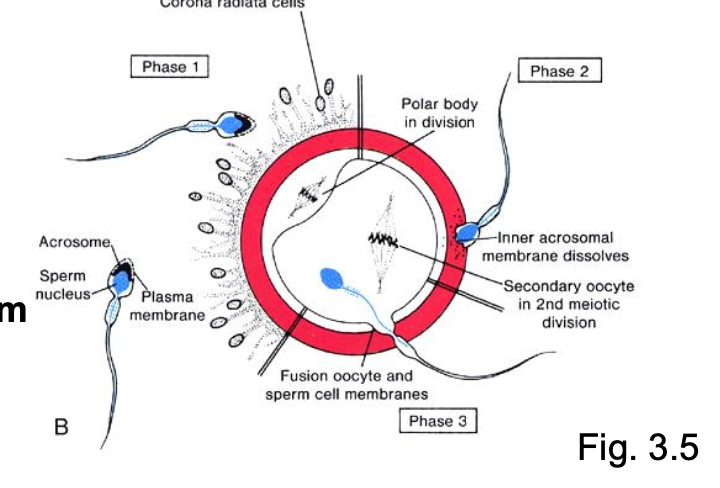
____ of the oocyte occurs in the uterine tube.
_____* sperm must penetrate:
This requires a few hours of sperm exposure to ____ in the upper oviduct.
Capacitated sperm digest the zona pellucida, and the first to arrive at the oocyte membrane triggers a cortical reaction.
Fertilization
Capacitated
- corona radiata
- zona pellucida (acrosome reaction)-oocyte membrane
soluble factors
Consequences of fertilization in the egg:
Barrier to polyspermy by _____.
____ activation of the fertilized egg
Resumption, by maternal pronucleus, of _____.
Fusion of sperm and egg ____
Completion of _____ by fused spindles to form two daughter cells.
oocyte cortical reaction
Metabolic
2nd meiosis from arrested metaphase
pronuclei mitotic spindles
first mitotic division
The oocyte completes ____, and the pronuclei fuse to ___.
Then several mitotic cleavages result in ____.
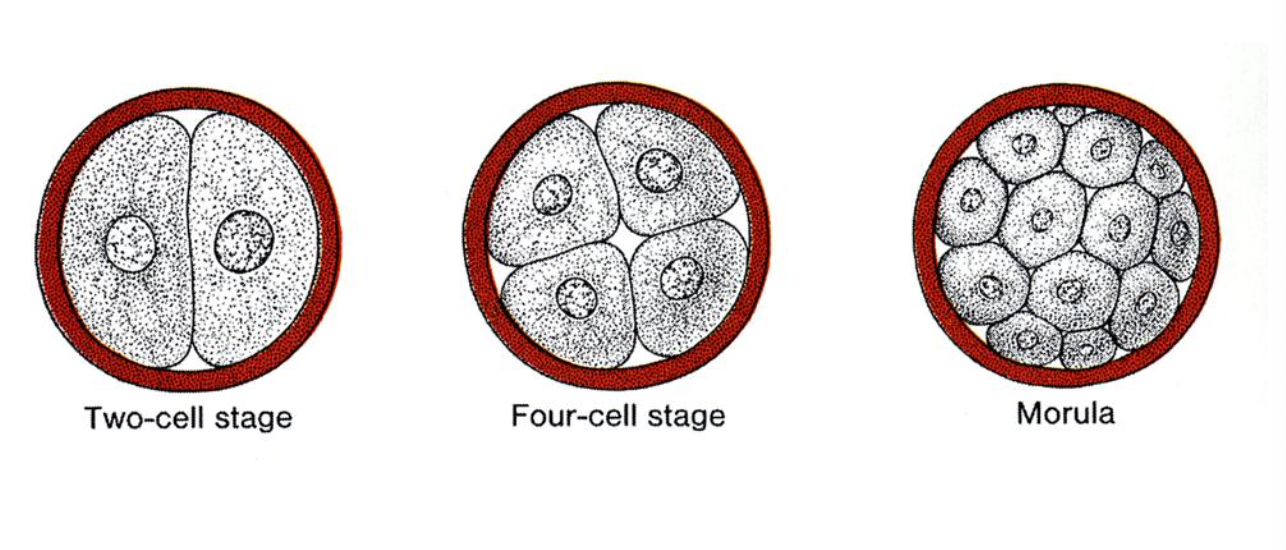
The oocyte completes meiosis 2, and the pronuclei fuse to restore diploidy. Several mitotic cleavages result in a solid morula.
