DNA Replication & Biotechnology Applications: IB HL Biology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is DNA replication?
The process by which exact copies of DNA are created for reproduction, growth, and tissue replacement in multicellular organisms.
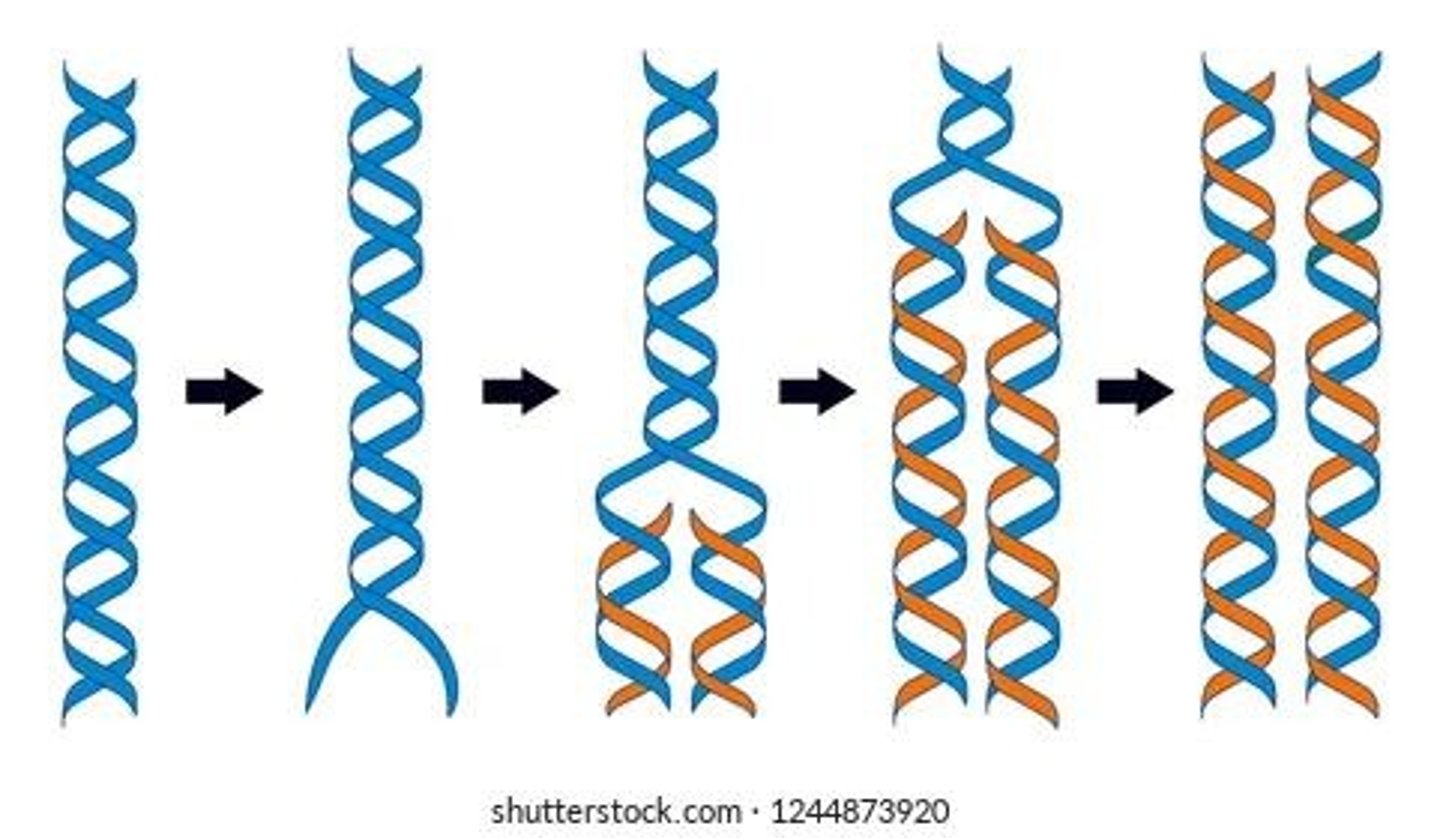
What does semi-conservative DNA replication mean?
