W4: Measurement of Stereopsis and Colour Vision
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Why is it important to measure stereopsis in children?
Assesses overall binocularity
Define:
Stereopsis
Stereoacuity
SO:
Awareness of relative dists of objects from the observer, by means of BV only + based on retinal disparity. Req’s:
Ocular alignment
Good VA
SA:
Ability to detect the smallest diff in depth btwn 2 objects
How is stereopsis interpreted and tested in practice?
Normal threshold: Around 60“, though often better
Poor stereopsis may indicate BV issues:
Strabismus
Amblyopia
Monocular vision loss
Communication tip: Say, “I’m going to do a test to measure your 3-D vision.”
Tip: Hold the test yourself
Give examples of stereopsis tests
Lang stereotest
Randot Stereo Test
Frisby Test
TNO stereo test
What are the features and differences between Lang I and Lang II Stereo Tests?
WD=40cm
Suitable for v young children : 18mo-2 years
Lang I: 3 pics
Star: 600”
Cat: 1200”
Car: 550”
Lang II: 4 pics
Star: 200” (always visible; attracts attention)
Moon: 200”
Truck: 400”
Elephant: 600”

Record stereopsis tests appropriately.
How is the Lang Stereo Test performed, interpreted, and recorded?
Procedure: Ask child what shapes they see
Verbal children: name the shapes
Non-verbal children: use preferential looking
Recording: Note which shapes were seen or not
Example: “Lang 400–600” (Elephant +, Car –)
What is the Randot Stereo Test and how is it set up?
Vectograph comprising of 2 similar patterns polarized at right angles to each other.
Polarising glasses
Ensure glasses are on before patient sees test.
Monocular cues
Animals: 400” to 100”
Circles: 400” to 20”
20” Doesn’t matter as long as they can see 60”
Includes a suppression test

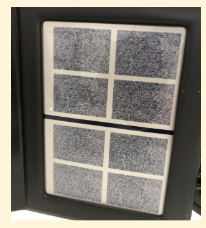
How are the Randot Stereo Test shapes structured and graded?
Top half: Circle, star, letter E → 500”
Bottom half: Square, triangle, cross → 250”
Series of shapes
Other variants of stereopsis tests
Titmus Fly test
Random Dot E test
Butterfly Stereo test

Discuss how to use measures of stereoacuity commonly found in practice.
How should results be recorded for a stereoacuity test?
Record smallest disparity seen + element used
Example: “Titmus fly, 200”, “cartoon”
If pt sees the lowest acuity, record as “≤” as pt may be able to see better
Example: “Titmus fly, ≤ 40” (graded circles)
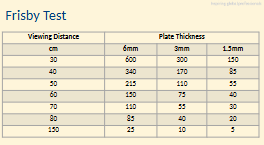
What is the Frisby Stereo Test and what is its main advantage?
Measures real depth
No goggles req’d
Plates: 6/3/1 mm thickness
Discuss how to use measures of stereoacuity commonly found in practice.
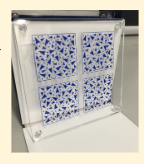
How is the Frisby Stereo Test performed and how are results recorded?
Circle-shaped contour printed on one side of Perspex; pt identifies which of four targets shows depth
Correct answer: flat button, others are round
Recording:
Note stereoacuity found, e.g., “Frisby, 30”
If all responses correct at one distance, use “≤”, e.g., “Frisby, ≤ 85” (for 40 cm)
Discuss how to use measures of stereoacuity commonly found in practice.
What is the TNO Stereo Test and how is it set up?
Random-dot stereopsis test
First 4 plates screen, last 3 measure stereoacuity
Uses R+G goggles
WD: 40 cm
How are the TNO Test plates I–IV performed?
Plate I: Two butterflies
One always visible, the other only if stereopsis present
Ask: “How many butterflies can you see?”
Plate II: 4 discs, two always visible
Ask: “Which is biggest?” or “How many are there?”
Plate III: Pt matches shapes; practitioner must remember shape locations
Plate IV: Suppression test
Ask: “How many circles can you see?”
3 = no suppression, 2 = suppression
Plate V-VII: 480-15’
2 discs for each disparity “where is the piece of cake/pizza missing?”
Give pt time- can take a while to see whole image

Record stereopsis tests appropriately.
How are TNO Stereo Test results recorded?
If Plates I-III seen and Plates V-VII not
Record “TNO test, Gross Stereopsis, Plates I-III seen”
If suppression present record which eye.
Record Stereoacuity for Plates V-VII
“TNO test, ≤ 30”
Discuss recent developments in stereopsis assessment
How is recent technology used to assess and manage stereoacuity?
Computer game tests are now being employed as measure of stereoacuity (Portela- Camino et al., 2021).
Allows for more intervals to be measured.
Potential for better management of Amblyopia