meiosis 2
restore diploidy
a solid morula
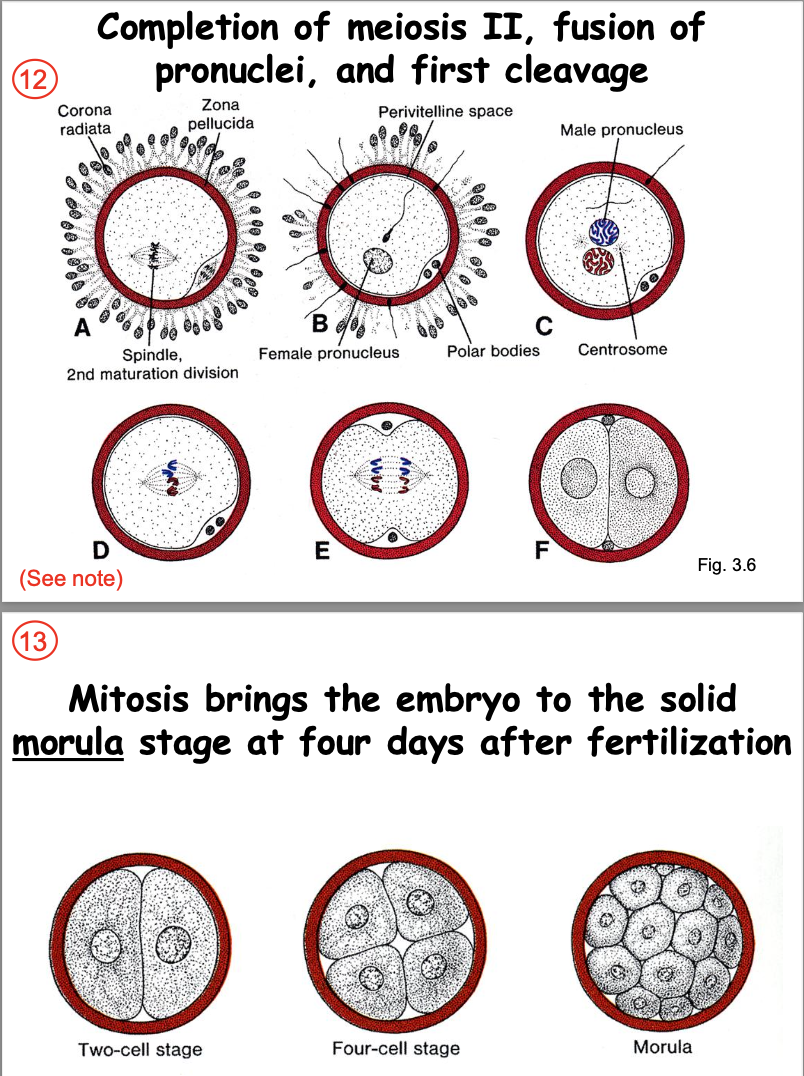
Timing and location of fertilization and implantation:

Mitosis brings the embryo to the ____ stage at four days after fertilization
solid morula
*corpus luteum stays in ovary
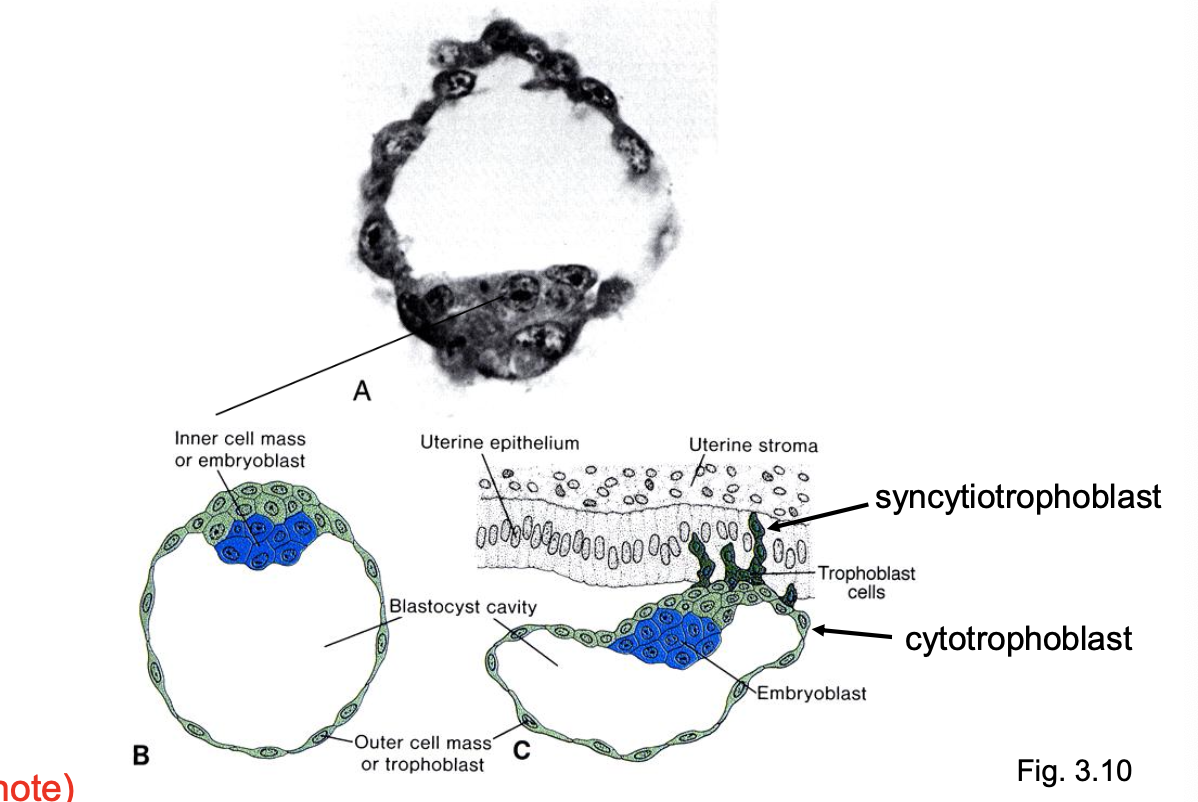
The _____, with an inner cell mass and ____ wall, implants/attaches to the _____ at day 6; ____ production maintains the corpus luteum.
