FPC3: Pathology Week 3
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Soft tissue tumors are derived from _________ prolilferations
Mesenchymal
The major of soft tissue tumors are ______
reactive
low grade chronic irritation
Fibrosarcoma
Malignant tumor of fibroblasts
10-19% occur in H&N--more common extremities
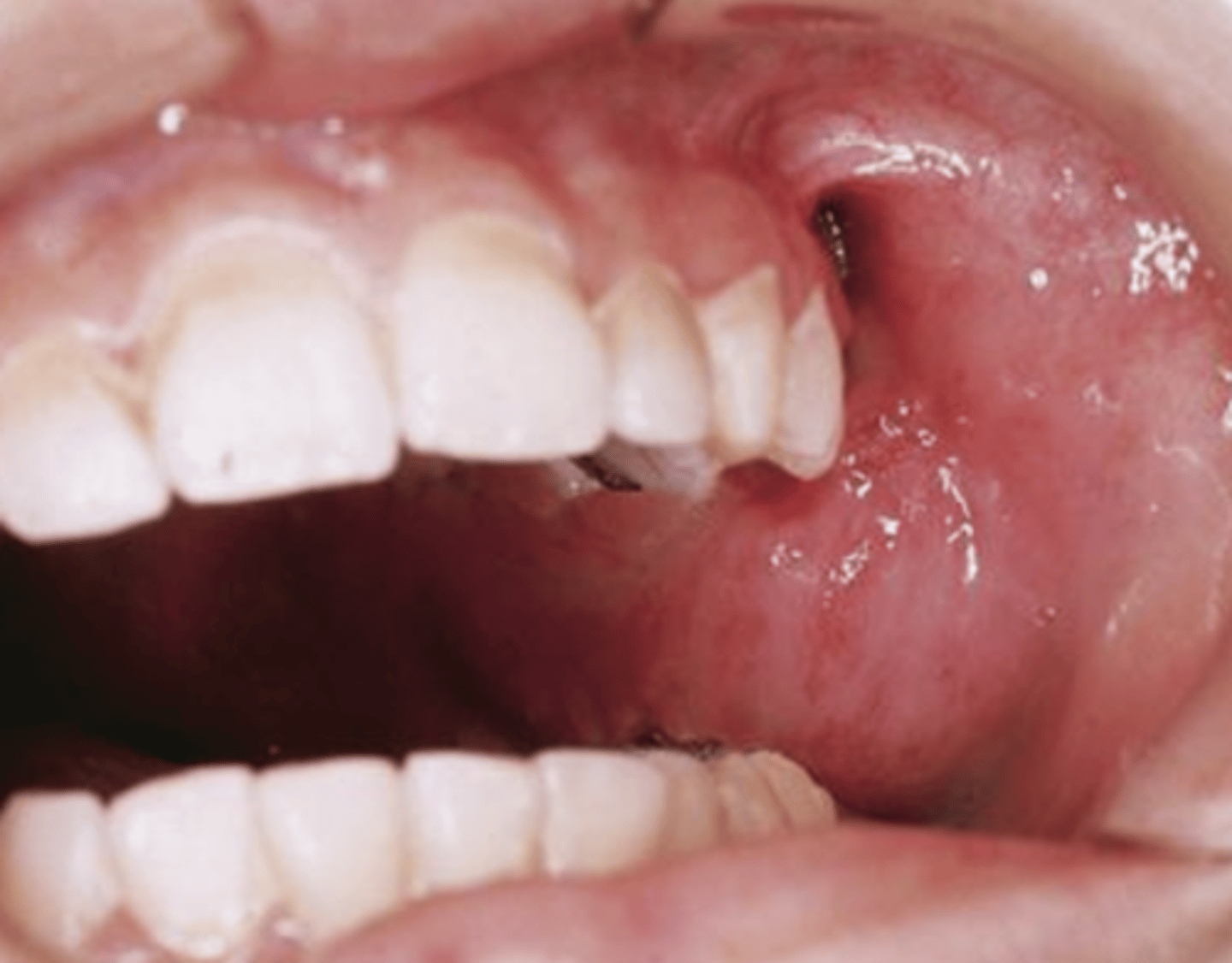
What are the clinical presentations of fibrosarcoma?
Slow growing masses
can present at ANY age
can present ANYWHERE
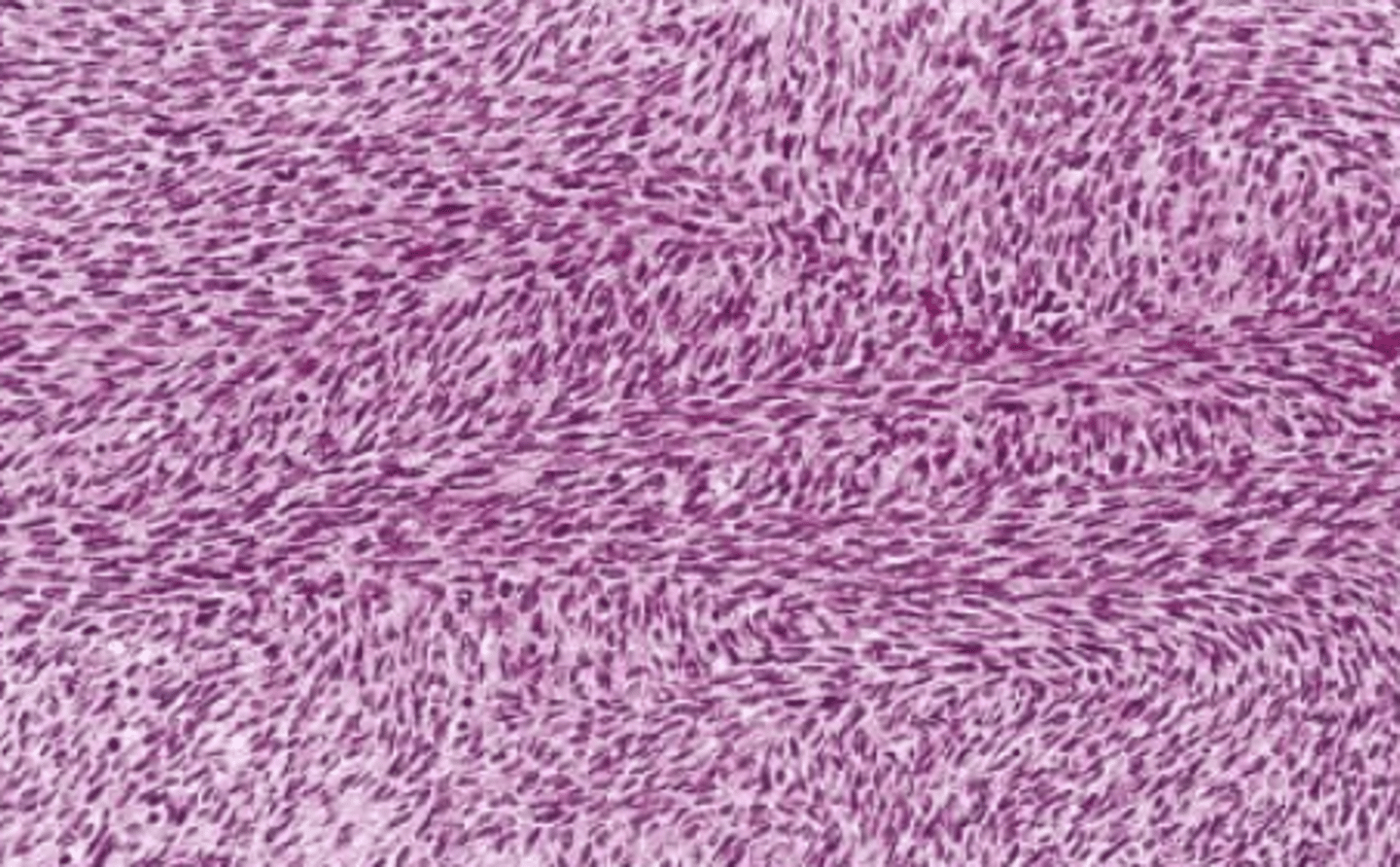
