Week 1 - Self study -Brain Anatomy: Cerebral Cortex, White Matter, and Tracts (Flashcards)
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering brain regions, cortex vs. white matter, major tracts, lobes, language/speech areas, and key clinical implications based on the provided notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
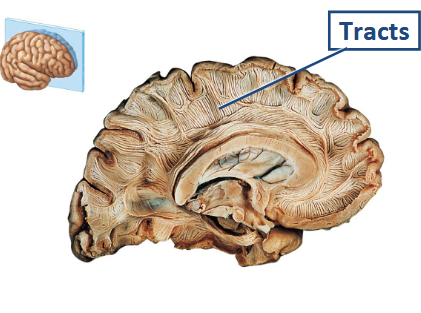
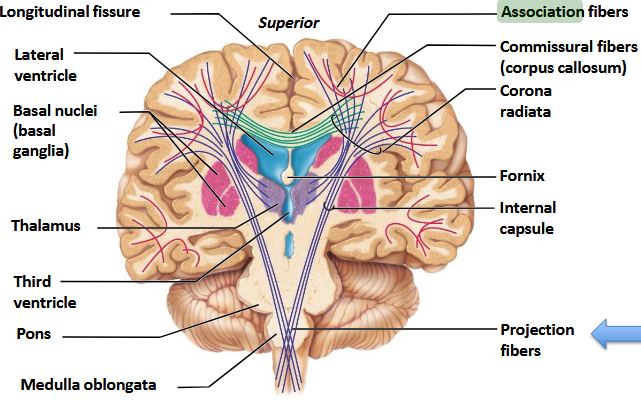
What tracts are used in cerebral white matter?
Association, Commissural, and Projection tracts.
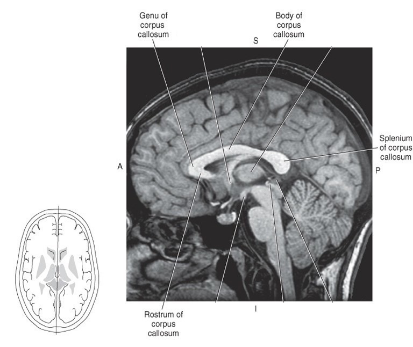
What is the Corpus Callosum and what is its function?
An important commissural tract connecting the two cerebral hemispheres, containing rostrum, genu, body, and splenium.
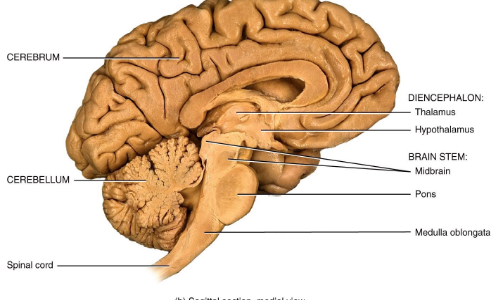
Name four major brain regions.
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brainstem, and Cerebellum.
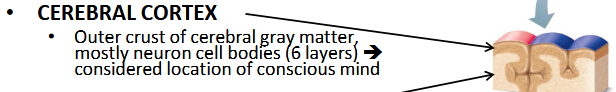
What is the function of the cerebral cortex?
Conscious mind (cognitive processes, awareness, and higher-order functions).
What does cerebral white matter consist of?
Neuron fiber tracts (myelinated axons).
What is another name for gray matter?
Basal nuclei.
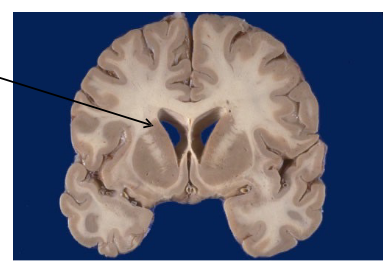
What system involves both gray and white matter?
The limbic system.
The folds that increase surface area are called what?
Gyri.
What feature lies between the Gyri?
Sulci.