hollow asymmetric blastocyt
trophoblast
uterine epithelium
hCG
Human embryos _____ mimic blastocyst formation and initiate implantation on a culture dish.
-can
Syncytial trophoblast connects with ______.
maternal blood vessels.
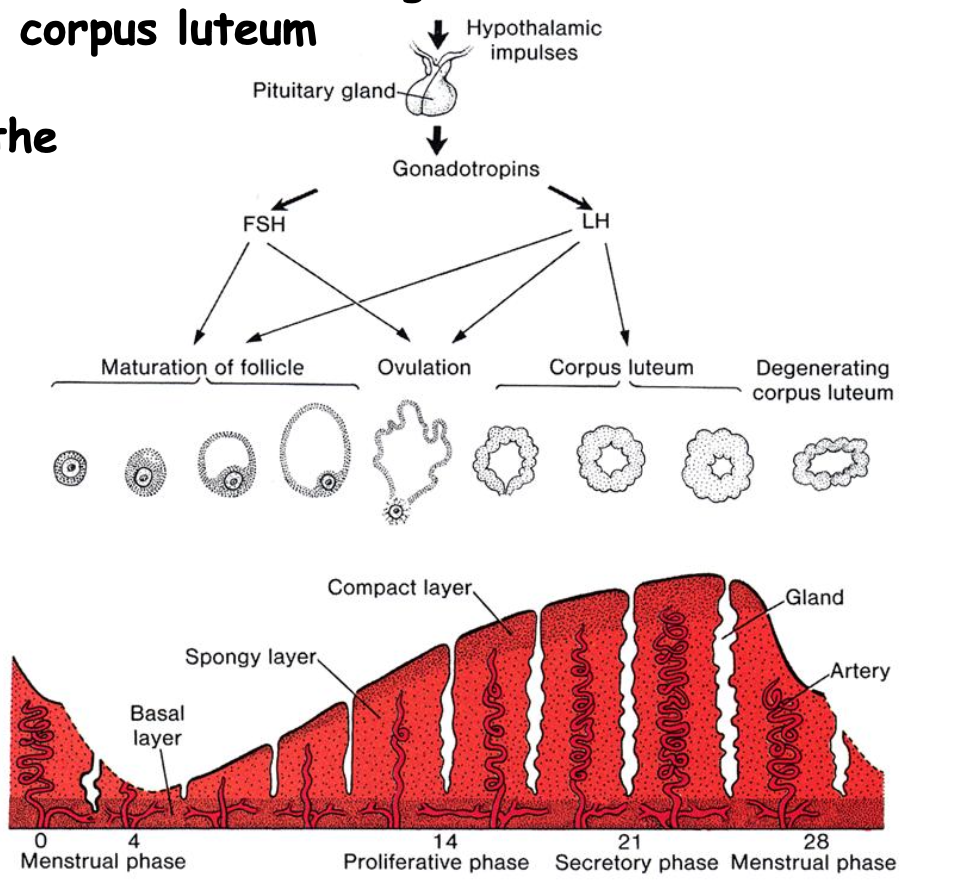
Pituitary FSH and LH sequentially initiate _______, but without implantation, the corpus luteum and endometrium ______.