Fibrosarcoma histology
Liposarcoma
Sarcoma of adipocytes
adults ages 40-60
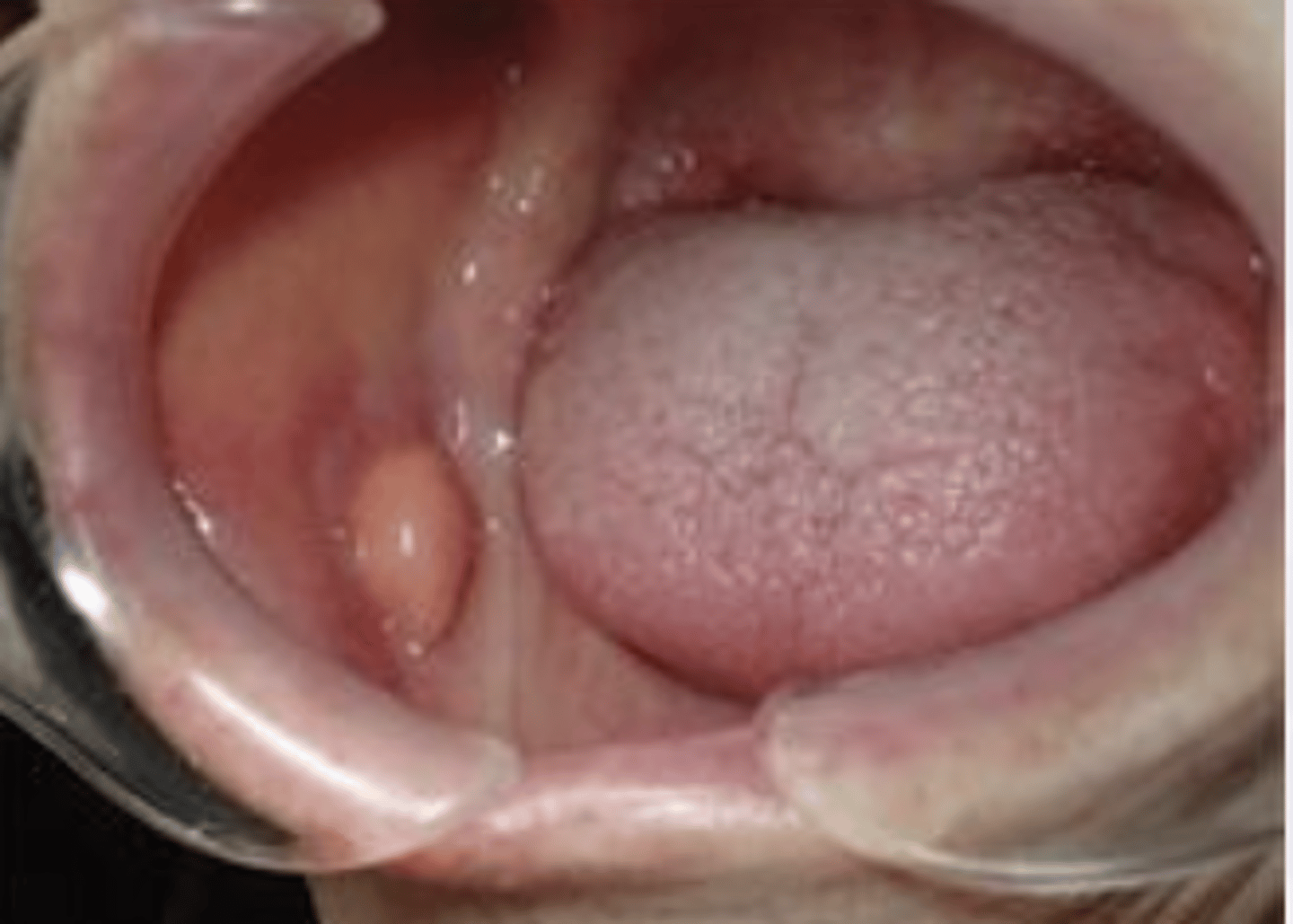
What are the clinical features of liposarcoma?
Slow growing, soft lesion
pain is a late feature
Where are common locations for liposarcoma?
Thigh
Retroperitoneum
inguinal area
H&N is rare---> 3% is neck and cheek
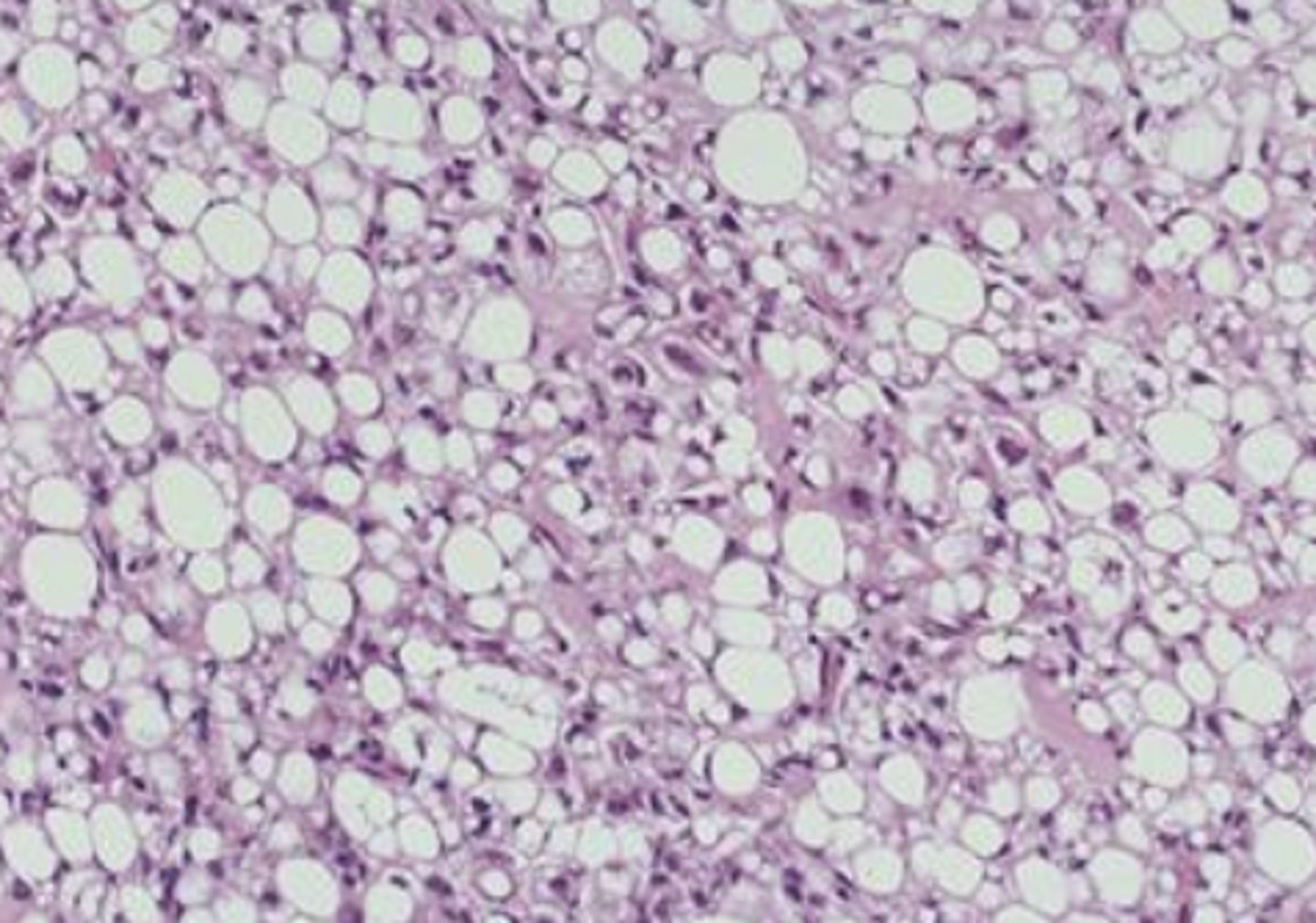
Liposarcoma histology
Struge-Weber Angiomatosis Syndrome
Port wine stain of skin- follows distribution of TRIGEMINAL N.