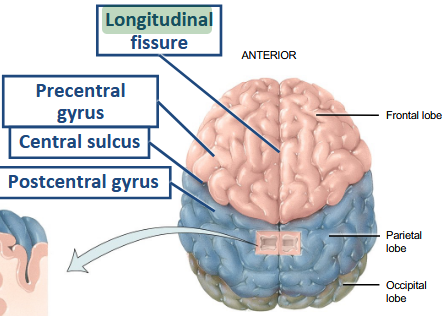
What structure separates the cerebral hemispheres along the length of the brain?
The longitudinal (interhemispheric) fissure.
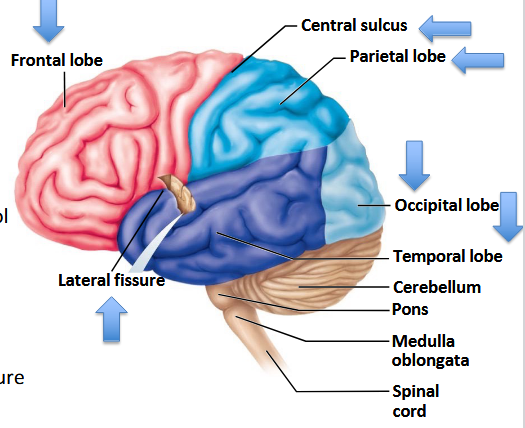
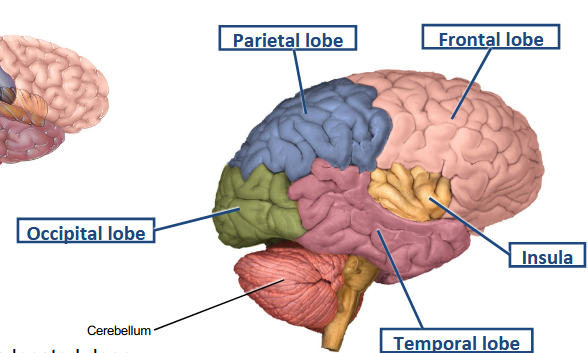
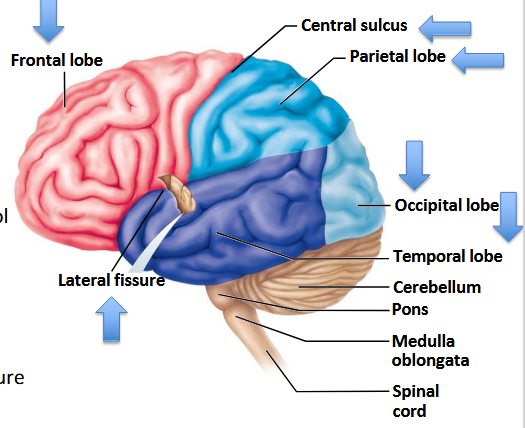
What major action does the frontal lobe control?
Voluntary movement and higher cognitive functions.
Perception of touch, pain, temperature, etc., is a function of which major lobe?
Parietal lobe.
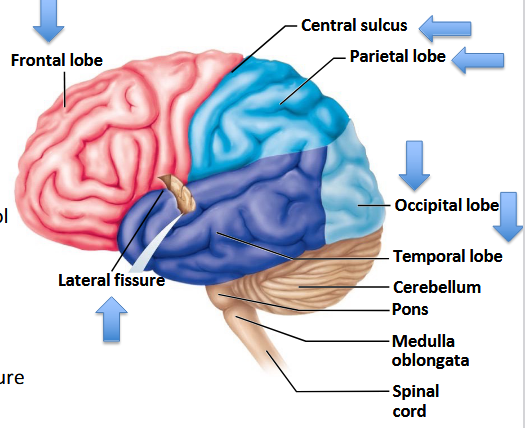
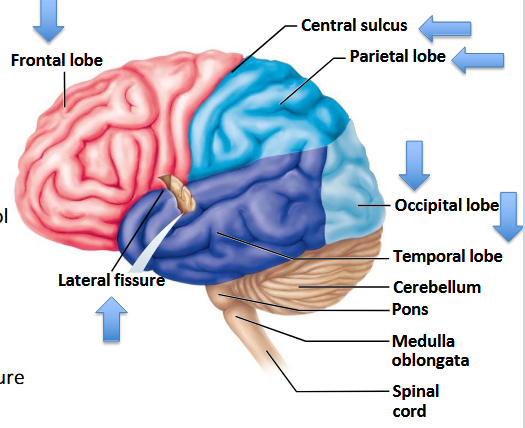
Which lobe is responsible for visual stimuli?
