UNLV BIO 191L FINAL
1/746
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
747 Terms
population
group of individuals of the same species in a defined area
ex: all pine trees on campus
community
“all” organisms in a define area
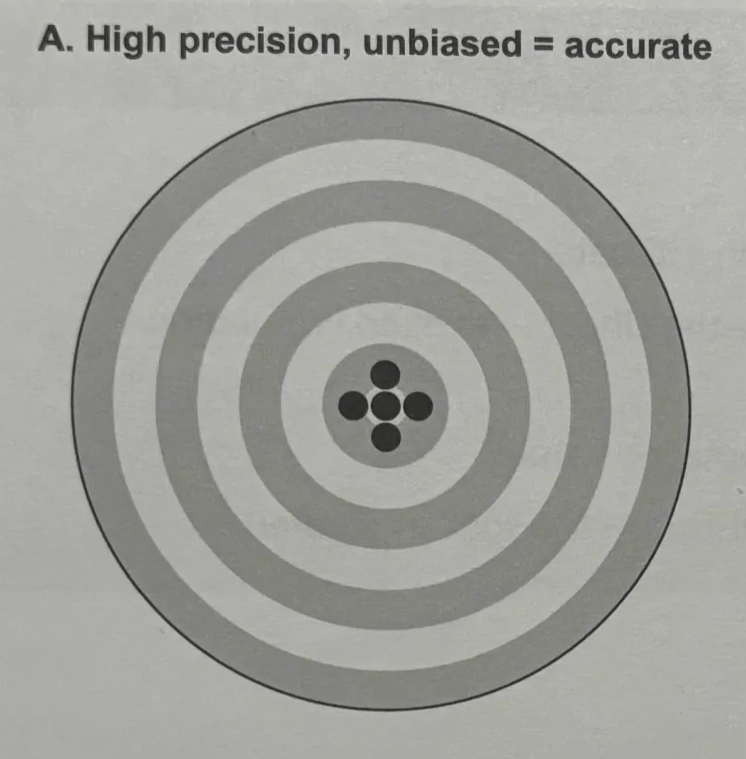
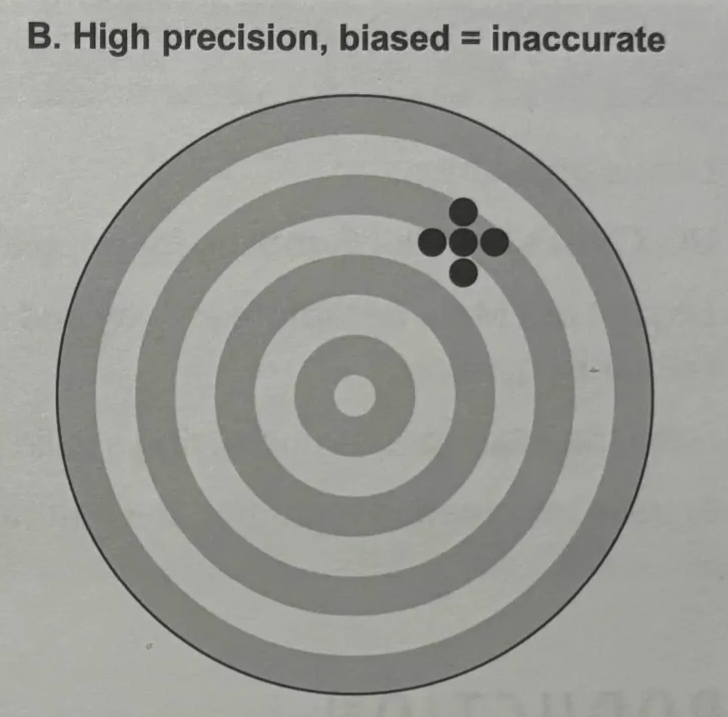
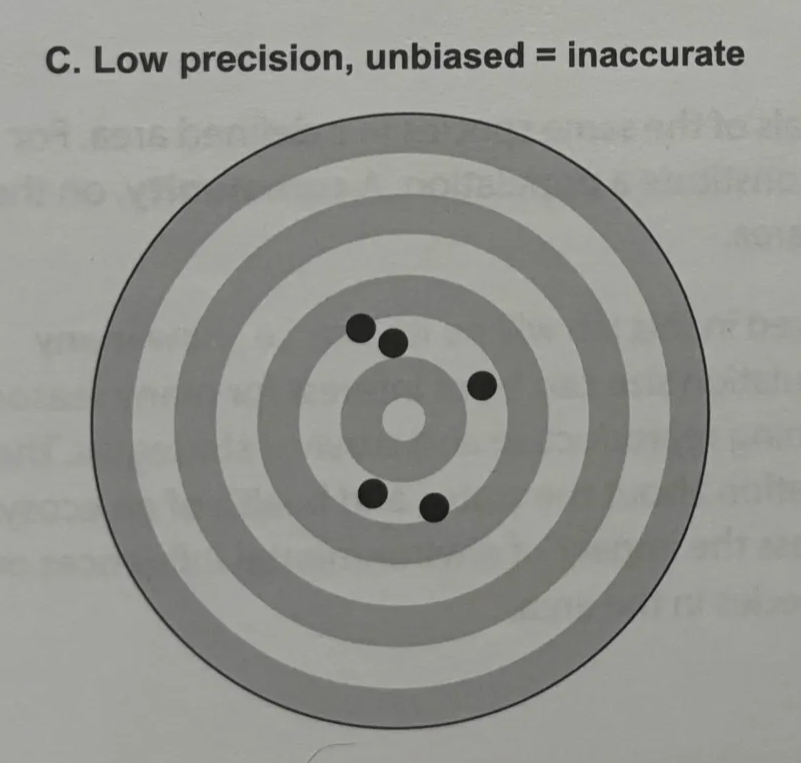
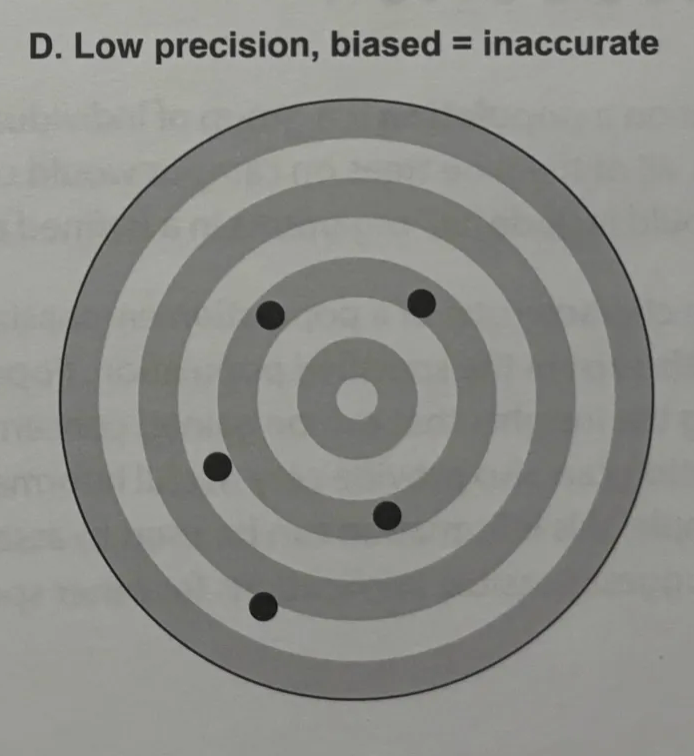
precision
depends on size of sample and variation
larger sample = more precision
less variation = more precision
more variation = less precision
statistical varience
often measures precision
smaller varience = greater precision
biased
if mean point of impact is far from the bull’s eye, or true population size, then the estimator is biased
accurate
centers on true population size
low varience
must be unbiased and precise
high precision, unbiased
accurate
high precision, biased
inaccurate
low precision, unbiased
inaccurate
low precision, biased
inaccurate
census
arrive at the population size, useful in smaller areas, accounting for every member
plot sampling
divide larger area into smaller areas called plots
in smaller areas, direct count method then employed
assumes all plots accurate representation of larger area
calculate from plot sampling technique
[ (P1 + P2) / 2 ] * Ptotal
count from 1st plot
count from 2nd plot
get total of both plots
divide to get average (Avrg of two nums, divide by 2)
multiply by total # of plots
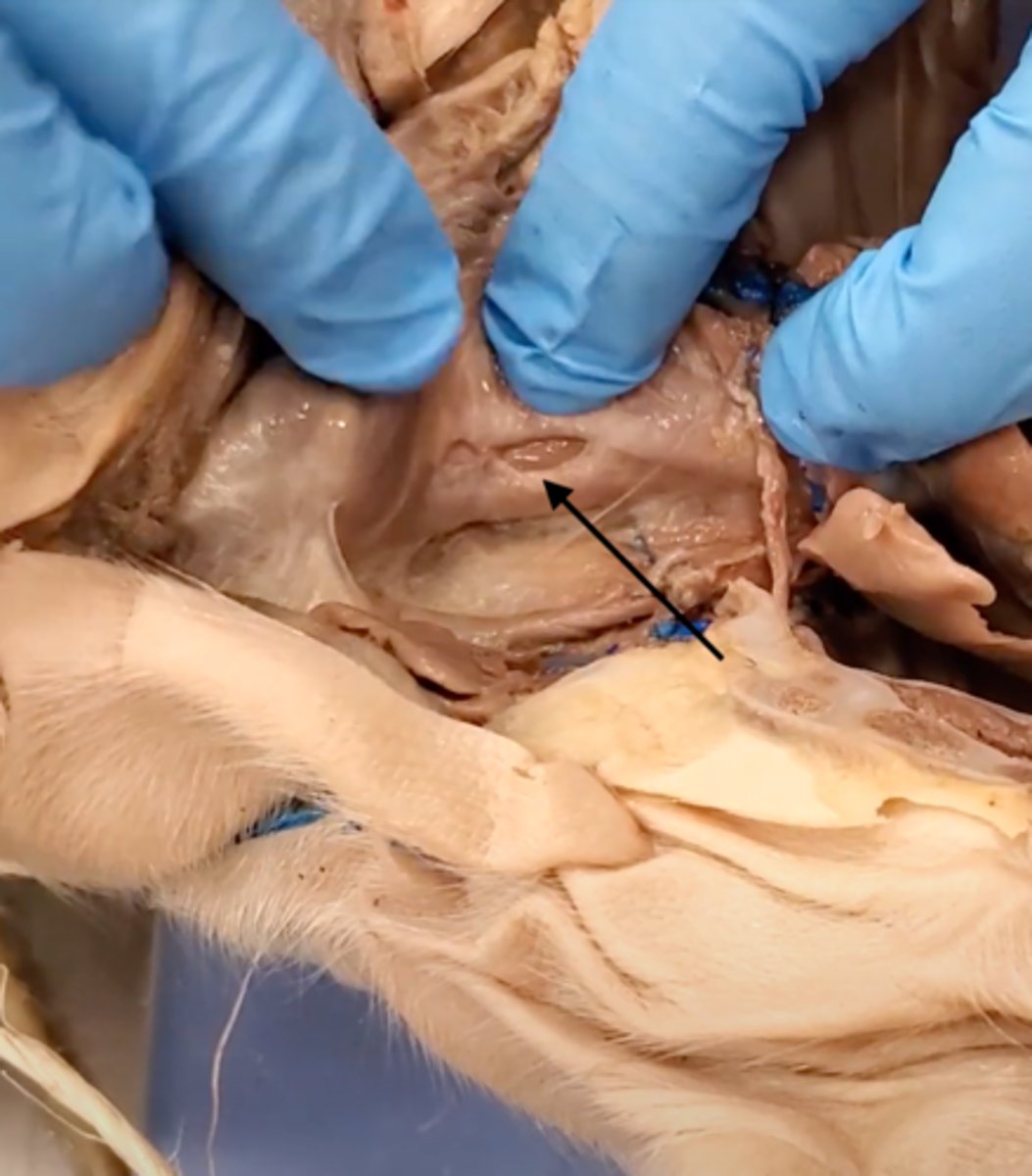
Mark-recapture method and assumptions
METHOD
after area under investigation is defined, the investigator attempts to capture as many of the individuals as possible
caught individuals are marked, then released back into the same area
ASSUMPTIONS
between sampling period, population is closed
no births or deaths
no individuals leave or enter (immigartion or emigration)
All animlas (marked and unmarked) are equally likely to be captured in each sample
marks are not lost, gained, or overlooked
Lincoln-Peterson index
N = MC / R
N = total estimated population
M = individuals captured and marked the 1st time
C = individuals captured 2nd time
R = individuals recaptured, or already marked from the 1st time this 2nd time
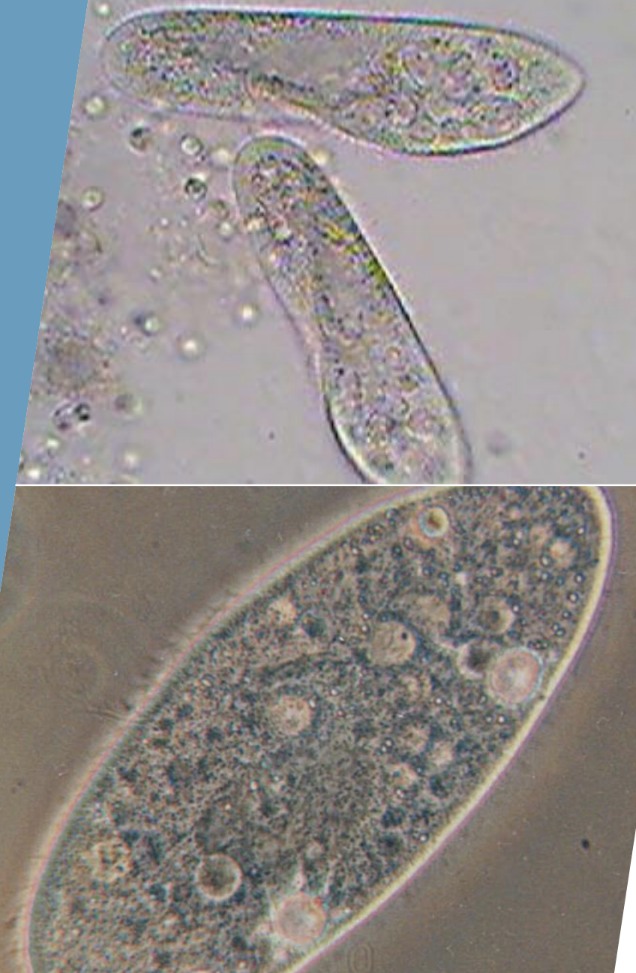
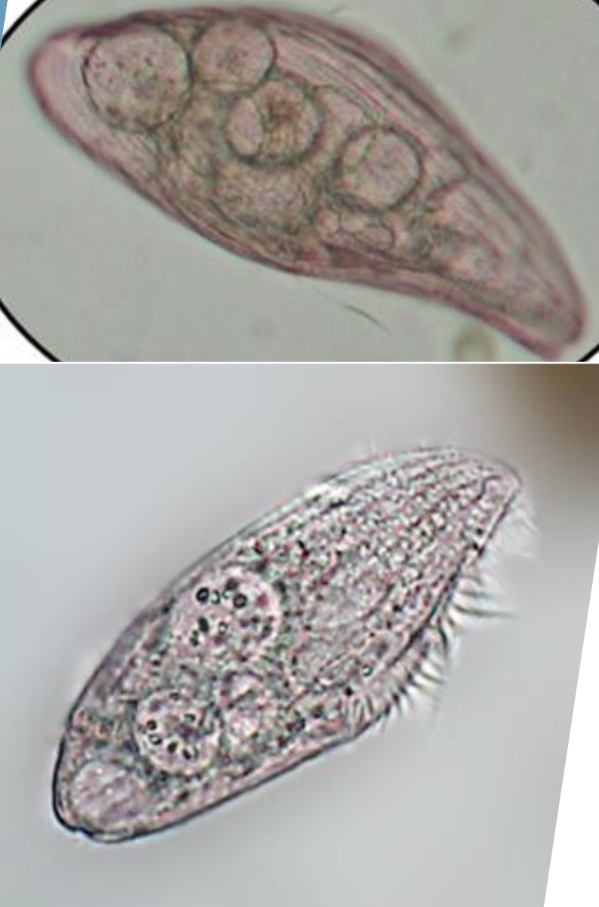
Shape: Slipper shaped
Size: Large, 250-300μm
Paramecium caudatum
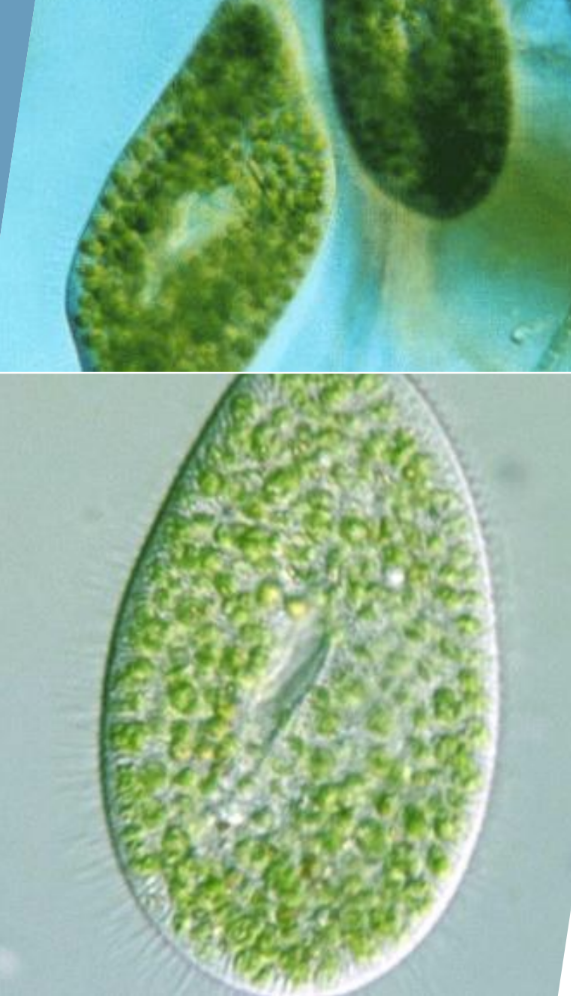
Symbiotic green
algae (Zoochlorella)
Shape: Rotund
Size: 100-150μm
Paramecium bursaria
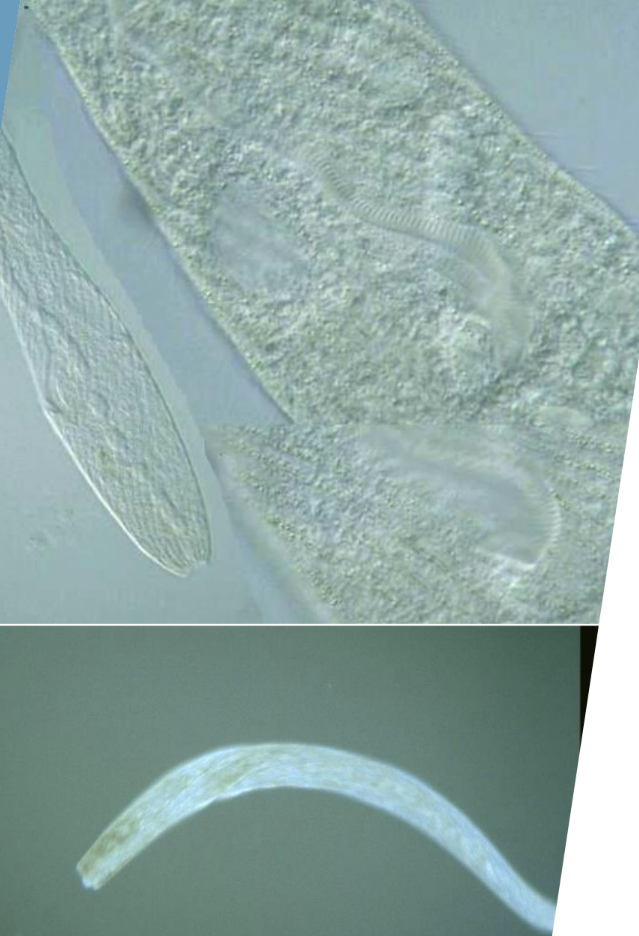
Shape: Club shaped
Size: Very long (up to 2-3mm)
Size and shape are unique
Spirostomum ambiguum
Pink color
Shape: Pear shaped
Size: ~175μm
Blepharisma lateritium
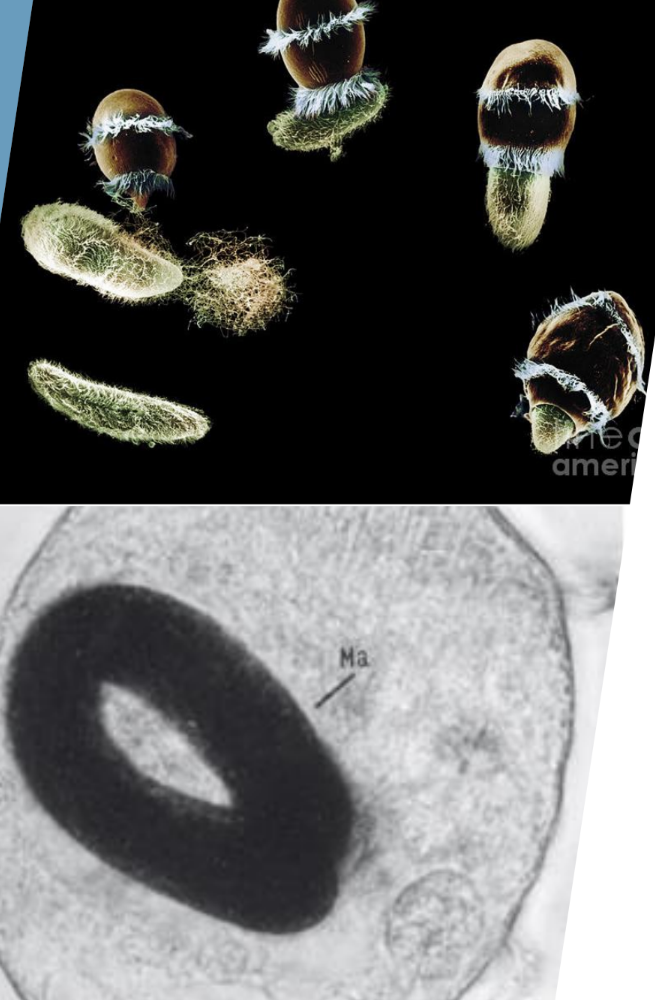
Two girdles of cilia
Predatory
Didinium nasutum
initial population density

total # individuals desired in diluted 40 mL solution
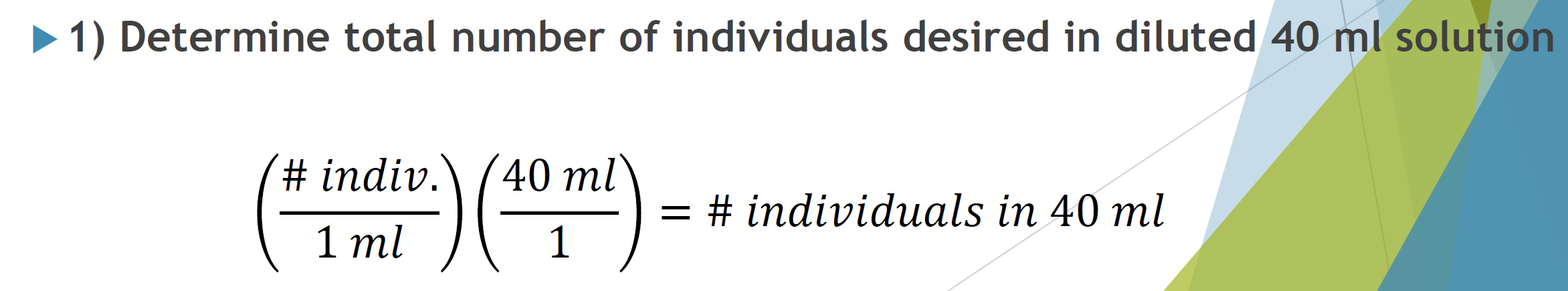
volume stock reqiored to obtained desired # individuals
H2O needed to get desired vial volume
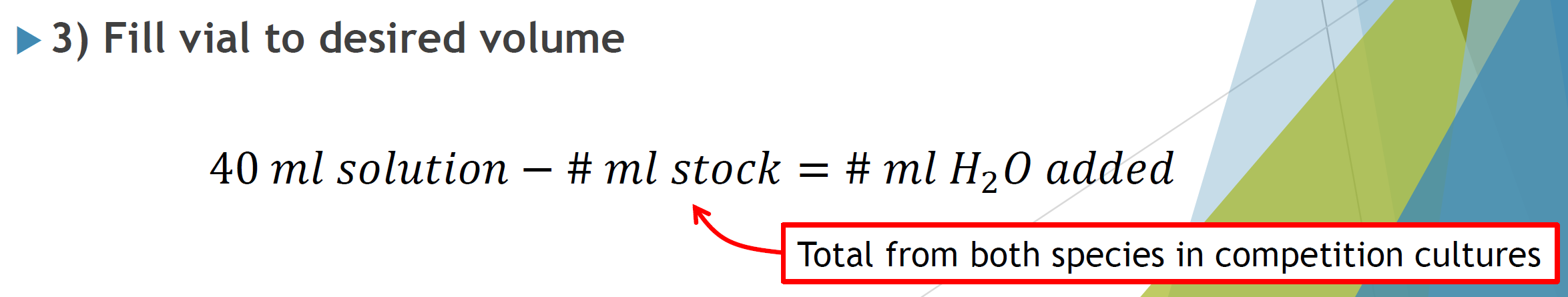
desired concentration: 40 indv/mL
initial stock pop: 320 indv./mL
total # individuals desired in 40 mL solution

desired concentration: 40 indv/ mL
initial stock pop: 320 indv./mL
volume of stock needed to obtain desired number of individuals
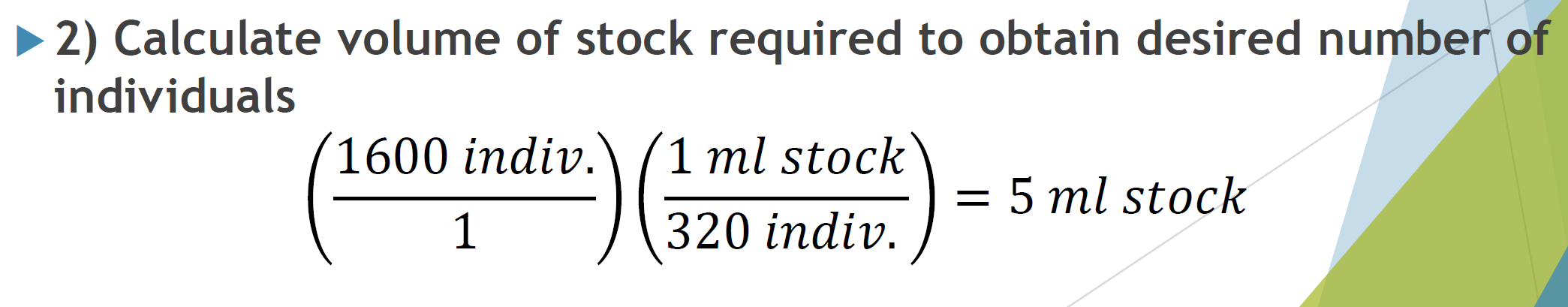
desired concentration: 40 indv./mL
initial stock pop: 320 indv./mL
desired volume

#indv / mL if diluting slides

tissues
composed of more than one type of cell coming together to perform a function
organ
structure with a defined shape that is composed of more than one type of tissue and performs a general role in the body, includes brain, heart, stomach, and urinary bladder
organ systems
combinations of organs which perform a more general role to support health, there are 11 systems of the body
homeostasis
the physiological state of equilibrium maintained by organ systems
Integumentary-Skin
Protection of underlying structures, prevention of fluid loss, temperature regulation
Skeletal-Bones, joints
Support and protection of softer body parts, store minerals, produce blood cells
Muscular-Skeletal muscles
provide body movement, produce heat
Nervous-brain, spinal cord, nerves
monitor changes in the environment, interpret the changes, and initiate responses
Endocrine-Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal and pancreas glands
alter the activities of cells by the release of hormones in an effort to respond to changes int he body
Cardiovascular-heart, blood vessels
transport of blood throughout all areas of the body
Lymphatic-spleen, thymus, tonsils, lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels
protection of the body from foreign particles and cells, removal of dead and diseased cells, recycling of fluid back to cardiovascular system
Respiratory-nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
exchange of gases between the bloodstream and the external environment
Digestive-mouth salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, pancreas, liver, large intestine gallbladder
simplify food particles into their basic components to enable their absorption in the blood stream
Urinary-kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, uretha
form urine in order to maintain water balance salt balance, pH, and nitrogenous waste levels in the blood
Reproductive-Male: testes, ductus deferens, urethra, penis, scrotum; Female: ovaries, uterine tube, uterus, vagina
produce gametes for fertilization in order to create new individuals
axial skeleton
supports the torso and includes the spine, rib cage, skull and other associated bones
appendicular skeleton
includes the bones in all four limbs in addition to the pelvic and shoulder girdles
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.
smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body
cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
renal pyramid
2
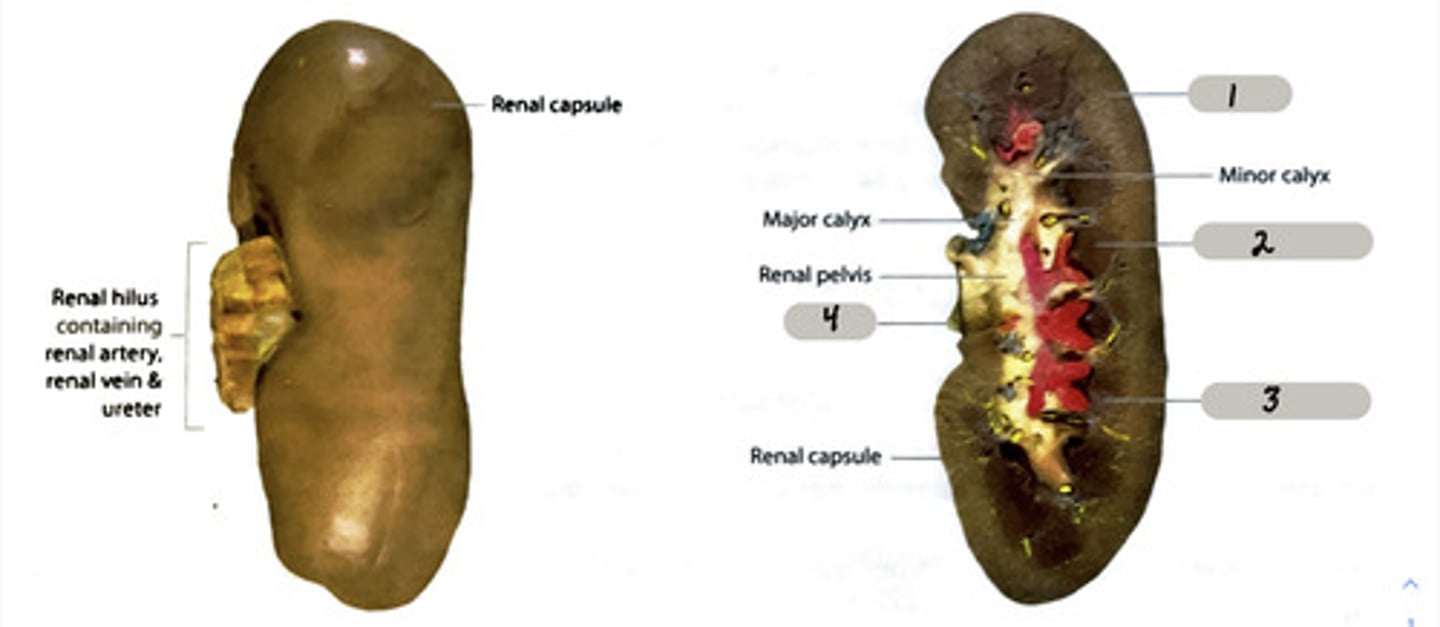
renal column
3
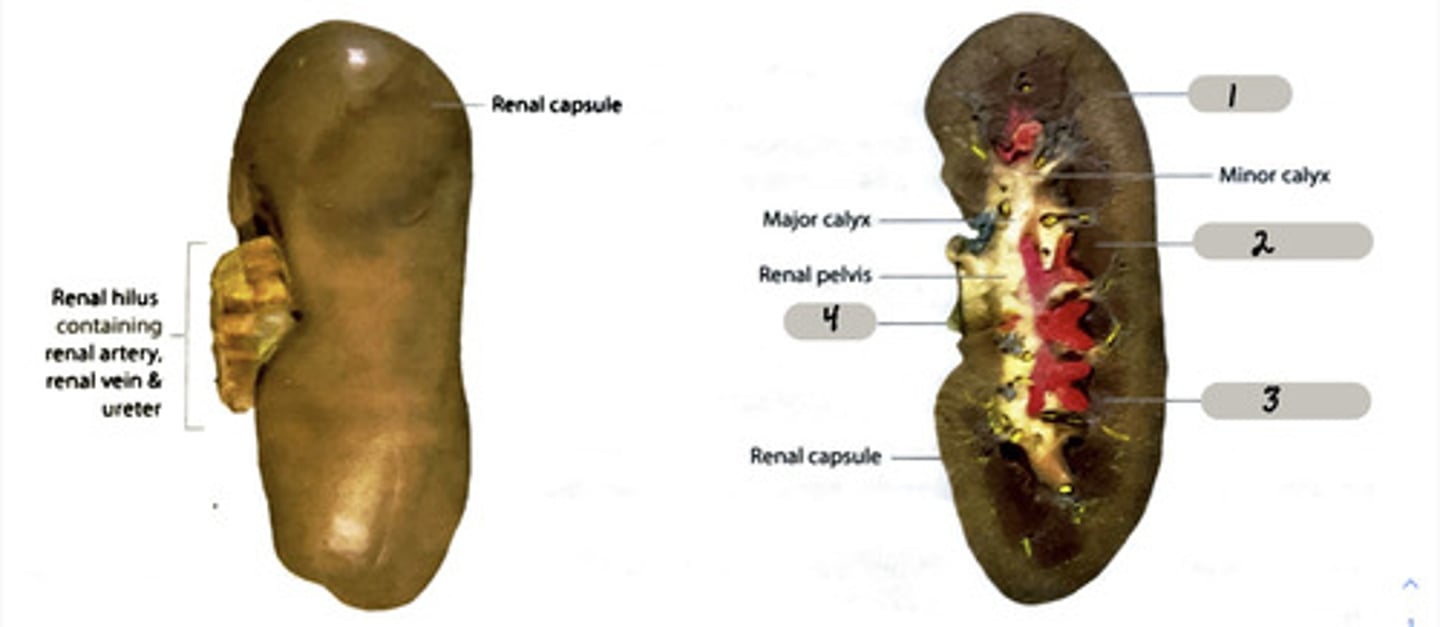
cortex
outer layer of the kidney
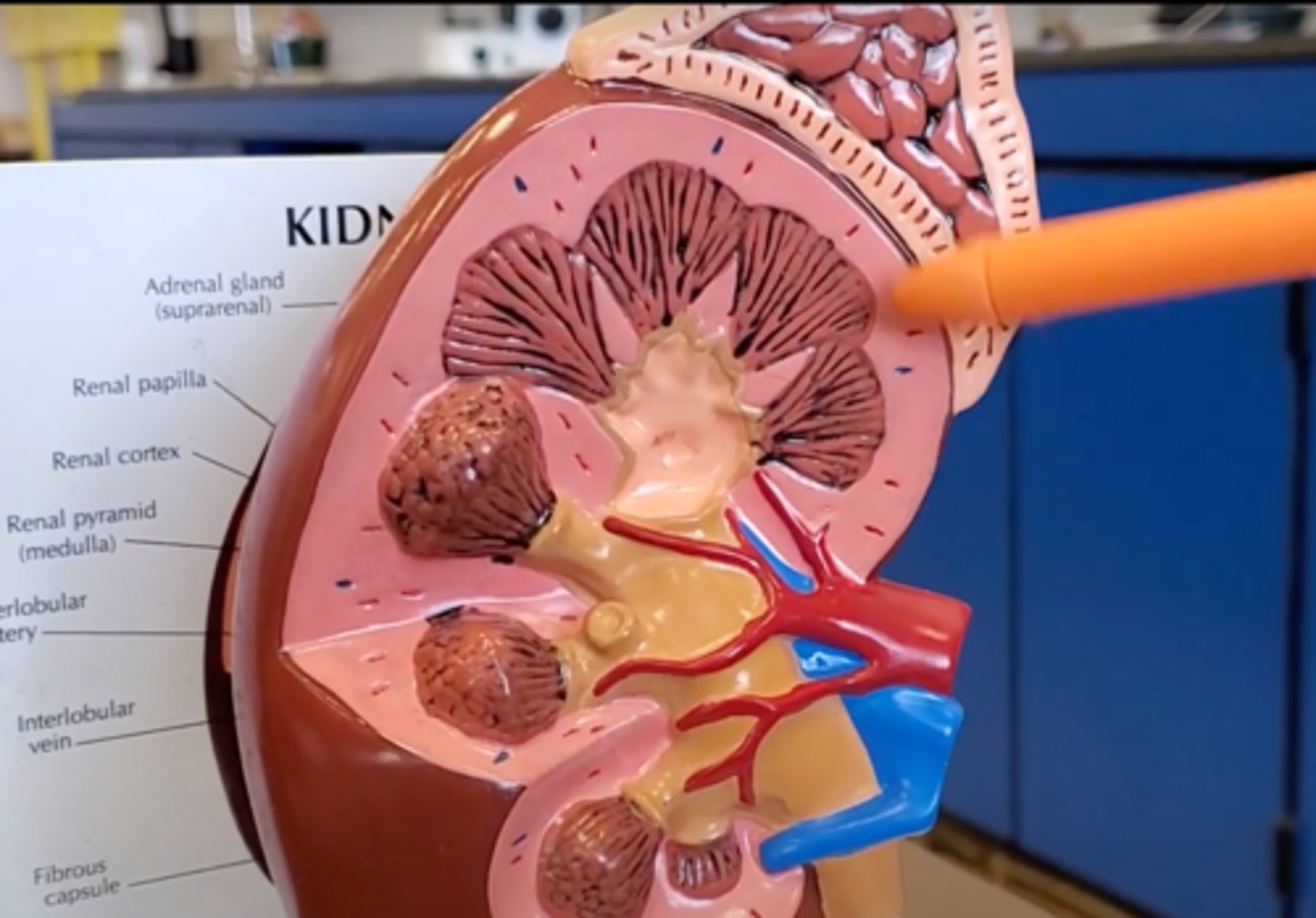
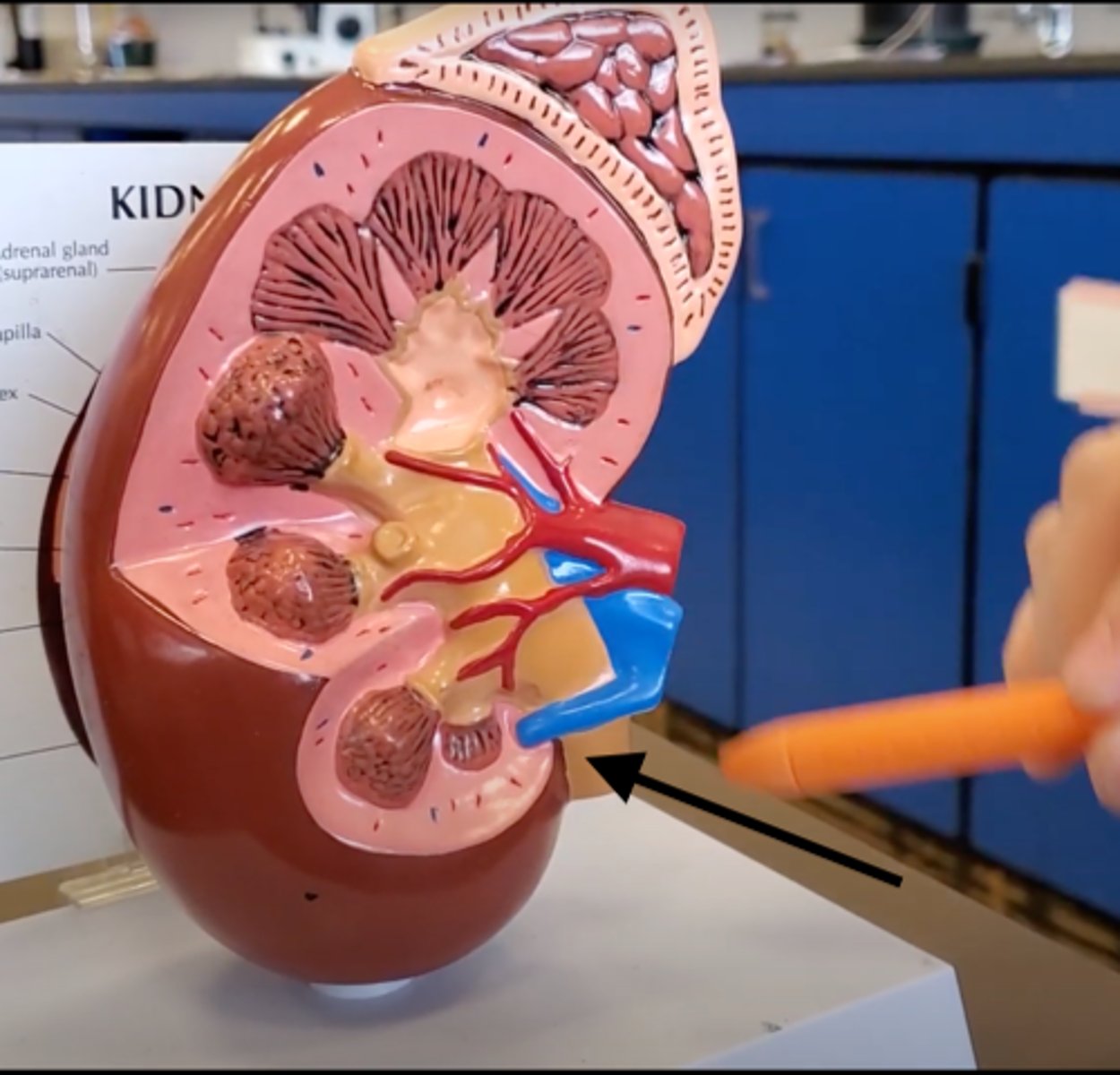
ureter
A duct leading from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
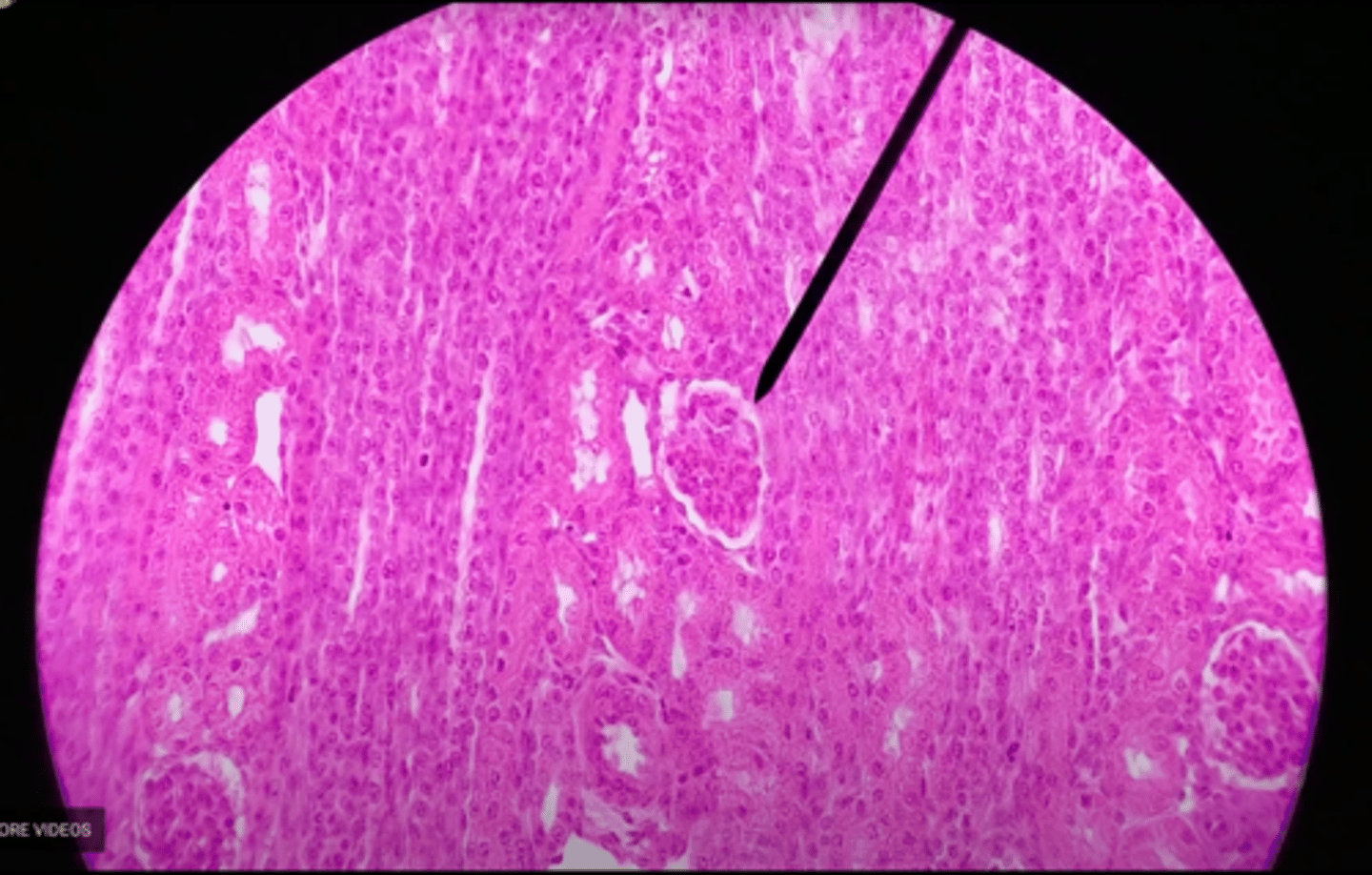
nephron
the functional unit of the kidney
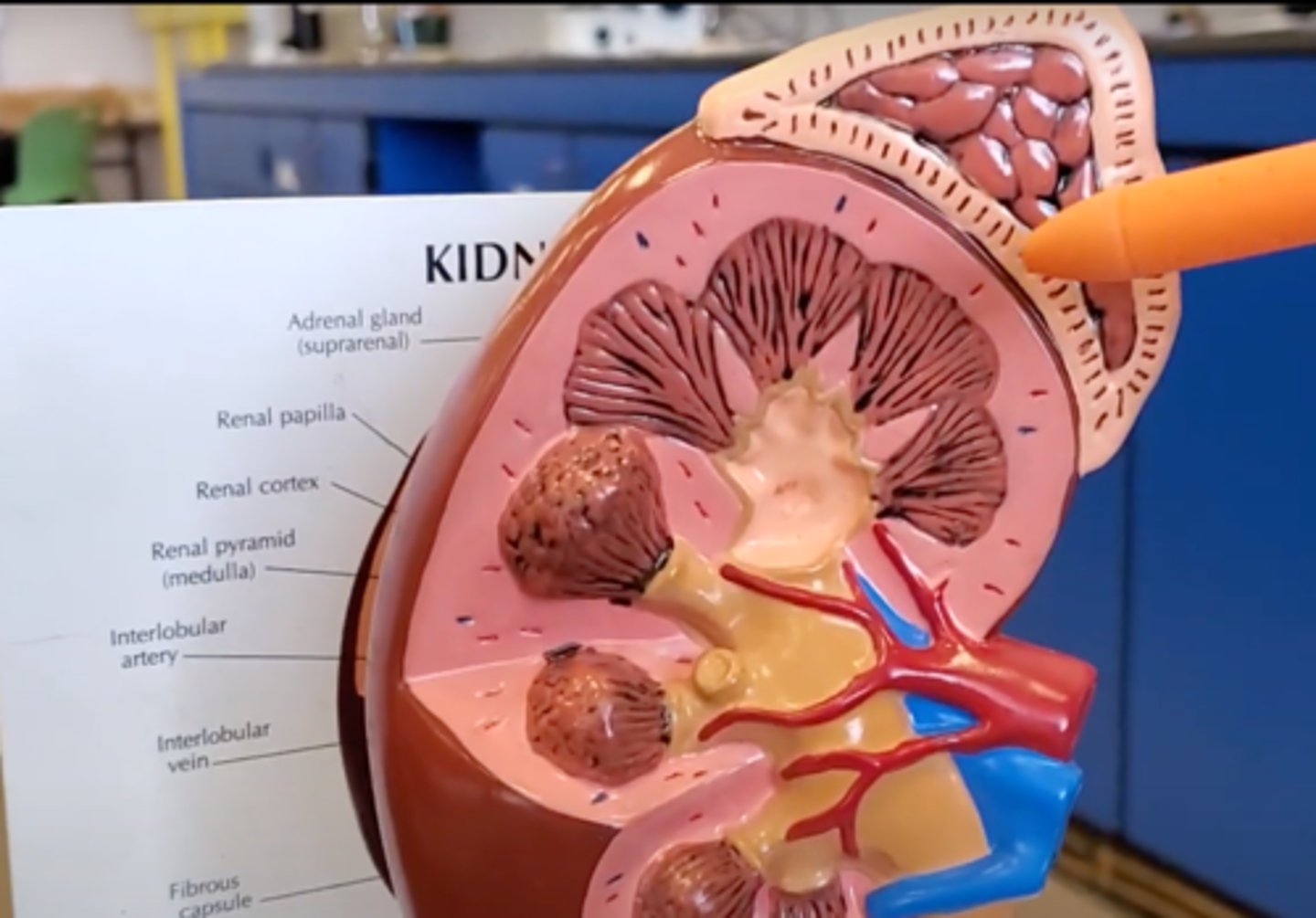
Adrenal gland
A pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord, receives information from sensory receptors, coordinates and integrates the information, and initiates and transmits a response
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
nerves and ganglia, afferent (sensory) nerves channel impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS, and efferent (motor) nerves, which transmit impulses from the CNS to effector organs such as neurons, muscles, and glands.
cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
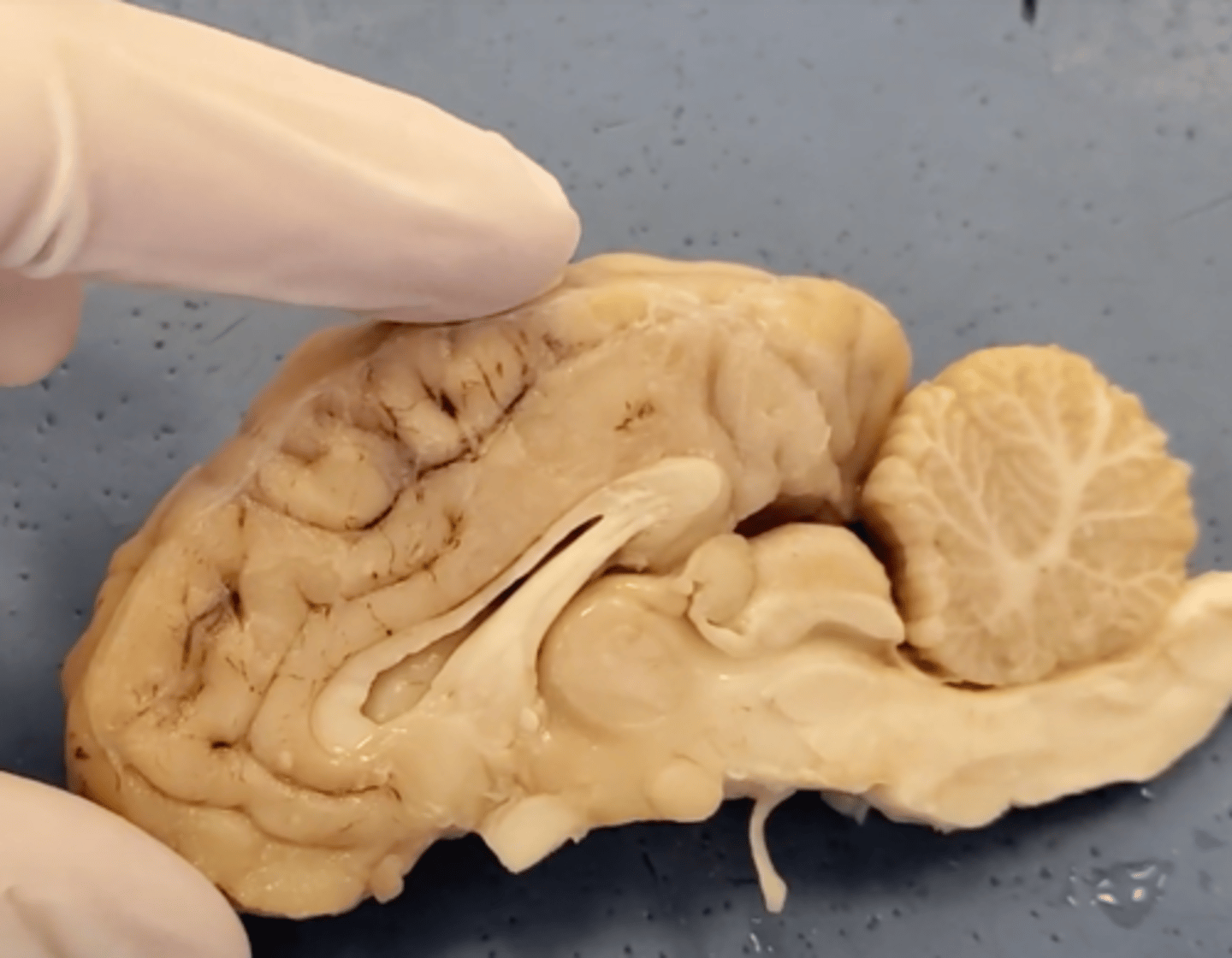
cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
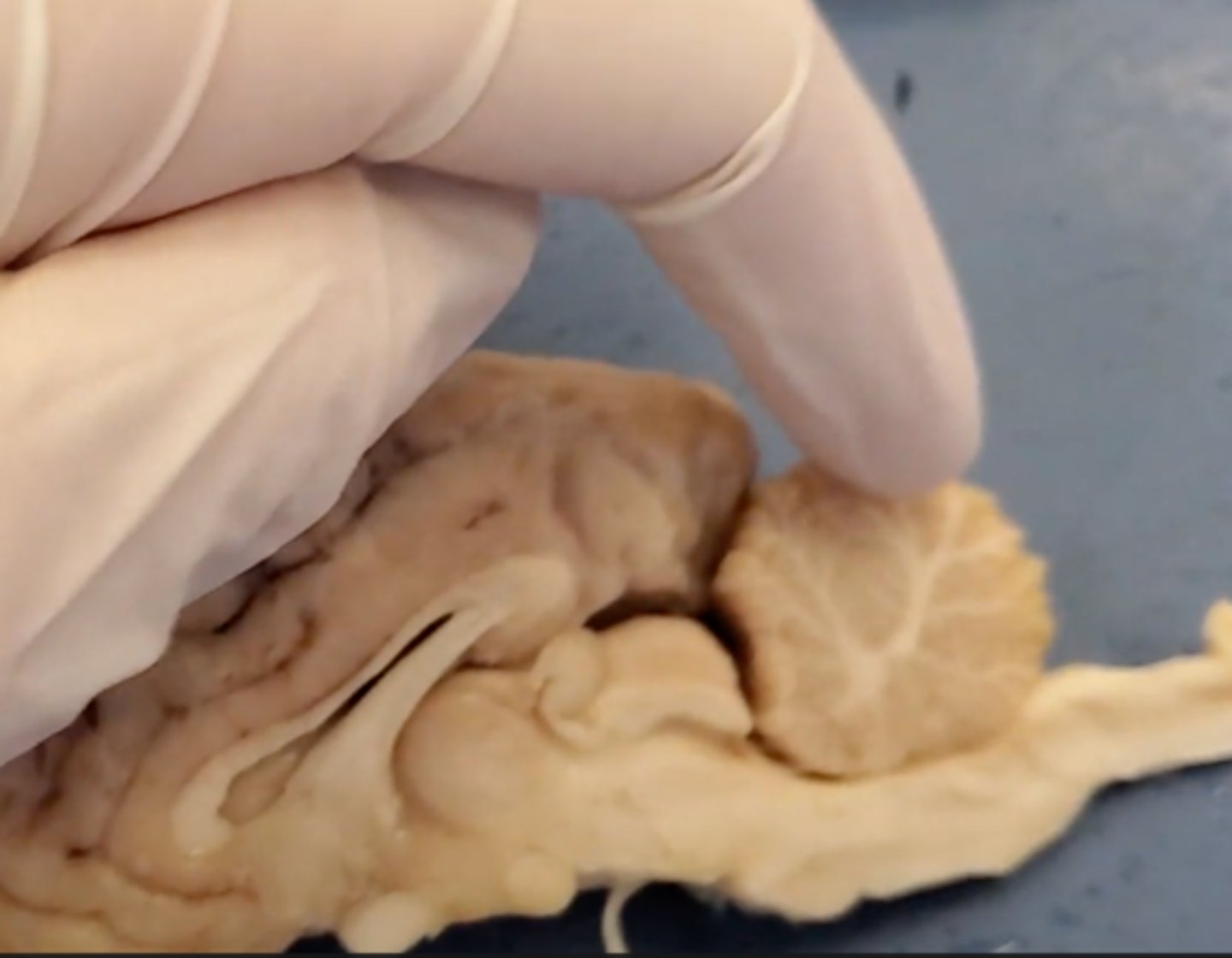
olfactory bulb
a brain structure located above the nasal cavity beneath the frontal lobes
medula oblongata
part of the brain that controls breathing, heartbeat, and the size of blood vessels
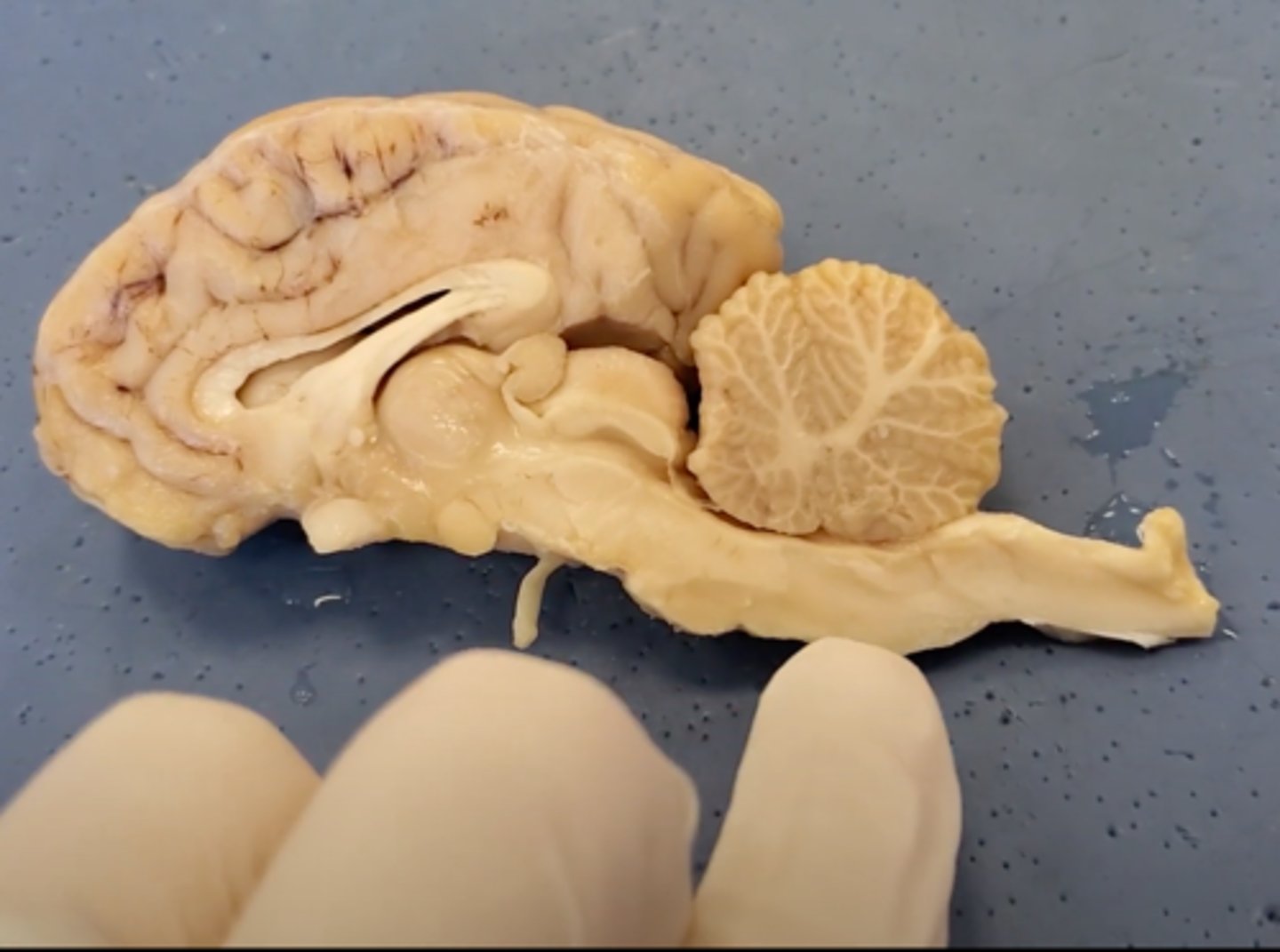
optic chiasma
the crossing of the optic nerves from the two eyes at the base of the brain

optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
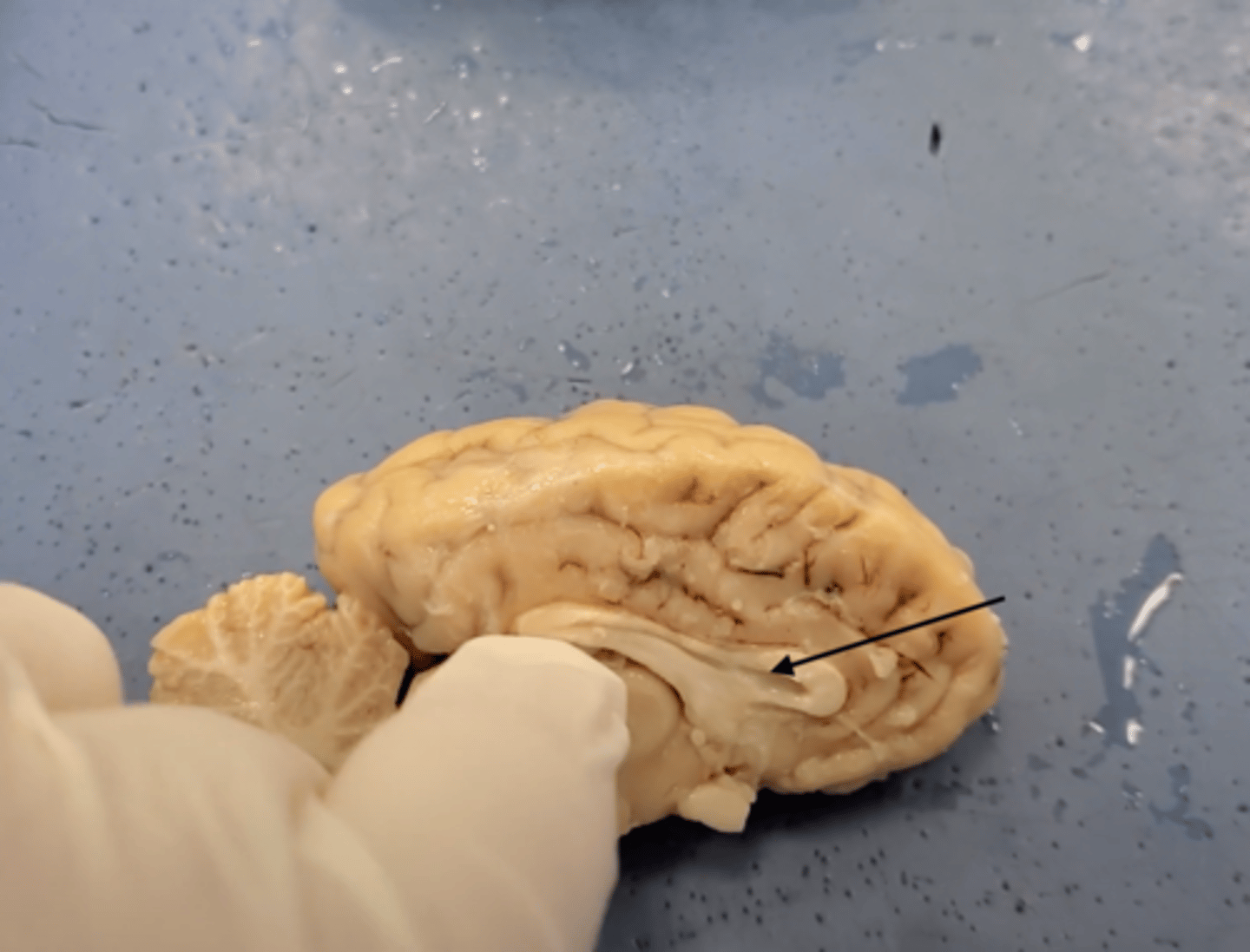
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
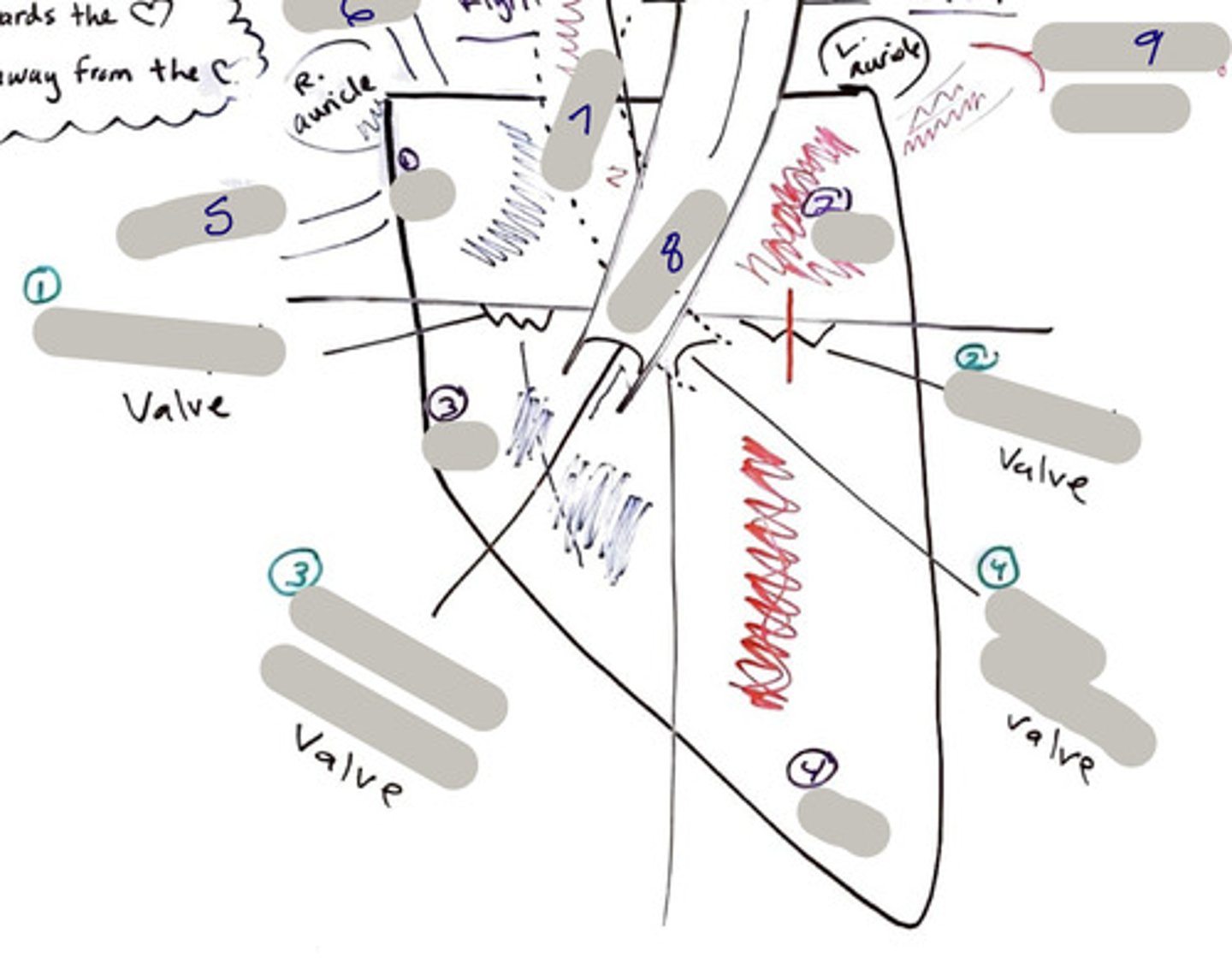
Tricuspid Valve (Right Atrioventricular Valve)
1-valve
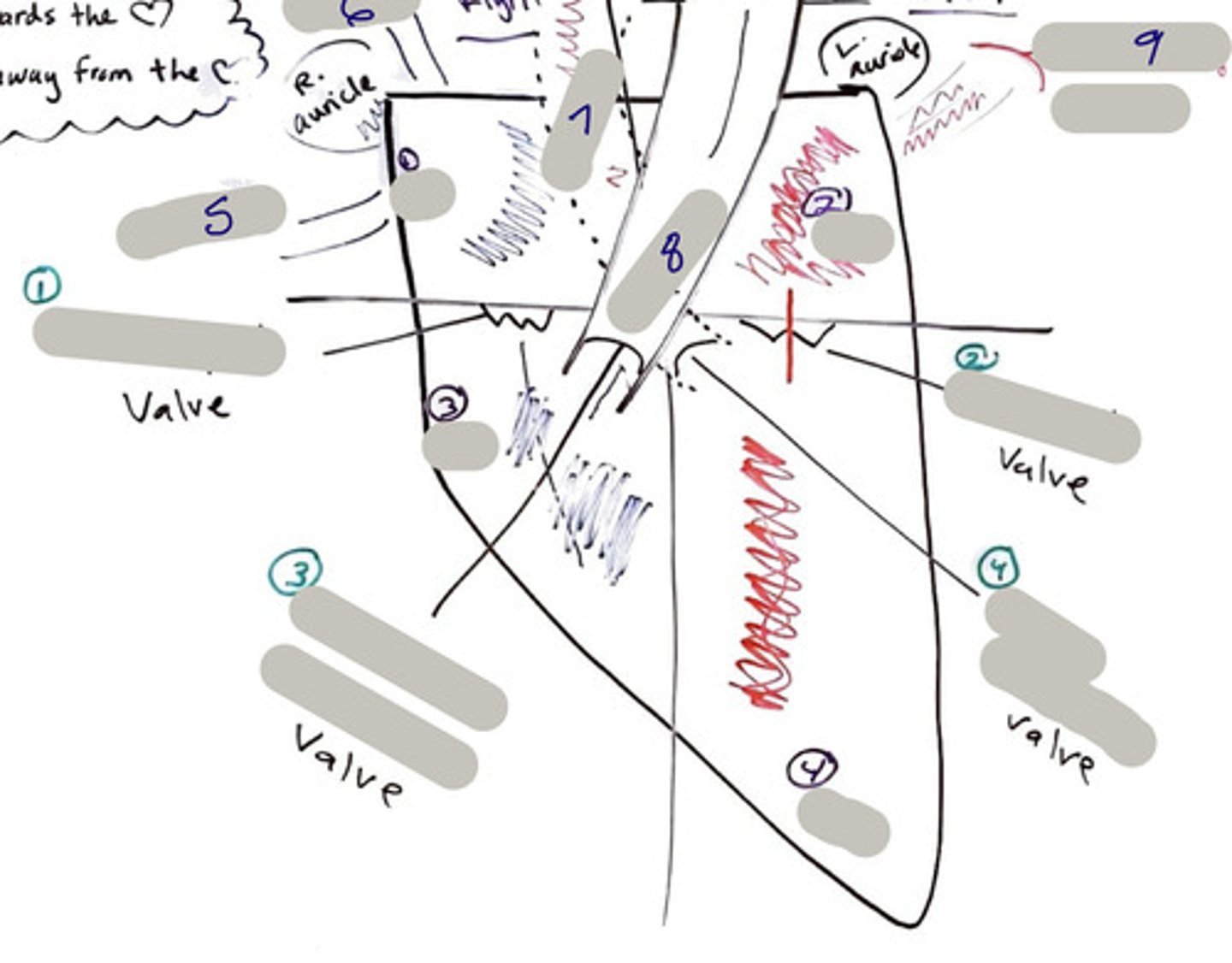
