Early Rome
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Ampitheater
A multi-story sporting arena, like the Colosseum, built in an oval plan. They featured gladiatorial battles, not dramatic plays.
Arch
A curved symmetrical structure spanning an opening and typically supporting the weight of a bridge, roof, or wall above it. can support greater weight than a post-and-lintel can, because it displaces its weight downwards to the piers.
Damniato Memoriae
Latin term meaning “damnation of memory,” a punishment for political crimes that resulted in the erasure of one’s likeness from public monuments and other imagery.
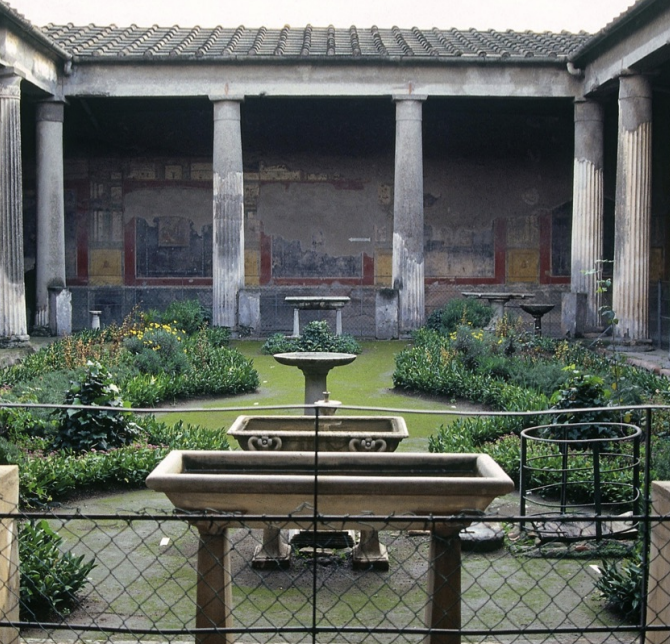
Atrium
An open courtyard just inside the entrance of a Roman house, typically outfitted with a sunken pool (impluvium) where rain water would be collected. The main focal point of a Roman house’s social and practical function.
Domus
Latin term for “house.”
Engaged Column
A column that is vertically sliced in half and attached to a wall.
Forum
The commercial, political and religious center of a Roman city. Public space.
Keystone
A wedge-shaped stone that locks voussoirs together to form an arch. Produces a downward thrust.
Oculus
Circular opening at the top of a dome. Solidifies the dome structure and allows natural light into the space.
Podium
A high stone base on top of which Roman and Etruscan temples stood.
Verism (veristic Style)
from the Latin word “verus (truth).” A form of realism in art that shows an interest in the faithful reproduction of the immediate visual and tactile appearance of subjects. Another translation might be the “Truthful style.”
Voussiour
Wedge-shaped blocks that make up an arch. They spring from an impost block of a pier, and are topped by a key-stone in the center.