ovulation, corpus luteum formation, and endometrial growth
degenerate and the menstrual phase ensues.
Changes occur in the _____ after implantation.
Source of hCG maintains the ______.
Source of progesterone maintains the ______.
corpus luteum & uterine lining
corpus luteum
implantation site
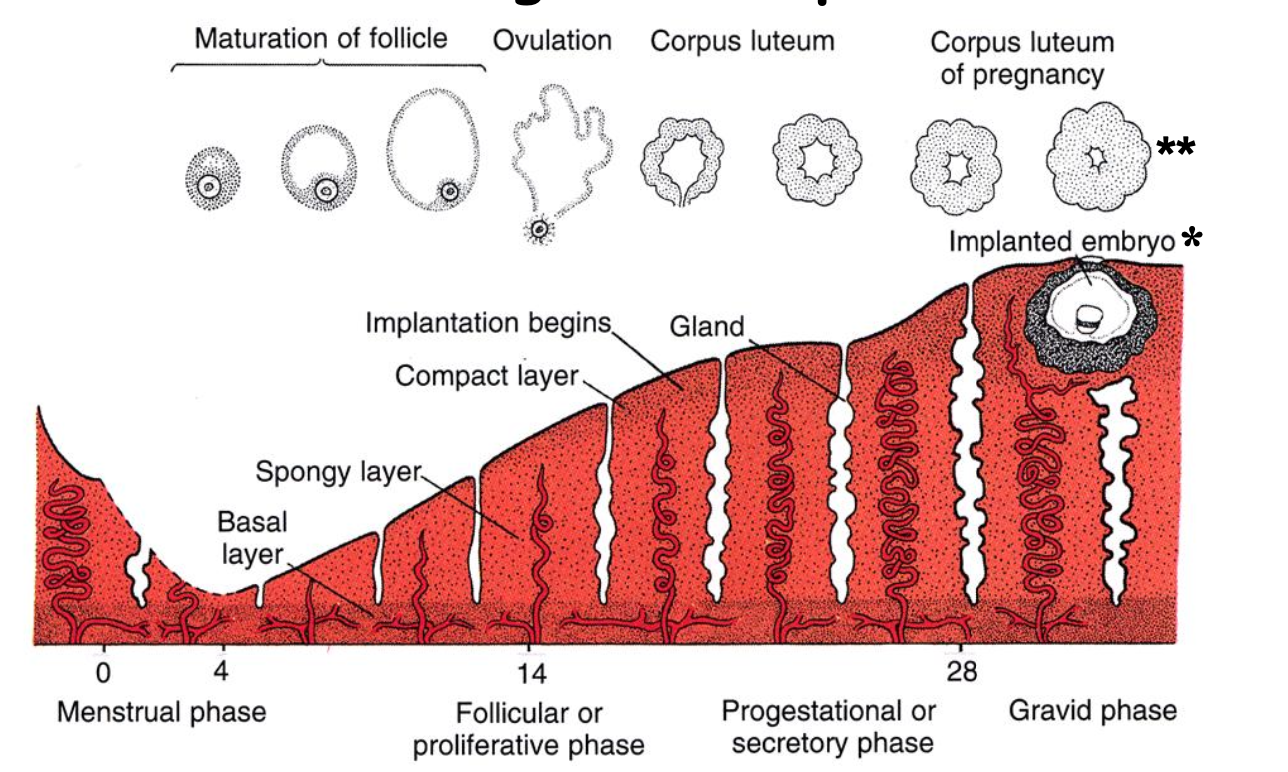
Inflammation, implantation, and maintenance of pregnancy
One half of all human uterine implantations result in _____. It is now believed that successful implantation requires _____ by the uterus that aids in successful development of the implantation site.