Discuss the educational and occupational factors affecting colour vision
Why is it important to test colour vision in children?
Can have effects on education/future occupations
If father has it may affect female child-could be a carrier
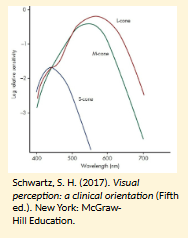
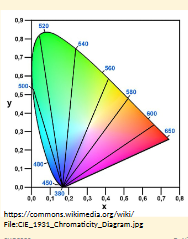
How do we see colours?
Trichromacy
3 diff photopigments w/ overlapping absorption spectra
L cones
M cones
S cones
CIE 1931 Chromaticity Diagram
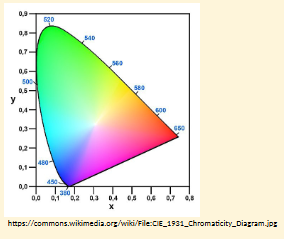
Discuss how different colour vision conditions can affect the patient.
What colour confusions occur in Protanopia?
Black with many shades of red
Dark brown with dark green, dark orange and dark red
Some blues with some reds, purples and dark pinks
Mid-greens with some orange
R-G related
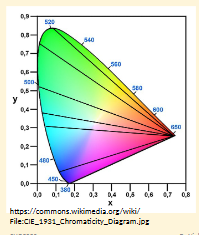
Discuss how different colour vision conditions can affect the patient.
What colour confusions occur in Deuteranopia?
Mid-reds with mid-greens
Blue-greens with grey and mid-pinks
Bright greens with yellows
Pale pinks with light grey
Mid-reds with mid-brown
Light blues with lilac
Won’t mix up blue + red if deuteranomalous but will if protanomalous
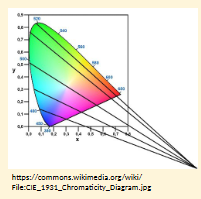
Discuss how different colour vision conditions can affect the patient.
What colour confusions occur in Tritanopia?
Light blues with greys
Dark purples with black
Mid-greens with blues
Oranges with reds.
Affects Blues/yellows-orientation flipped
What do CV tests like Ishihara primarily take into account?
Based on which lines will be mixed up when looking at Ishihara for congenital defects
Primarily takes into account lines of confusion of protanopia + deuteranopia
Not good for tritanopes because it doesn’t take into account lines of confusion
But City CV test will
How do Ishihara and City CV tests differ in detail and application?
City CV test doesn’t go into as much detail as Ishihara for lines of confusion for deuteranopia + protanopia
Can tell a moderate defect well but milder defects it isn’t as good at
If congenital → HAS to be Ishihara
Acquired → Ishihara is NO good because it doesn’t test for tritanopia
Use Farnsworth or City CV for acquired defects
Discuss the tests used to assess colour vision and determine which are appropriate for paediatric testing.
Give examples of colour vision tests
Ishihara
City Colour Vision Test
Farnsworth D-15
Farnsworth-Munsell 100 hue test
What are the key clinical indicators of retrobulbar neuritis, and which colour vision test is useful?
Good for detecting when there is a swollen optic disc that can’t be seen on fundoscopy
Based on case history findings
Hurts more when moving eyes as ON affected
Will present with a blue–yellow (tritan) CV deficiency
City Colour Vision Test =useful
How do congenital and acquired colour vision defects differ in testing approach?
C:
Can screen using BE.
Ishihara Test
A:
One eye at a time.
City Colour Vision Test
D-15 Farnsworth
What are the key features and uses of the Ishihara Test (1907)?
Series of pseudoisochromatic plates
Good for assessing congenital R-G defects
Not so good for acquired defects.
Doesn’t test for Tritanopia
Suitable for children.
What illumination conditions are required for the Ishihara Test?
Colour temp needs to be similar to natural daylight conditions
High Colour rendering fluorescent lighting (>5000 K)
Pt observes test through Kodak Wratten #78AA filter with 100-W incandescent light source
How is the Ishihara Test performed?
Viewing dist=75 cm.
Better for practitioner to hold.
Present each plate for 3s
Recommended but doesn’t appear to make a difference (Long et al., 1985).
Ask pt to read the numbers.
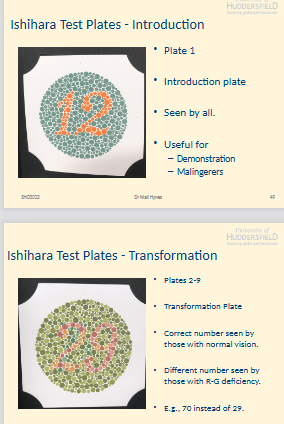
What are the different Ishihara plate types and their purposes (Plates 1–9)?
Plate 1: Introduction plate - seen by all, useful for :
demonstration
malingerers
Plates 2–9: Transformation plates
Normal vision: correct no seen
R–G deficiency: Diff no seen (e.g., 70 instead of 29)
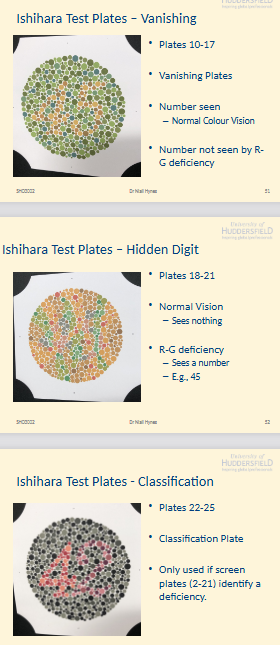
What are the different Ishihara plate types and their purposes (Plates 10–25)?
Plates 10–17: Vanishing plates
Seen by normal vision, not seen by R–G deficiency
Plates 18–21: Hidden digit plates
Normal vision: sees nothing
R–G deficiency: sees a no (e.g., 45)
Plates 22–25: Classification plates
Used only if screening plates (2–21) indicate a CV deficiency
What are tracing plates in the Ishihara Test and who are they used for?
Found toward the end of the test
Designed for pts not no literate
Protans: See numbers on the right (e.g., 2)
Deutans: See numbers on the left (e.g., 4)
Those w/ severe R-G defects (esp protanopia) may not see either