10% of port wine stains are bilateral
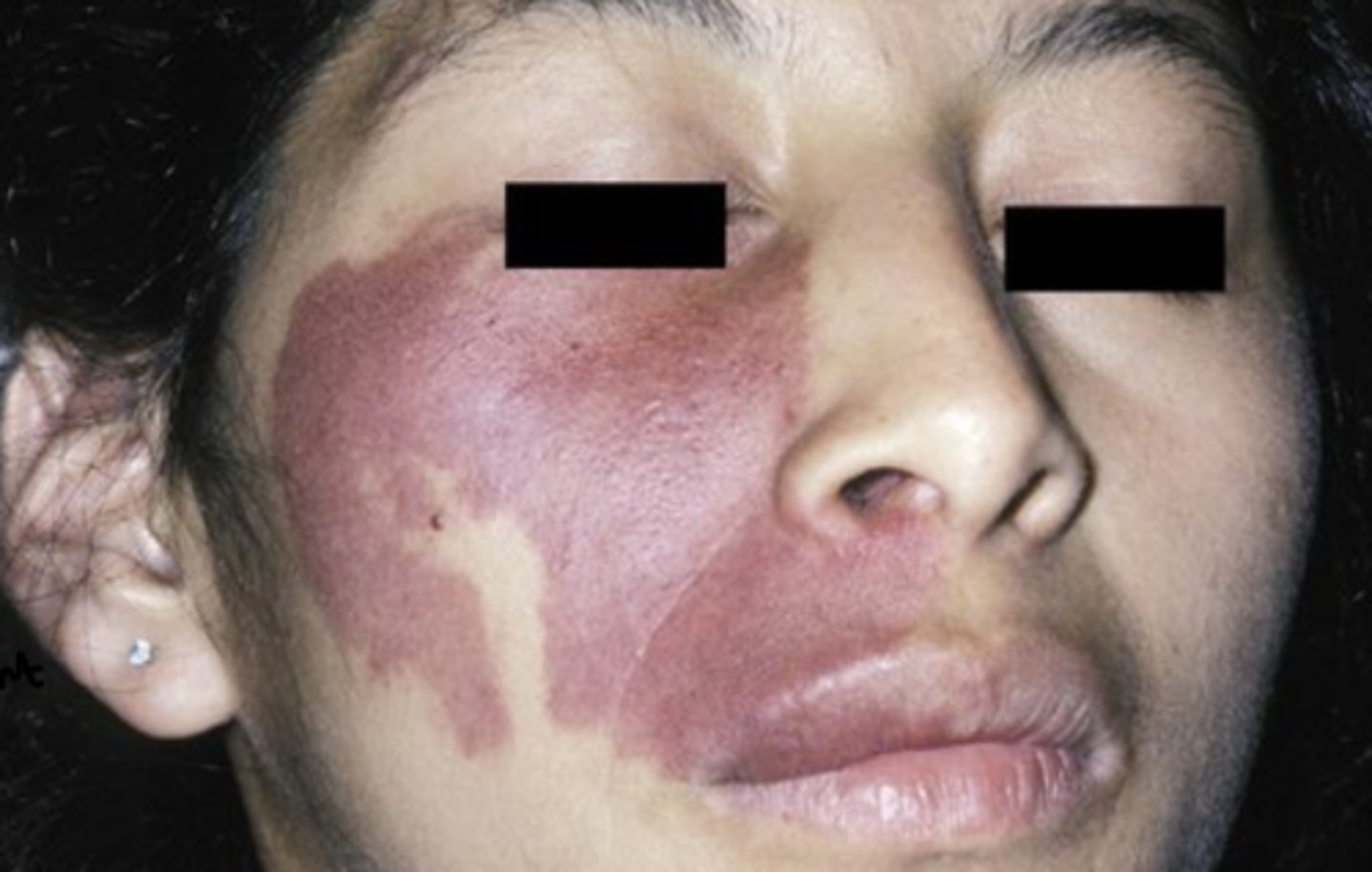
Patients with Sturge-Weber Angiomatosis are more likely to also have these disorders:
Seizure disorders
cognitive disabilities
parallel calcifications in the brain's cortex (Tram-Line)
Intraoral hypervascularization
What is the treatment for Sturge-Weber Angiomatosis?
Depends on severity
lasors
Surgical excision (may need more extensive surgery)
intra-oral lesions surgery
Angiosarcoma
Sarcoma of vascular endothelium
Seen in elderly patients
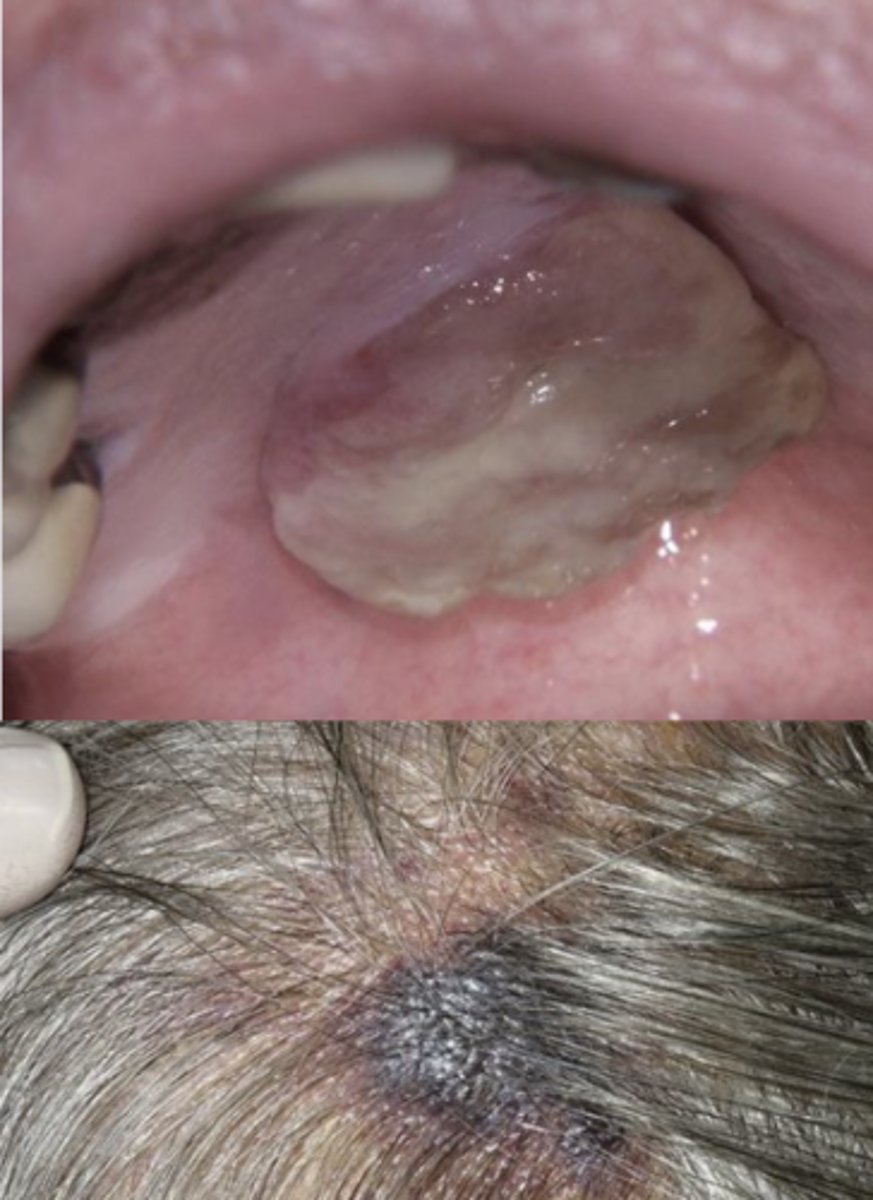
What is a common site for angiosarcoma?
Scalp & forehead
can present orally --rare
What are the clinical features of angiosarcoma?
Early lesions appear as a bruise
Enlarges to create an ulcerated, nodular elevated surface
Angiosarcoma histology
Are there malignant soft tissue pathologies of the lymphatic tissue?
No
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (syndrome)
Most common + presents with oral lesions
Heredity condition
Autosomal dominant
Mapped on Chromosome 17
--NF1 gene
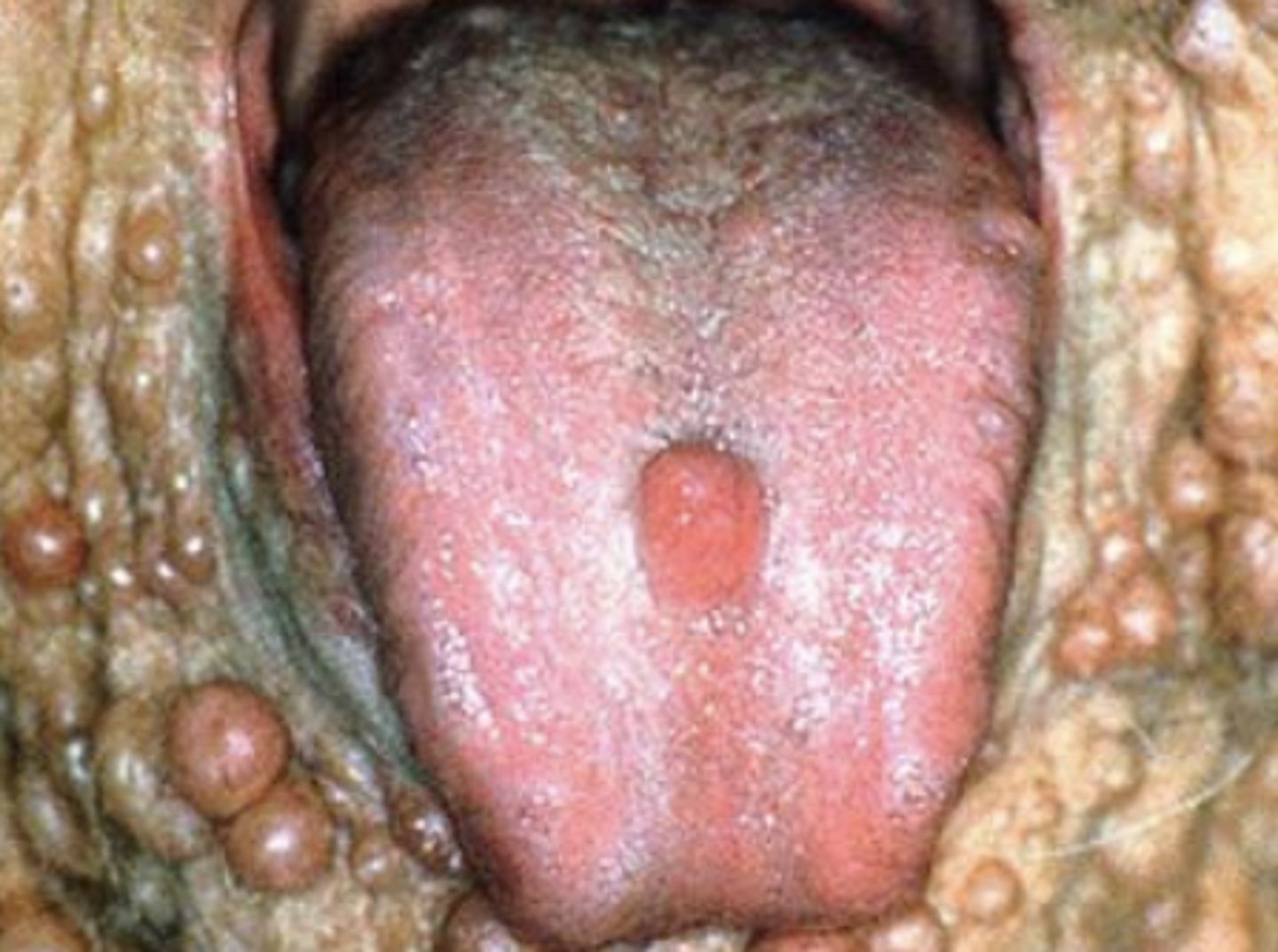
What are the clinical features of neurofibromatosis Type 1?