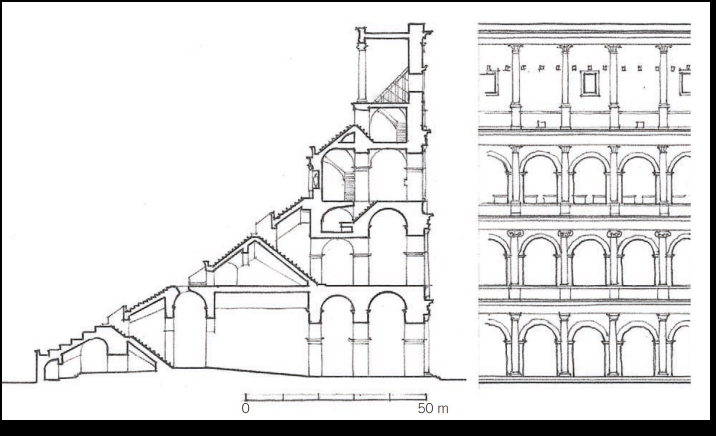
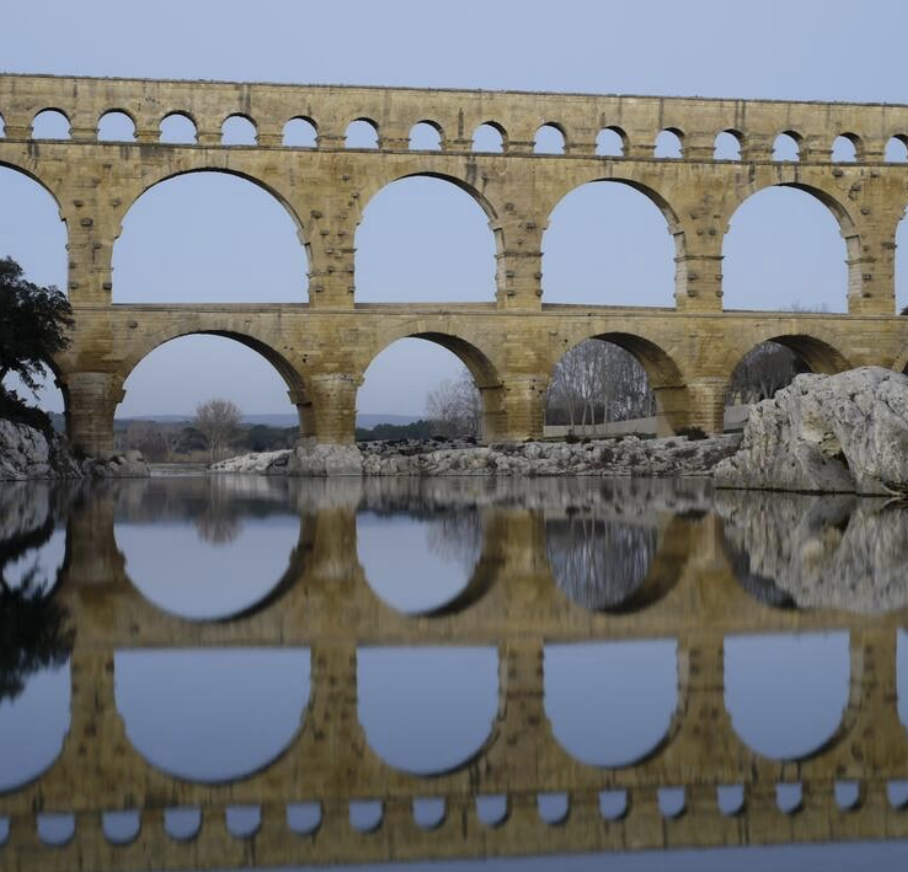
Pont du Gard

Domus of the Vettii
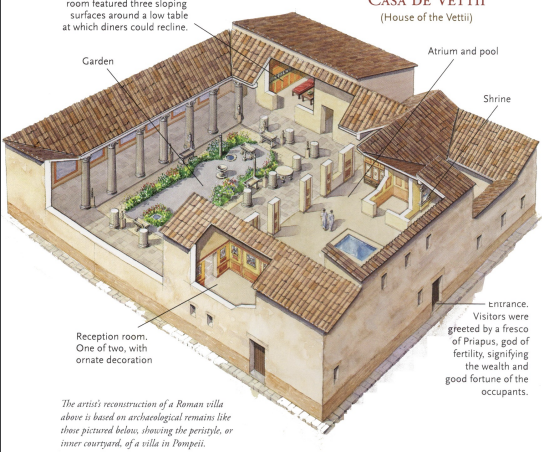