It means that after replication, each double-stranded DNA contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What is the role of helicase in DNA replication?
Helicase binds to the origin of replication and unzips the double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between bases.

What do single-strand binding proteins do?
They bind to single-stranded DNA to keep the strands separate and prevent hydrogen bonds from reforming.
What is the function of gyrase/topoisomerase during DNA replication?
It relieves the tension created by supercoils ahead of the replication fork.
Which enzyme synthesizes the complementary DNA strand?
DNA Polymerase III (DNA pol III).
In which direction does DNA Polymerase III build the new DNA strand?
In the 5' to 3' direction.
What is the role of primase in DNA replication?
Primase creates a short RNA primer for DNA polymerase III to add nucleotides to.
How does DNA Polymerase III proofread DNA?
It checks for mismatched bases during synthesis and replaces them with the correct ones.
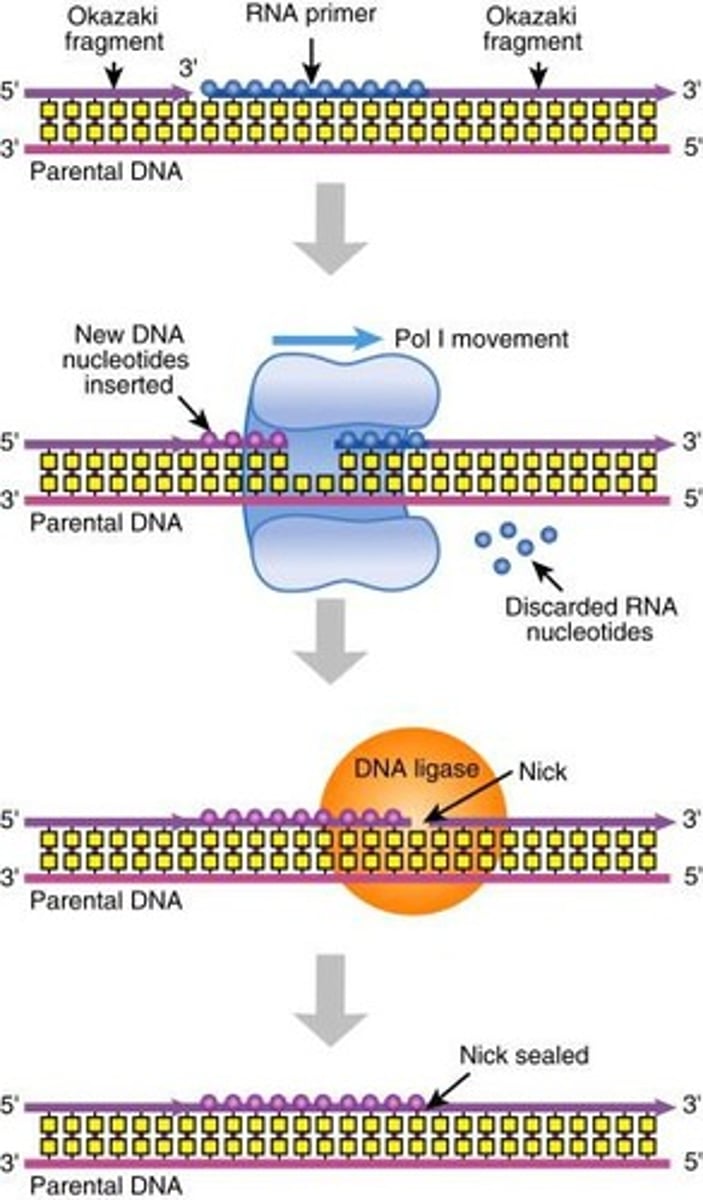
What happens to RNA primers after DNA replication?
DNA Polymerase I removes the RNA primers and replaces them with DNA nucleotides.
What are Okazaki fragments?
Short DNA segments synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
What is the difference between the leading and lagging strands?