Record stereopsis tests appropriately.
How are Ishihara Test results interpreted and recorded?
If 3+ plates wrong, proceed to classification plates
Recording e.g:
“Ishihara, all plates seen – normal colour vision.”
Ishihara, 3/16 seen, protan – pt + parent counselled regarding future career restrictions.
What are the key features and purpose of the Farnsworth D-15 test (1947)?
15 small isochromatic discs, each of a different hue
Detects moderate to severe CV deficiencies
Not a screening test
ppl w/ normal or mild CV defs will pass

Farnsworth D-15
Normal or Near Normal
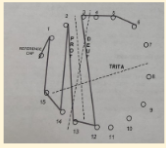
Farnsworth D-15
Strong Protan
Protan+deutan close tog as they share similar lines of confusion .Tritans on diff orientation.
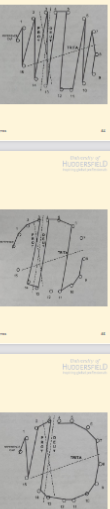
SEE PIC
Farnsworth D-15
Strong deutan
Medium deutan
Near normal or mild deutan
Mix up first few then get along fine for rest of test
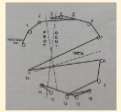
Farnsworth D-15
Tritan
What are the features and clinical considerations of the Farnsworth-Munsell 100 Hue test?
More sensitive than the D-15.
Req’s more time (about 15 min) + concentration.
Not suitable for children.
May be suitable for teenager
What are the key features and uses of the City Colour Vision Test?
Orig derived from D-15 test.
Good to use if suspecting acquired defect.
Not as sensitive to mild R-G defects as Ishihara
Not a screening test
How should patients and parents be counselled regarding congenital colour deficiency?
Explain genetics of a congenital colour deficiency to parent
No cure for congenital colour deficiency
What advice should be given to schools and parents for children with colour vision defects?
Need to advise teachers + parents.
May confuse colour coded schoolwork.
Coloured writing may be more diffic to see
Partic on a colour background.
Crayons / Colour pencils should be marked.
May need help w/ assignments
E.g., Colour coding a pie chart etc.
Discuss the educational and occupational factors affecting colour vision
How does colour vision testing vary for different occupations?
British Army
Req’s Ishihara Pass for Army Air Corps
Royal Navy
Pt’s w/ impaired colour perception may be restricted the branches that are available to them.
Royal Air Force
Can still join but colour deficiencies will limit roles.
Discuss the educational and occupational factors affecting colour vision
What are the colour vision requirements for the fire service?
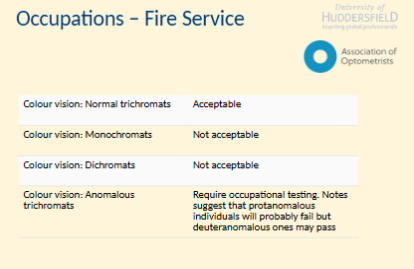
Discuss the educational and occupational factors affecting colour vision
What are the colour vision requirements for lifeboat crew members?
Tested using Ishihara.
3+ plates failed = Fail
Discuss the educational and occupational factors affecting colour vision
What are the colour vision requirements for police officers?
Monochromats: not acceptable
Mild anomalous trichromats: acceptable
Severe anomalous trichromats + dichromats: acceptable but must be trained in coping strategies
Discuss the educational and occupational factors affecting colour vision
What are the colour vision requirements for electrical engineers?
Normal CV req’d due to extensive colour coding in electronics + safety implications
No more than 2 failed Ishihara plates
Lantern test may be req’d for some roles
Discuss the educational and occupational factors affecting colour vision
What are the colour vision requirements for civilian pilots?
Must pass first 15 Ishihara plates w/o error
If Ishihara failed, further testing req’d:
Anomaloscopy (Nagel or equiv)
Colour Assessment + Diagnosis Test