Domus of the Vettii
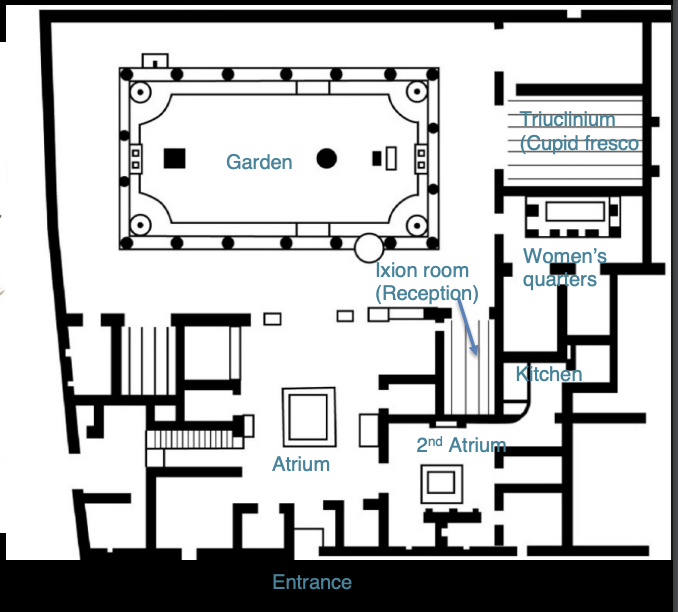
Domus of the Vettii

Insula of Diana
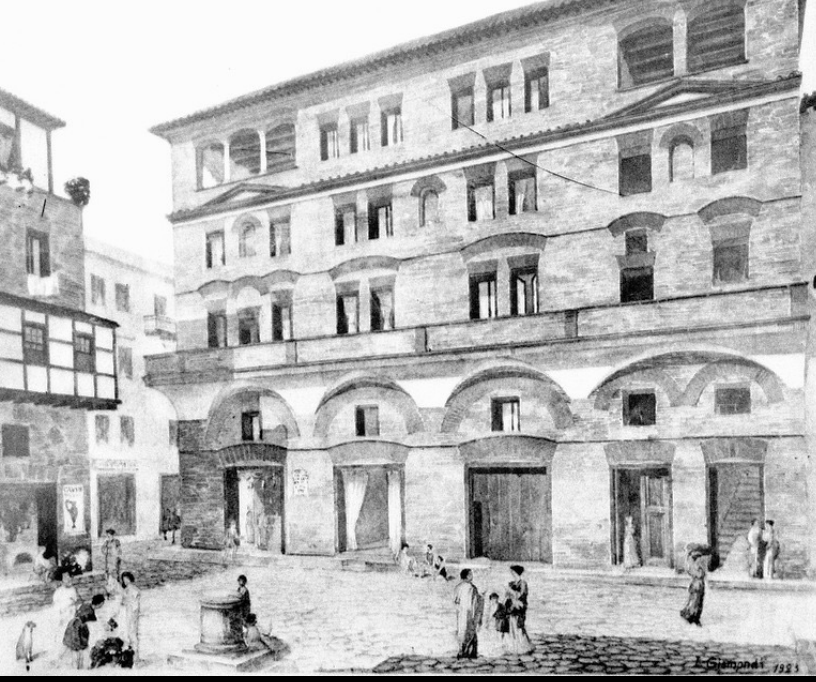