The leading strand is synthesized continuously, while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in fragments.
What enzyme connects Okazaki fragments?
DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds between Okazaki fragments.
What is the purpose of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
To amplify small fragments of DNA, creating millions or billions of copies.
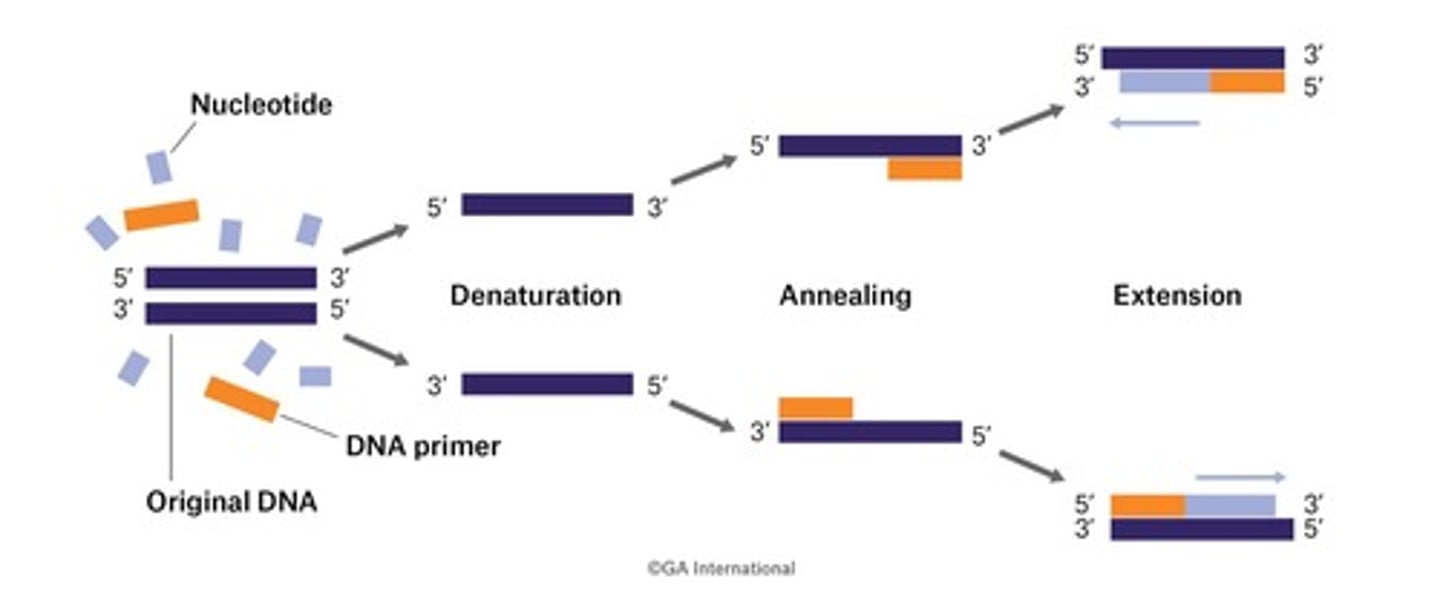
What are the three main steps of PCR?
Denaturation, annealing, and extension.
What is Taq Polymerase?
A heat-stable DNA polymerase enzyme used in PCR, originally found in a prokaryote living in hot springs.