Bicuspid valve (Left Atrioventricular Valve)
2-valve
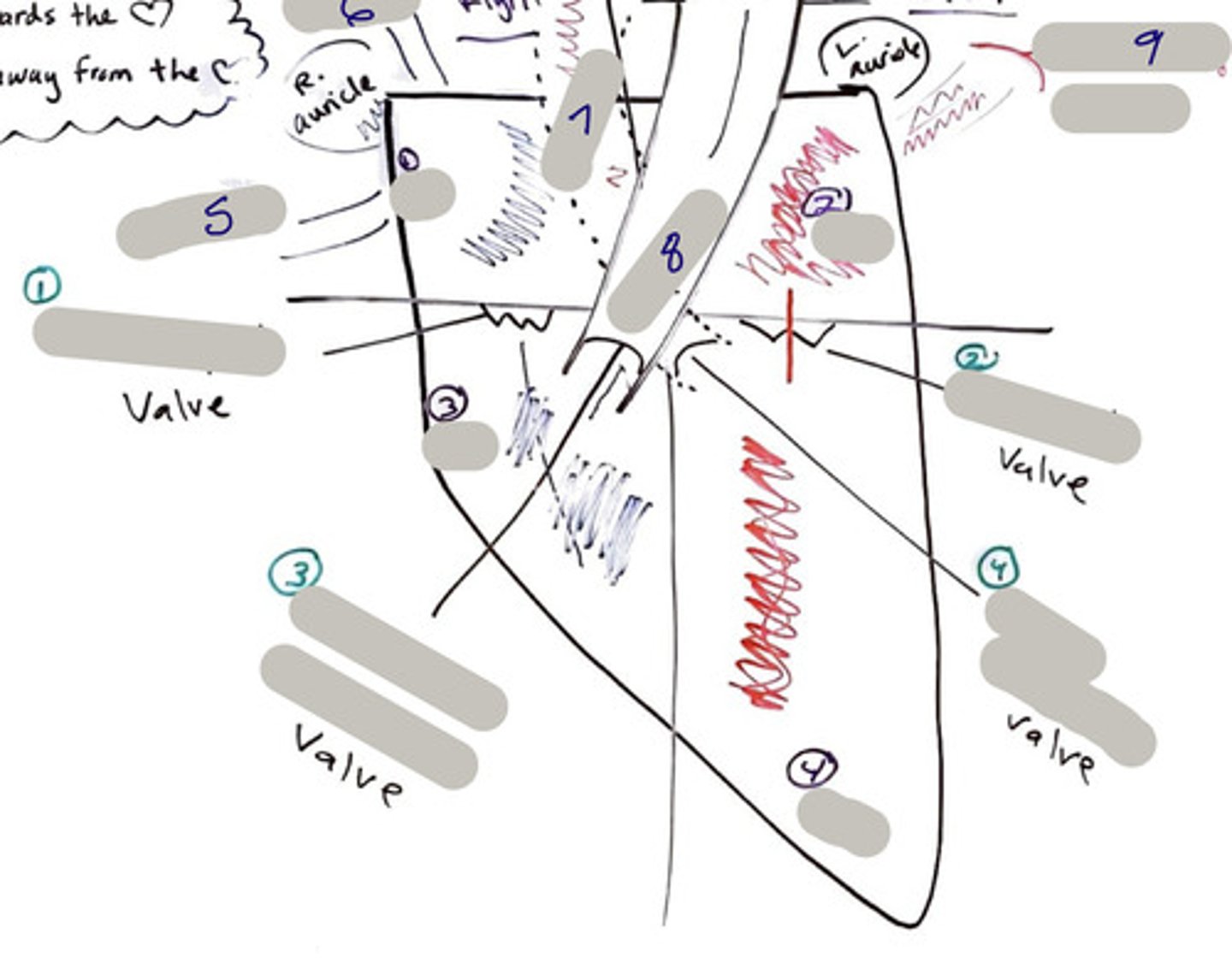
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
3-valve
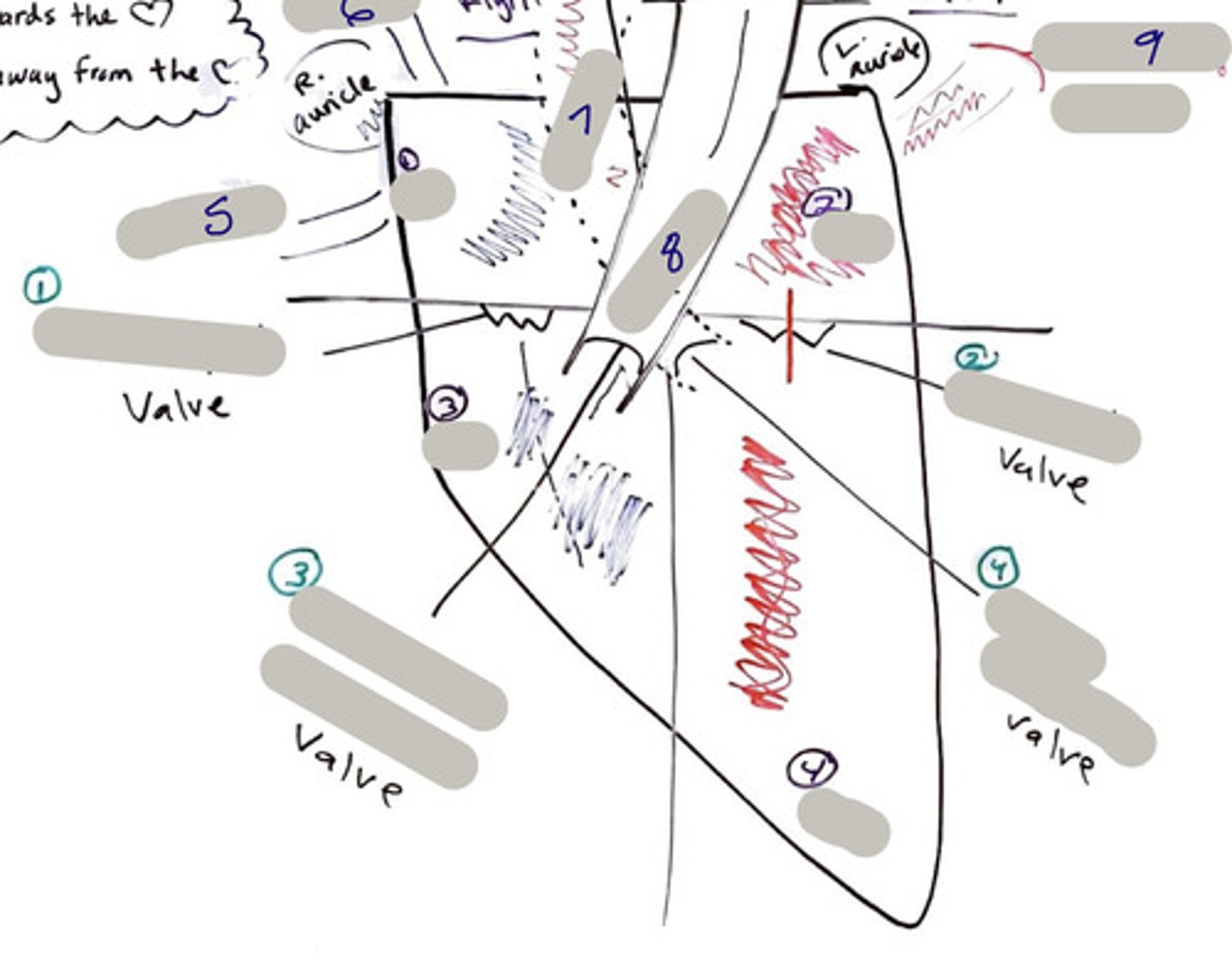
Aortic Semilunar Valve
4-valve
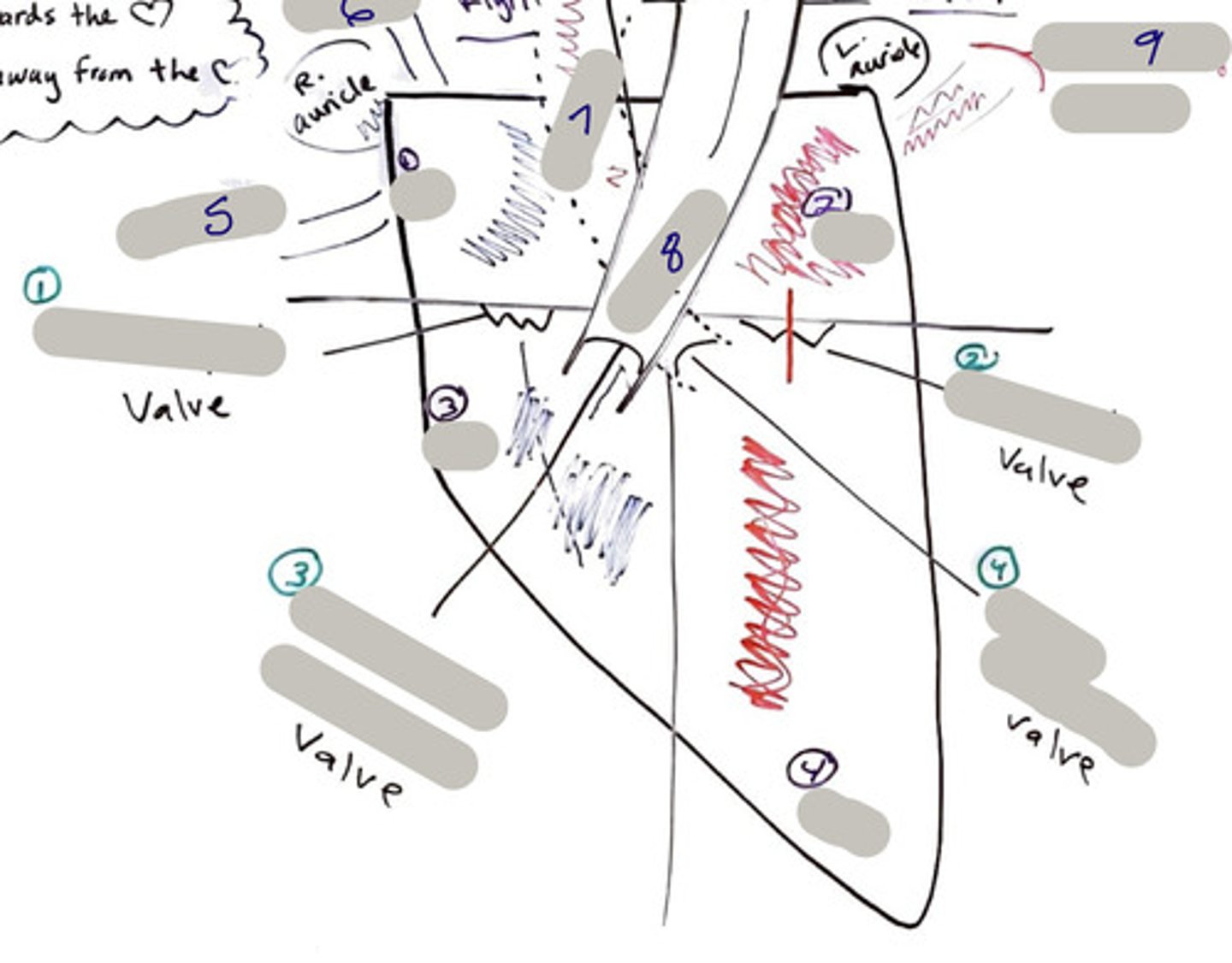
Right Atrium
1-chamber
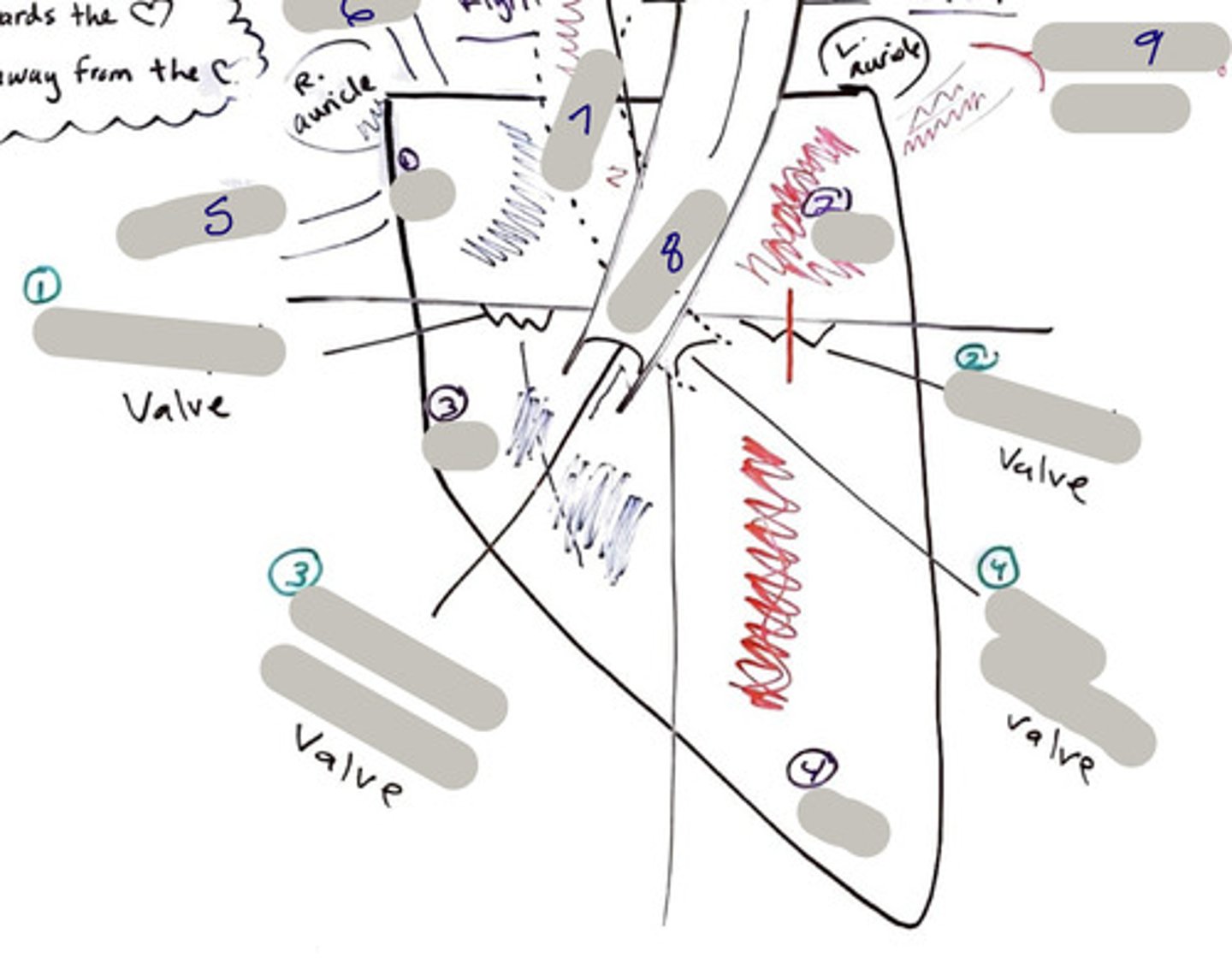
Left Atrium
2-chamber
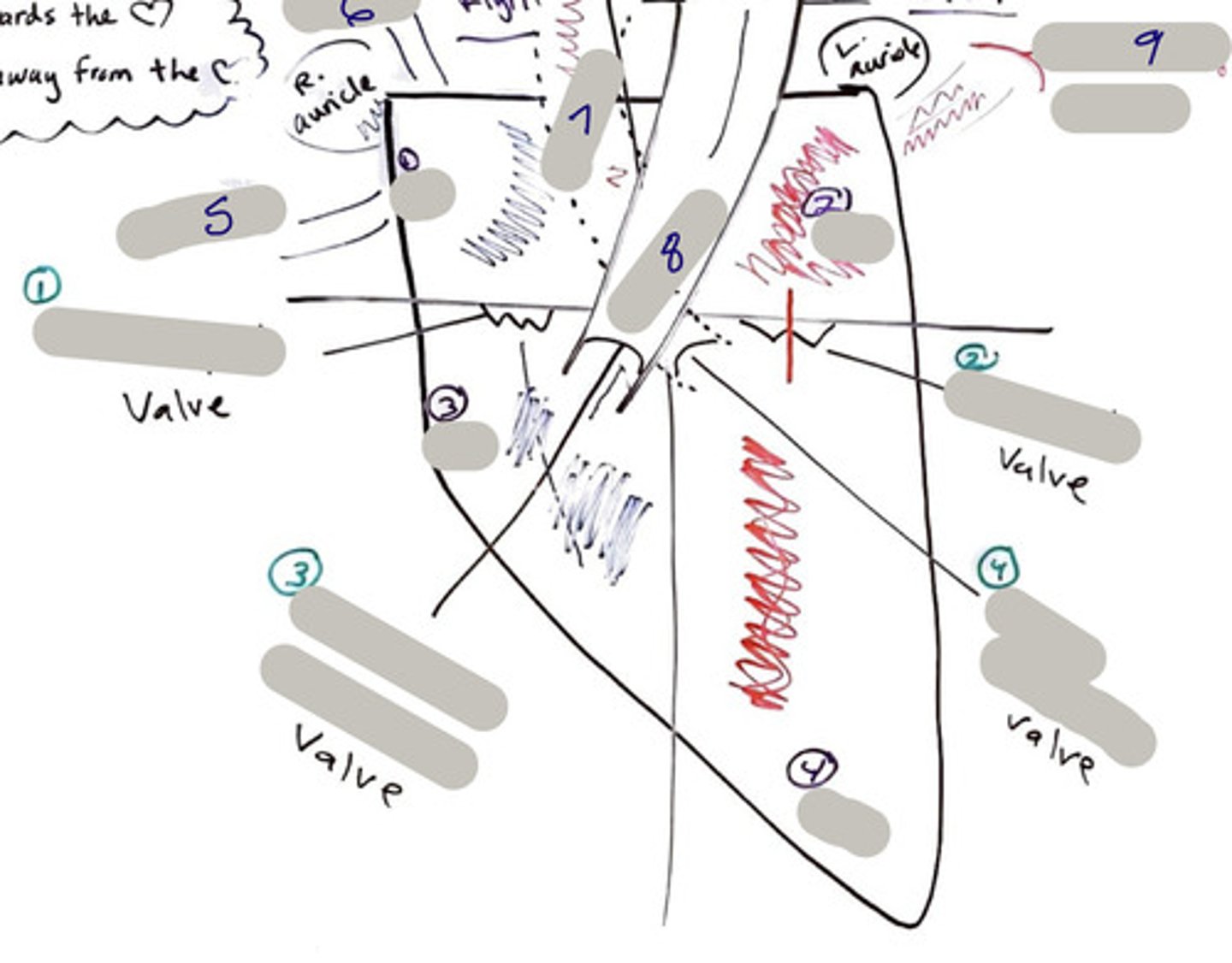
Right Ventricle
3-chamber
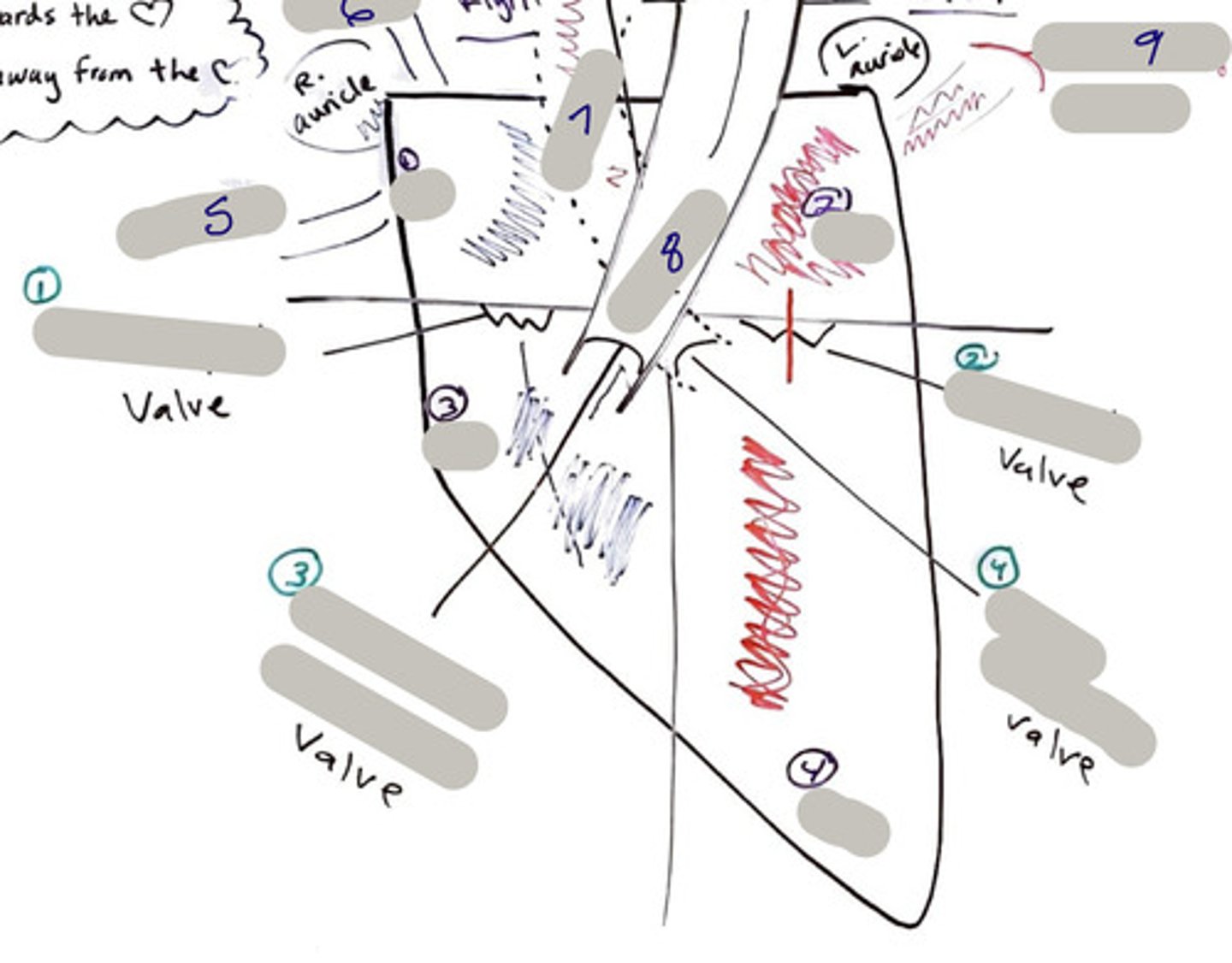
Left Ventricle
4-chamber
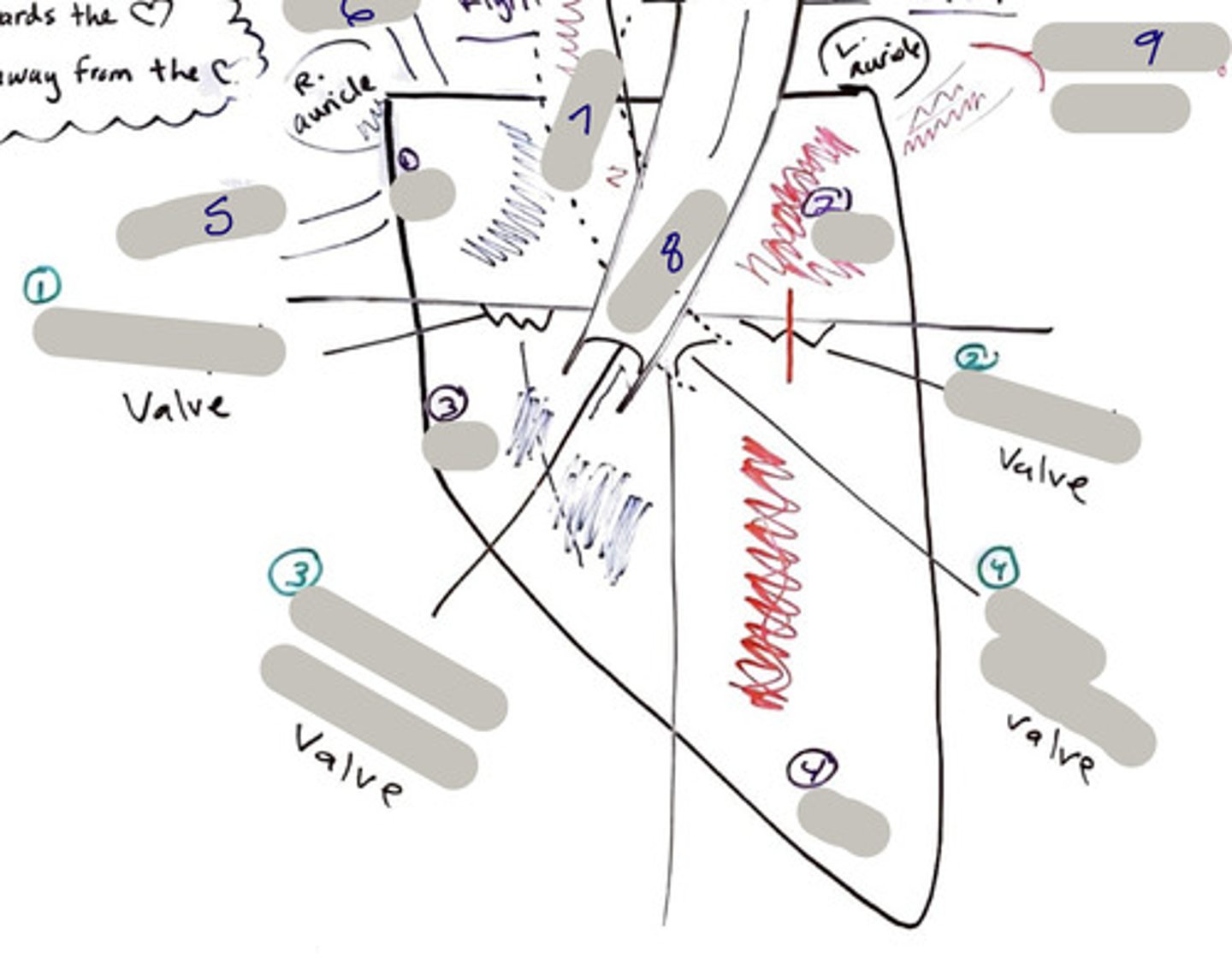
Inferior Vena Cava
5-A vein that is the largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from bodily parts below the diaphragm.
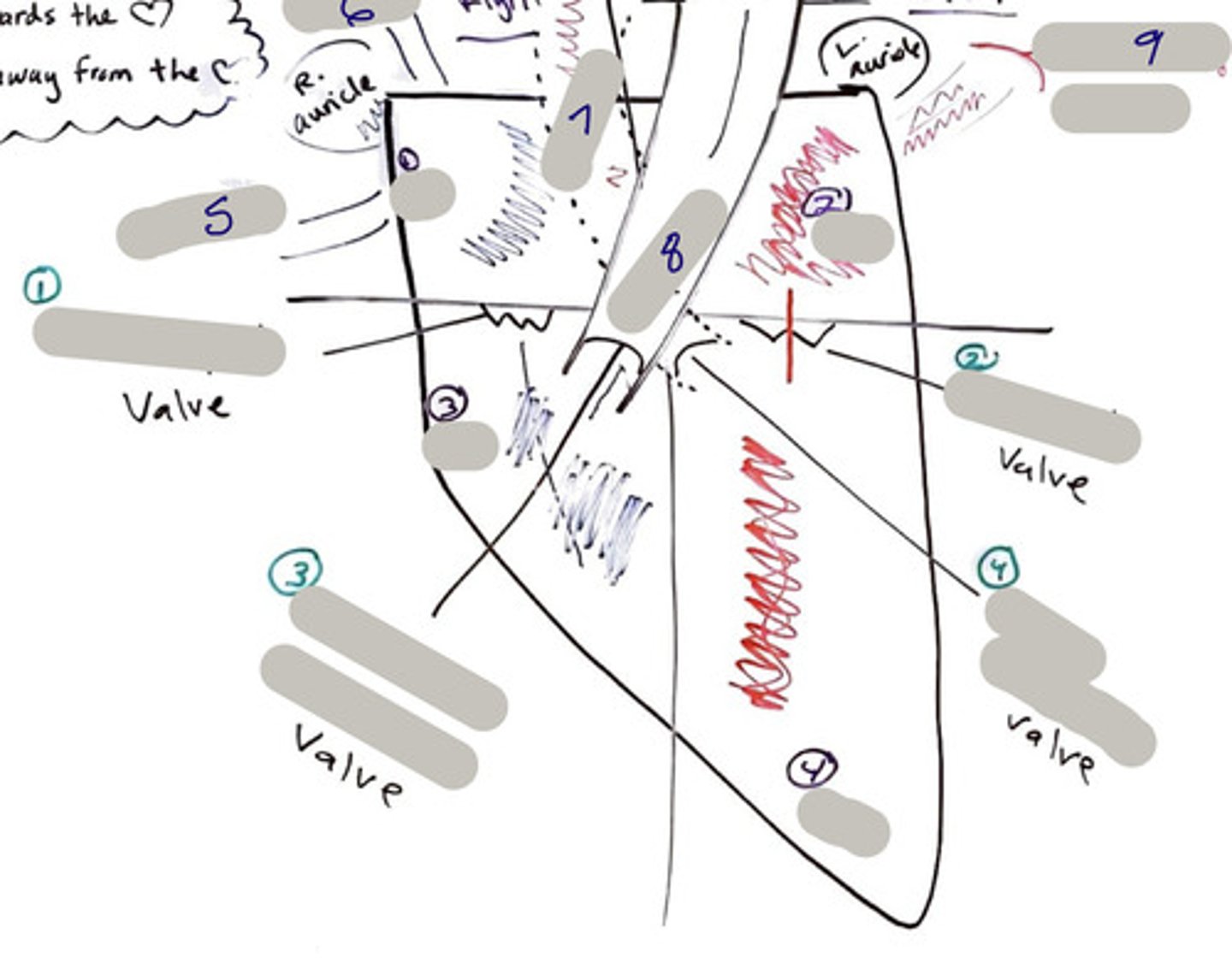
Superior Vena Cava
6-A vein that is the second largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from the upper half of the body.
