The Early embryonic stage of the first trimester
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Chorionic villi sampling (CVS)
diagnostic genetic testing performed in the first trimester between 11 and 13 weeks.
Gestational Age
menstrual age; used to date the pregnancy with the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP) as the beginning of gestation.
would add 2 weeks onto the conceptual age
Zygote
for 12 days after conception, during the implantation process
buries itself into one wall of the uterus by the end of the implantation process.
Embryo
time of implantation until the end of the 10th week menstrual age
Fetus
embryo after the first 10 weeks
How is the 16 cell morula formed?
rapid cellular division of the zygote. continued cell proliferation creates the blastoma.
Human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG)
secreted by trophoblastic cells and is absorbed within the tubes; stimulates maternal pregnancy responses.
decidua
a glycogen rich mucosa that nourishes the early pregnancy.
hcg causes the uterine endometrium to convert to this.
when does the blastocyst typically enter the uterus?
4 to 5 days after fertilization
when is implantation into the uterus decidua completed?
within 12 days after fertilization.
Lacunae
blood pools created by enzymes eating into decidual tissues.
maternal capillaries that erode and nourish the proliferative cells
along with the trophoblastic cells- develops into the placenta
Secondary yolk sac
seen sonographically as the first identifiable structure throughout the first trimester
at 5.5 weeks the primitive yolk sac gradually reduces in size and becomes the secondary sac.
Amniotic and chorionic cavities
cavities that develop and evolve during the first trimester.
amniotic cavity
contains the fetus
Gestational sac should be visible by TV ultrasound at weeks, and the yolk sac may be visible at ____ weeks
5; 5.5
what is seen on US at 6 weeks?
the embryo; appears as a 1 to 4 mm echogenic structure within the gestational sac
when is the amnion visualized and what is the embryo measurement?
7 weeks; measures 10 mm in length
Crown rump length (CRL)
measures 35 mm by the end of the 10th week.
embryo changes rapidly from a disk-like configuration to a C-shaped structure
measurement of the mean sac diameter (MSD)
gestational sac size and hCG levels increase until 10 menstrual weeks where it will measure approximately 45 mm
hCG levels where a normal gestational sac is expected to be visible?
greater than 1000mIU/mL to 2000 mIU/mL
hCG indications of a possible ectopic
greater than 2000- 3000 mIU/mL
IUP
intrauterine pregnancy
Normal IUP less than 7 weeks _____
doubles hCG levels every 3.5 days
what happens to hCG levels at 9 to 10 weeks?
