Adult Echo - Module 3
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 5-10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Start of Lecture 5
5
Explain the purpose of using M-mode.
precise recording of the position and motion of cardiac muscle, valves, and surrounding tissue
measurements can be compared against normal values
What is represented in the x and y axis of M-mode
x axis - time
y axis - depth
Name the primary limitation of M-mode.
If the M-mode line is not perpendicular with the anatomy, the measurement will be inaccurate
In an M-mode tracing of LV basal wall in PSLAX, list the measurements made and describe how to measure them
AoV
curser where the AoV leaflets close in diastole
aortic root diameter measured at end diastole from the tissue interface of the anterior wall of aortic root to posterior wall of aortic root
LA measured at end systole from the trailing tissue interface to posterior tissue interface
MV
cursor at the mitral valve leaflet tips
E point septal separation - space between the anterior leaflet and anterior LA wall
LV basal wall
cursor just past the mitral valve leaflets
IVS measured at end diastole from the right to left surfaces of the IVS
LVIDd measured at end diastole from the tissue edge of anteroseptal interface to tissue edge of inferolateral interface
Inferolateral wall diameter measured in end diastole from the endocardial surface to epicardial surface of the posterior wall
LVIDs measured at end systole from the tissue edge of anteroseptal interface to tissue edge of inferolateral interface
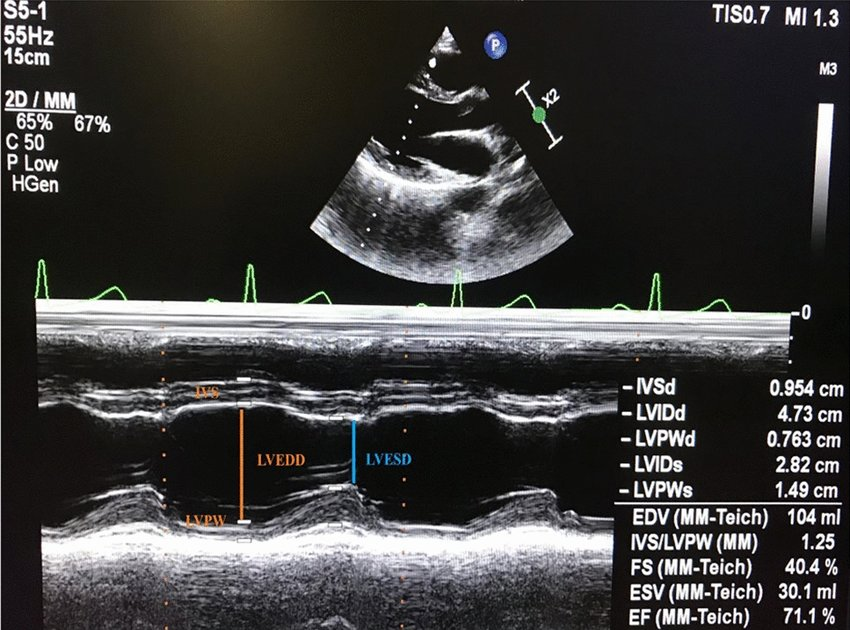
Normal value for LVIDd
W: 3.8 - 5.2cm
M: 4.2 - 5.8cm
Normal value for LVIDs
W: 2.2 - 3.5cm
M: 2.5 - 4.0cm
Normal value for IVS wall thickness
W: 0.6 - 0.9 cm
M: 0.6 - 1.0 cm
Normal value for posterior wall thickness
W: 0.6 - 0.9 cm
M: 0.6 - 1.0 cm
Normal range for aortic root
2.2 - 3.6 cm
Normal range for LA diameter
W: 2.7 - 3.8 cm
M: 3.0 - 4.0
What could cause a high EPSS (>5mm)?
dilated LV
mitral stenosis
aortic regurgitation
Define TAPSE
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion
from RV focused view
TAPSE<16mm = RV dysfunction
How much does the IVC collapse during the sniff test with a healthy RA? What is expected with an unhealthy RA?
Healthy - collapse more than 50%
Unhealthy - collapse less than 50%
Why measure echocardiograms?
echo exams can be standardized
study reproducibility
distances can be measures accurately
provides important diagnostic information
compare to normal values
important for follow ups (progress)
List the phases of the cardiac cycle.
atrial systole
isovolumetric contraction time
rapid ejection
reduced ejection
isovolumetric relaxation time
rapid filling
reduced filling
Name the two methods for calculating LV volumes from LV linear dimensions. Why are these not recommended for clinical use?
Teichholtz Method
Guinones Prolate Ellipsoid Method
Both rely on the assumption that the LV is a fixed geometric shape (prolate ellipse) - inaccurate assumption for many cardiac pathologies
Normal range for LV EF%
W: 54 - 74%
M: 52 - 72%
Normal range for FS
25 - 45%
A female patient has an EF of 45%. Is this normal? If no, what should the sonographer be looking for?