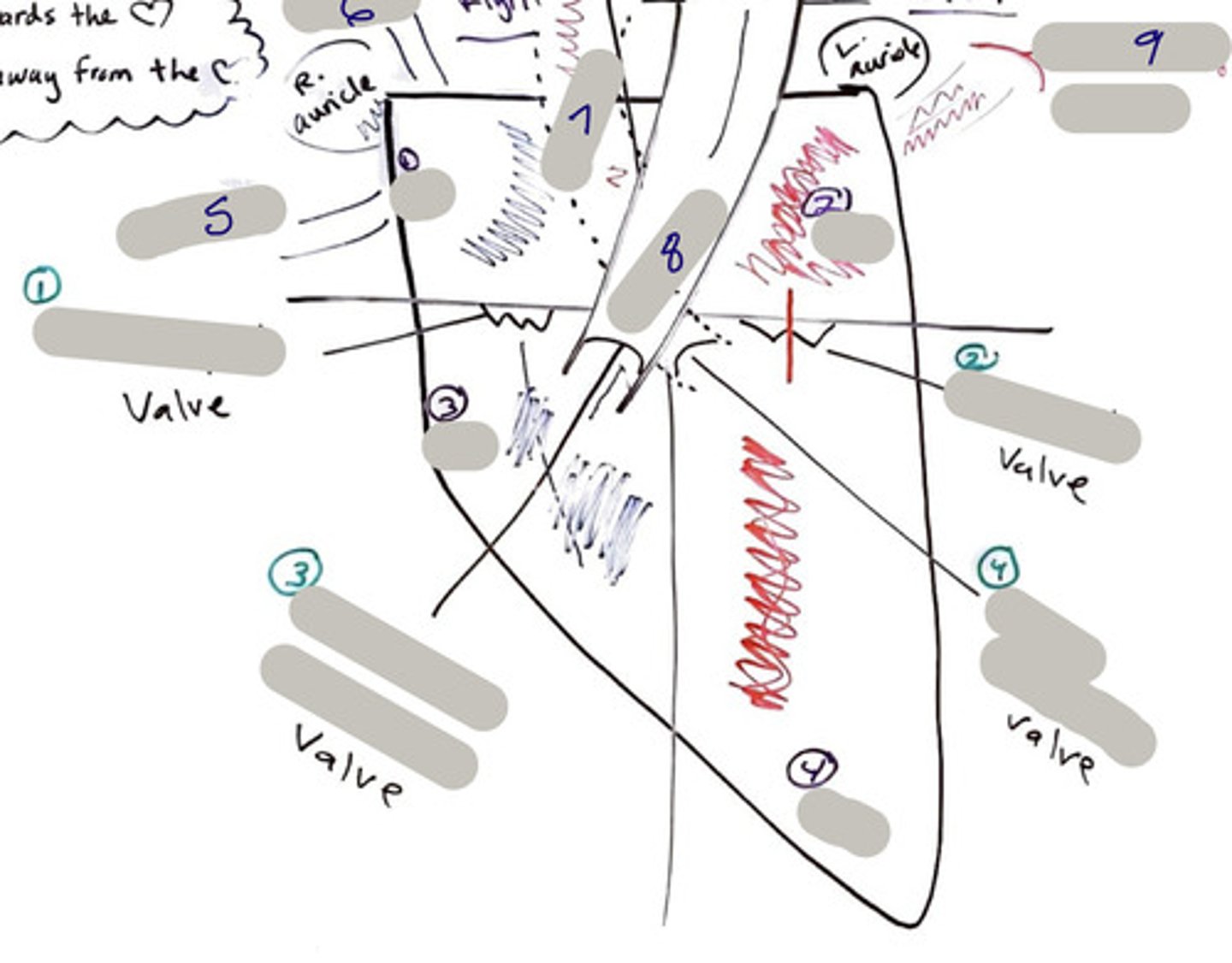
Aorta
7-The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body.
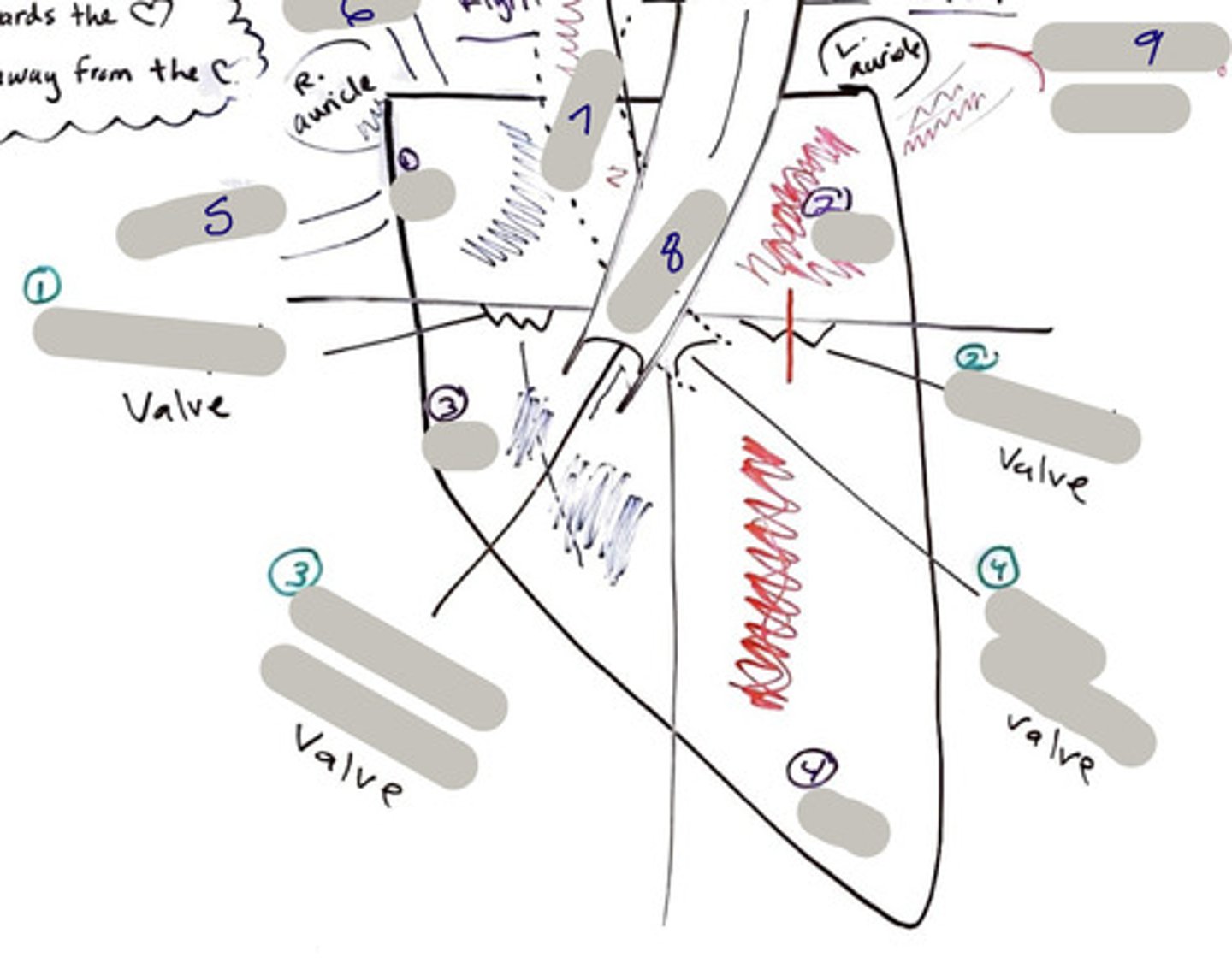
Pulmonary Trunk
8-carries blood from right ventricle to pulmonary arteries
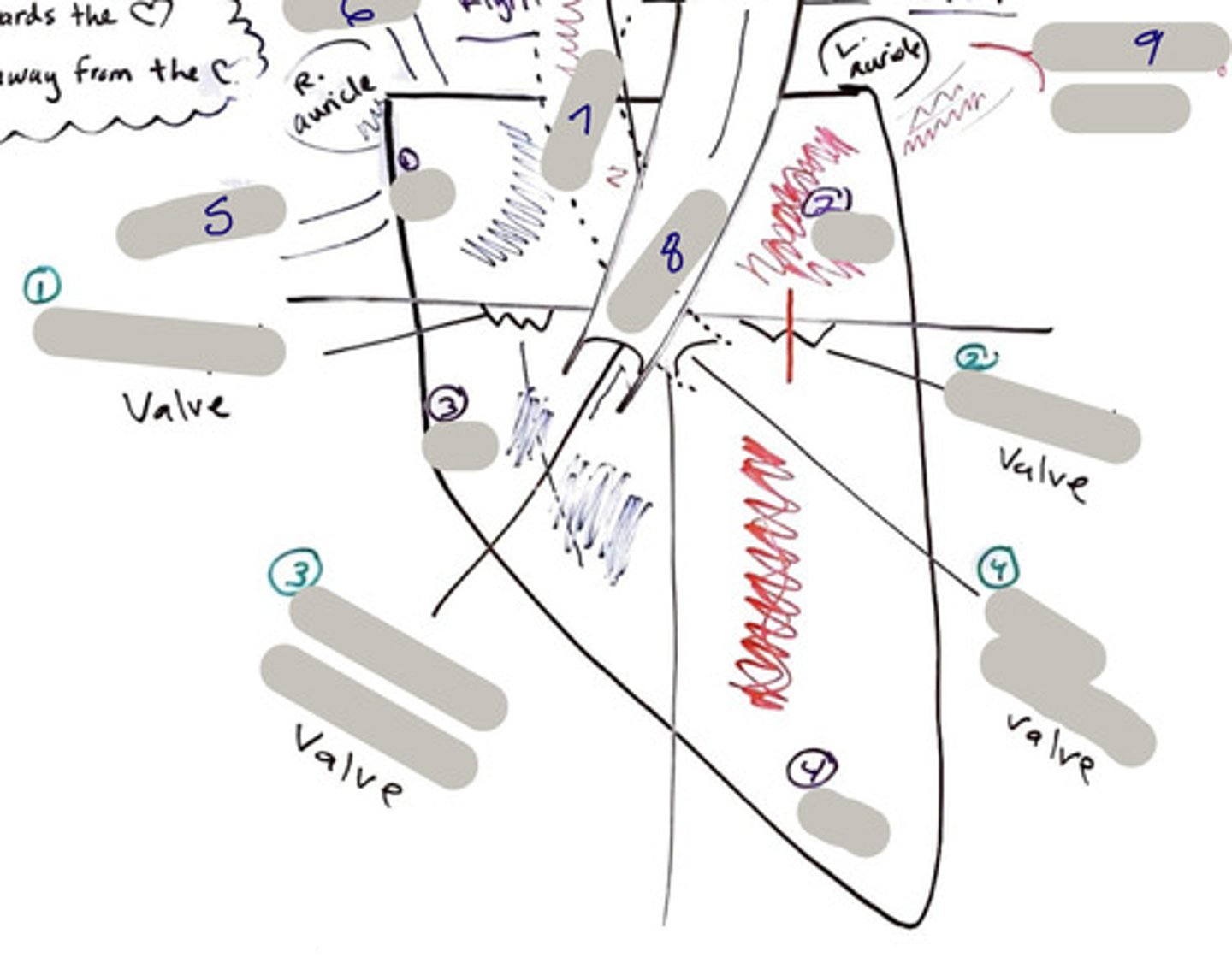
Pulmonary veins
9-a vein carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
pulmonary trunk (model)
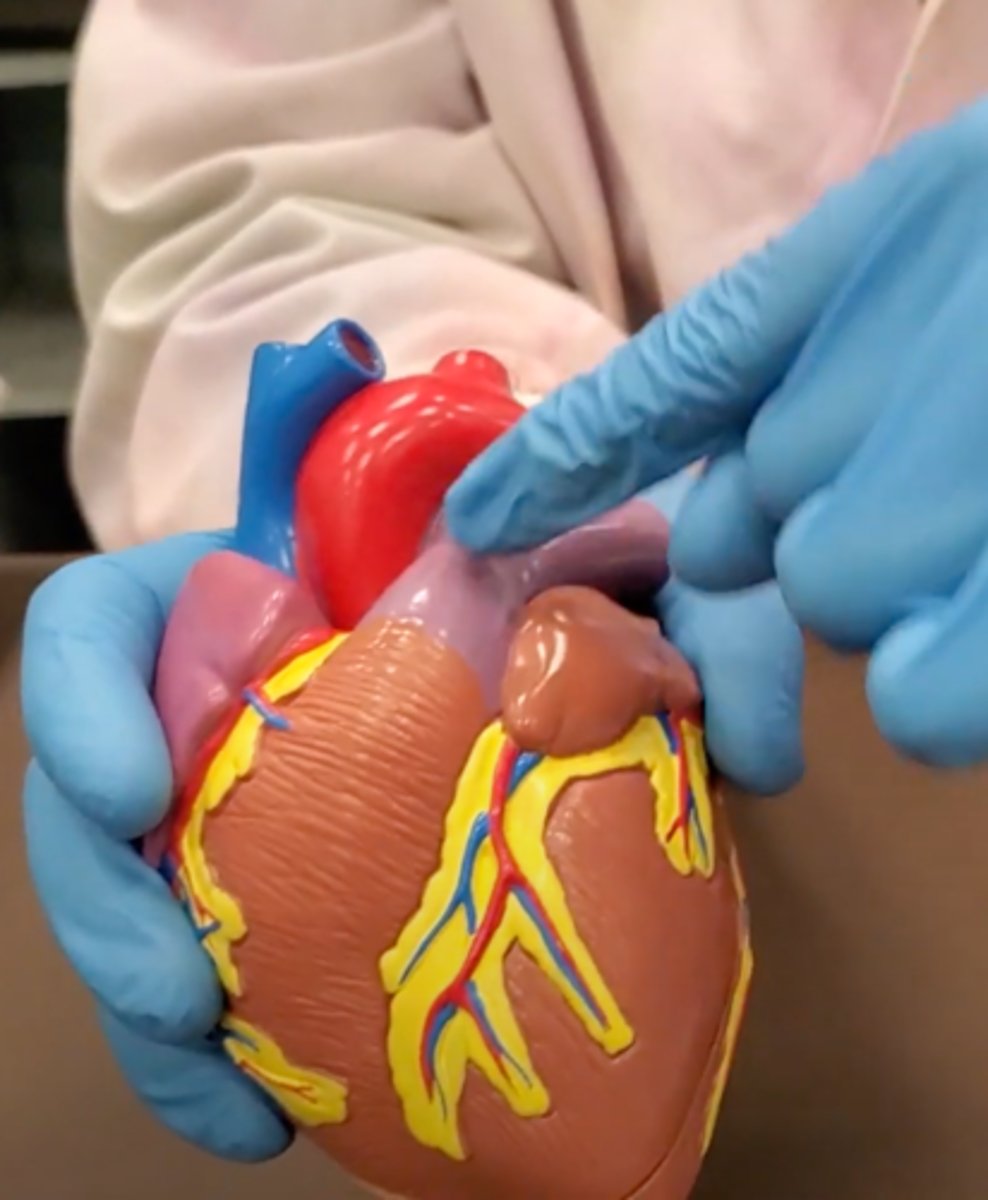
yellow sash of fat that tells you this if the front side of the heart (model)
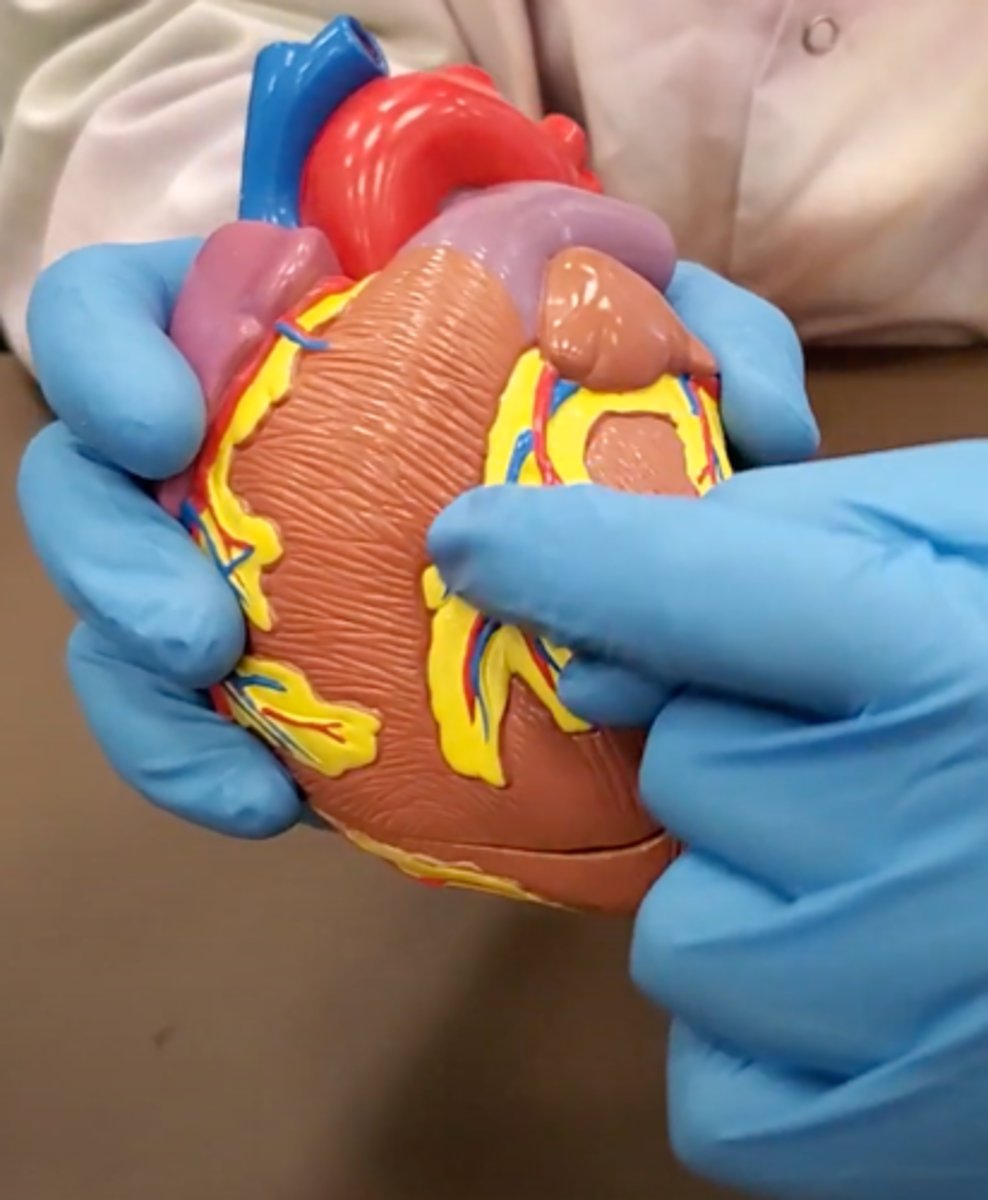
t-shaped ribbon of fat on back side of heart (model)
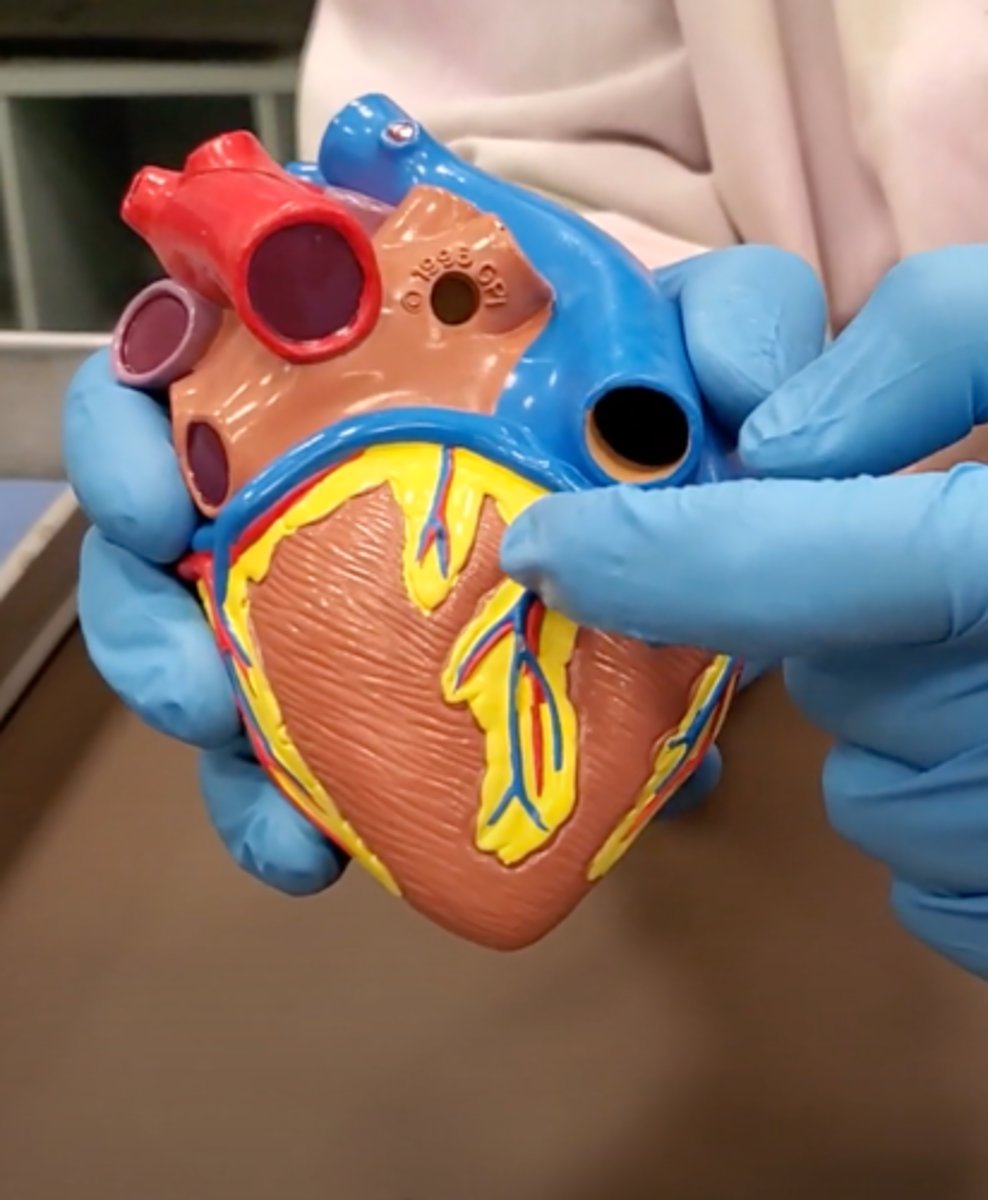
