HISTECH LAB INTRO
Histology
science concerned with the microscopic
aka microanatomy
Pathology
study of disease
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Histology
science concerned with the microscopic
aka microanatomy
Pathology
study of disease
Pathologist
a physician highly skilled in the identification and diagnosis of both normal and diseased tissues
Anatomic pathology
microscopic analysis of tissue changes
Clinical pathology
hema, microbio, immuno, cc, bb, lab data management
Histopathology
branch of pathology which concerns with the demo of minute structural alterations in tissues as a result of disease
Permanent sections
most convenient way to study morbid tissues
Tertiary hospital
What hospital level has a histopathology section?
Large, variably shaped nuclei
many dividing cells
disorganized arrangement
variation in size and shape
loss of normal features.
5 features of cancerous cells
Specimen accessioning
Gross examination
Tissue fixation
Tissue processing
Tissue embedding
Tissue sectioning
Slide staining
Histology procedure (7)
Dehydration
Clearing
Impregnation
3 parts of tissue processing (DCI)
Histopathology remains a neglected branch of medical
technology in the Philippines
Majority of hospital laboratories do not have basic equipment
(such as pH meter)
Most laboratories are neglected with old, obsolete, defective,
and missing apparatuses.
Inadequately - trained medical technicians and non -
paramedical personnel
Production of low quality slides given to the pathologists
5 Challenges of Histopathology in the
Philippine Setting
True
T/F
Xylene, alcohol, and formalin may be reused by investing in distillation and filtration systems
Identification of the specimen and all of its components
First step in specimen processing in histopath
Gross examination
How do pathologists examine tissue?
A process by which pathology specimens are inspected with the bare eye to obtain diagnostic information, while being processed for further microscopic examination
The specimen consists of
TSCO means:
Category A specimen
Endometrium
Breast core biopsies
Colonic series
Category B specimen
Small lipoma
Small skin biopsy
Cervical LLETZ
Category C specimen
Prepuce
Haemorrhoids
Gallbladder
Appendix
Category D specimen
Pigmented skin lesions
Large intestine (Crohn's)
Skin with markers
Salivary gland tumor
Category E specimen
Thryoid (medullary Ca)
Breast cancer
Testis (seminoma)
Uterus (endometrium Ca)
Block 3 in 1
3 types of tissues, 1 casette
Identify all hazards in and emanating from the laboratory
First step in risk management
Standard operating procedure
Control of hazardous substances
Risk assessments
Health and safety information
Microscope
Microtome
Cryostat
Autotechnicon
Automated coverslipper
Automated H&E stainer
Instrumentation in histopathology (MMCAAA)
1. Name, Manufacturer, Model Number and Serial Number
2. Record of preventive maintenance performed, as prescribed by the manufacturer
3. Record of service calls and repairs performed
4. Copy of operating manual
It is imperative that the laboratory maintain a current file for every piece of equipment in the laboratory.
This file should contain the following information: (4) (NRRC)
Read the manual that accompanies the equipment
What is the 1st and most important step in the operation of equipment?
Manual
-provides information to the machines operation
Presentation of checklist
What is the recommended step for every new employee?
Checklist
provides a step-by-step approach to the machine's operation
Small spill
defined as a spill that can be sagely handled by immediate staff
Simply wipe off with towel or sponge while protecting hands with suitable gloves.
How to handle small spills? (only a few grams or mL)
Area must be sealed off and an emergency team must be called.
How to handle large spills?
Ingestion
Eyecontact
Extensive skin contact
Splashing of dangerous chemicals into the eyes
Most common accidents requiring first aid (4)
15-30 minutes
accidental splashing of eyes how many mins to wash
15-30 minutes
accidental skin contact, how many minutes to wash?