45% is lower than the normal range of 54-74%
This can be indictive of hypokinetic walls due to decreased contractility.
A female patient has an EF of 58%. Is this normal? If no, what should the sonographer be looking for?
58% falls within the normal range for a female.
When are 2D measurements used?
When M-mode is not optimal due to structures oblique to the cursor
What are some limitations of 2D measurements?
Lack of temporal resolution - may not get the optimal frame for measuring
Subject to more sonographer variability
Name the measurements made in PSLAX and when they are made.
End-diastole:
Ao root
IVS diameter
LVIDd
PW diameter
End-systole:
LA diameter
LVIDs
What are mechanical and electrical indicators of end systole?
Mechanical: frame after aortic closure, LV is smallest
Electrical: end of T-wave
What are the mechanical and electrical indicators of end diastole?
Mechanical: frame after MV closure
Electrical: peak R-wave
Where are measurements for the right heart imaged from?
Modified apical 4 chamber
SC 4 chamber
The LA used to be measured from the PSLAX anterior-posterior walls. Why is this no longer standard?
The relationship between the LA dimensions and the AP dimension is not maintained as the LA enlarges - inaccurate prediction of LA volume
Describe how the LA is measured.
In apical 4 chamber at end systole using an biplane area-length calculation
What is the difference between LAV and LAVI?
LAVI is the LAV indexed to body mass to make the measurement more diagnostic
Start of Lecture 6
6
The _______ method and ______ ______ ______ method are based on a single linear measurement of LV cavity made using 2D measurements in PSSLAX. These methods are not recommended for clinical use.
Teichholtz, Quinones prolate ellipsoid
Why are Teichholtz and Quinones methods not recommended for clinical practice?
Assumes fixed ellipsoid shape, which does not apply to many cardiac pathologies
Relationship between AP dimension and all other LA dimensions is not maintained as the atrium enlarges
FS =
(LVIDd-LVIDs) / LVIDd x 100%
EF =
(EDV-ESV) / EDV x 100%
When would a sonographer measure on a 2D image rather than in M-mode?
2D used when anatomy is not perpendicular to the scan line.
Name some advantages and limitations for 2D measurements.
Advantages
able to be perpendicular to anatomy
can be done in low PSLAX
can be done in other standard windows
Limitations
decreased temporal resolution
can’t know the same wall position is measured in systole and diastole
high intra-sonographer variability
single dimension not representative for distorted ventricles
List some advantages and limitations for M-mode.
Advantages
reproducible
high temporal resolution
Limitations
needs to be perpendicular to anatomy
single dimension not representative for distorted ventricles
According to ASE, if the walls are not perpendicular in M-mode, you don’t need to acquire a trace if 2D measurements are used. (True/False)
False - ASE requires M-mode trace but can be without measurements.
What imaging plane and method is used for RV measurements?
Modified apical 4 chamber (RV focused apical 4 chamber)
2D measurements
What phase of the cardiac cycle is RV measurements made from? What 2D measurements are made?
End-diastole
4 measurements: one of length and 3 of width (basal, mid, and apical)
Normal range for RV wall thickness.
1-5mm
A sonographer collects measurements of the LA volume through a linear M-mode measurement and a biplane area-length calculation. Which value is smaller? Which value is more accurate?
Linear measurement is smaller because it underestimates LA volume
Biplane area-length calculation is more accurate
Normal range for LA volume indexed.
16-34mL/m2
LAVI =
LA volume / BSA
Start of lecture 7.
7
If an echo is done accurately, it can…
improve patient care and management
reduce downstream repetitive testing (↑cost effectiveness)
guide clinical outcome
diagnosis
prognosis
therapy
Achieving a reliable echo exam requires…
understanding the standard imaging planes
recognizing the optimal image
utilize required modalities
perform standard measurements with accuracy and precision
recognize pathology and alter the scope of the exam to investigate
Reliability of a diagnostic test requires:
accuracy
measurements are sensitive and specific
correct recognition of pathologies
precision
reproducibility of study
expertise
quality is dependent on sonographer and interpreting physician expertise
List some limitations to performing a reliable echo.
small acoustic windows
patient body habitus (poor images)
pulmonary disease (artifact)
patient cooperation (duration of study)
presence of prosthetic valves (artifact)
technical limitations and artifact
sonographer expertise
An appropriate indication requires…
initial diagnosis that will change clinical status
results will change patient management
Start of lecture 8.
8
A Doppler shift is a measurement of…
The difference between the original frequency and the received frequency
The received frequency is less than the original frequency. What kind of Doppler shift is this? How would this appear on colour Doppler vs spectral Doppler.
Negative Doppler shift.
Appears as blue on colour Doppler.
Appears below the baseline in spectral Doppler.