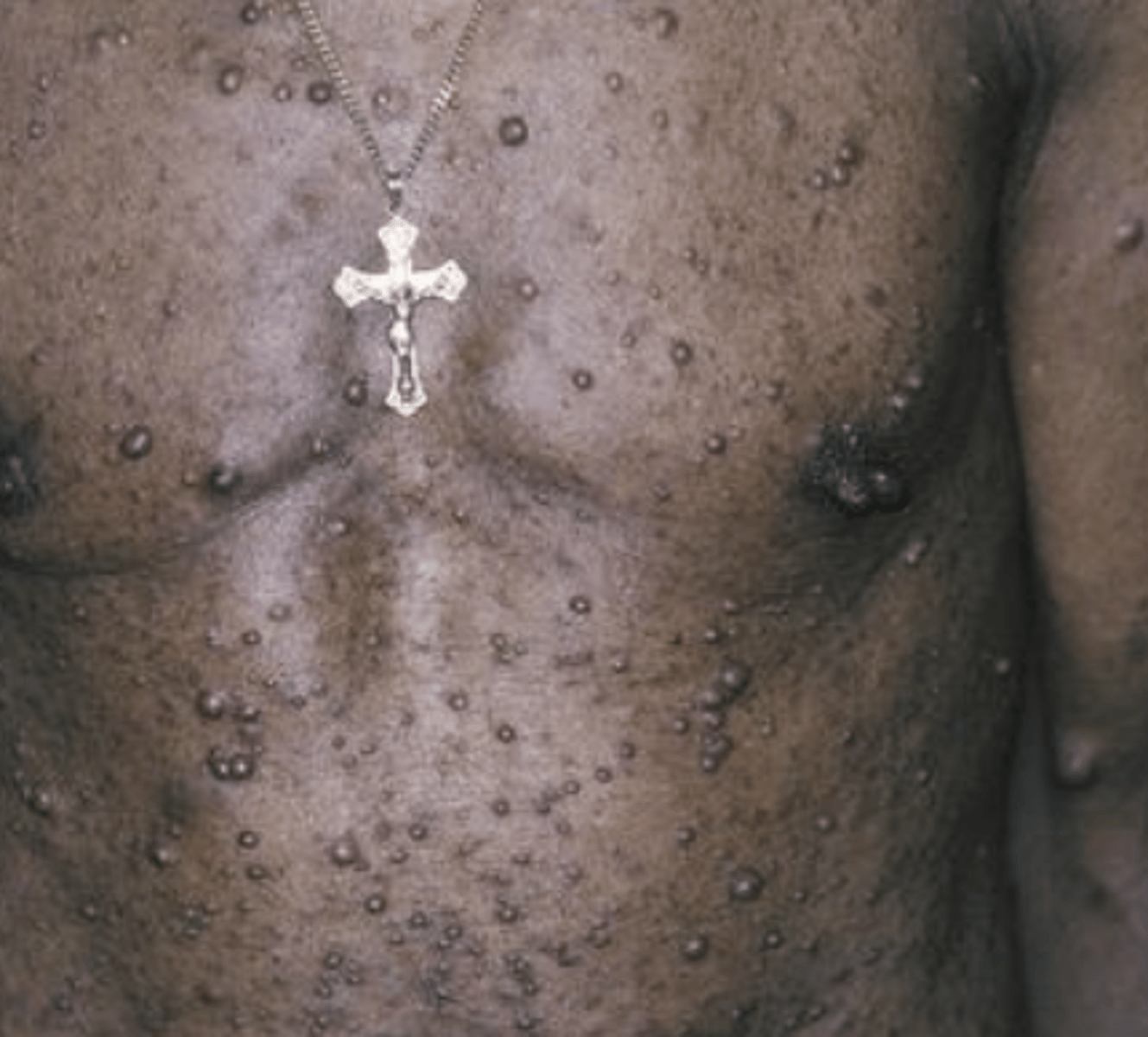
Multiple fibromas on the body
Cafe au lait pigmentation
Axillary freckling
Lisch nodules
Neurofibromas occur at a young age
What is the treatment of neurofibromatosis Type 1?
No specific treatment
Removal of neurofibromas
**Neurofibromas may undergo malignant transformation
Patients with neurofibromatosis Type 1 can undergo malignant transformation into what cancer?
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 patients are more susceptible to what other tumors?
Leukemia
Wilms Tumor
CNS tumors
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 characteristics
Autosomal dominant -NF2 gene
Bilateral Schwannomas (CN VIII)
Café au lait pigmentation (less
common than in NF1)
Cutaneous neurofibromas are
uncommon
MEN type 2B
Genetic mutation -- autosomal dominant
Mucosal neuromas on lip, tongue, BM, gingiva, & palate (can be 1st sign of disease)
Pheochromocytomas
Marfanoid appearance
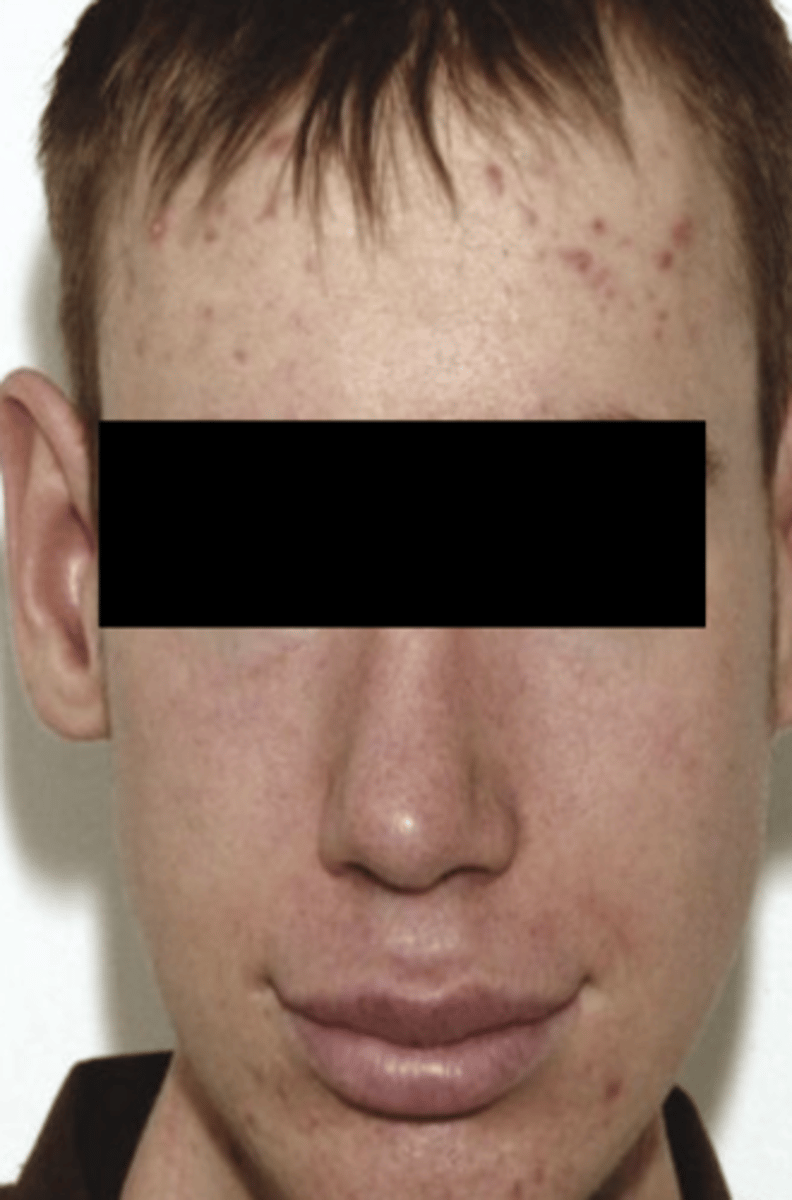
MEN type 2b patients are almost 100% likely to get what type of malignant soft tissue pathology?