Fresh tissue and body fluids
must always be considered potentially infectious
Grossing of specimen
has the highest risk of all histological activities
Fixed specimens
have a much less risk because of nearly all infectious agents are deactivated by histological fixation
Prions
Infectious agents that cause spongiform encephalopathies
Creutzfeld-Jakob disease
Mad cow disease
2 examples of prions
Biohazards
Corrosive chemicals
Sensitizers
Carcinogens
Toxic materials
Health hazards in the histopath section (BCSCT)
Combustibles
Flammables
Explosive chemicals
Oxidizers
Physical hazards in the histopath section (CFEO)
PELs
Permissible Exposure Limits
TLVs
Threshold Limit Values
OELs
Occupational Exposure Limits
Dangerous liquids
stored below countertop height
Dangerous reagents
Stored in plastic or plastic - coated glass bottles
Flammable liquids
• Never store in refrigerator or freezer
• If usage cannot be avoided, small amount must be available and used up asap
• Fine needle aspiration
• Core needle biopsy
• Incisional biopsy
• Excisional biopsy
• Punch biopsy
• Shave biopsy
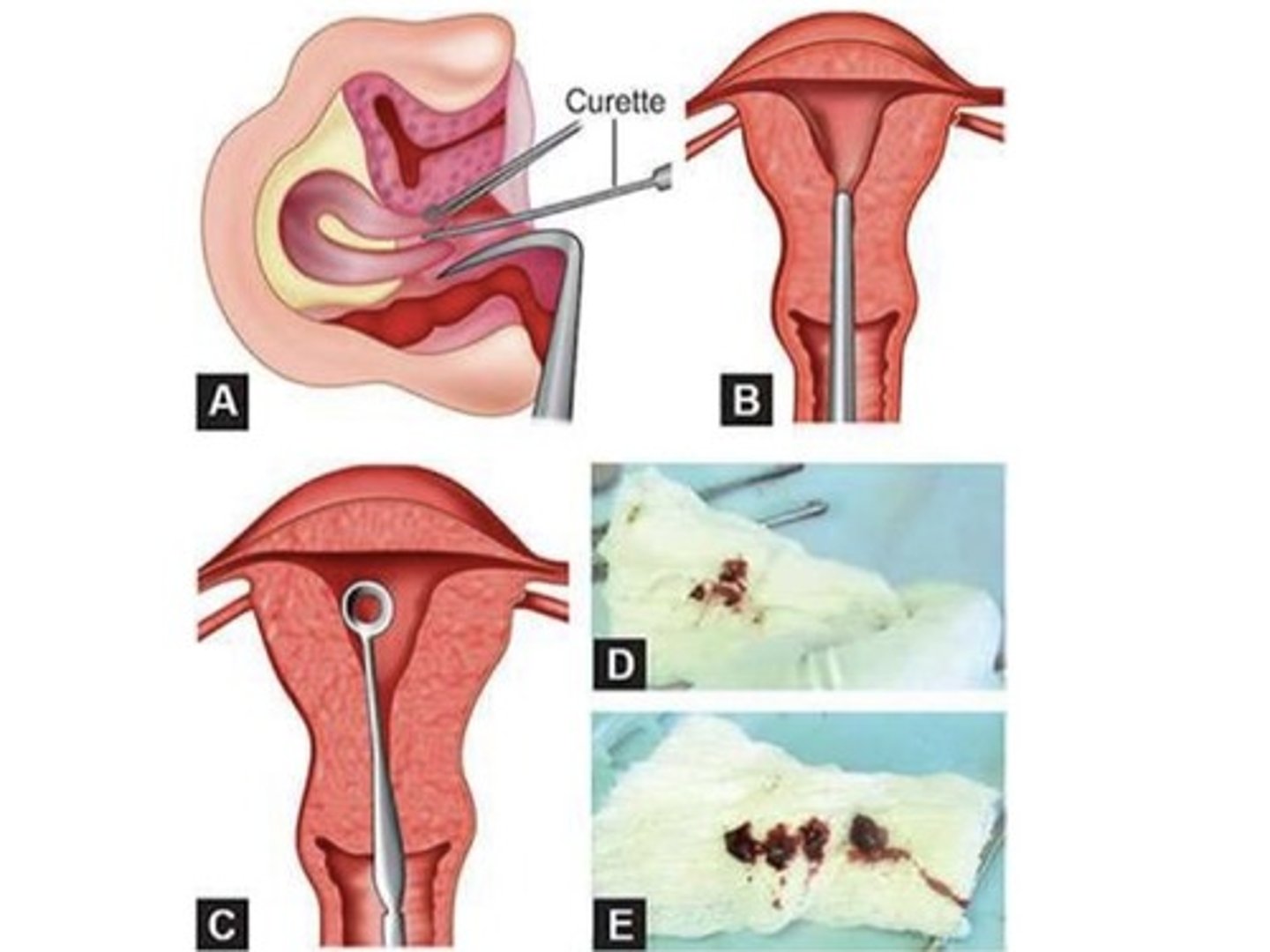
• Curettings
Methods of fresh tissue examination (FCIEPSC)
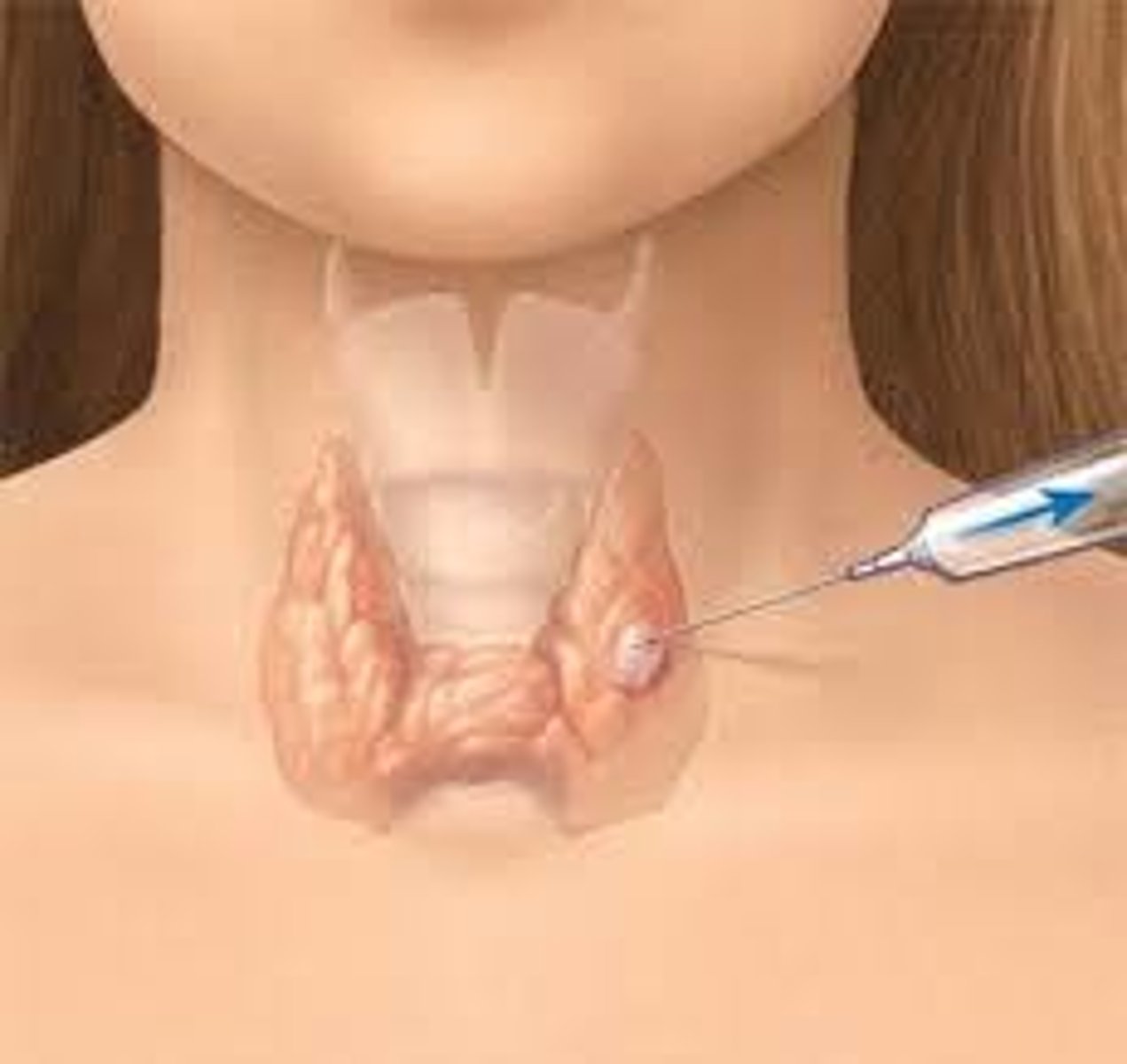
Fine needle aspiration
is the simplest, least invasive test and uses the smallest needle to simply remove cells from the area of abnormality.
This is not always adequate to obtain a diagnosis, depending on the area to be biopsied.