Insula of Diana
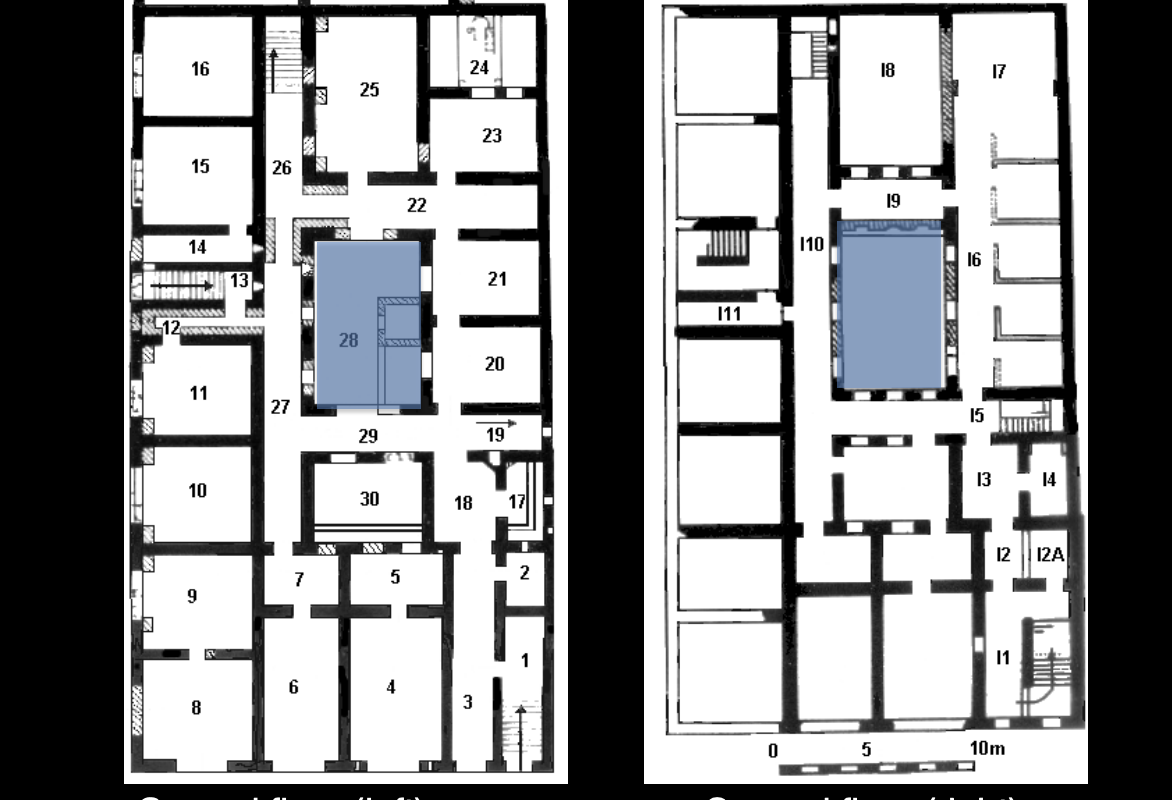
Insula of Diana
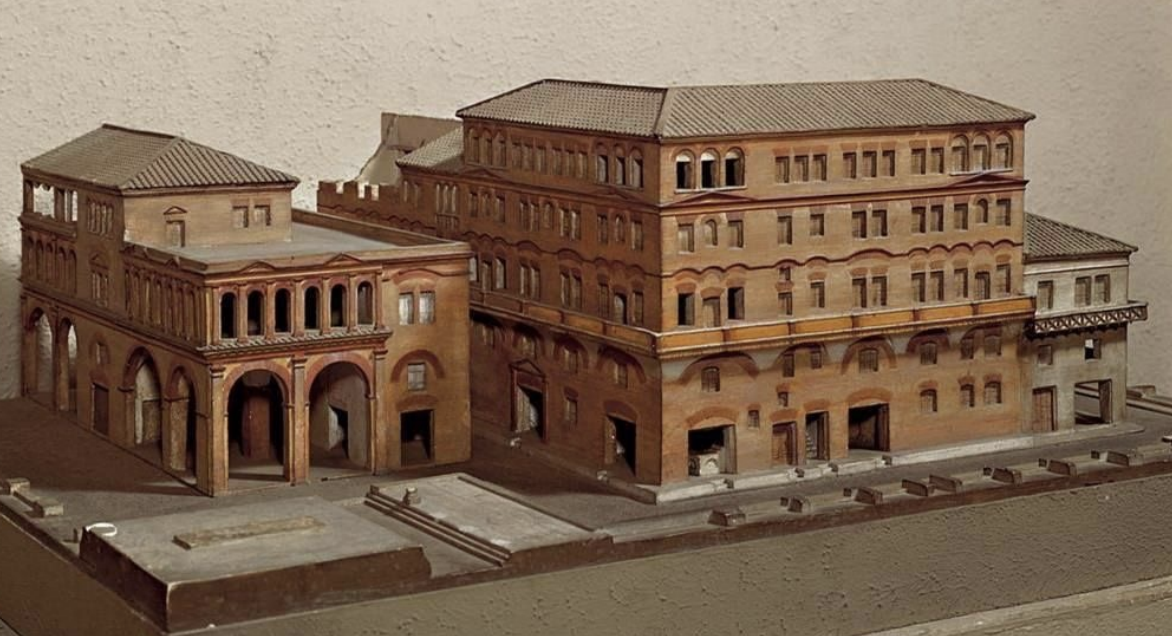

Domus Aurea Golden House of Nero