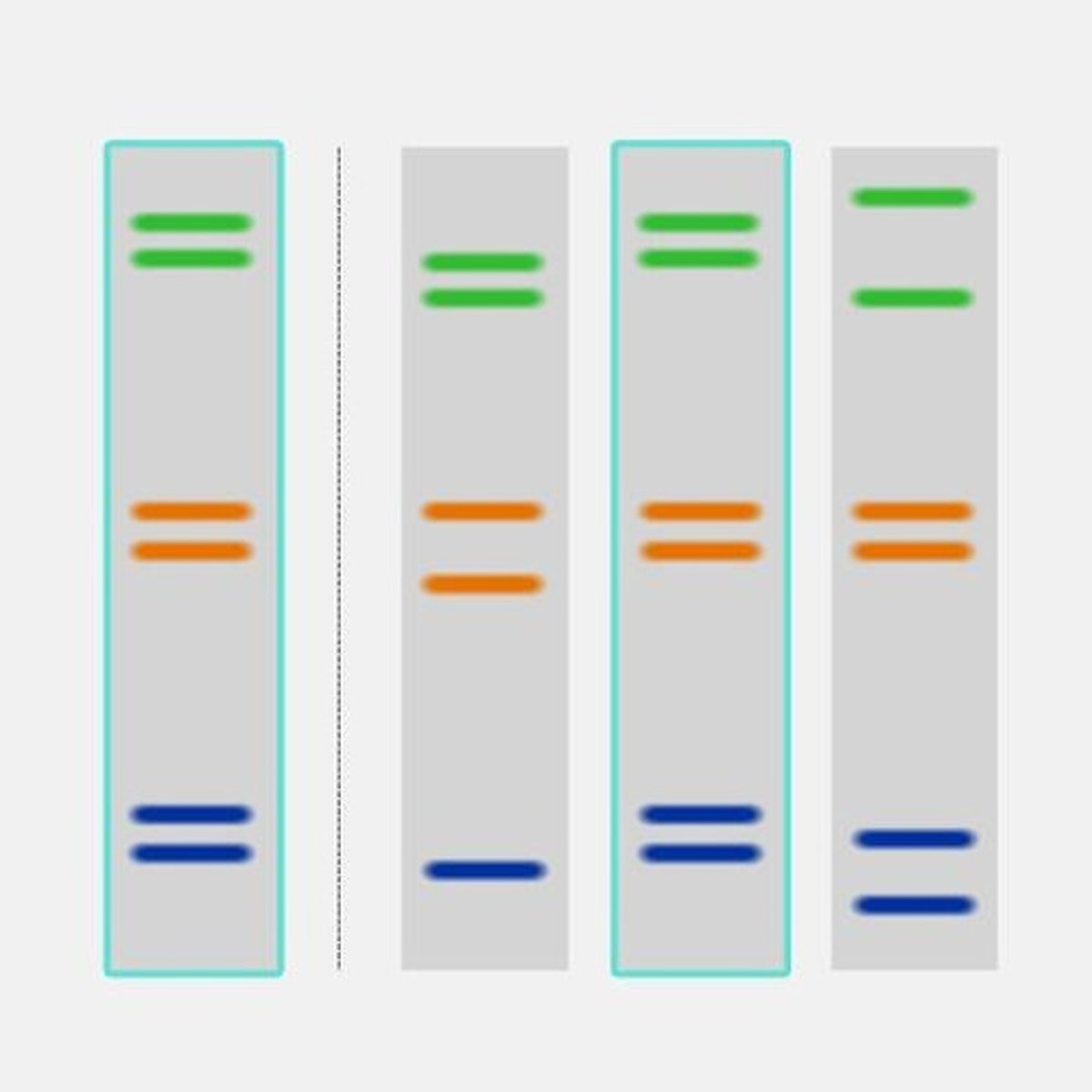
What is gel electrophoresis used for?
To separate DNA fragments based on size using an electrical current.
What are restriction enzymes?
Enzymes that cut DNA molecules at specific sequences, often used before gel electrophoresis.
What is a DNA fingerprint?
A unique pattern of bands created when a DNA sample is run through a gel after being cut by restriction enzymes.