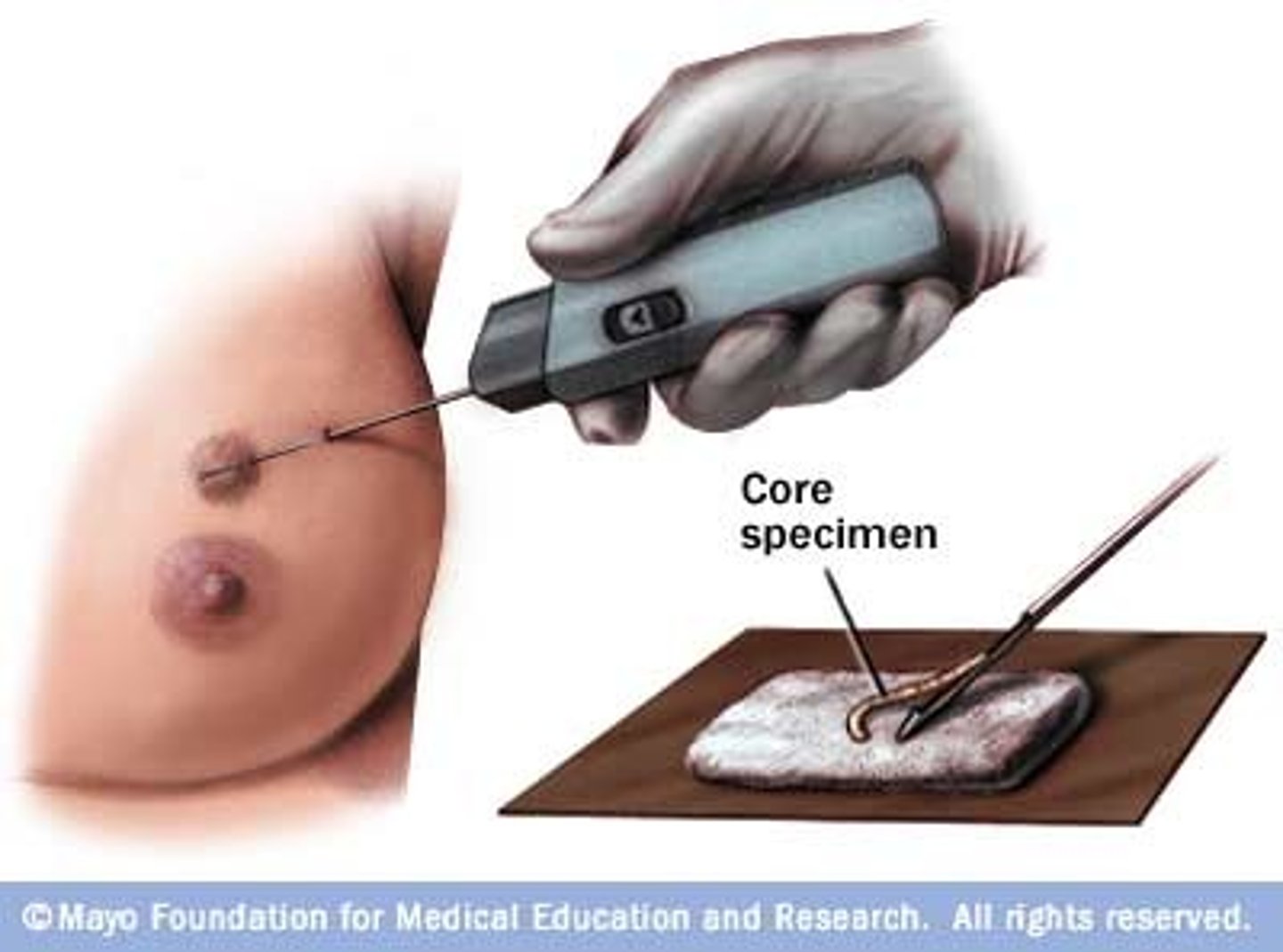
Core needle biopsy
removes not only cells, but also a small amount of the surrounding tissue.