This hypothesis is supported by studies that show that uterine biopsies prior to IVF implantations stimulate ______.
Maintenance of pregnancy in ____ requires that the uterine inflammation be suppressed following implantation to prevent the implantation being rejected as a foreign body.
In _____, the implantation site is rejected within a few days and they are born early and poorly developed.
Work presented at a recent conference in 2017* provides evidence that _____ have evolved a mechanism whereby decidual cells in the uterus secrete factors that inhibit the inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL17) that promote rejection, allowing pregnancy to be maintained until rejection comes back into play at full term to stimulate the uterine contractions that initiate birth.
miscarriage
an inflammatory response
inflammation and increase the rate of successful implantations
mammals
marsupials
eutherian mammals
At 7.5 days, formation of _____ occurs.
epiblast, hypoblast, and amniotic cavity
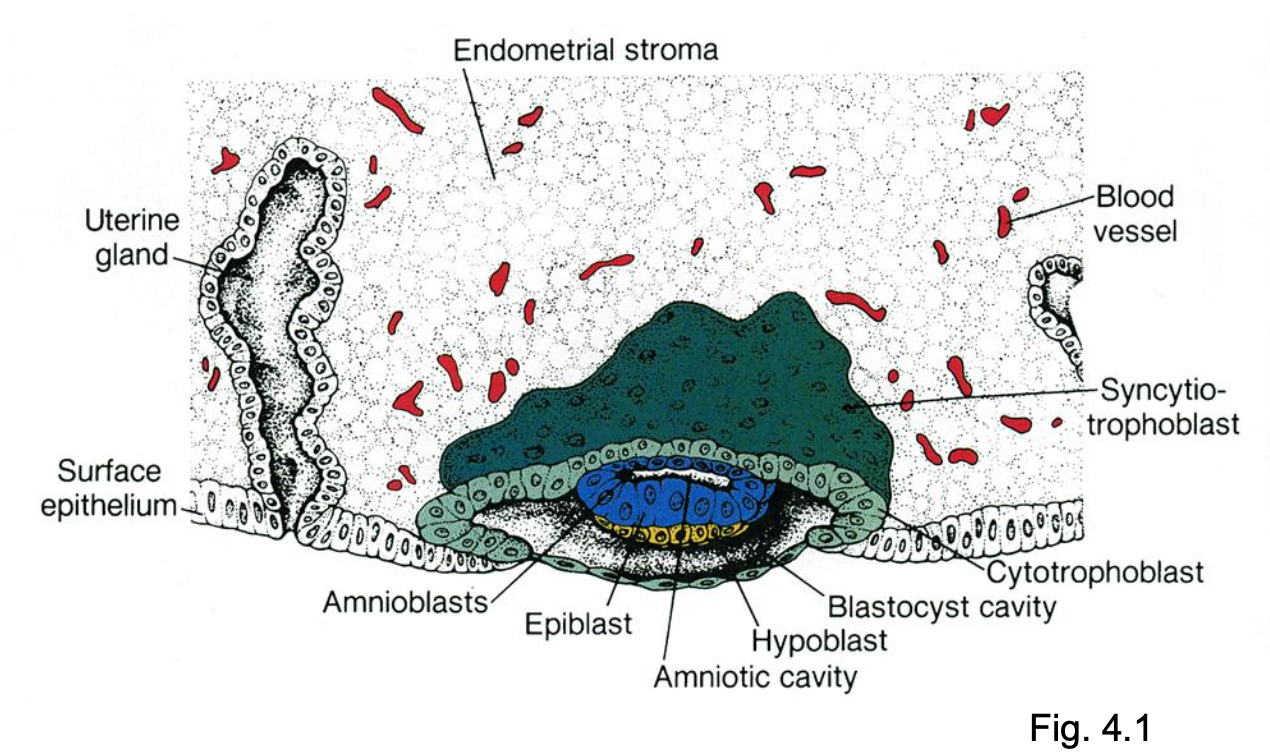
By day 9, _____ are now formed.