Doppler in ultrasound is used to detect and quantify ______ and ______ in RBC.
direction, velocity
Doppler shift (Δf) =
(2 ft V) cosθ / c
Doppler shift is ______ dependent.
angle
Why are most Doppler measurements made in the apical window instead of the PSLAX?
Doppler shift is only accurate when flow is parallel to the soundwave. Flow is most perpendicular in the apical window.
When Doppler is measured at a 20° angle from flow, there is __% and at 60°, error is __%.
7,50
List some advantages and limitations of pulsed wave Doppler.
Advantages:
depth precision/range resolution
distinguish laminar vs turbulent flow
Limitations:
depth dependent → limited velocity range
What is the maximum velocity range of spectral PW Doppler? What is this limit called?
2 m/s → Nyquist limit
Define aliasing.
When the abnormal velocity exceeds the sampling rate, the PW system cannot record it properly and the display is of the other end of the velocity spectrum.
Velocity exceeds the Nyquist limit.
List some advantages and limitations of continuous wave Doppler.
Advantages:
no Nyquist limit → information is displayed accurately
not depth dependent
Limitation
range ambiguity
cannot differentiate turbulent and laminar flow
A spectral trace provides information about:
direction of flow
velocity of flow
quality of flow
On a spectral trace, x-axis represents _____ and y-axis represents _____.
time, velocity
List some advantages and limitations of colour Doppler.
Advantages:
displays quality of flow
larimar vs turbulent
antegrade vs retrograde
hematologic information in relation to anatomy
guides spectral Doppler sampling
Limitations:
limited quantification
averaged velocity, not exact
limited maximum velocity (Nyquist limit)
Name the types of ultrasound Doppler.
tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)
spectral pulsed wave Doppler
spectral continuous wave Doppler
colour Doppler
TDI can assess…
strain and strain rate
myocardial mechanics and velocities
What modifications in signal processing does the machine need to do to accurately demonstrate TDI?
increase amplification (receiving very low signals)
filter blood flow signals (filter high velocities)
Why would a sonographer choose to listen to Doppler sounds?
More sensitive to audible changes than visible.
Compare 2D imaging and Doppler in terms of:
what is measured
goal of diagnosis
type of information
optimal alignment
preferred operating frequency
2D imaging:
measures tissue
assesses anatomy
structural information
optimal perpendicular to structures
prefers high frequency (↓SPL)
Doppler:
measures blood (and tissue in TDI)
assesses physiology
functional information
optimal parallel to blood flow
prefers low frequency (↑SPL)
In a PW tracing, there is significant aliasing. Is there anything the sonographer can do to reduce aliasing?
Yes
optimize baseline position
increase velocity scale
switch to CW
Provide some other names for sample volume box (SVB).
sample volume (SV)
range gate
gate
Define vena contracta.
Narrowest central flow region a jet that occurs at the orifice of the valve. Characterized by high velocity, laminar flow.
What drives blood flow during the cardiac cycle?
Pressure gradients.
What is a pressure gradient?
Flow from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
In an apical 5 chamber, CD shows blue at the AoV during systole. Does this represent antegrade or retrograde flow?
Antegrade.
In an apical 5 chamber, CD shows blue at the MV during systole. Does this represent antegrade or retrograde flow?
Retrograde.
List the windows and views the velocity and direction of LV inflow can be assessed.
apical 4 chamber
apical 3 chamber
apical 2 chamber
Define the E wave and what flows demonstrate an E wave.
Early diastolic filling (phase 6 of cardiac cycle)
flow accelerates quickly to a maximum velocity
flow decelerates as atria and ventricle pressures equalize
Seen with:
LV inflow
RV inflow
Define diastasis and what flows demonstrate diastasis.
Reduced filling (phase 7 of cardiac cycle)
slow flow as atria and ventricle pressures equalize
Seen in:
LV inflow
RV inflow
Explain what happens to diastasis with increasing HR.
A fast HR has a very small diastasis because there is less time between rapid filling and atrial filling. This makes the E and A wave compressed closer because flow remains fast.
Define A wave and what flows demonstrate an A wave.
Atrial systole (phase 1 of cardiac cycle)
atrial contraction reestablishes pressure gradient between atria and ventricle → ↑flow and velocity
Seen in:
LV inflow
RV inflow
Normal velocity range of E wave in LV inflow.
0.6-1.3 m/s
Normal velocity range of A wave in LV inflow.
0.2-0.7 m/s
Describe the E/A ratio. When would the E/A>1? When would E/A<1?
Difference between the pressure gradient in rapid filling and atrial systole.
>1 in young adults
<1 in older adults (>65 years old)
List the windows and views the velocity and direction of RV inflow can be assessed.
modified apical 4 chamber
PSSAX at AoV
PSLAX RV inflow
Normal velocity range for RV inflow.