Medullary thyroid carcinoma
what is the treatment for MEN type 2B?
Thyroid removal ASAP
Lab values show serum or urinary calcitonin
Pheochromycytomas may result in increased levels of urinary vanillymandellic acid (VMA)
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
Common in people with neurofibromas (50%)
10% of all soft tissue sarcomas
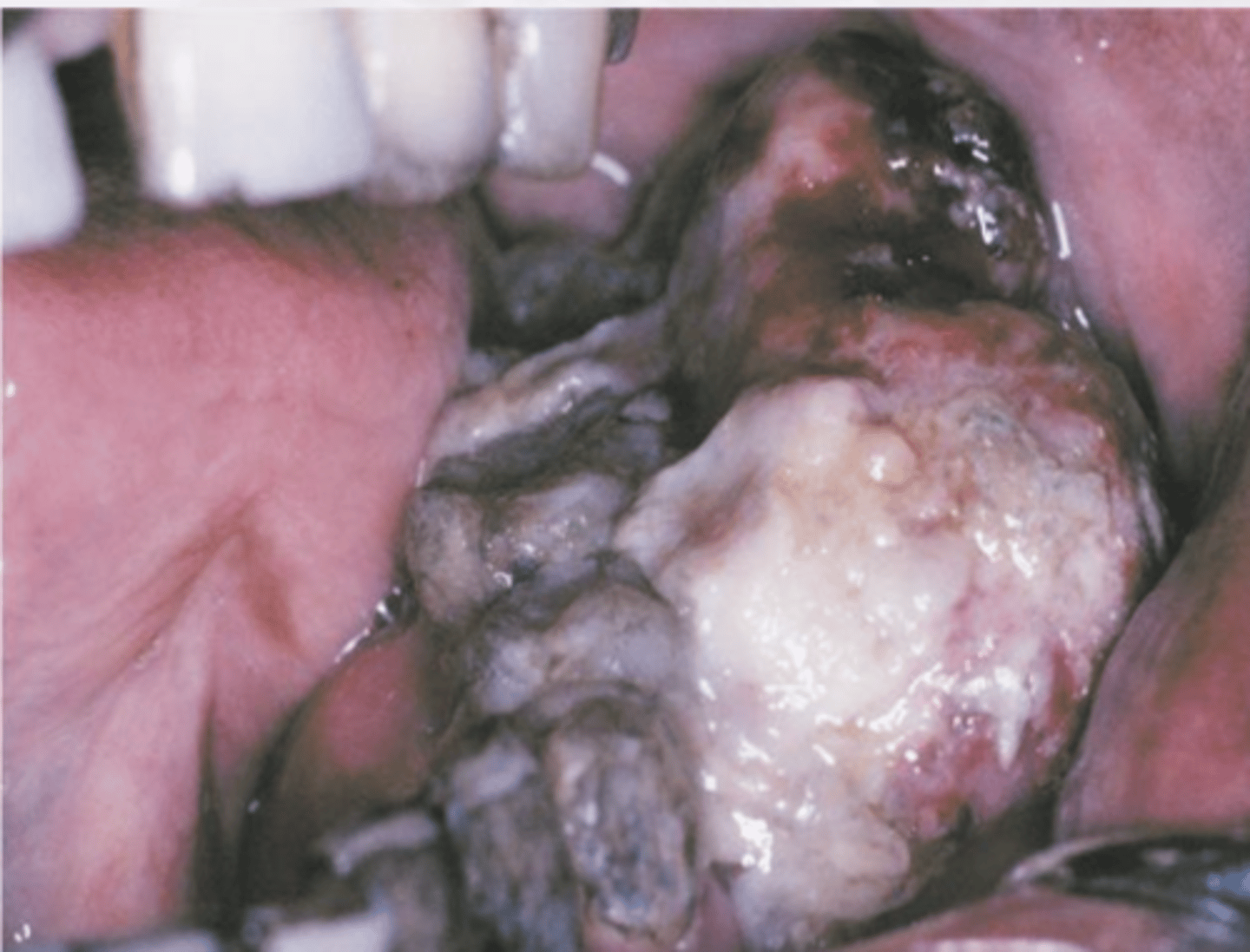
What are the clinical features of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor?
Asymptomatic
Expansile mass
Young patients
radiographs can show widening of mandibular canal or mental foramen
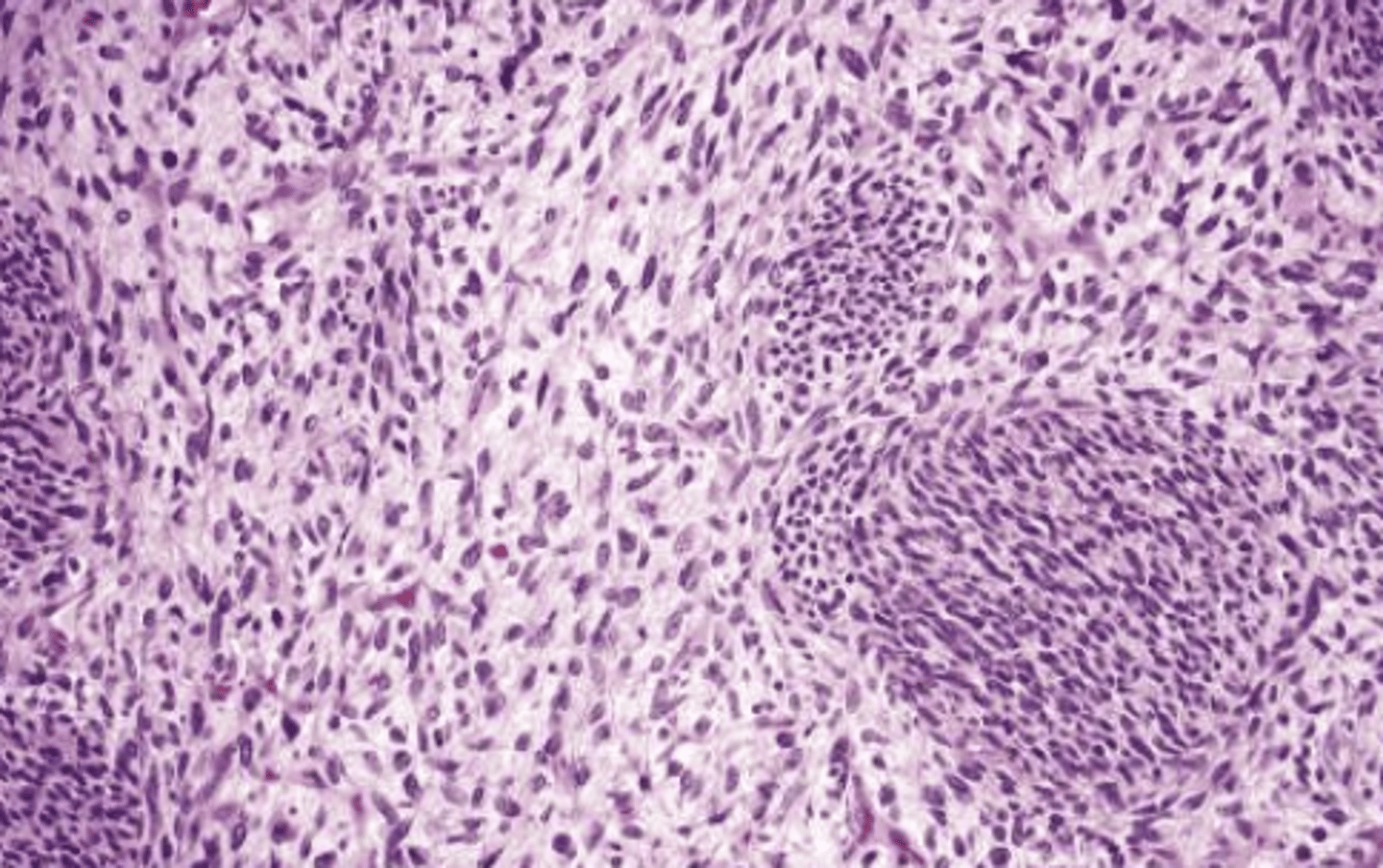
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor histology
What is the most common site for an angiosarcoma?