This provides additional information to assist in the examination of the lesion
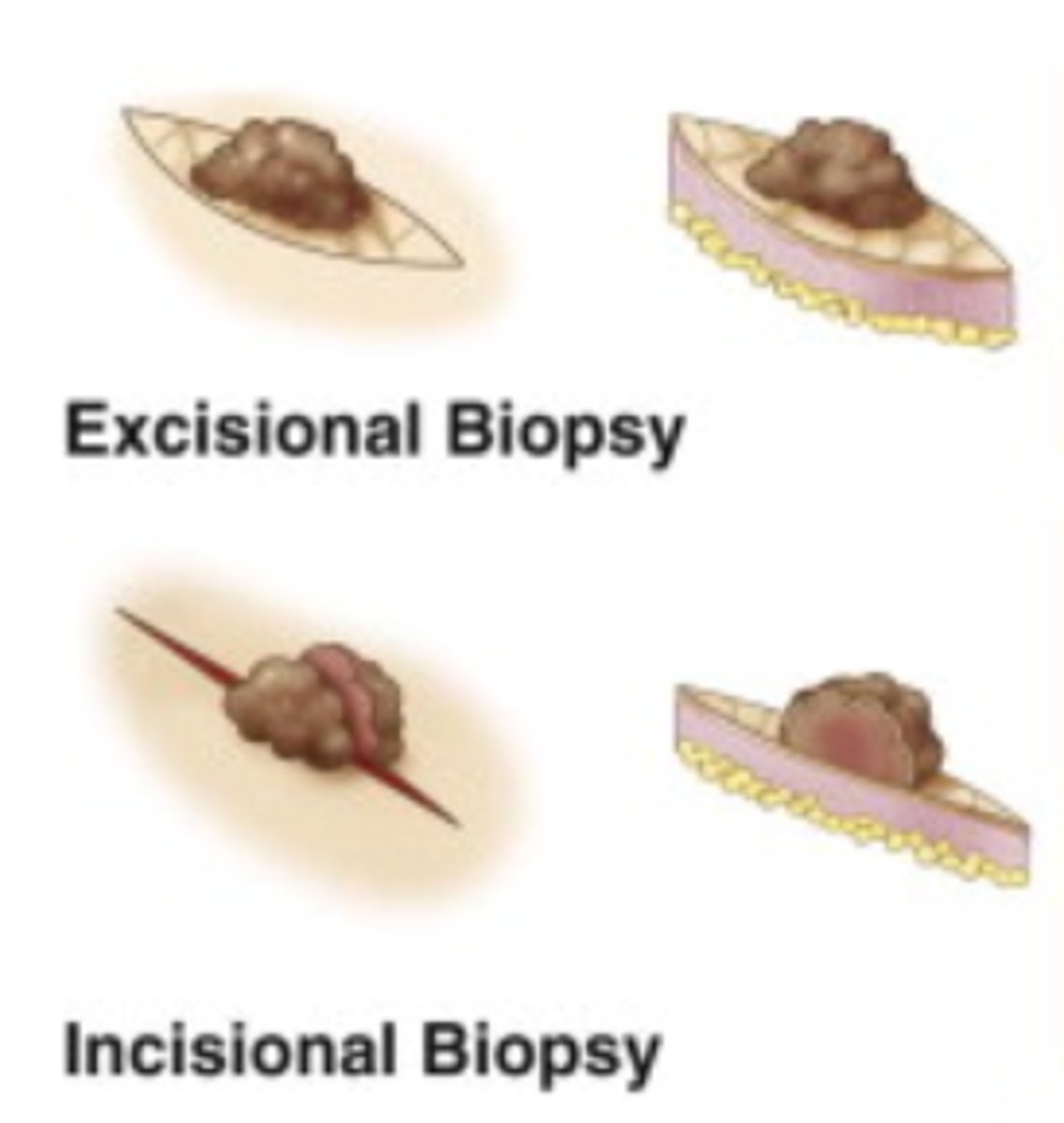
Incisional and excisional biopsy
Incisional biopsy takes out even more surrounding tissue. It takes out some of the abnormality, but not all. The doctor will slice into the lesion and remove only a portion of it. If the lesion is found to be cancerous, further surgery may be needed to remove or excise the entire lesion.