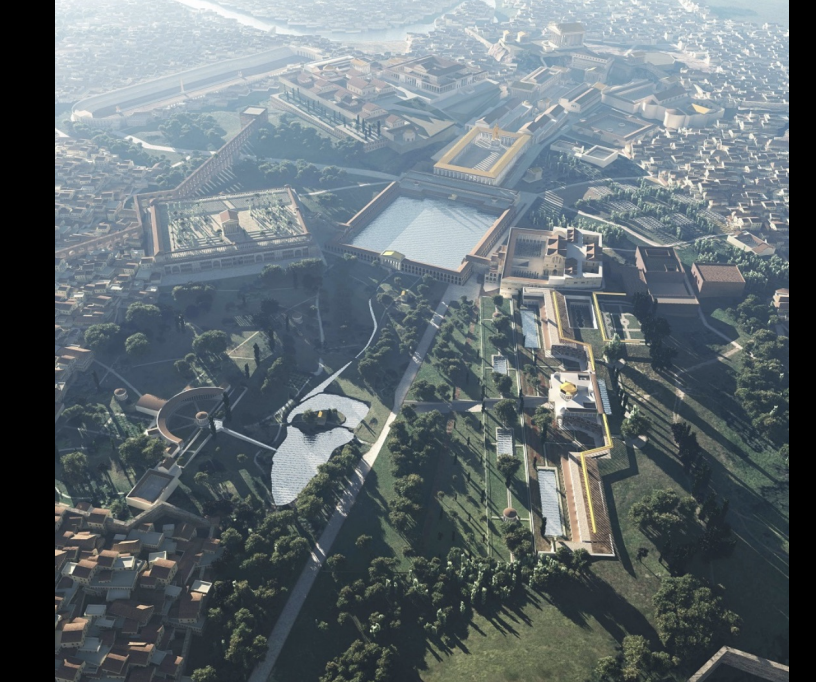

Octagonal room Domus Aurea
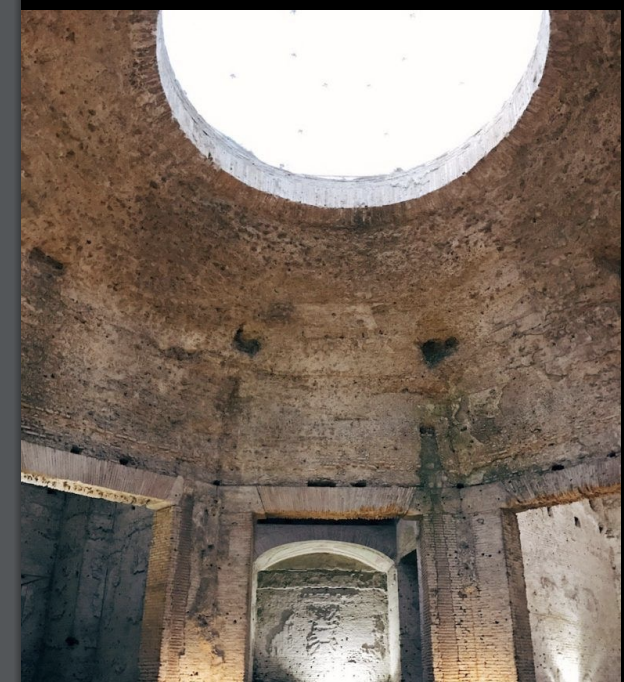

The Colosseum The Flavian Amphitheater