Left ventricle (model)
has the most muscle mass because it has to pump blood to the whole body
apex (model)
base (model)
where everything connects
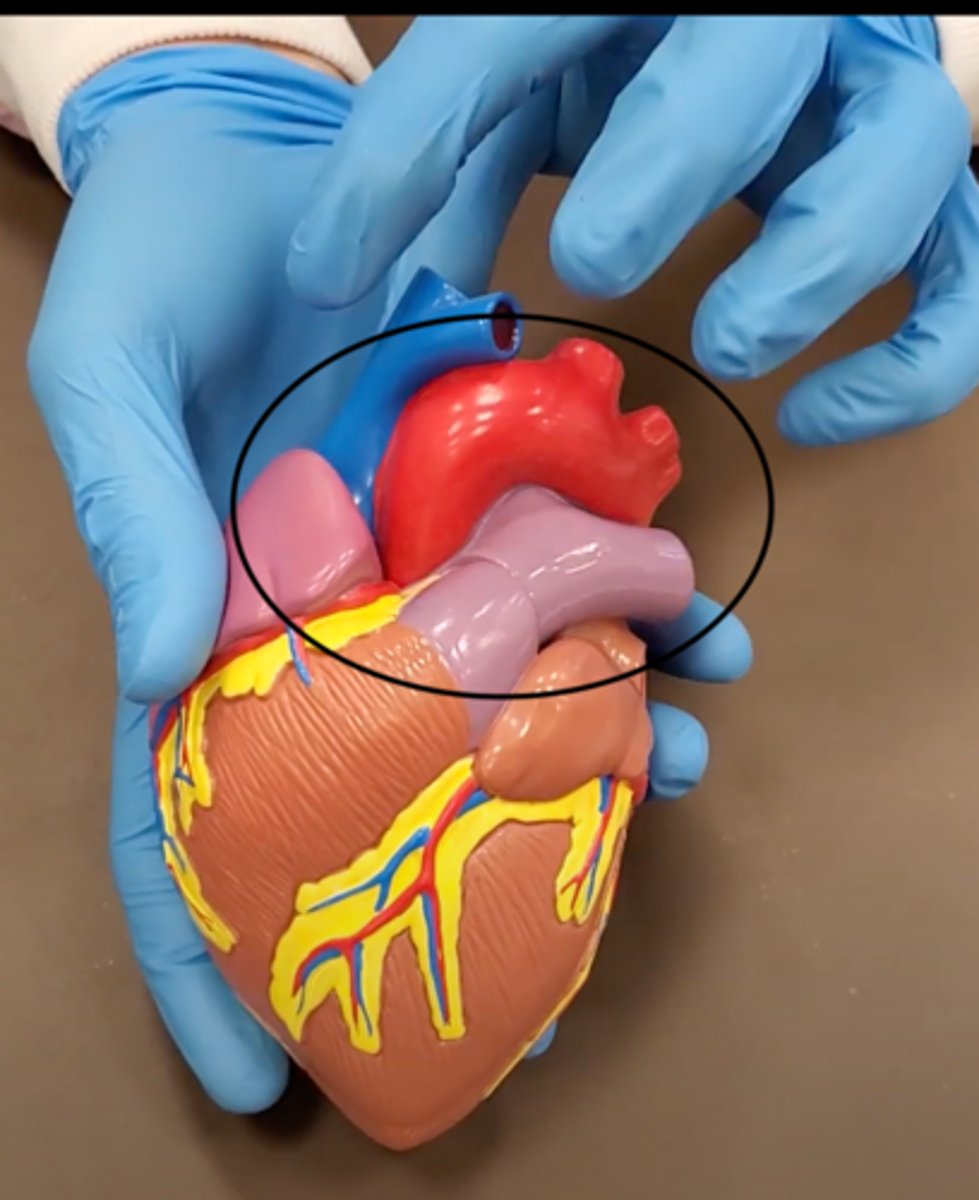
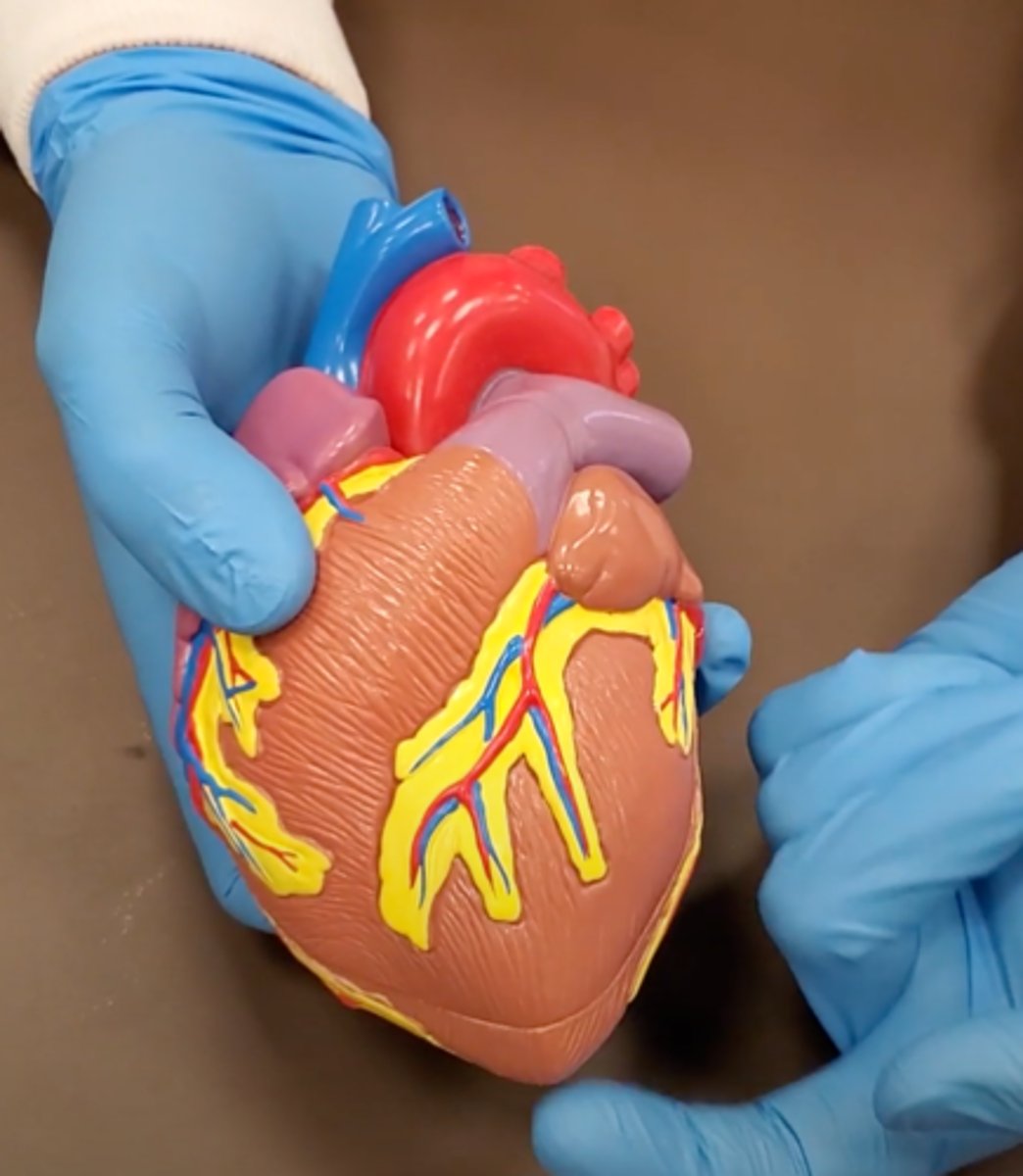
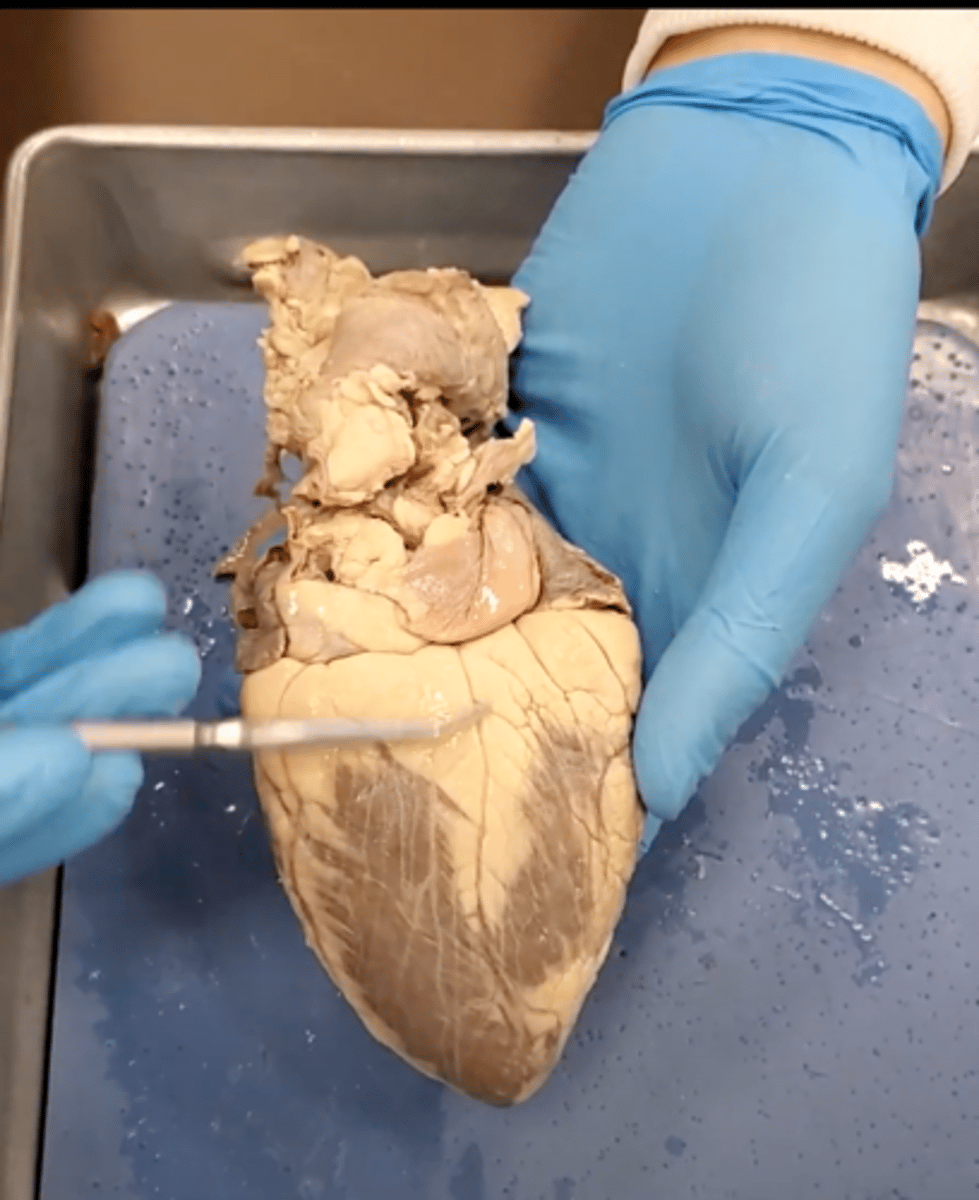
yellow sash of fat that tells you this if the front side of the heart (dissection)
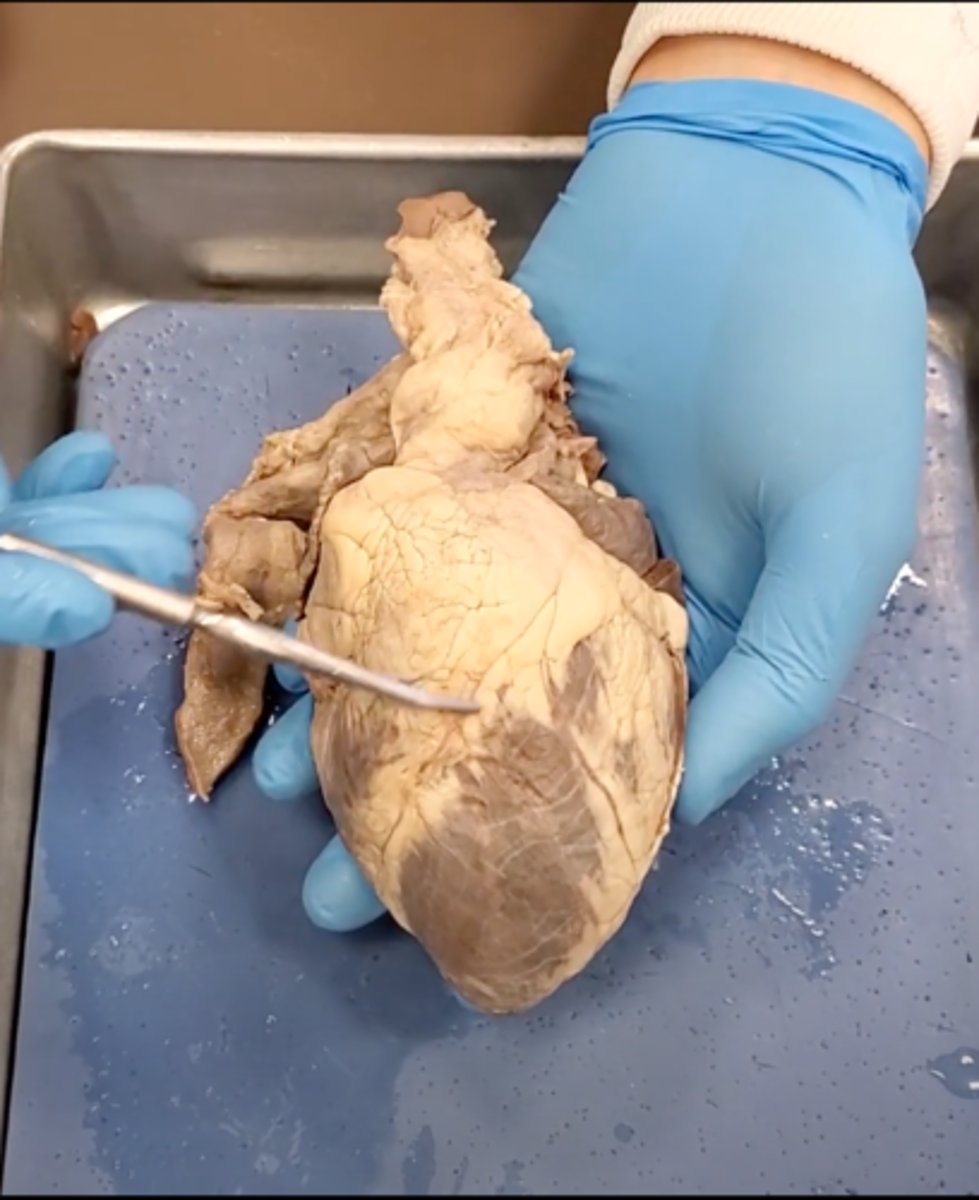
pulmonary trunk (dissection)
t-shaped ribbon of fat on back side of heart (dissection)
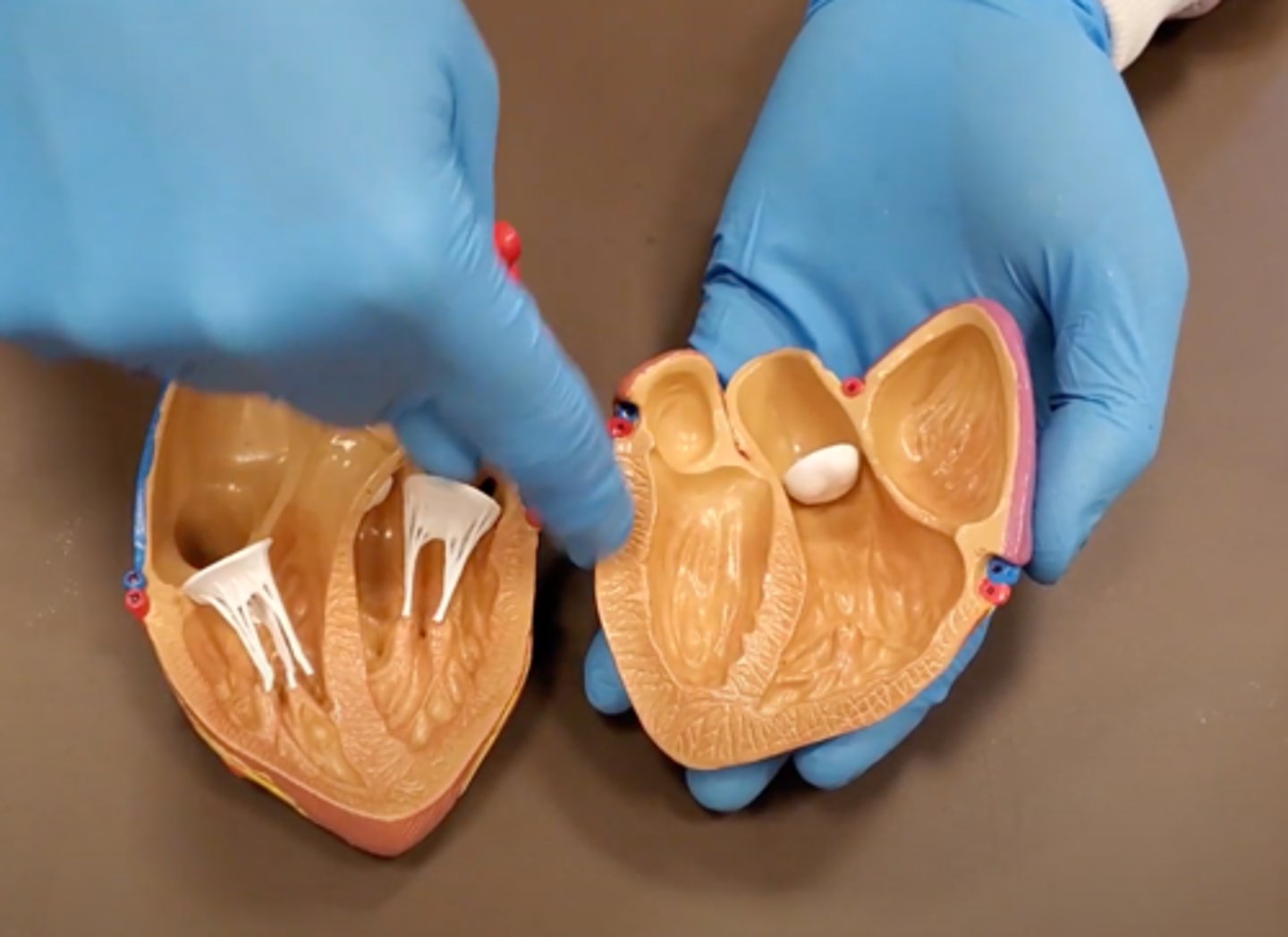
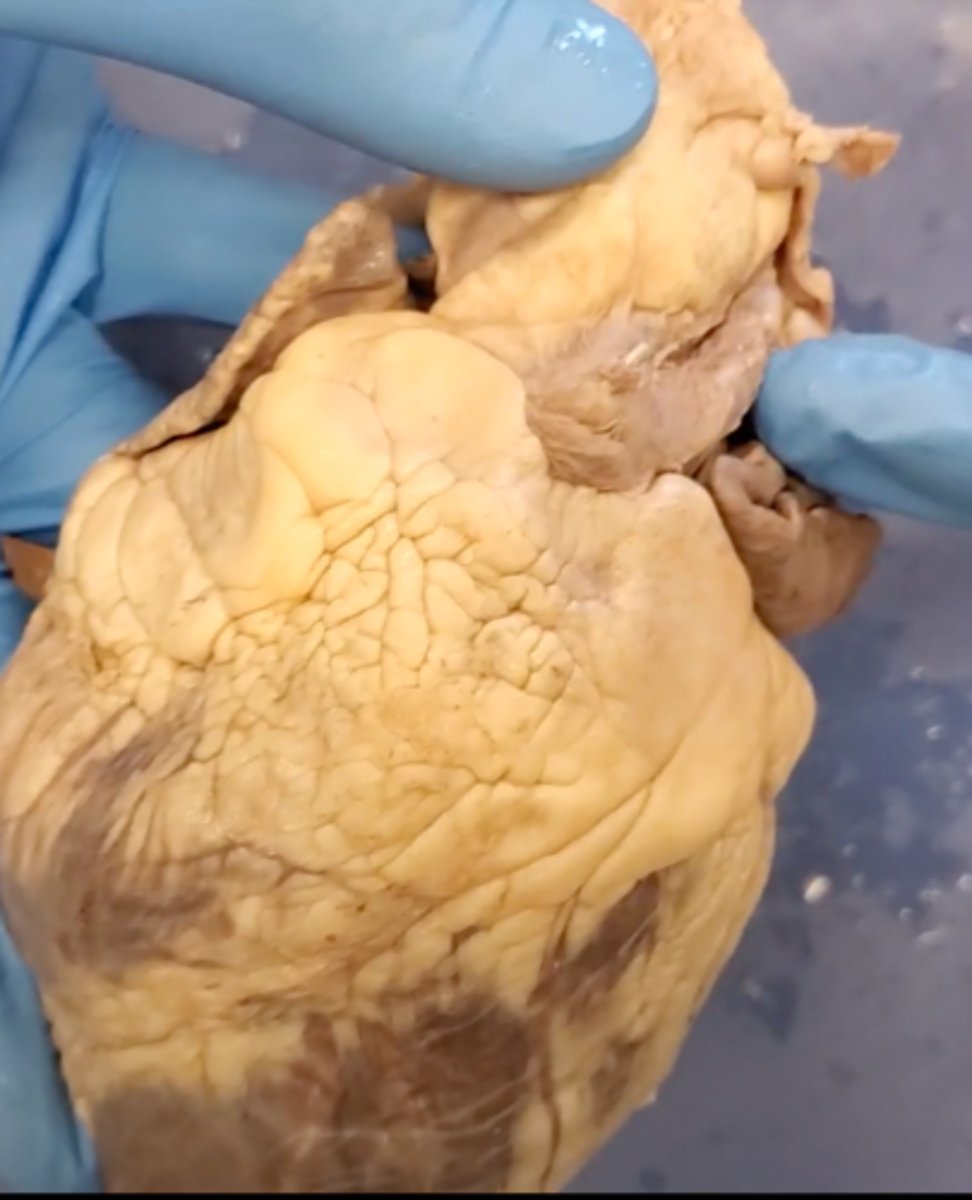
left auricle (dissection)
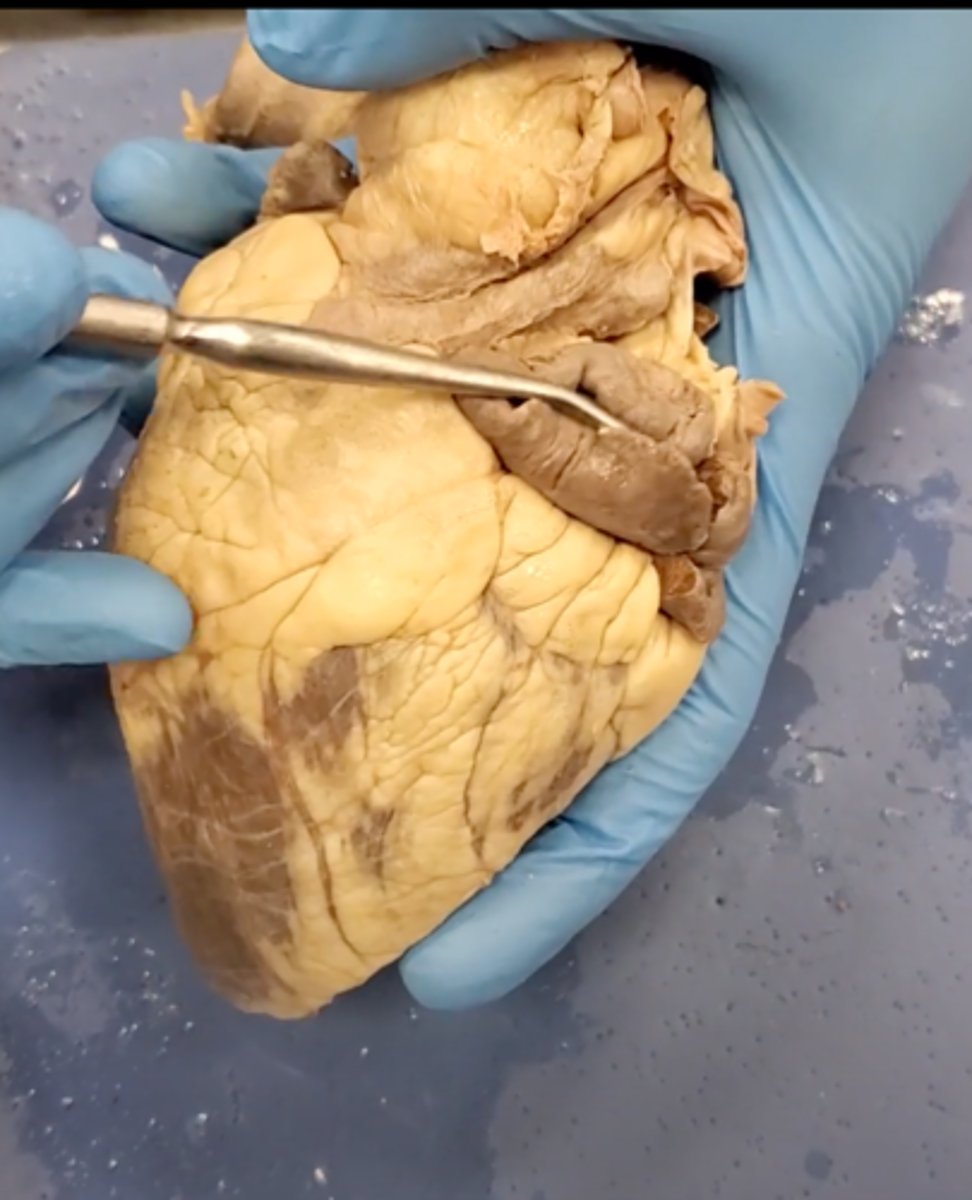
right auricle (dissection)