Occipital lobe.
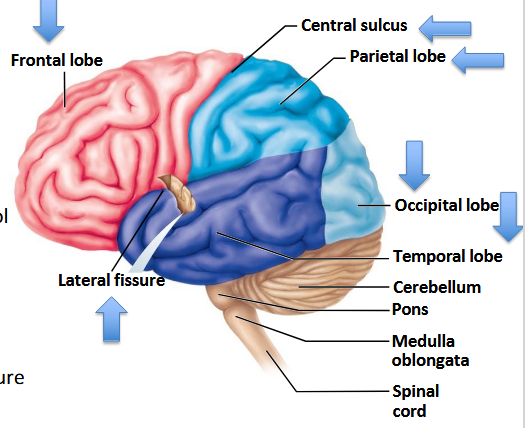
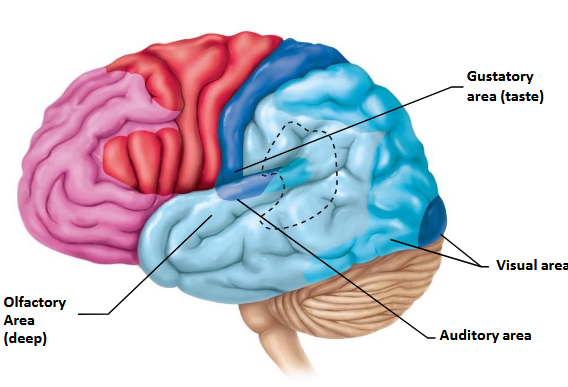
Which lobe houses the auditory and olfactory cortex?
Temporal lobe.
Which lobe is associated with sensory processing (gustatory) among others?
Insula.
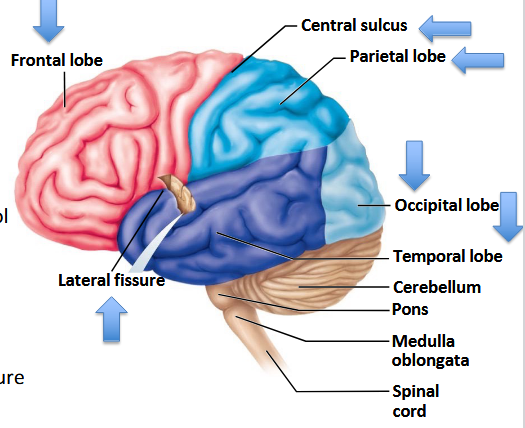
What should the anatomy of the cerebral hemispheres look like?
Roughly symmetrical.
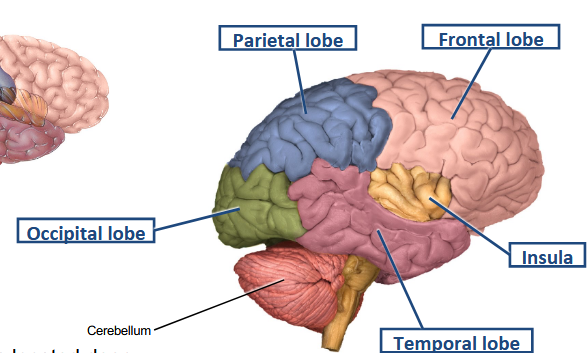
What perspective posits that each hemisphere generates opposite motor functions of the body?
Functional perspective — hemispheric lateralization.
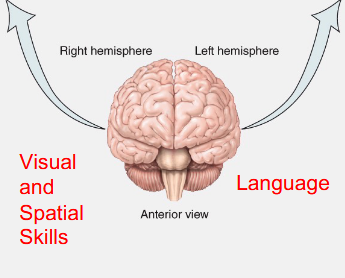
The left hemisphere is dominant for what functions?