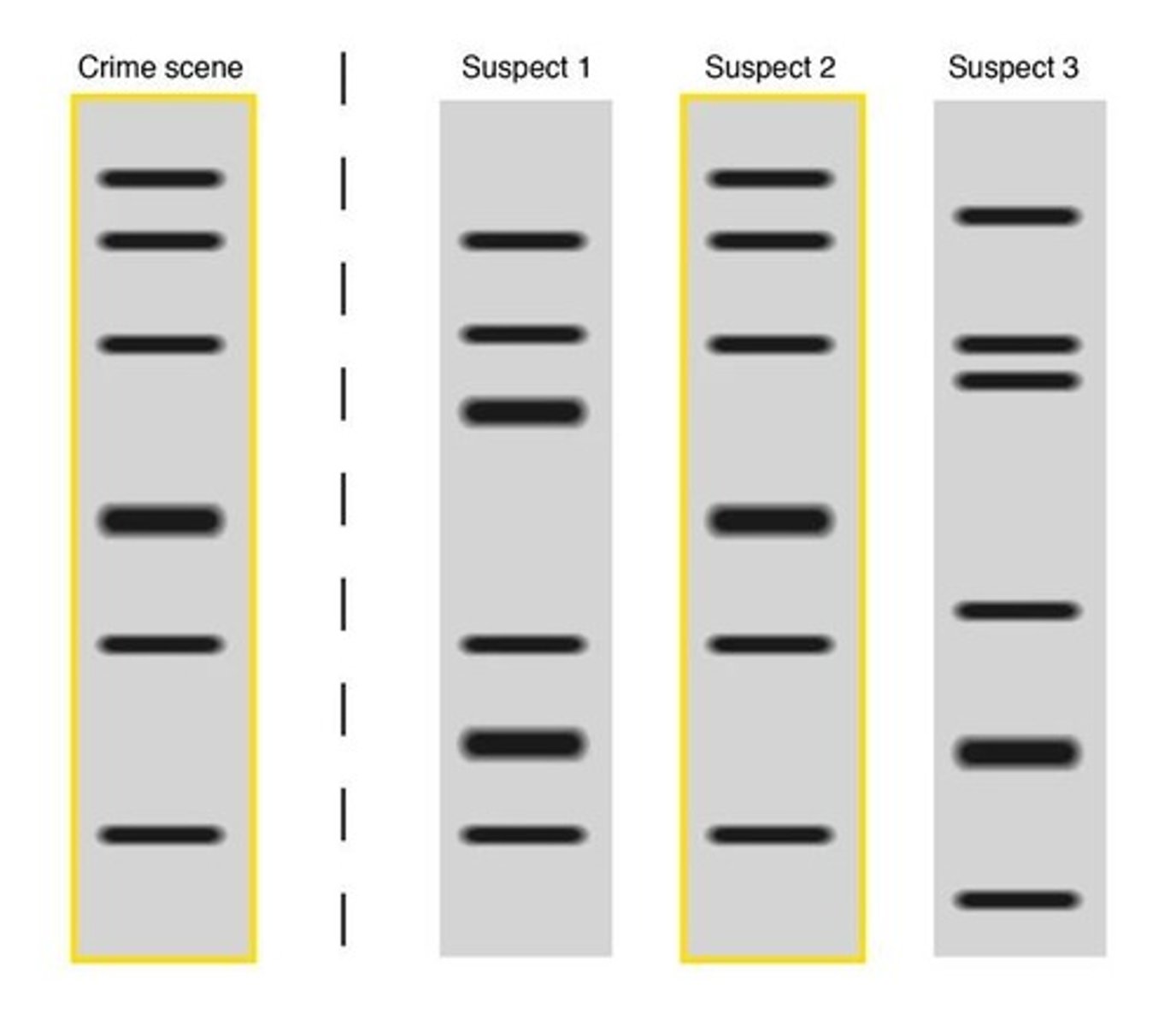
How can PCR and gel electrophoresis be applied in real life?
They are used in COVID-19 testing, paternity testing, and forensic investigations.
What is the significance of mutations during DNA replication?
Mutations can create variation for natural selection to act upon.
What is the directionality of DNA strands?
DNA strands are antiparallel; one runs 5' to 3' and the other runs 3' to 5'.
What is the role of DNA polymerase I?
To remove RNA primers and replace them with DNA nucleotides.
What is the replication fork?
The region where the original DNA double helix splits into two strands during replication.
What is the function of complementary base pairing in DNA replication?
It ensures that each new DNA molecule is identical to the original.
What is the significance of the 3' sticky end in DNA synthesis?
DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of an existing strand.