Excisional biopsy generally removes the entire area in question
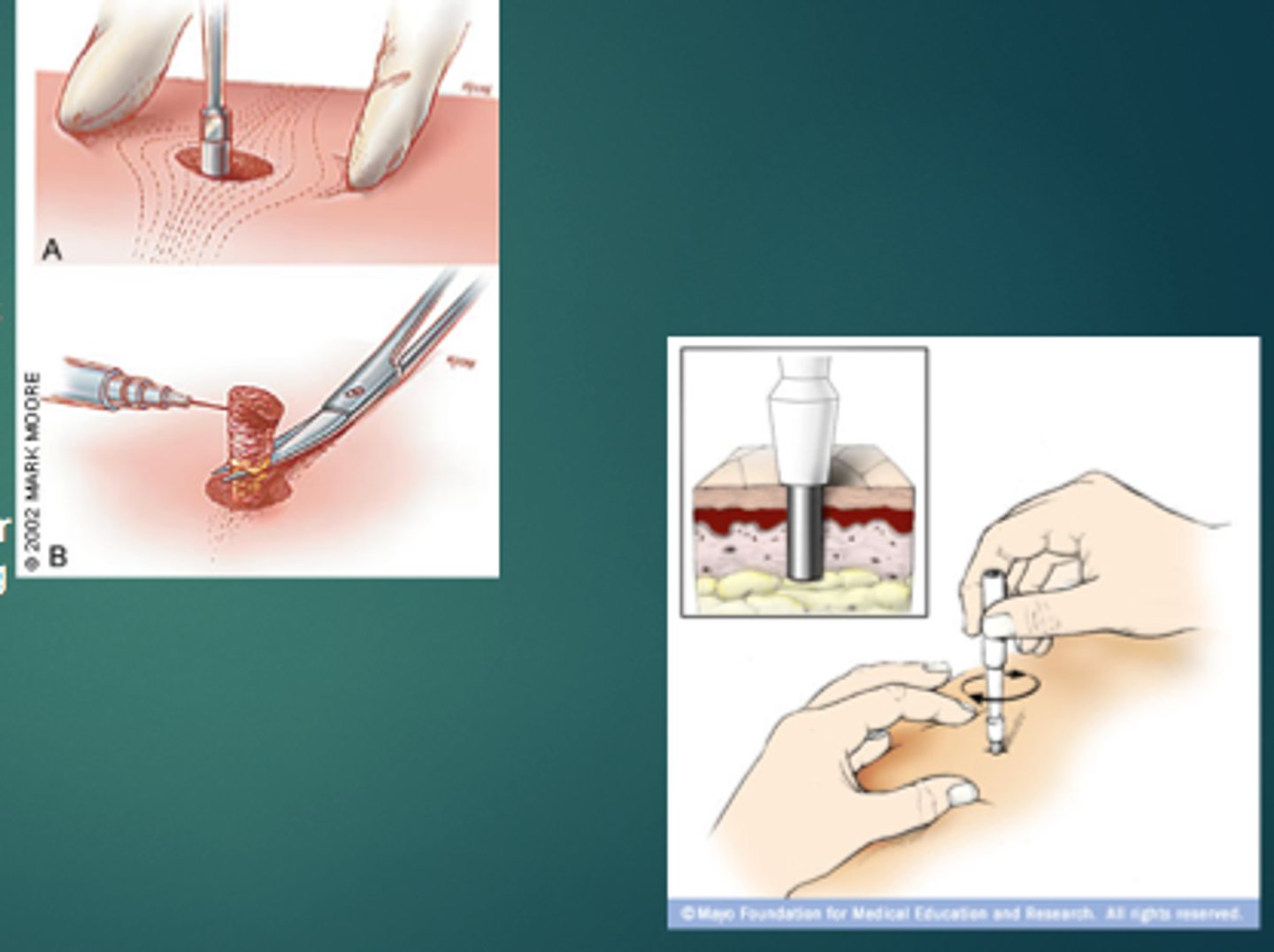
Punch biopsy
is considered the primary technique for obtaining diagnostic full-thickness skin specimens.
It requires basic general surgical and suture-tying skills and is easy to learn.
The technique involves the use of a circular blade that is rotated down through the epidermis and dermis, and into the subcutaneous fat, yielding a 3- to 4- mm cylindrical core of tissue sample.
Shave biopsy
where small fragments of tissue are “shaved” from a surface (usually skin).
