Supply Side Policies
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Interventionist and Market Based
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are supply side policies?
Aim to shift long run AS
What are the two types of supply side policies?
Interventionist
Market based
What do interventionist supply side policies require?
Government interventionist in order to increase the full employment level of output
mainly used to correct market failure
What do market based supply side policies aim to do?
Remove obstructions in the free market that are holding back improvements to the long run potential
What is market failure?
Occurs when there is less that optimal allocation of resources from society’s POV
Why are supply side policies useful?
Generating long term growth
Lowering average PL
Creating new jobs in the economy
What are the macroeconomic goals of supply side policies?
Economic growth
Inflation
Unemployment
Net external demand
Redistribution of income
How does the goal of economic growth relate to supply side policies?
Potential national output increases leading to higher GDP
How does the goal of inflation relate to supply side policies?
A greater supply in the economy results in reductions in the prices of goods/services leading to disinflation and making the exports of the nation more competitive
How does the goal of unemployment relate to supply side policies?
Should fall as lower wage bills allow firms to recruit more workers
How does the goal of net external demand relate to supply side policies?
Due to increased supply, the prices of goods/services often decrease which makes them relatively more attractive to foreigners so exports increase
How does the goal of redistribution of income relate to supply side policies?
Often worsens with the use of supply side policies as wages fall and government tax revenue has fallen too
What is the market based policy to increase incentives?
Reducing income/corporation tax rates incentivises workers to work harder (they keep more money for themselves) and provides firms with extra funds which they can use to invest in new machinery/technology
Reduces capital gains tax (a tax that is imposed on the profit that an investor makes when selling an asset)
What are the possible effects on the aims of supply side policies from the market based policy increasing incentives?
Taxes decreases > causes firms and individuals to retain more money for themselves
Incentives increase > productivity improves > long term growth increases
What is the market based policy to improve competition and efficiency?
Deregulation: decreases costs which may result in greater supply
Privatisation: encourages new firms to enter the market and compete, increasing the AS in the economy
Anti-monopoly regulation: helps to increase competition in an economy which leads to a more efficient allocation of resources
What are the possible effects on the aims of supply side policies from the market based policy to improve competition and efficiency?
Deregulation on firms decrease > costs of production for firms fall > firms lower selling prices > international competitor improves
State owned firms are privatised > more firms enter the market to compete > competition and efficiency improves
What is the market based policy to reduce labour costs and create labour market flexibility?
Decreasing trade union power so wages can be decreased
Decreasing or abolishing minimum wages to lower costs of production
Restructuring the unemployment benefits system to incentivise the unemployed to seek work
What are the possible effects on the aims of supply side policies from the market based policy to reduce labour costs and create labour market flexibility?
Wages decrease > costs of production for firms fall > firms lower selling prices > international competitiveness improves
What is the possible impact of abolishing minimum wages?
Removing it will allow wage levels to fall, reducing the costs of production for firms
However this could be seen as unethical as firms may pay workers less than a sustainable amount of live

What is a real world example of market based supply side policies?
Privatisation in China in the 1990s-2000s
China transitioned from a centrally planned economy to a more market-orientated one by privatising state owned enterprises
The goal was to increase competition, efficiency and innovation within industries
Improved productivity and reduced government inefficiencies
Encouraged FDI, enhancing technological and infrastructure growth
What is the interventionist supply side policy education and training?
Increasing government spending on education and retraining raises the quality of the workforce resulting in productivity improvements
What are the possible effects on the aims of supply side policies from the interventionist policy education and training?
Skill level increases > productivity improves
Cost of production for firms falls > firms lower selling prices > international competitiveness improves
What is the interventionist supply side policy improving quality, quantity, and access to health care?
Increasing government spending on healthcare so that productivity improves
What are the possible effects on the aims of supply side policies from the interventionist policy improving quality, quantity and access to healthcare?
Human capital improves > productivity improves
Cost of production for firms falls > firms lower selling prices > international competitiveness improves
What is the interventionist supply side policy research and development?
Increased government spending on innovation increases the supply of potential jobs in the economy
What are the possible effects on the aims of the supply side policies from the interventionist policy research and development?
A new industry emerges > new infrastructure is developed > more jobs created
Real GDP increases > increase in long term economic growth
What is the interventionist supply side policy provision of infrastructure?
Increased government spending on infrastructure helps to facilitate the movement of people and goods which increases AS
What are the possible effects on the aim of supply side policies from the interventionist policy provision of infrastructure?
New infrastructure is developed > costs of production decrease
Supply increases > firms lower selling prices > international competitiveness improves
What is the supply side policy industrial policies?
Industrial policies are direct and targeted to support to firms or industries in the form of subsidies
What are the possible effects on the aims of supply side policies from the interventionist policy industrial policies?
Industries receive subsidies > cost of production decrease
Supply increases > firms lower selling prices > international competitiveness improves
What is a real life example of interventionist supply side policies?
South Korea’s investment in technology and innovation
SK’s government heavily invests in research and development (R&D) to boost technological innovation, especially in sectors like electronics and semiconductors (eg Samsung and LG)
There is direct funding for R&D programs in universities and businesses and support for startup ecosystems and innovation hubs
There is a supply side impact of increased productivity and technological advancement and long term economic growth by enhancing the quality of capital and shifting LRAS curve to the right
How does the Classical diagram look like for supply side policies?