(video question)
Scalp
rhabdomyosarcoma
Malignant tumor of skeletal muscle
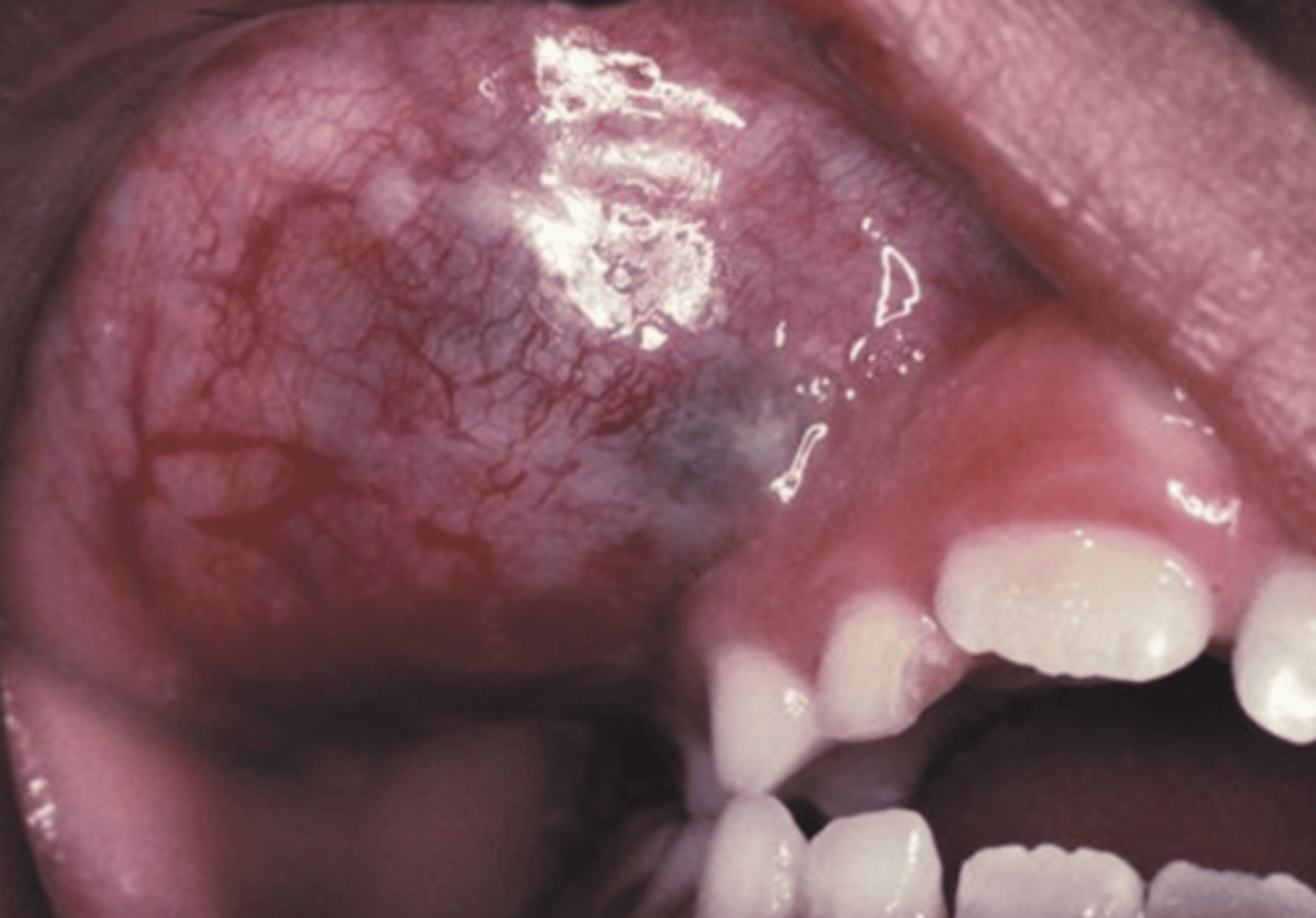
What are the clinical features of rhabdomyosarcoma?
Common in young children (1st decade)
2-5% in adults
Presents as an infiltration mass
What are the common sites for rhabdomyosarcoma?
Eye and nasal cavity
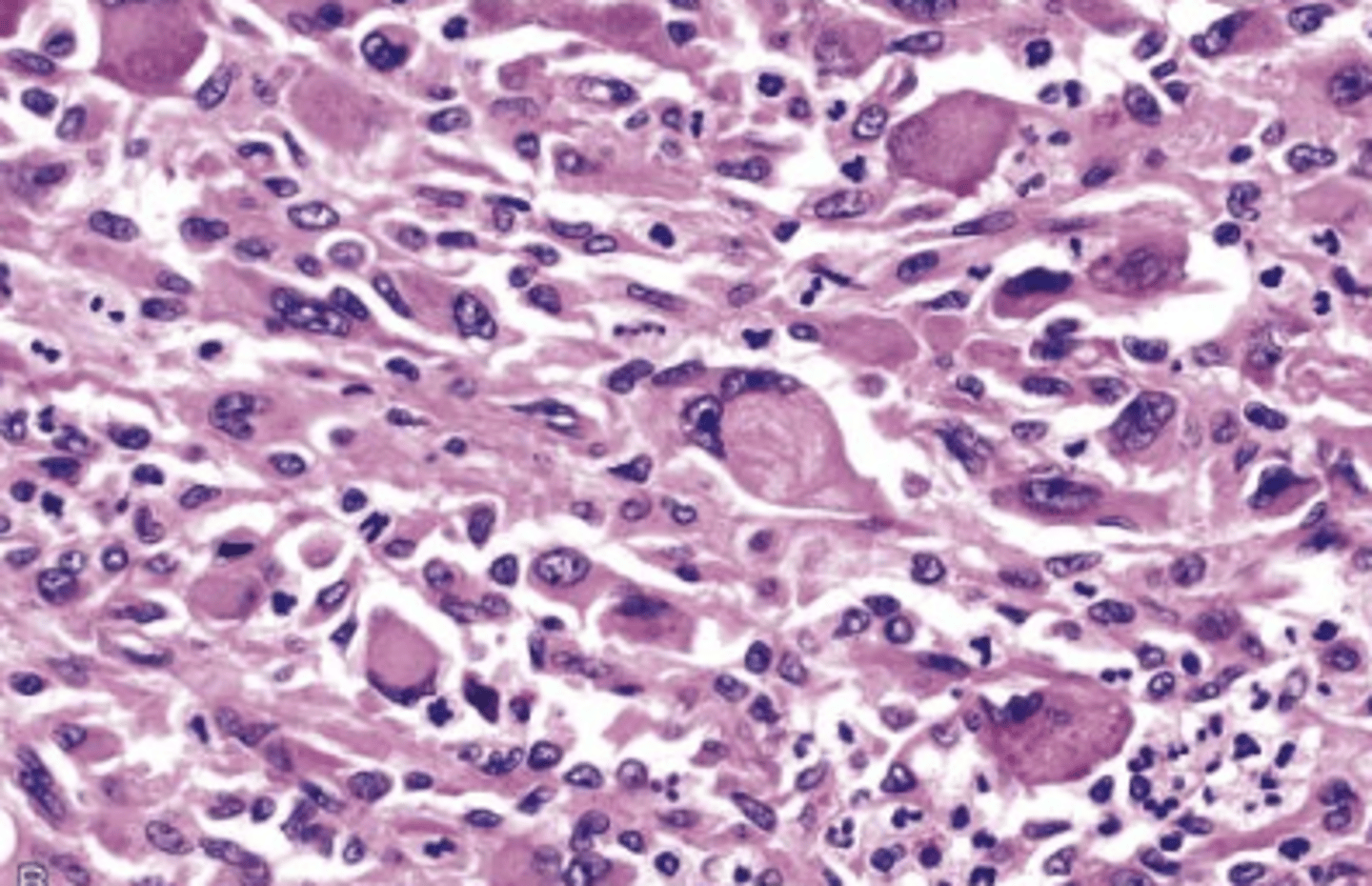
Rhabdomyosarcoma histology
Leiomyosarcoma
Derived from vascular smooth muscle
7% of all soft tissue sarcomas
RARE in oral cavity
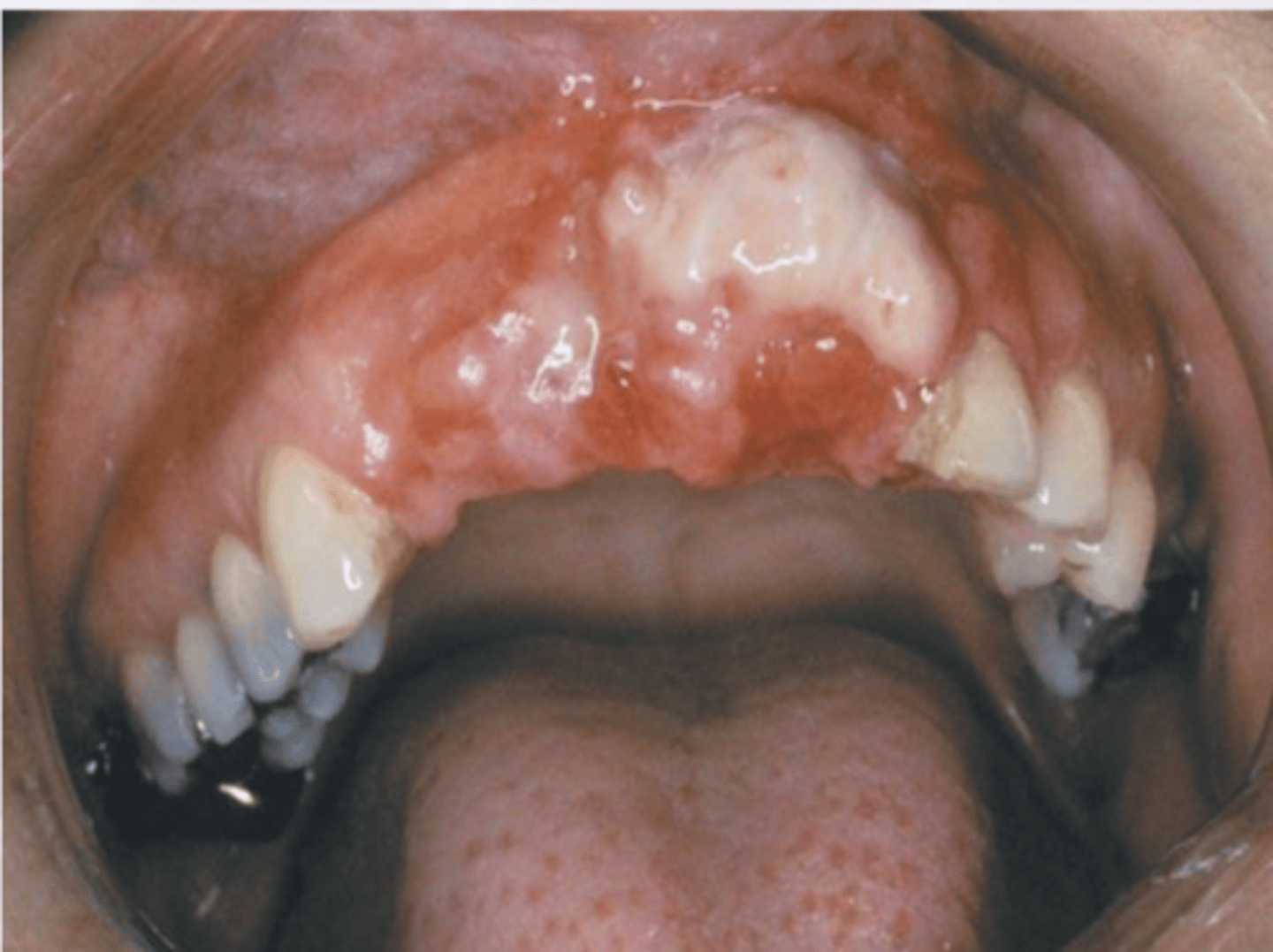
What are the clinical features of leiomyosarcoma?