Language and numerical skills.
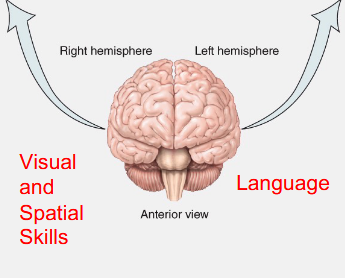
The right hemisphere is dominant for what functions?
Visual/spatial abilities and music.
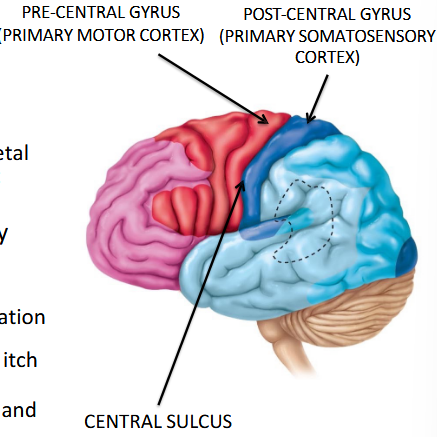
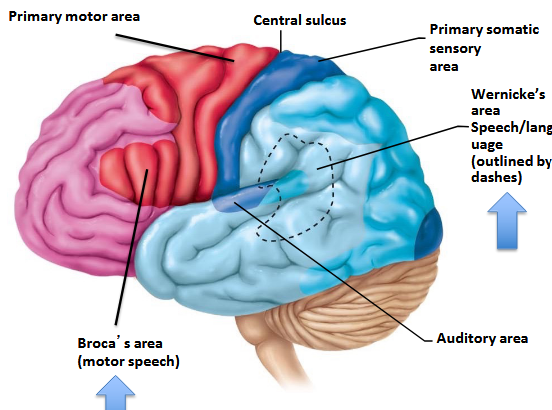
What major action does the pre-central gyrus control?
Primary motor cortex for voluntary movement (Frontal lobe).
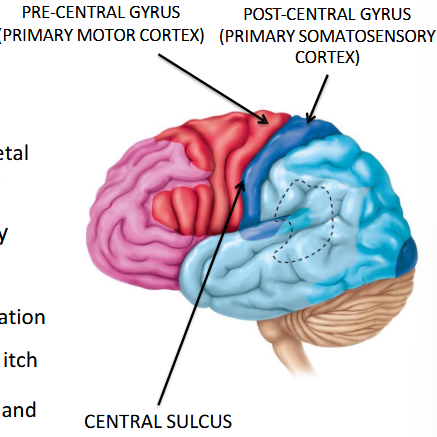
Which gyrus is used for receiving sensory information?
Post-central gyrus.
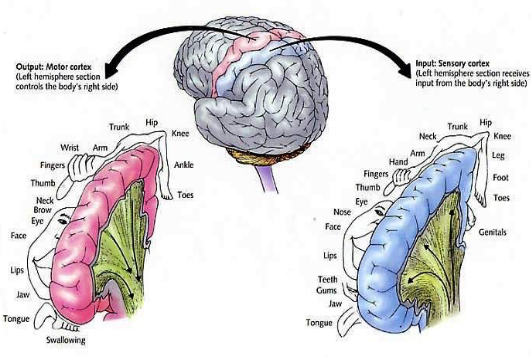
What does the Homunculus model represent in the brain?
The sensory and motor areas of the cortex.
If the Homunculus is damaged, what losses could occur?
Contralateral loss of sensation and contralateral paralysis.
The base of the post-central gyrus is associated with which sense?
Gustatory (taste) sense.
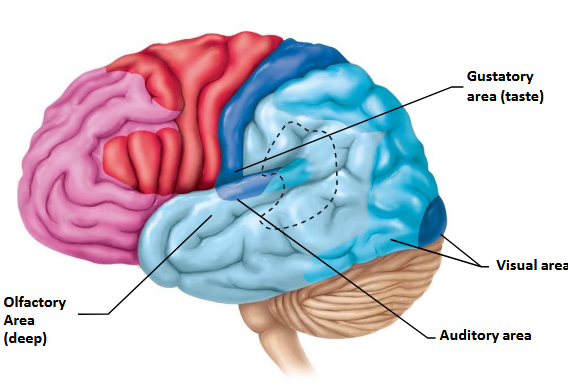
In what lobe would you locate visual processing?