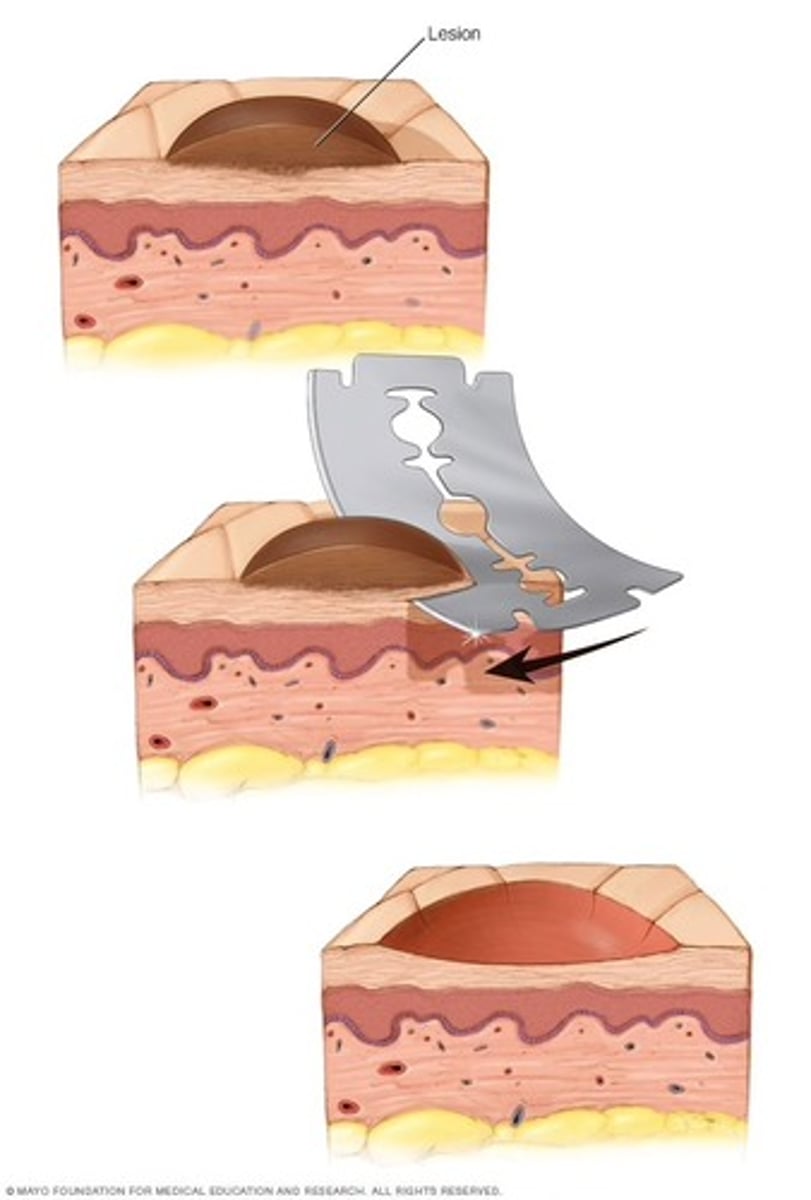
Curettings
where tissue is scooped or spooned to remove tissue or growths from body cavity such as endometrium or cervical canal.
Teasing or dissociation
Immersed in a watch glass containing isotonic salt solution, carefully dissected or separated, and examined under the microscope
Unstained teasing
for phase contrast or bright field microscopy
Stained teasing
differential dyes
Squash preparation
Small pieces of tissue not more than 1mm in diameter are placed in a microscopic slide and forcibly compressed with another slide or with a cover slip
Smear preparation
Process of examination wherein cellular materials are spread lightly over a slide (wire loop, wire applicator, or apposition smear with another slide.)
Useful in cytological examinations particularly for cancer diagnosis
Streaking
With an applicator stick or a platinum loop, the material is rapidly and gently applied in a zigzag line throughout the slide, attempting to obtain a relatively uniform distribution of secretion.
Spreading
• A selected portion of the material is transferred to a clean slide and gently spread into a moderately thick film by teasing the mucous strands apart with an applicator stick.
• Has the advantage of maintaining cellular interrelationships of the material to be examined.
• Recommended for smear preparations of fresh sputum and bronchial aspirates and thick mucoid secretions
Pull-apart
Useful for preparing smears of thick secretions such as serous fluids, concentrated sputum, enzymatic lavage samples from the gastrointestinal tract and blood smears
Impression smear
A special method of smear preparation whereby the surface of a freshly cut piece of a clean slide, allowing the cells to be transferred directly to the slide for examination by Phase Contrast microscopy or stained for light microscopic study
Frozen section
Normally utilized when a rapid diagnosis of the tissue under question is required.
Lipids and nervous tissue elements
When is frozen section recommended?
10-15 micrometer in thickness and -10 degrees C to -20 degrees C
Frozen section are cut into very thin slices around how many micrometers in thickness and what temperature?
Slow freezing
Distortion of tissue due to ice crystal artifacts
Liquid nitrogen
Isopentane cooled by liquid nitrogen
Carbon dioxide gas
Aerosol sprays
Commonly used methods of freezing (LICA)