amniotic cavity, embryonic disc (bi-layered), trophoblastic lacunae & primitive yolk sac
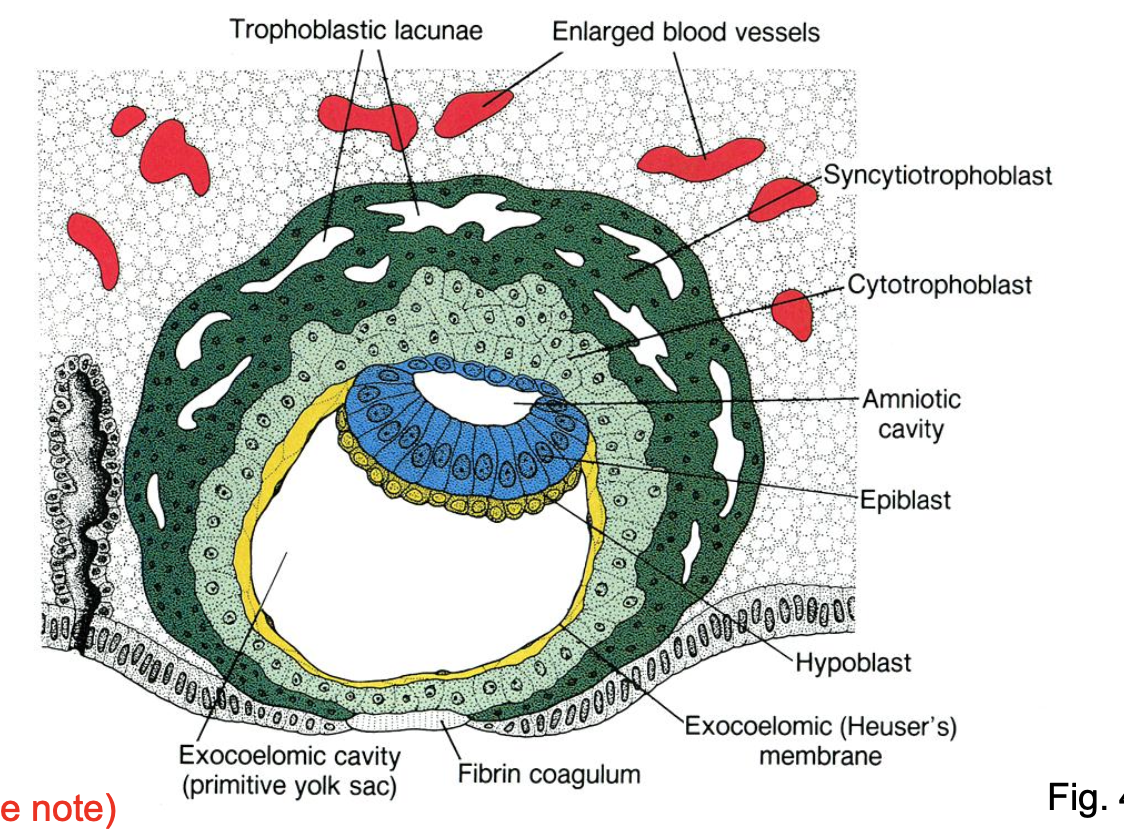
By day 12, the inner cell mass forms an embryonic disc of epiblast and hypoblast (bi-layered) between ______.
Maternal sinusoids also invade the ____.
the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac.
lacunae
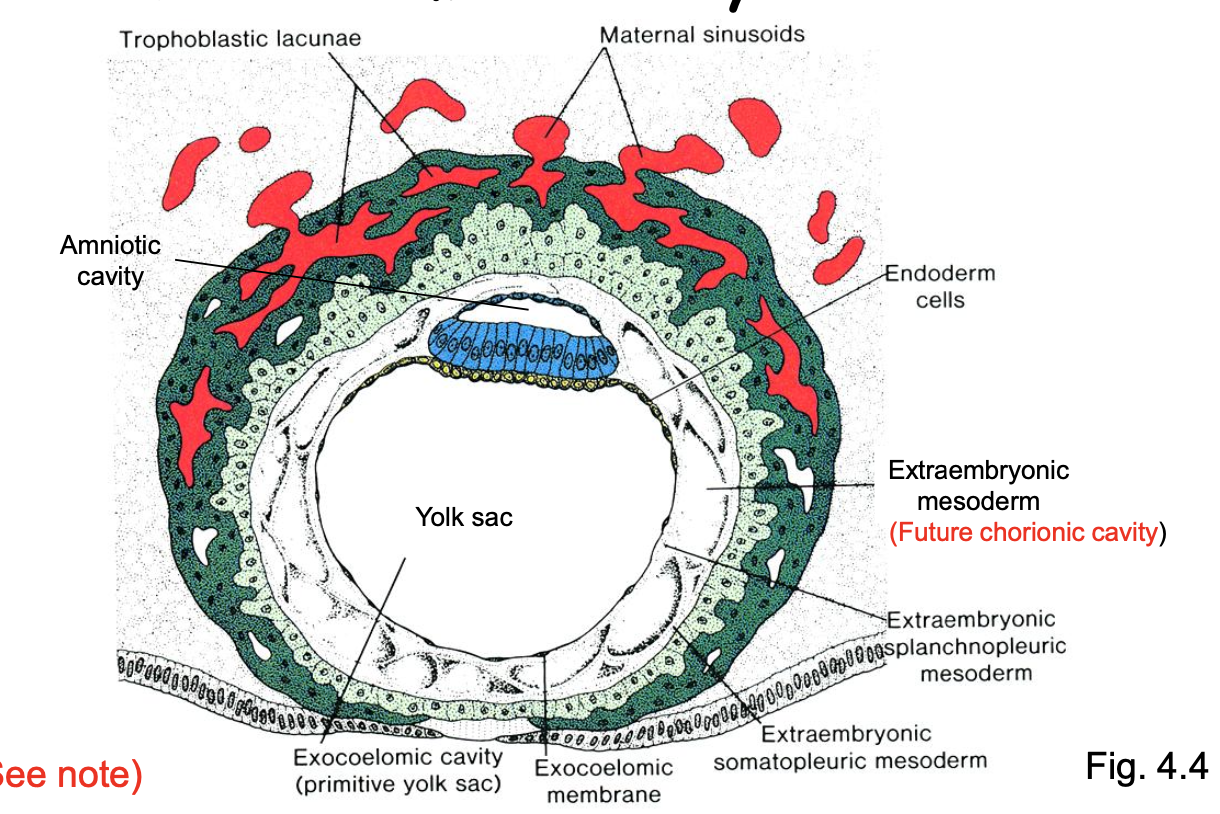
By Day 13, _____ are well- defined.
The _____ expands around the suspended embryo and its yolk sac.
amniotic cavity, yolk sac, and chorionic cavity
chorionic cavity
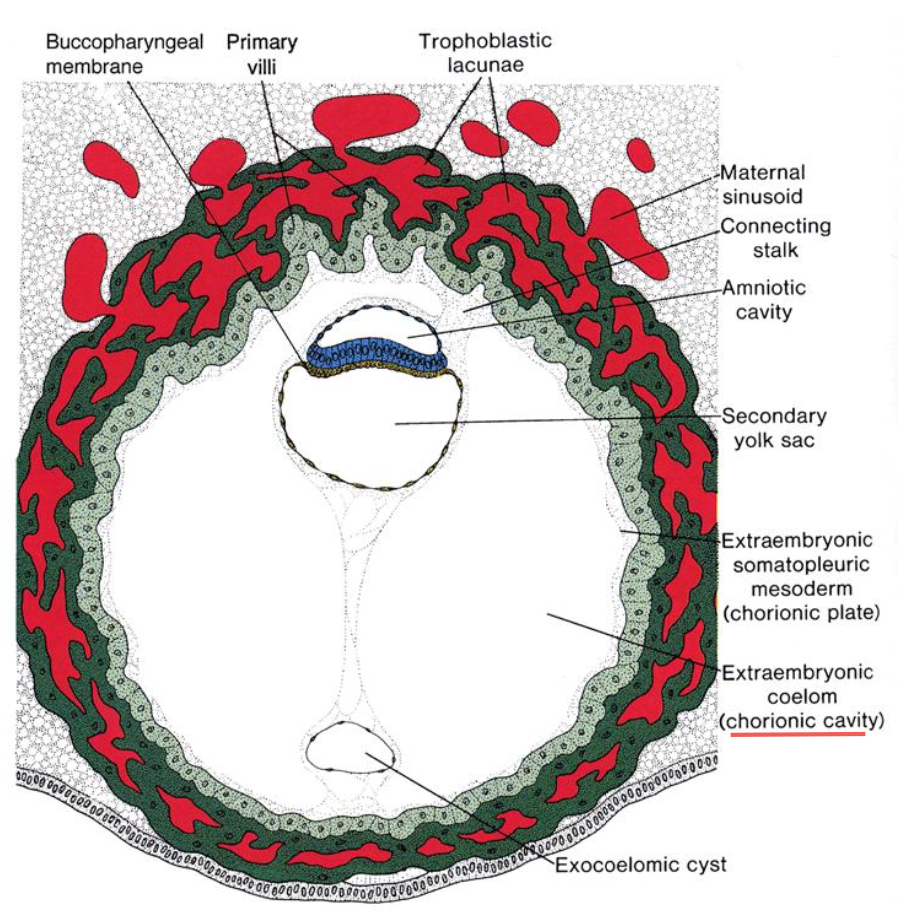
Implantation site, 14 days: Amniotic cavity, bi-layered embryonic disc, & yolk sac VIEW:

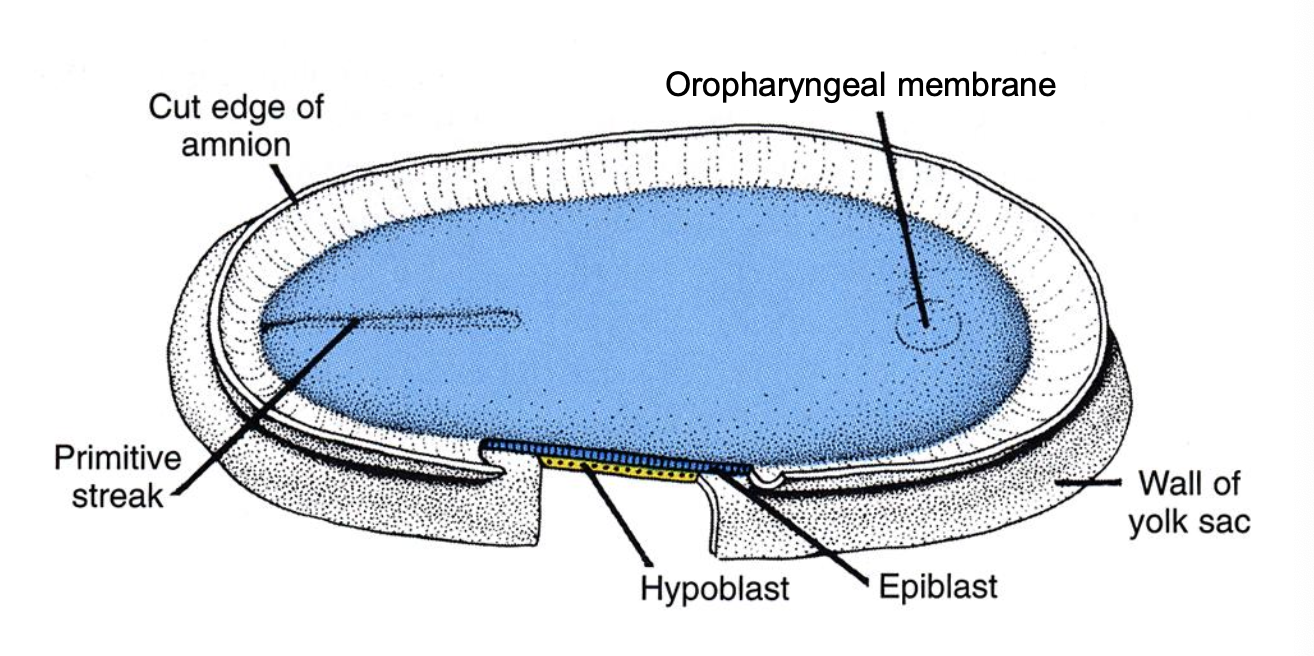
** The ______ signals the beginning of gastrulation.
The fetus develops from the _____ layer.
caudal primitive streak
epiblast
Learning Objectives:
Origin and migration of primordial germ cells.
The differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Origin, migration, and proliferation of primordial germ cells.
Arrest of primary oocytes at ______.
_____ stimulates follicular development.
_____ triggers ovulation, resumption of meiosis until re-arrest at _____, and corpus luteum formation.
Capacitated sperm digest the _____, and the first to arrive at the oocyte membrane triggers a cortical reaction.
The oocyte completes meiosis 2, and the pronuclei fuse to restore diploidy. Several mitotic cleavages result in a _____.
The _____, with an inner cell mass and trophoblast wall, implants at day 6; ____ production maintains the corpus luteum.
Syncytial _____ connects with maternal blood vessels.
The inner cell mass forms an embryonic disc of _____ between the amniotic cavity and the yolk sac.
The _____ expands around the suspended embryo and its yolk sac.
meiosis 1 prophase.
Pituitary FSH
Pituitary LH
metaphase of meiosis 2
zona pellucida
solid morula
hollow blastocyt
hCG
trophoblast
epiblast and hypoblast
chorionic cavity