Occipital lobe.
Where in the brain is the olfactory sense located?
Temporal lobe.
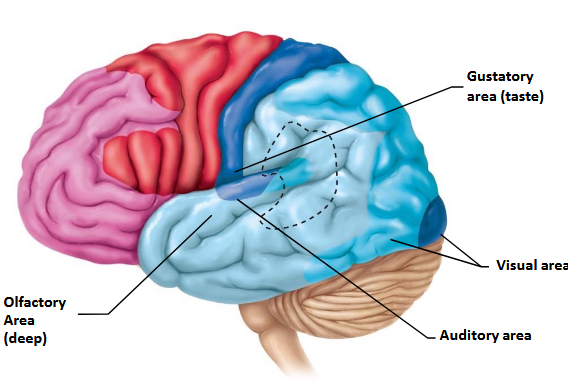
Where does the auditory sense fall under?
Temporal lobe.
Which lobe controls the muscles of speech?
Frontal lobe (Broca’s area).
What areas allow recognition of spoken and written language?
Parietal and Temporal lobes.
How does the brain transmit action potentials?
Via neuroglia and myelinated axons (neurons and their tracts).
Which tracts are confined to the same hemisphere?
Association tracts.
Which major tracts travel from one hemisphere to the other?
Commissural tracts.
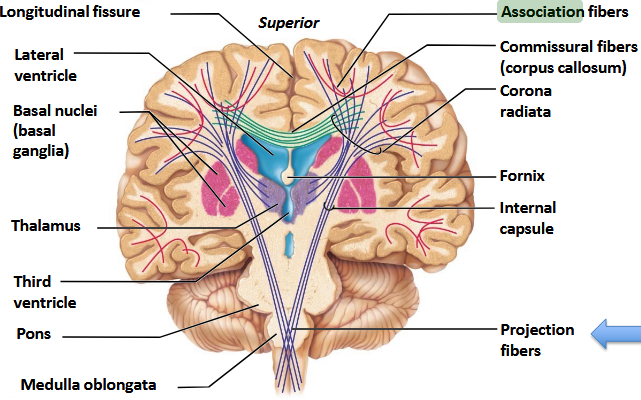
Which tracts project to and from the Cerebral Cortex?
Projection tracts.
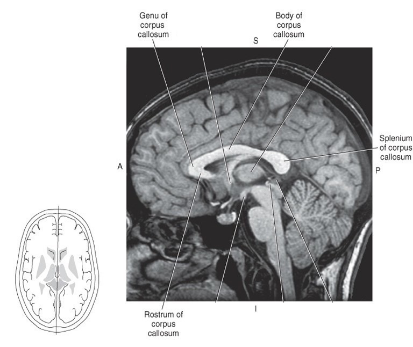
What are the four parts of the corpus callosum?
Rostrum, Genu, Body, Splenium.
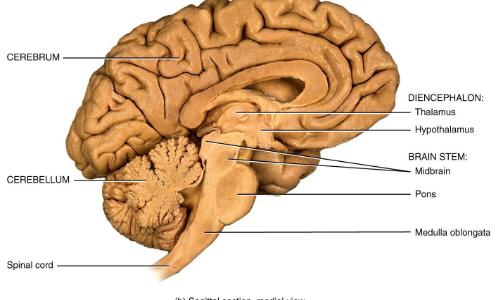
Name the four major regions in the brain (recap).
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brainstem, Cerebellum.
Explain which tissue contains gray and white matter.
Cerebral cortex is outer gray matter; cerebral white matter contains axon tracts.
What are the four main lobes of the brain?
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal.
What is the primary role of white matter?
Connects different regions of the nervous system.
What does the corpus callosum mainly connect?
The two cerebral hemispheres (primary commissural tract).