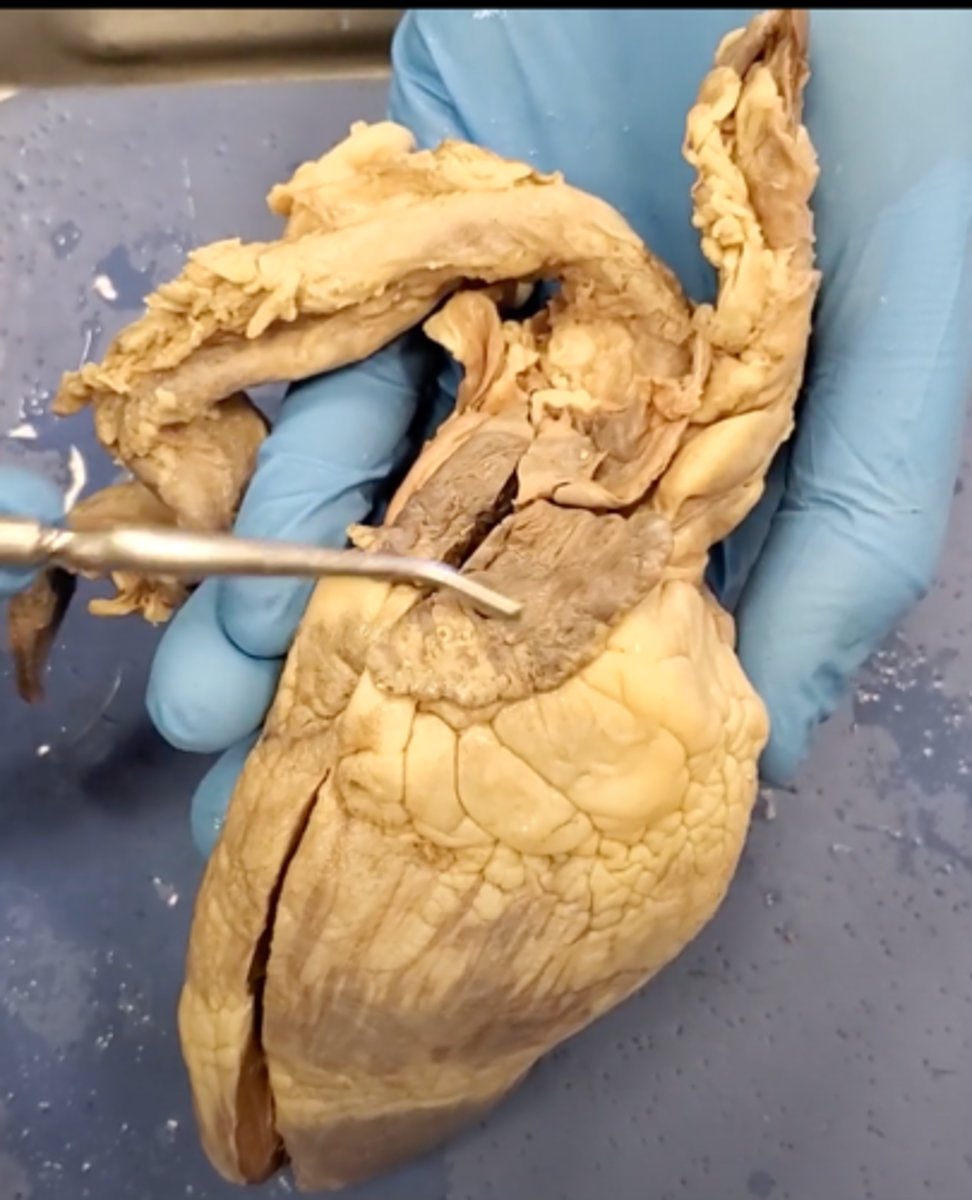
left ventricle (dissection)
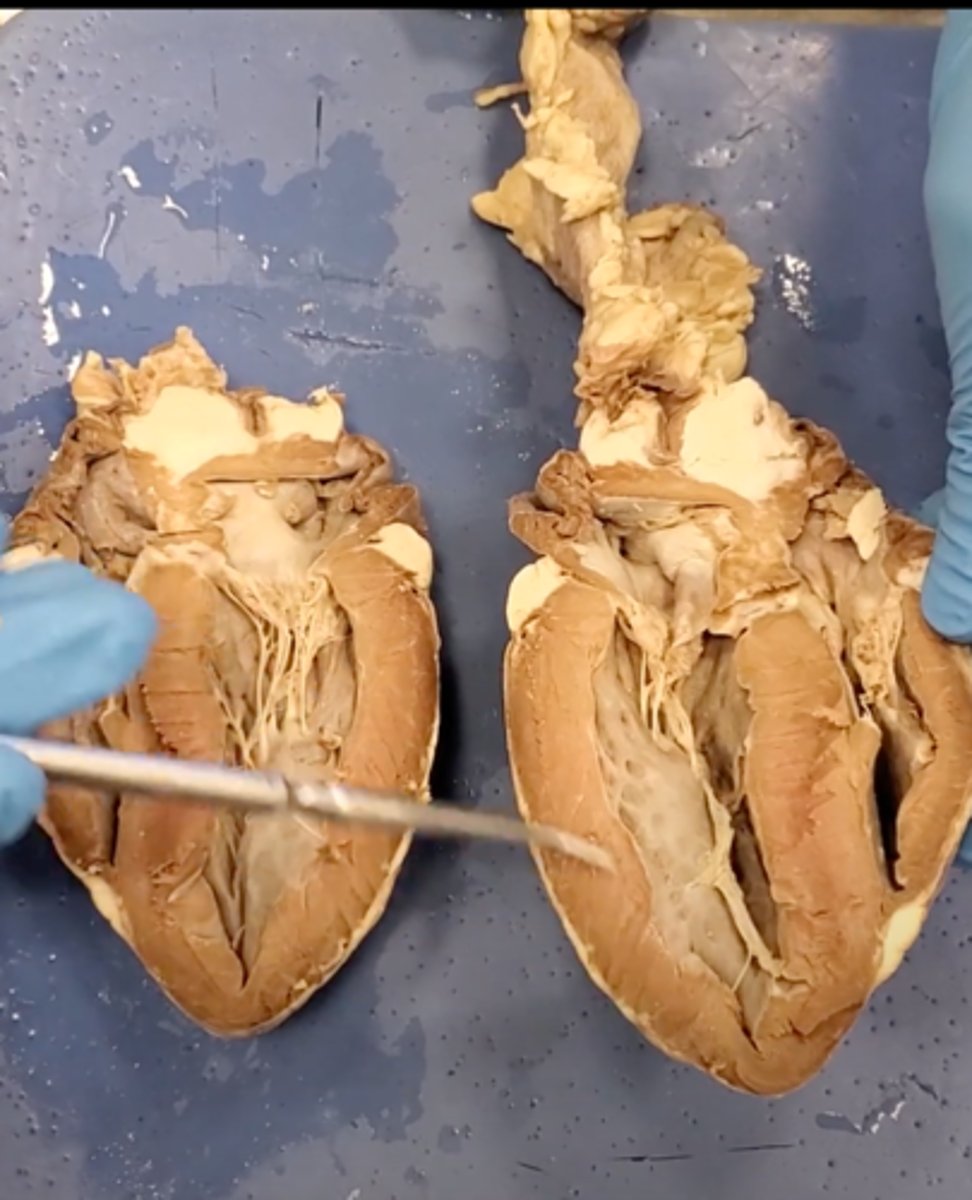
right ventricle (dissection)
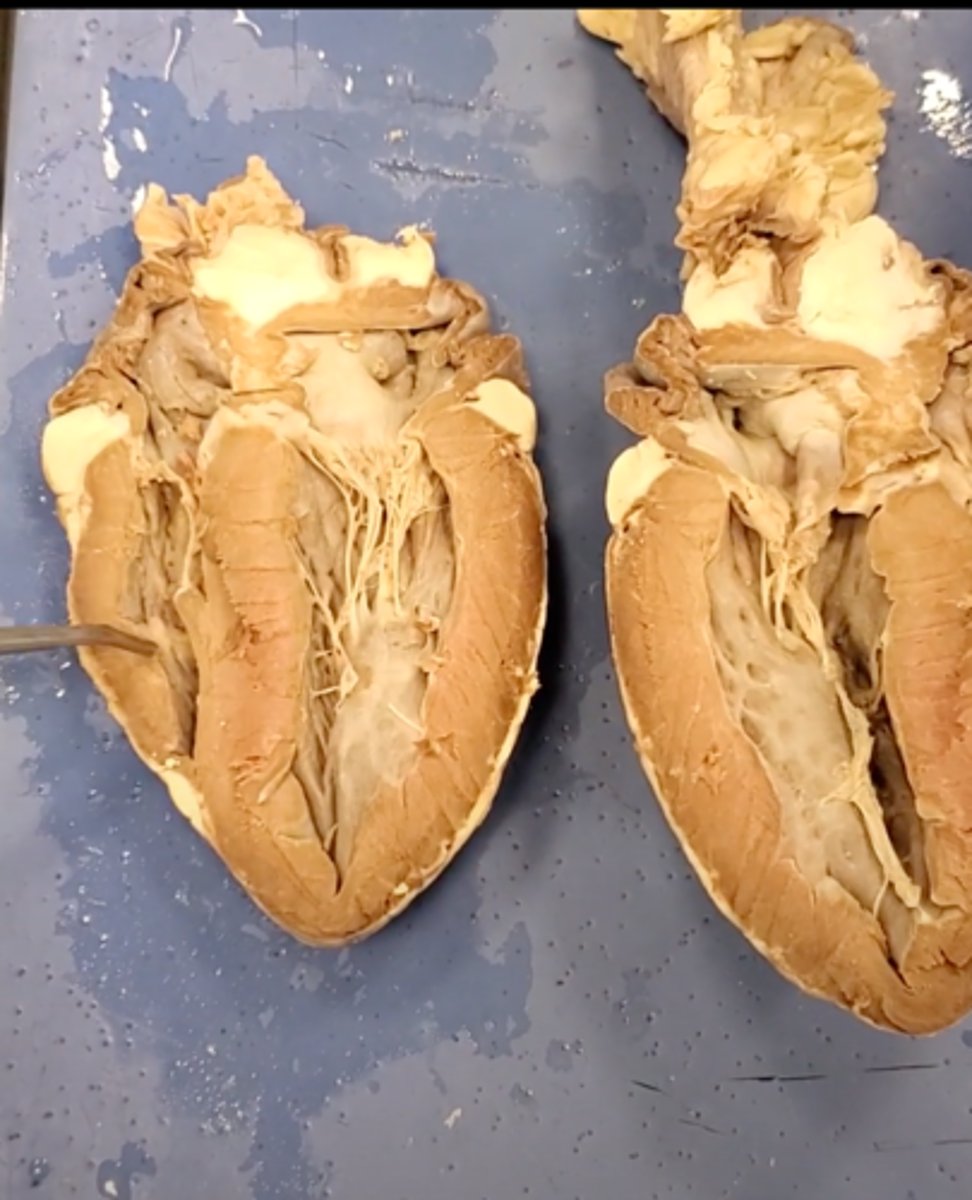
right atrium (dissection)
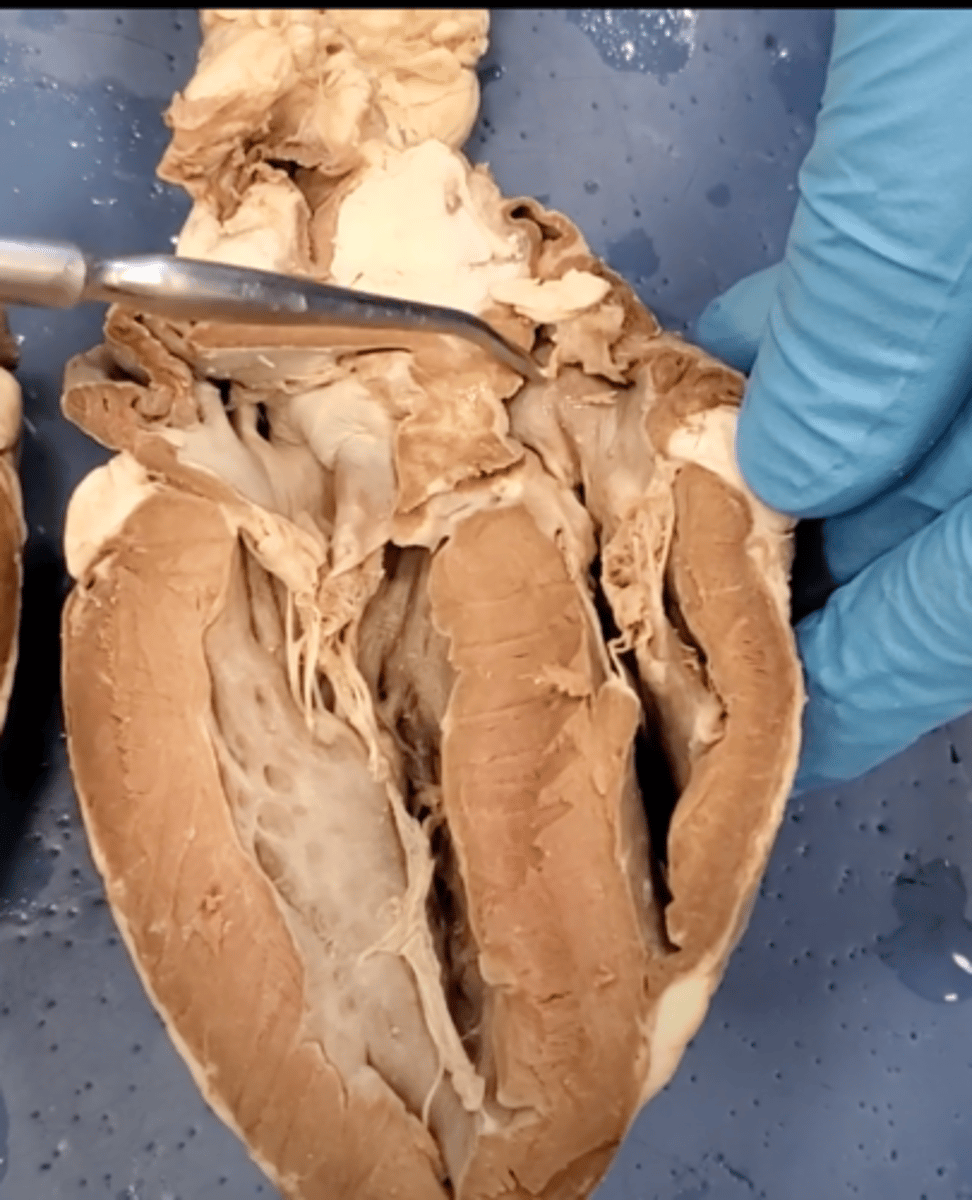
left atrium (dissection)
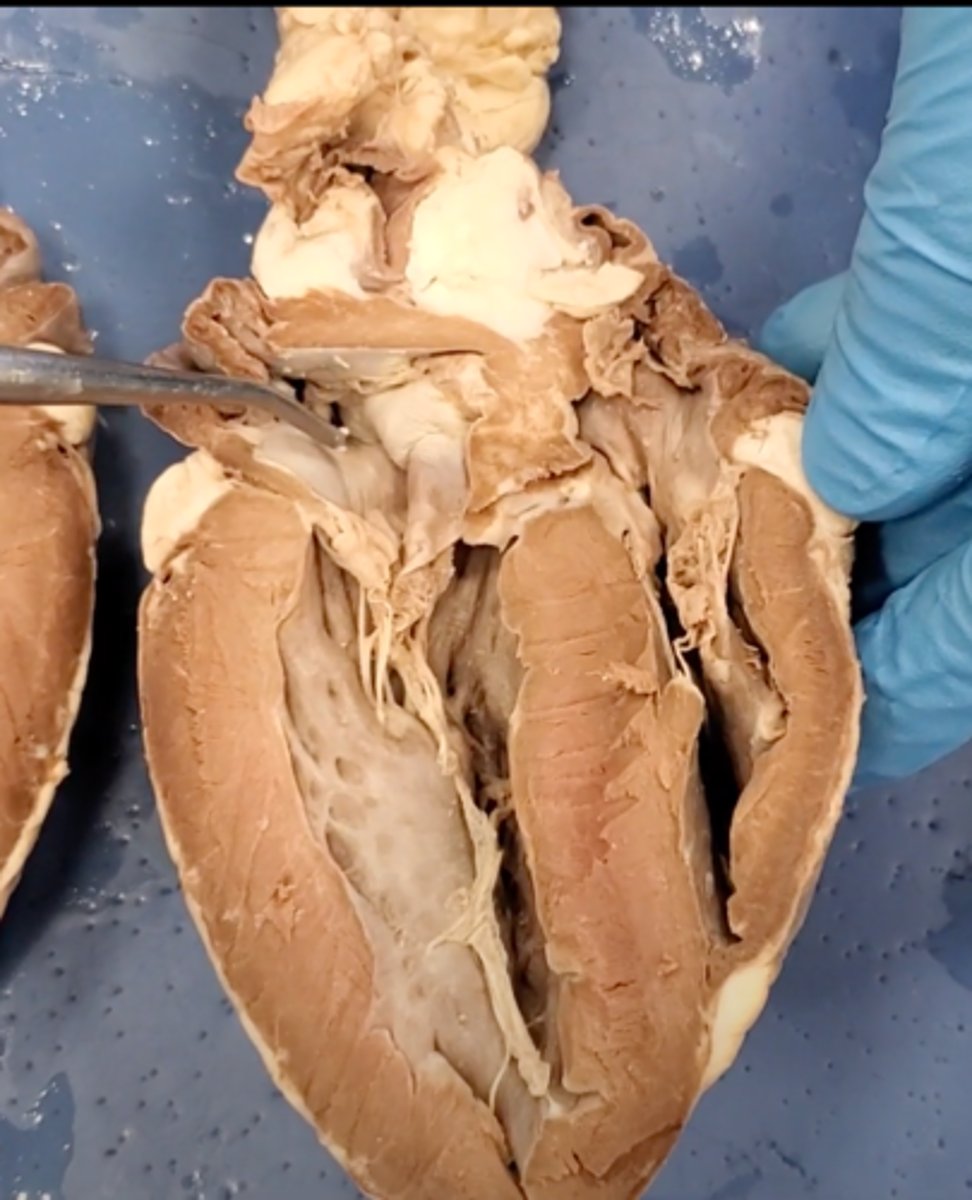
bicuspid valve (dissection)
tricuspid valve (dissection)
aortic semilunar valve (dissection)
located between the left ventricle and the aorta
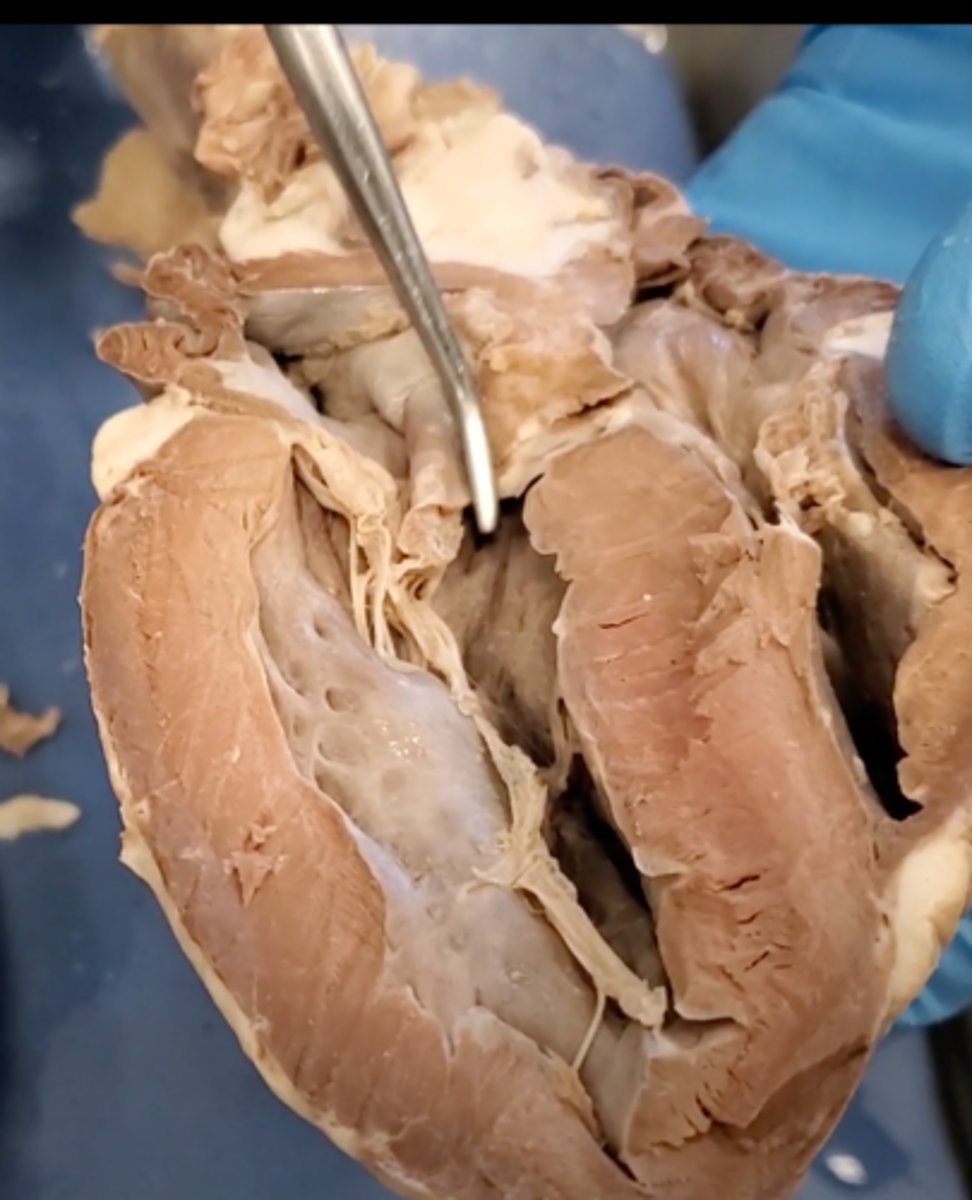
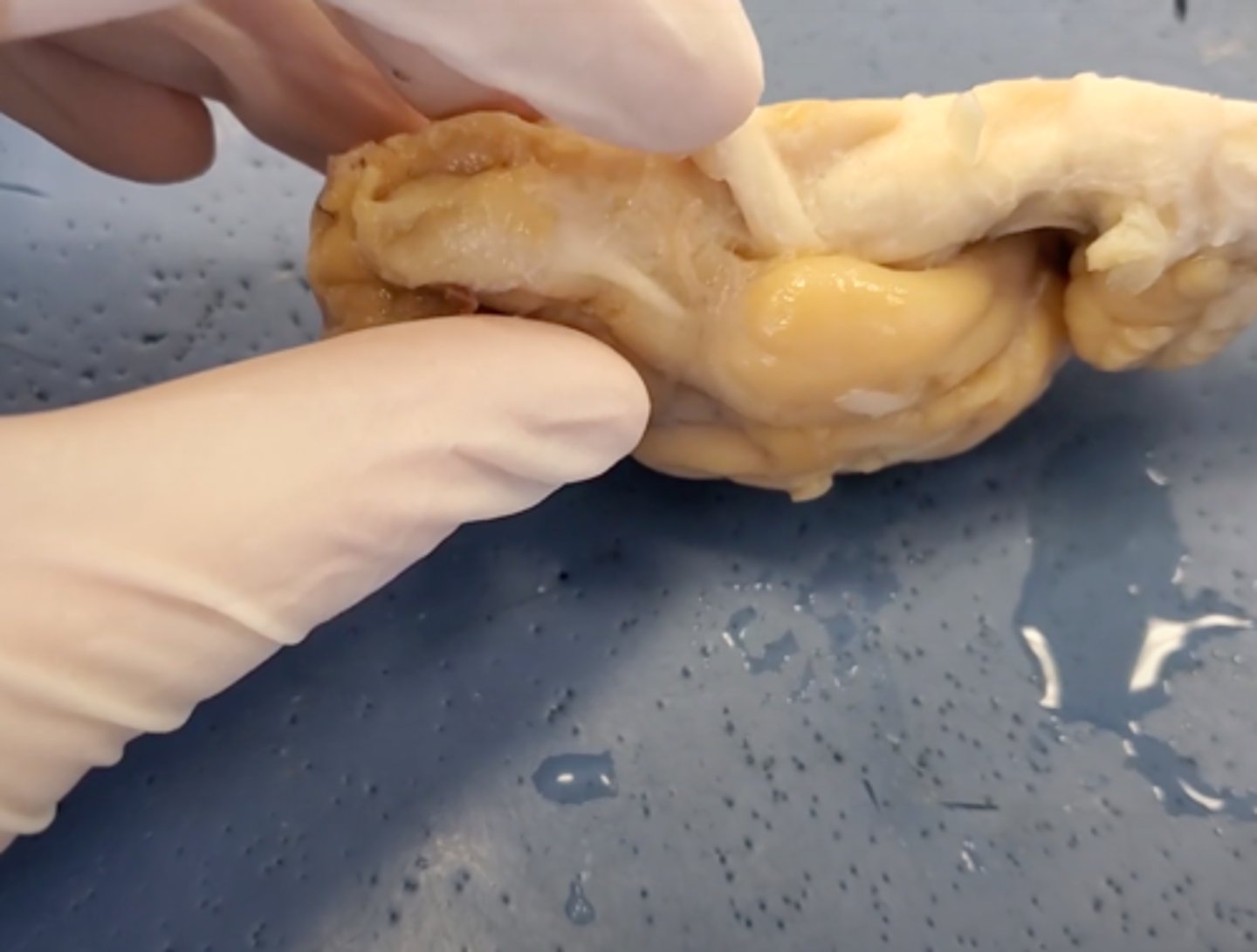
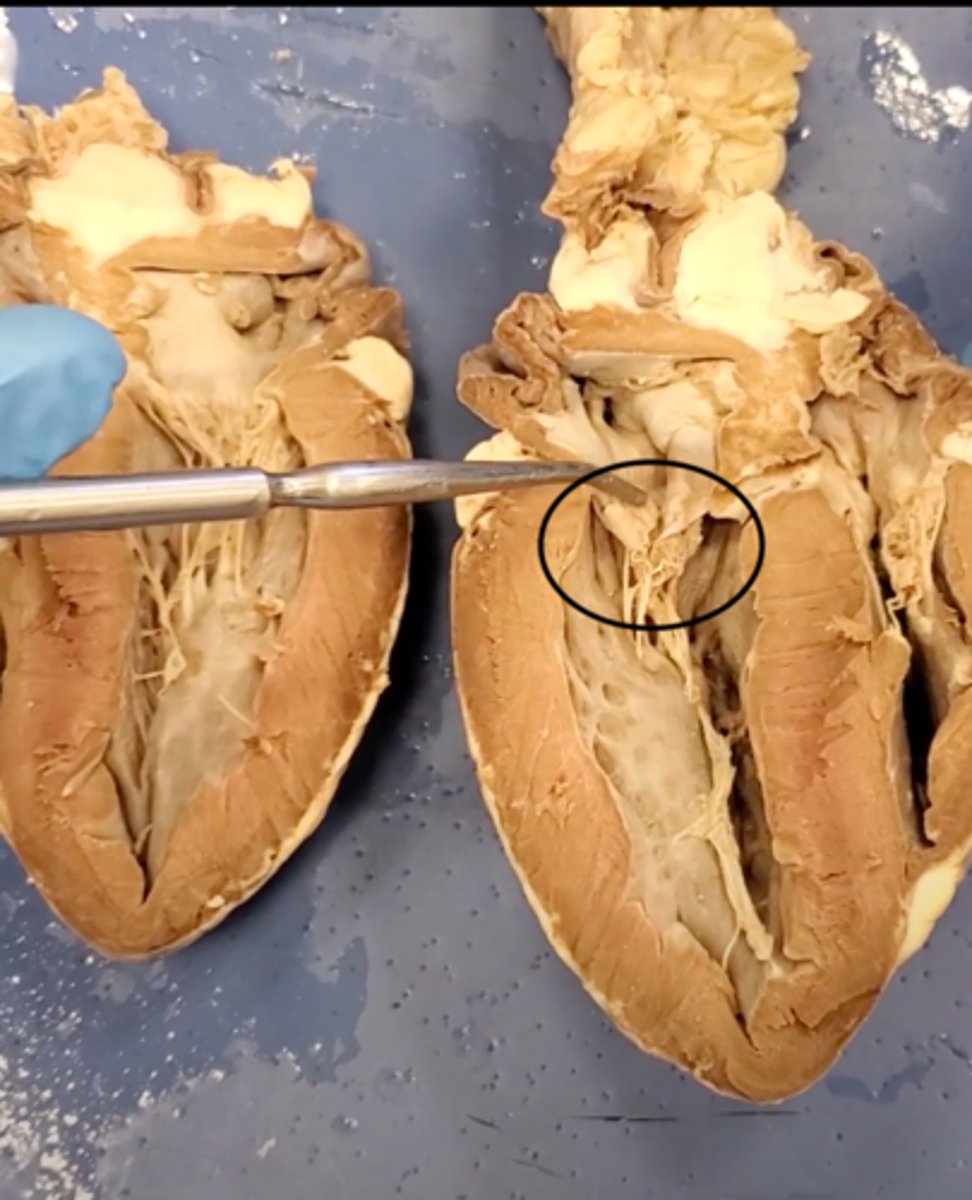
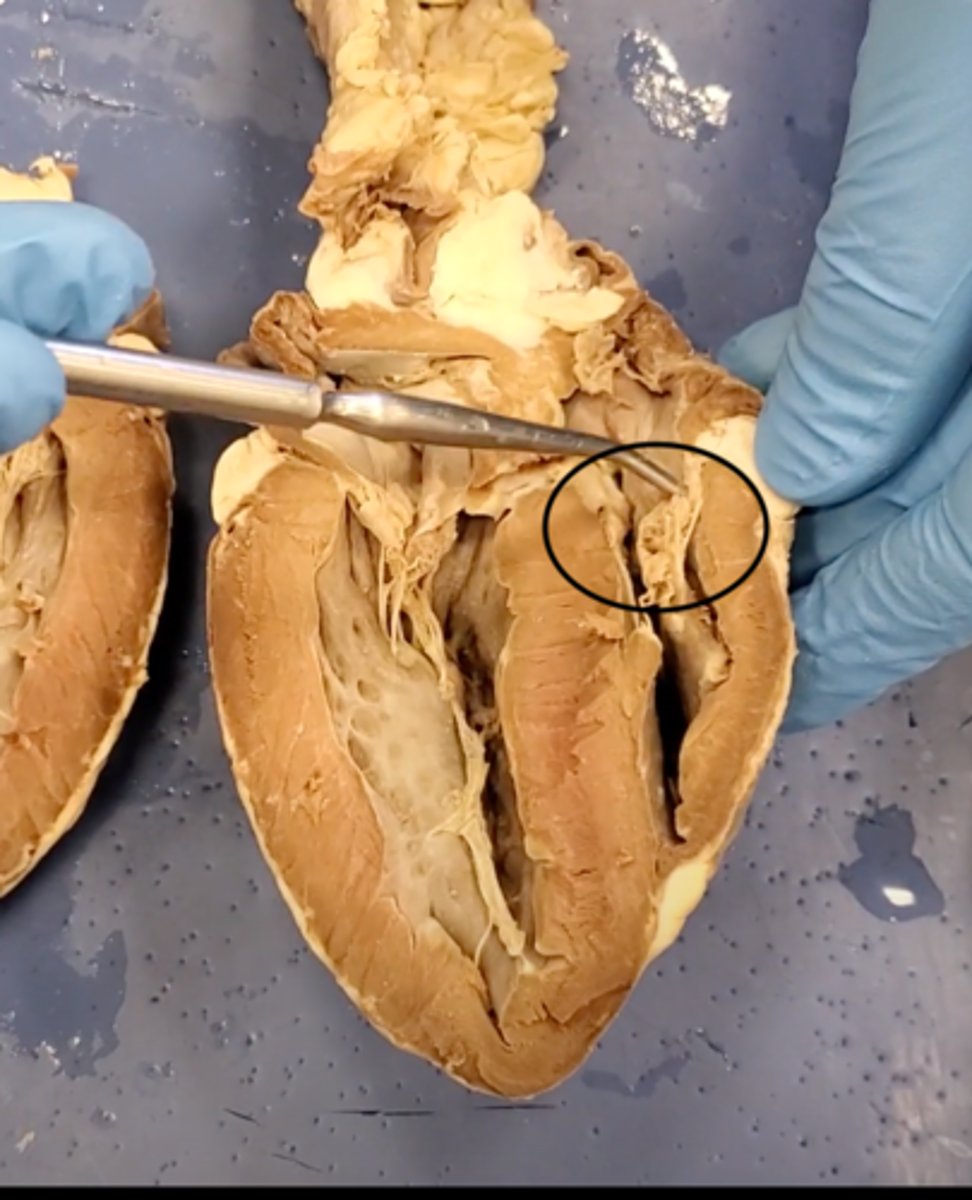