they plateau and decline while gestation continues
what happens to the hCG levels in a trisomy 21 pregnancy?
plateau later and decrease much slower.
trisomy 21
down syndrome
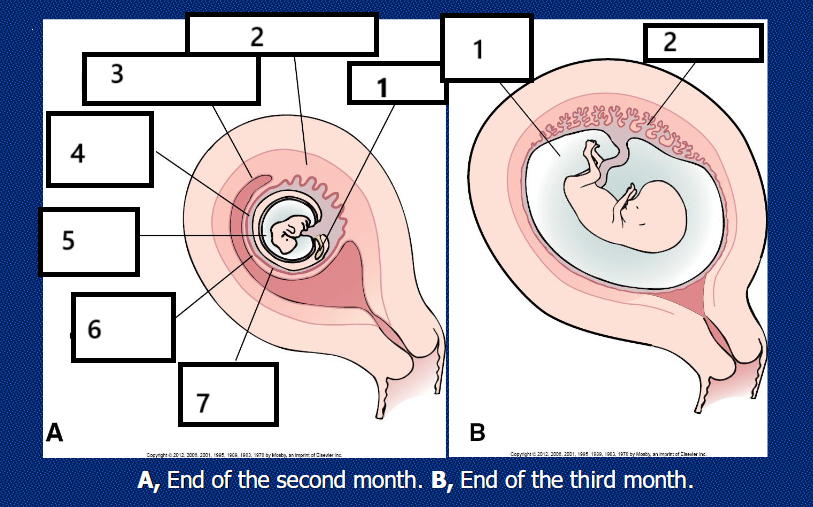
image A
yolk sac, decidua basalis, decidua parietalis, chorionic cavity, decidua capsularis, chorion laeve
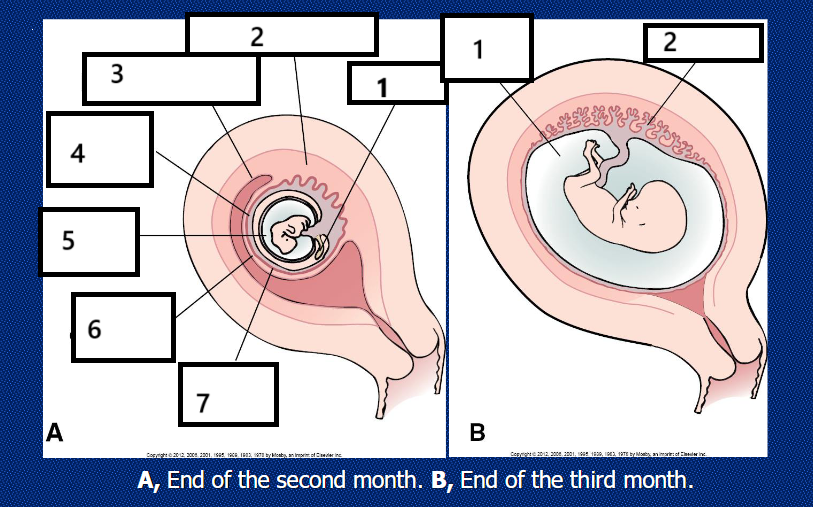
image B
amniotic cavity, placenta
yolk stalk
connects yolk sac to the embryo
at what week development do the intestines return to the abdominal cavity?
week 10, with a full return by the end of the 11th week.
gestational sac is also known as the
amniotic cavity
sonographic appearance of the gestational sac
anechoic fluid collection containing a yolk sac or an embryo with cardiac activity.
2 to 3 mm sac w/ an echogenic ring having a sonolucent center.
echogenic ring represents the chorion/ decidua capsularis; anechoic center represents the chorionic cavity.
decidua basalis
portion on the myometrial or burrowing side of the conceptus
decidua capsularis
villi covering the developing embryo
double decidual sac sign
interface between decidua capsularis & decidua on opposite endometrial cavity wall
gestational sac should be where?
eccentrically placed in relation to the endometrial
three essential functions in embryonic development are
providing nutrients to the developing embryo, hematopoiesis, development of embryonic endoderm (which forms the primitive gut)
diameter measurements of the yolk sac
2 to 6 mm diameter, and measured from inner border to inner border.
indications of fetal abnormality or pending loss?
yolk sac is abnormal in appearance (normal is a circular structure), too small or too large, calcified, misshapen, or highly echogenic
regarding TV scans, a failure to visualize ____ would be suspicious of abnormal pregnancy
the yolk sac with a minimum of 12 MSD
TA studies, yolk sac should be seen ___
within MSDs of 10 - 15 mm and should always be seen with an MSD of 20 mm
growth rate of the yolk sac
0.1 mm/mL of MSD growth when MSD measures less than 15mm,
and
0.03 mm/ mL of growth of MSD through 1st trimester
normal diameter of yolk sac
should not exceed 6mm
in twin pregnancies -monochorionic, monoamniotic pregnancy means what?
one yolk sac
in twin pregnancies two yolk sacs signifies
diamniotic, monochorionic
or
diamniotic, dichorionic
embryo heart motion is detected when?
about 5.5 to 6 weeks when CRL is about 3 mm
after 5.5 weeks the amniotic membrane can be seen separating what two cavities?
amniotic ca
choriamniotic fusion
fusion of the chorionic and amniotic membranes and occurs at 14 - 15 weeks.
what structure is closed at approximately the 6th week of gestation and how is it seen sonographically?
the spine; appears as parallel echogenic lines