Common in middle aged and older adults
Appear as enlarging mass
Can be painful or ulcerated
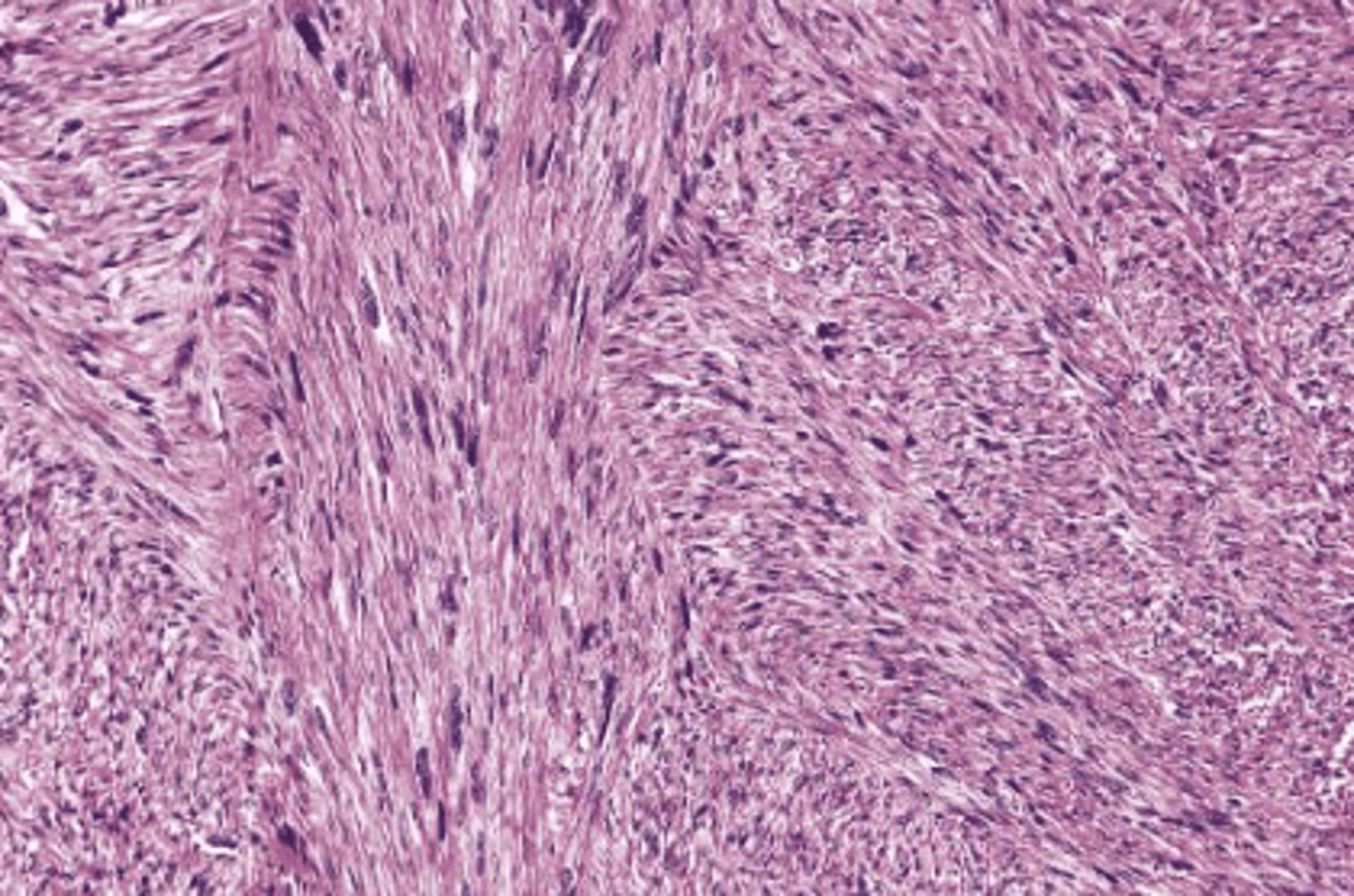
Leiomyosarcoma histology
What is the inheritance pattern for neurofibromatosis type I?
Autosomal Dominant
Metastases to the oral soft tissue accounts for ____% of oral malignancies
1
What are the clinical features of metastases to the oral soft tissues?
Gingiva is most common site** (mimic 4 P's)
Resembles hyperplastic/reactive growths
Can be ulcerated
Histology matches PRIMARY tumor
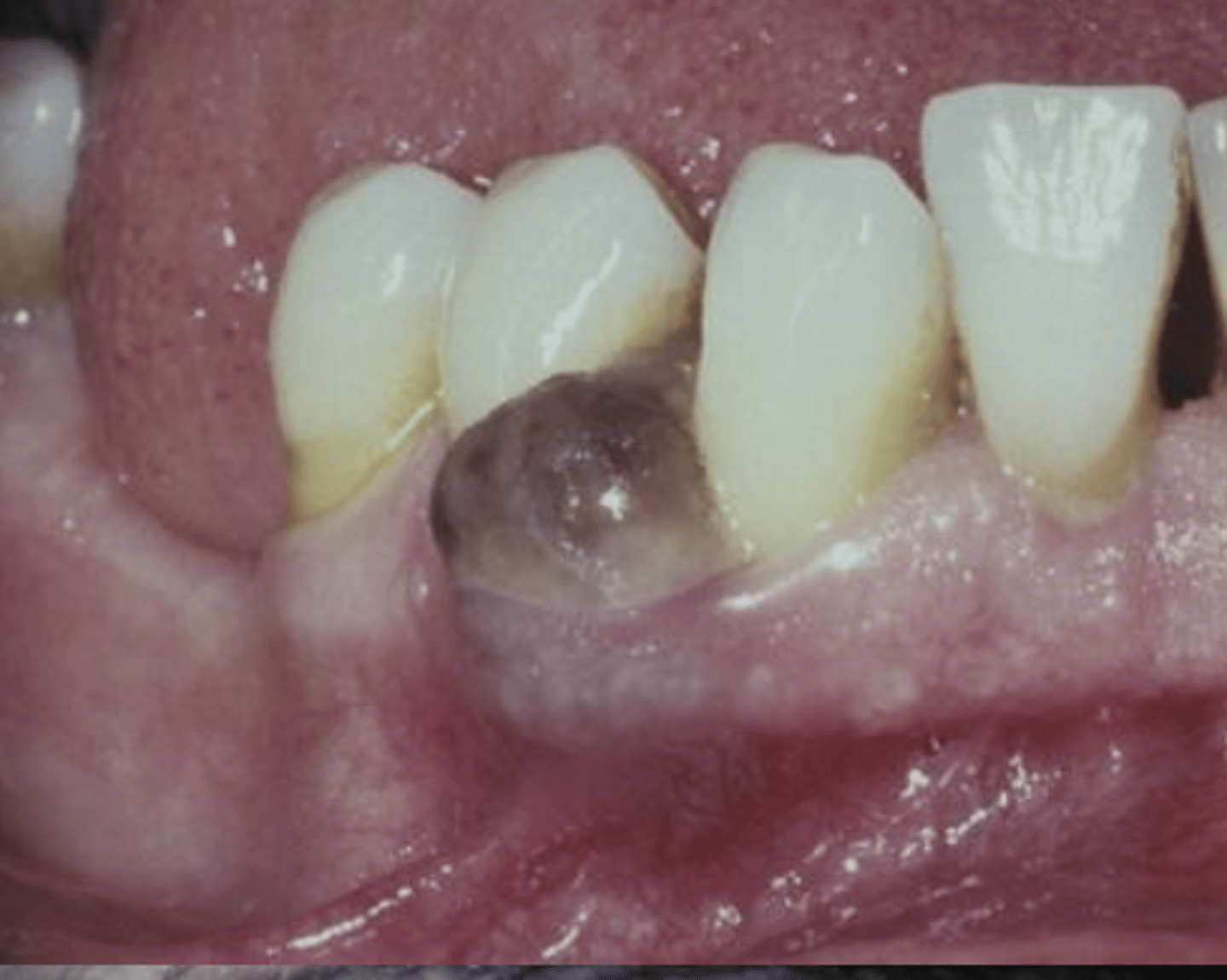
What is the most common site for metastasic tumors to the oral cavity?