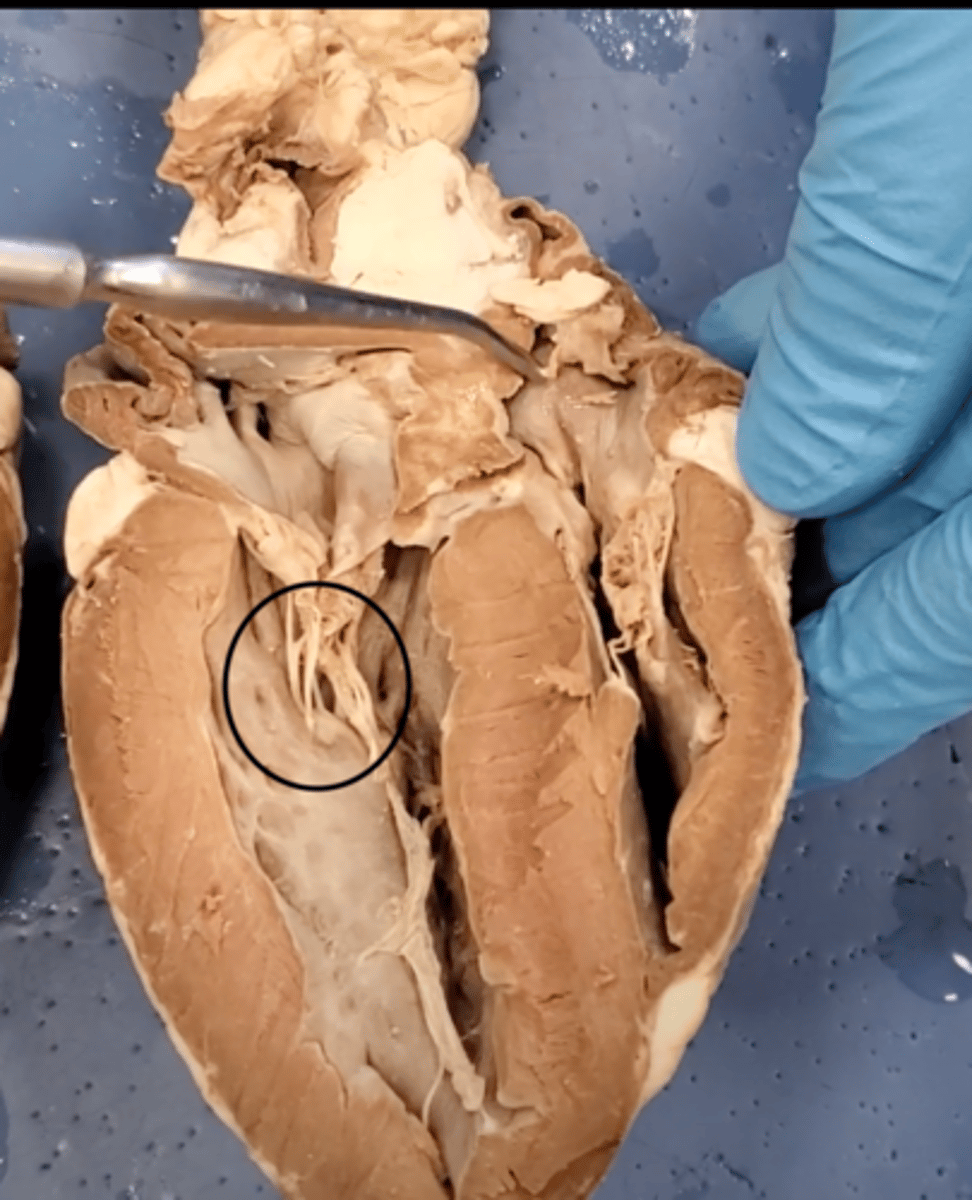
chordae tendineae (dissection)
thin bands of fibrous tissue that attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting
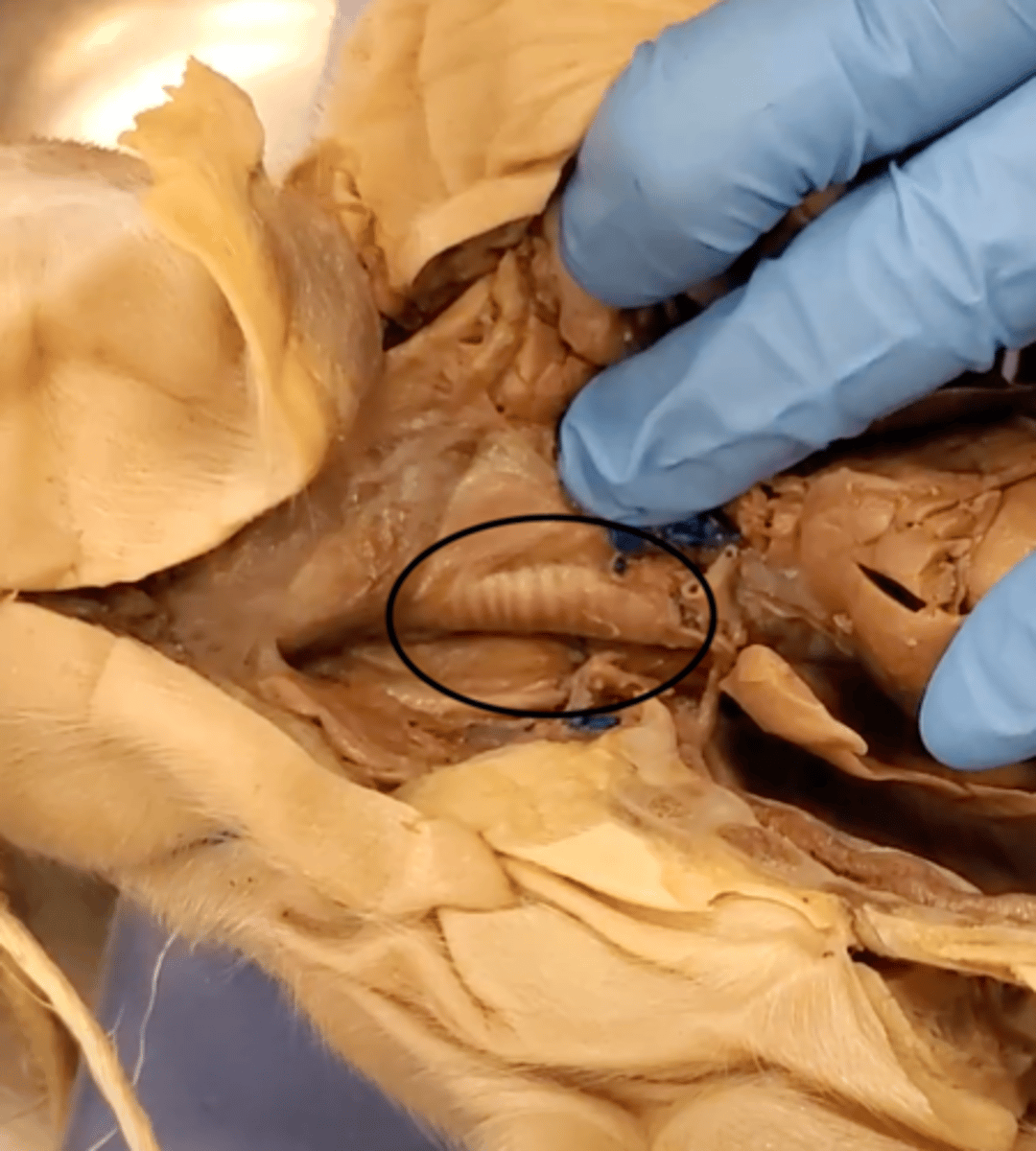
trachea
windpipe, with c-shaped cartilage ring which stiffens the windpipe for easy air passage.
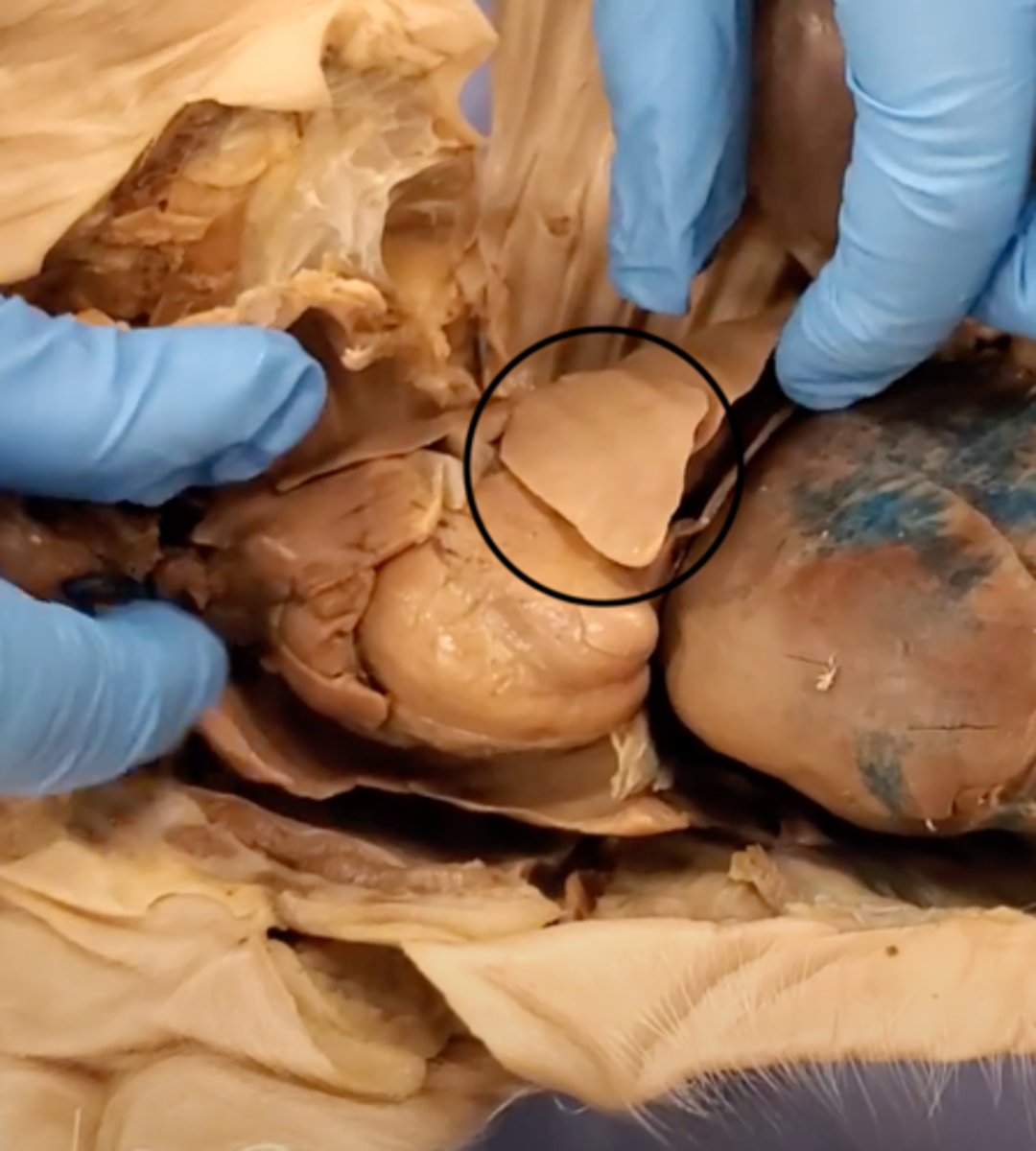
lungs
Main organs of the respiratory system
heart
A hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
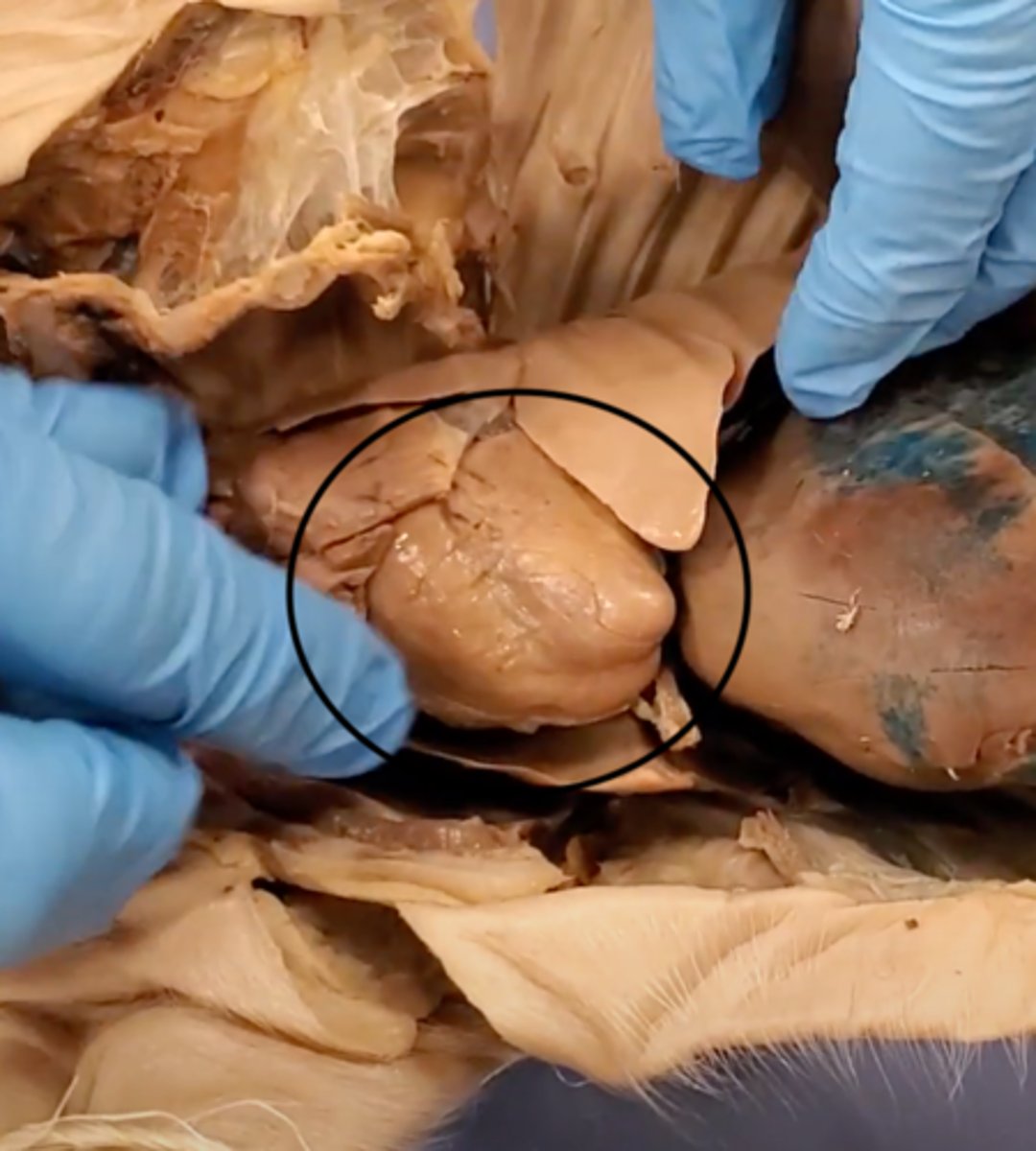
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
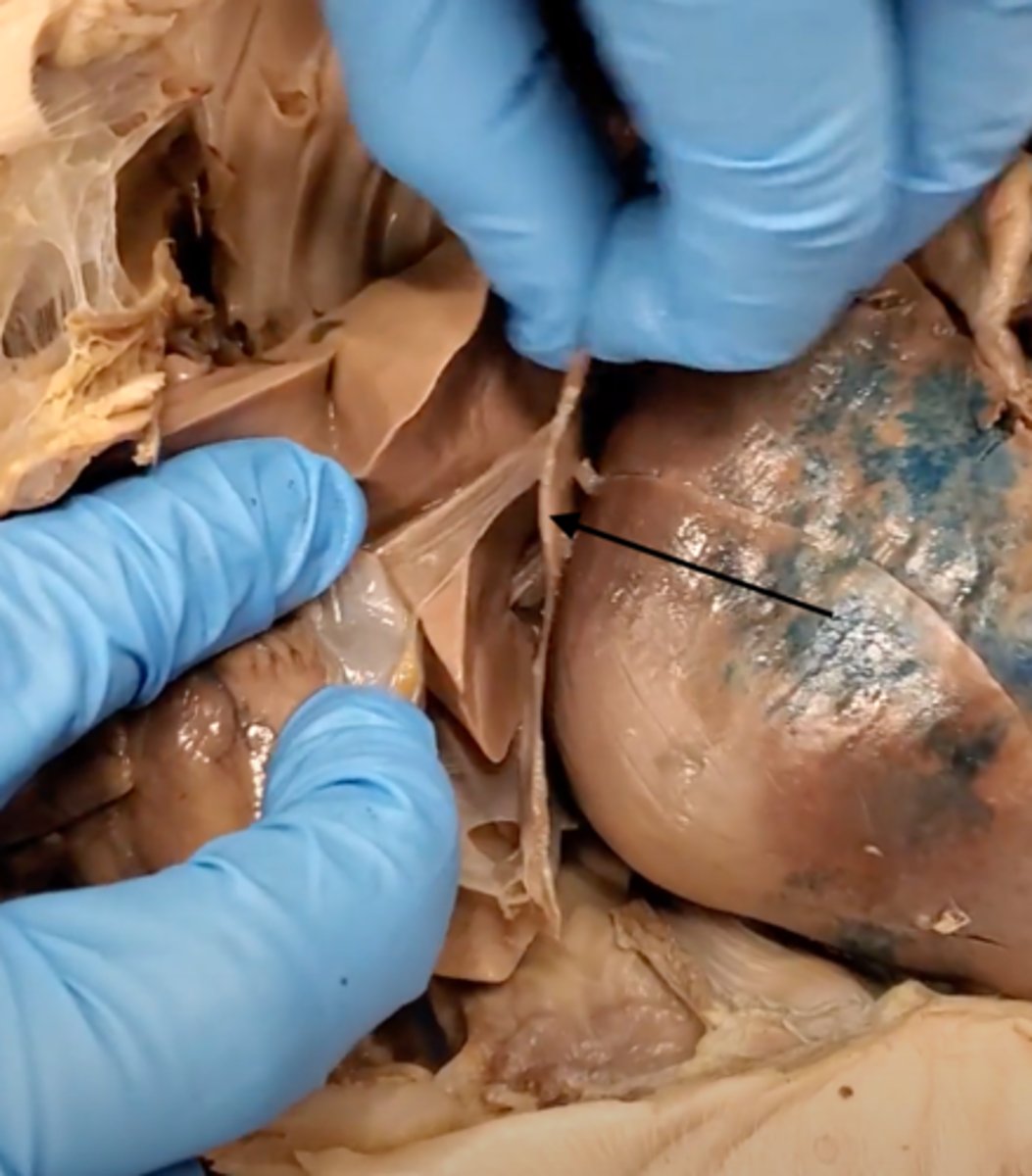
esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.