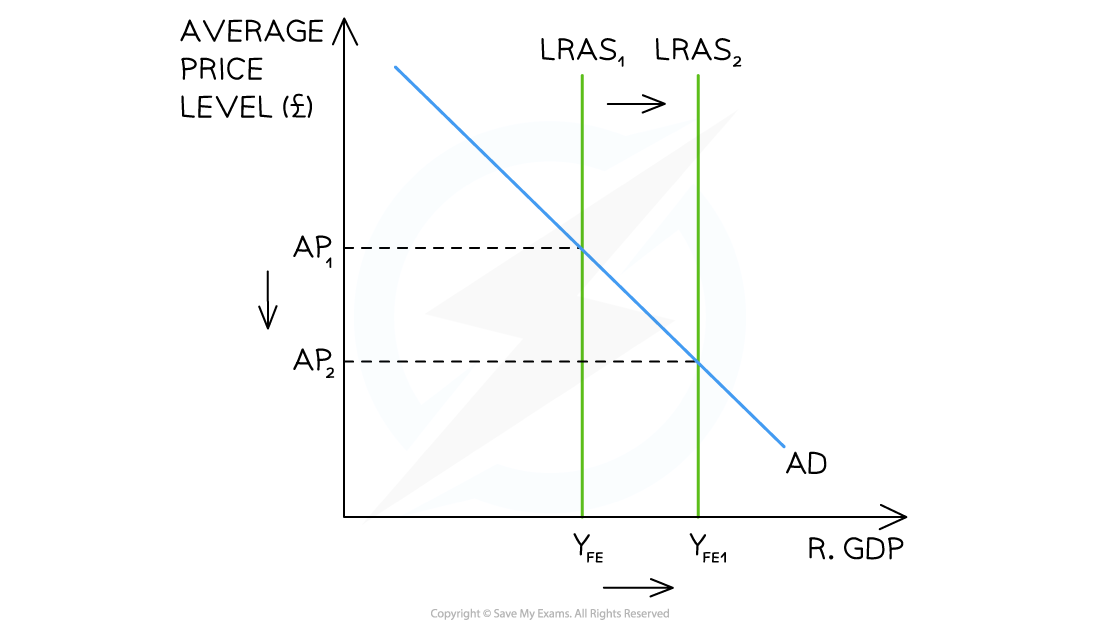
How does the Keynesian diagram look like for supply side policies?

What are the demand side effects of supply side policies?
These policies often take years to complete, but once completed, they add extra productive potential to the economy (eg building new roads, airports, hospitals, schools)
Supply side policies require government spending on an annual basis, which is a component of AD therefore helps boost the national output that year, boosting AD in the short term
Argued that the best government spending is that which boosts AD short term but increases LRAS in the long term
What are the supply side effects of fiscal policies?
Many fiscal policies have the ability to improve the productive potential (supply side) of an economy
Eg. education subsidies help the poorest households constitute an annual expenditure for the government. In the long term they will help improve human capital which boosts productivity and output
The fiscal policy is short term (annually) however the supply side impact occurs in the long term
Do the advantages of supply side policies outweigh the negatives?
Yes by a lot
What are general advantages to supply side policies?
Enhanced economic growth - due to the increase in the productive capacity of the economy (use SK or China example)
Reduction in inflationary pressure - increasing AS can help reduce cost push inflation as greater efficiency and productivity reduces production costs (eg. 2017 US tax reforms reduced corporate tax rates leading to higher investments in capital, potentially lowering inflation pressures by boosting supply)
Creation of employment - reduces structural unemployment by making the labour market more flexible and responsive to economic changes + creating jobs (use SK example)
Improvement in trade balance - making domestic industries more competitive internationally through lower costs and increased productivity (eg. SK’s focus on technological innovation and productivity strengthened its export sector, making it maintain a trade surplus)
Positive impact on government budget - long run can increase tax revenues due to higher economic growth and lower spending on welfare benefits as employment rises (eg. Scandinavian countries investing in education and social services has seen high returns in the form of robust tax revenues and low welfare dependency)
What are general disadvantages to supply side policies?
Time lags - takes time to show effects especially in infrastructure, education and research and development projects
Uncertain impact on employment - there is no guarantee that employment will rise proportionally. Labour market reforms such as reducing minimum wages may reduce costs for business but can lead to lower income and inequality (eg. China - no set minimum wages, high income inequality)
Potential for increased inequality - can disproportionality benefits the wealthy (eg. China or the 2017 US tax cuts primarily benefits corporations and high income individuals, increasing wealth disparity)
Negative environmental impact - may lead to environmental degradation if businesses prioritise cost cutting over sustainable practices (eg. Indonesia’s deforestation for the palm oil production due to deregulation and lack of environmental oversight)
Impact on government budget - tax cuts or increased spending on infrastructure and education can initially worsen the government budget deficit (eg. 2017 US tax reforms added significantly to the national debt with projections showing an increase in the budget deficit over the subsequent years)
Effectiveness in reducing inflationary pressure is limited - may not be effective in addressing demand pull inflation which is driven by AD rather than supply constraints (eg. 2022 global inflation spikes due to supply chain disruptions and energy price increases showed the limitations of supply side policies when tackling demand driven inflation)
What are the advantages of market based supply side policies?
Improved resource allocation
No burden on government budget
What are the disadvantaged of market based supply side policies?
Equity issues
Time lags
Vested interests
Environmental impact
What are the advantages to interventionist supply side policies?
Direct support of sectors for growth
Improvements in standards of living
What are the disadvantages in interventionist supply side policies?
Costs
Time lags