0.3-0.7 m/s
How can LV inflow and RV inflow be differentiated on a PW trace?
VMV > VTV
MV peak velocity closer to 1
↑spectral broadening in TV
↑variation in TV due to respiration (E and A wave height changes between cardiac cycles)
Normal velocity range for LVOT flow.
0.7-1.1 m/s
List the windows and views the velocity and direction of LVOT flow and AV flow can be assessed.
apical 5 chamber
apical 3 chamber
Normal velocity range for AV flow.
1.0-1.7 m/s
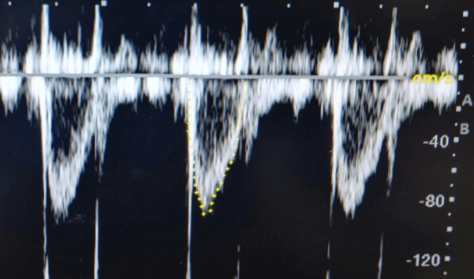
Describe this trace in terms of:
modality
quality of flow
peak velocity
shape of the flow
what is being measured
PW Doppler
laminar flow
peak velocity at ~90cm/s
monophasic laminar flow below the baseline that peaks at early systole
LVOT is being measured
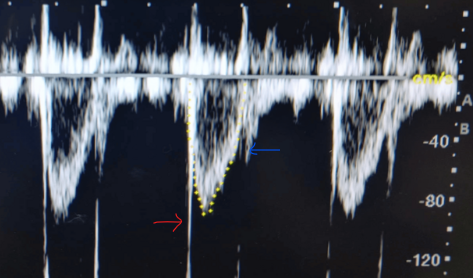
Describe what the red and blue arrows are indicating.
Red arrow → AoV opening (AoV opening click)
Blue arrow → AoV closing (AoV closing click)
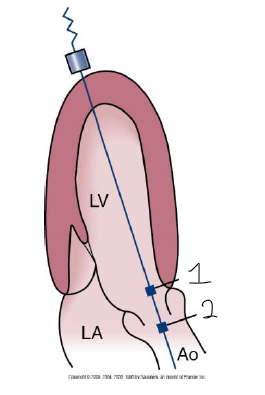
Describe the SVB positions displayed.
LVOT - just proximal to AoV annulus
Aortic flow - center of the aorta, close to cusp coaptation (vena contracta)
Normal velocity range for ascending aorta.
1.7 m/s
Normal velocity range for descending aorta.
1.7 m/s
What ultrasound modality would a cardiac sonographer use for quantifying flow through the aorta? Why? Name a limitation of using this modality.
CW
no aliasing
highest velocity will be flow through the aorta and can be measured
limitation - don’t know quality of flow
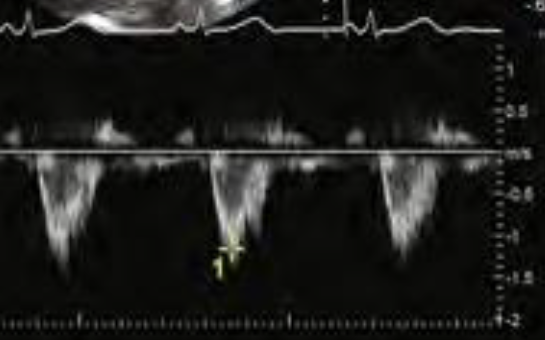
Describe this trace in terms of:
modality
quality of flow
peak velocity
shape of the flow
what is being measured
PW Doppler
laminar flow away from the transducer
peak velocity at ~1.2 m/s
monophasic laminar flow below the baseline that peaks in early systole
descending aorta or AV flow
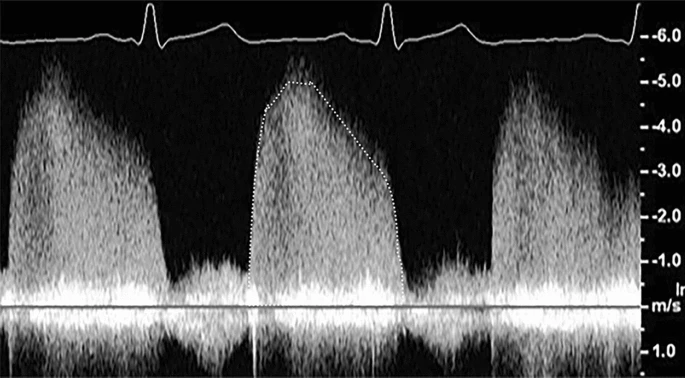
Describe this trace in terms of:
modality
quality of flow
peak velocity
shape of the flow
what is being measured
CW Doppler
CW does not assess quality of flow
peak velocity of 5 m/s in diastole and 1 m/s in systole
high velocity indicates pathology
no IVCT or IVRT - indicates regurgitation
high velocities suggest AoV regurgitation