(video question)
Gingiva
Cell division and proliferation is necessary and normal... Why is that?
Its needed for growth & injury repair
Its controlled by GENES
Proto-oncogenes
Encourage growth
Suppressor genes
Restrict growth
What is malignancy?
Its uncontrolled growth, damaging the growth of cells
So, What is cancer?
Uncontrolled growth with invasion +/- metastasis
Most cancers form tumors
ANY age affected
Genetic abnormalities
--cancer promoting oncogenes= ON
--tumor supressor genes = OFF
What cancer does NOT form a tumor?
Leukemia
What are 2 histological components of cancer?
Dysplasia
Anaplasia
Dysplasia
Disordered growth
Anaplasia
Cells assume a bizarre shape
OR lack of differentiation
Oral SCCa presentation
Variable pain
Red/white lesion
Non-healing ulcer
Exophytic growth or endophytic growth
HIGH risk locations --->
-Floor of mouth
-Posterior lateral border of tongue
What are adjuncts to oral cancer diagnosis?
Brush biopsy
Velscope
Vizilite
Identafi
What are the 3 types of treatment for oral cancers?
Surgery
radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Why are dental consultations with your cancer patients important?
The goal is to assist the patient in returning to as near normal life as possible!
Plan ahead: restore lost tissue/teeth
What should your examination consist of in your pretreatment dental exam for your cancer patient?
Radiographs
Examine Salivary glands
Maximum incisal opening
Eliminate foci of infection for your cancer patient, what does this mean?
Restore caries
Address perio
Plan extractions 2-3 weeks PRIOR to starting cancer treatment
What is chemotherapy?
Cytotoxic agents + antimetabolites
What is the goal of chemotherapy?
High kill rates
Target rapidly dividing cells
--tumor shrinkage
--eradicate micrometastases
What are the different types of chemotherapy?
Induction
Concurrent
Adjuvant
What are the side effects of chemotherapy?
Myelosuppression
Mucositis
Alopecia
What is adjuvant chemotherapy?
Additional treatment AFTER srugery
Helps reduce risk of relapse due to occult disease
Aim to improve overall survival
What is neoadjuvant chemotherapy?
BEFORE the main treatment
Reduction of tumor size to help minimize an invasive surgery
What is the goal of ionizing radiation?
Control malignant cells
-usually gamma
What are the uses of ionizing radiation?
Curative (Primary)
Adjuvant
Palliative
Total body irradiation
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Mucositis
Dermatitis
Altered pigmentation
Hair loss
damage taste buds
damage salivary glands
delayed bone/tissue necrosis
In radiation therapy, dose fractionation minimizes what?
Minimizes damage to normal tissue
What are complications to radiation therapy treatment?
Alteration of normal tissues
Complications can delay or limit treatment
Effective therapy does NOT eliminate risks for second cancer
What are the acute complications for chemotherapy?
Mucositis
Hemorrhage
What are the acute complications for radiation?
Mucositis
Dermatitis (acute)
Loss of taste (hypogeusia)
Pain
Infection
trismus
What are the chronic complications of cancer treatment?
Xerostomia
Loss of taste
Chronic dermatitis
Dental caries
Trismus
Osteoradionecrosis
Mucositis
inflammation of the mucosa
--thinning and breakdown
What are the symptoms of mucositis?
Pain
Ulceration
Odynophagia
Secondary infections
reduced oral intake
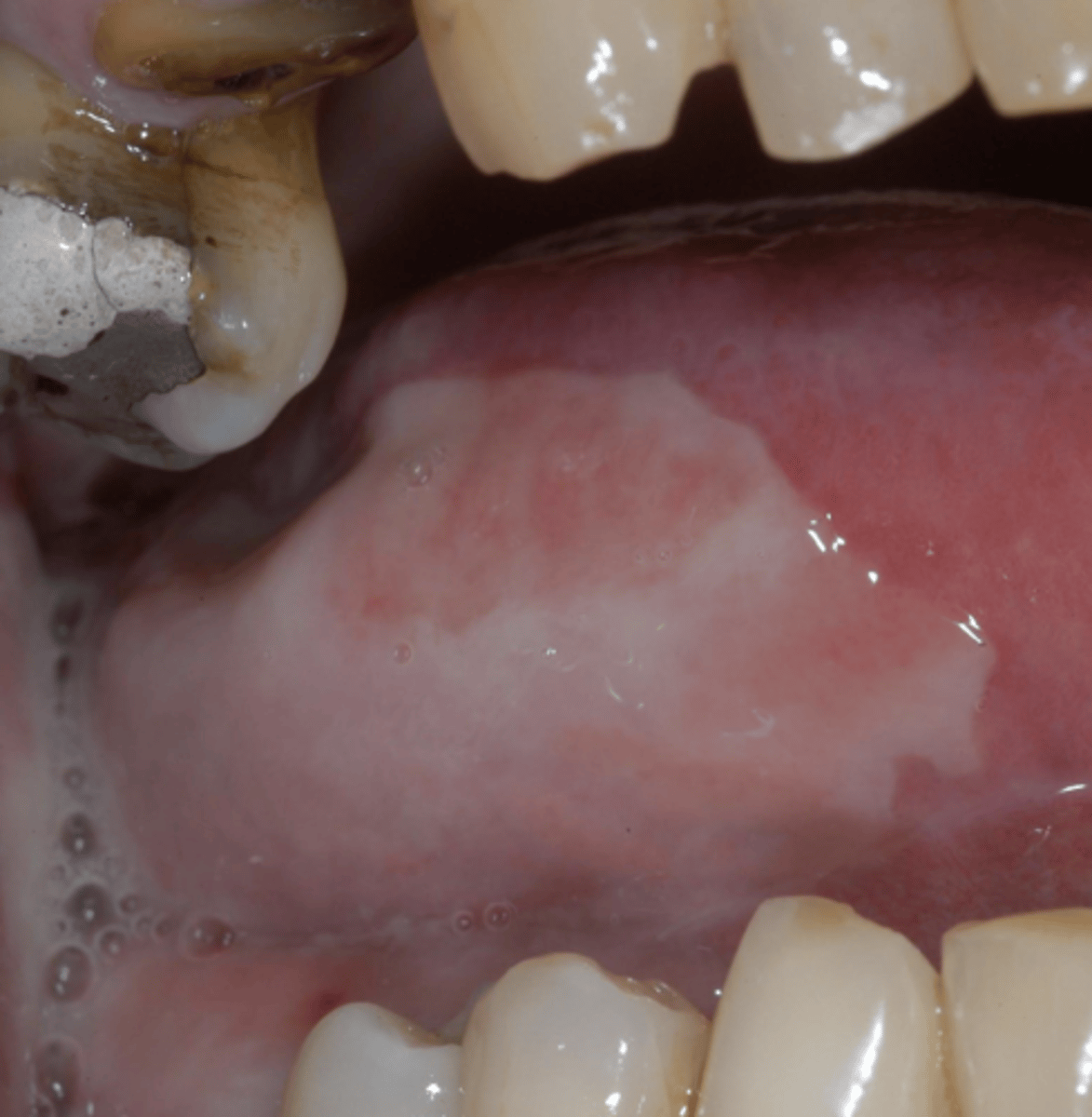
________ can last up the 6 months AFTER cancer therapy
mucositis
Characteristics of grade 1 mucositis?
Soreness
Erythema
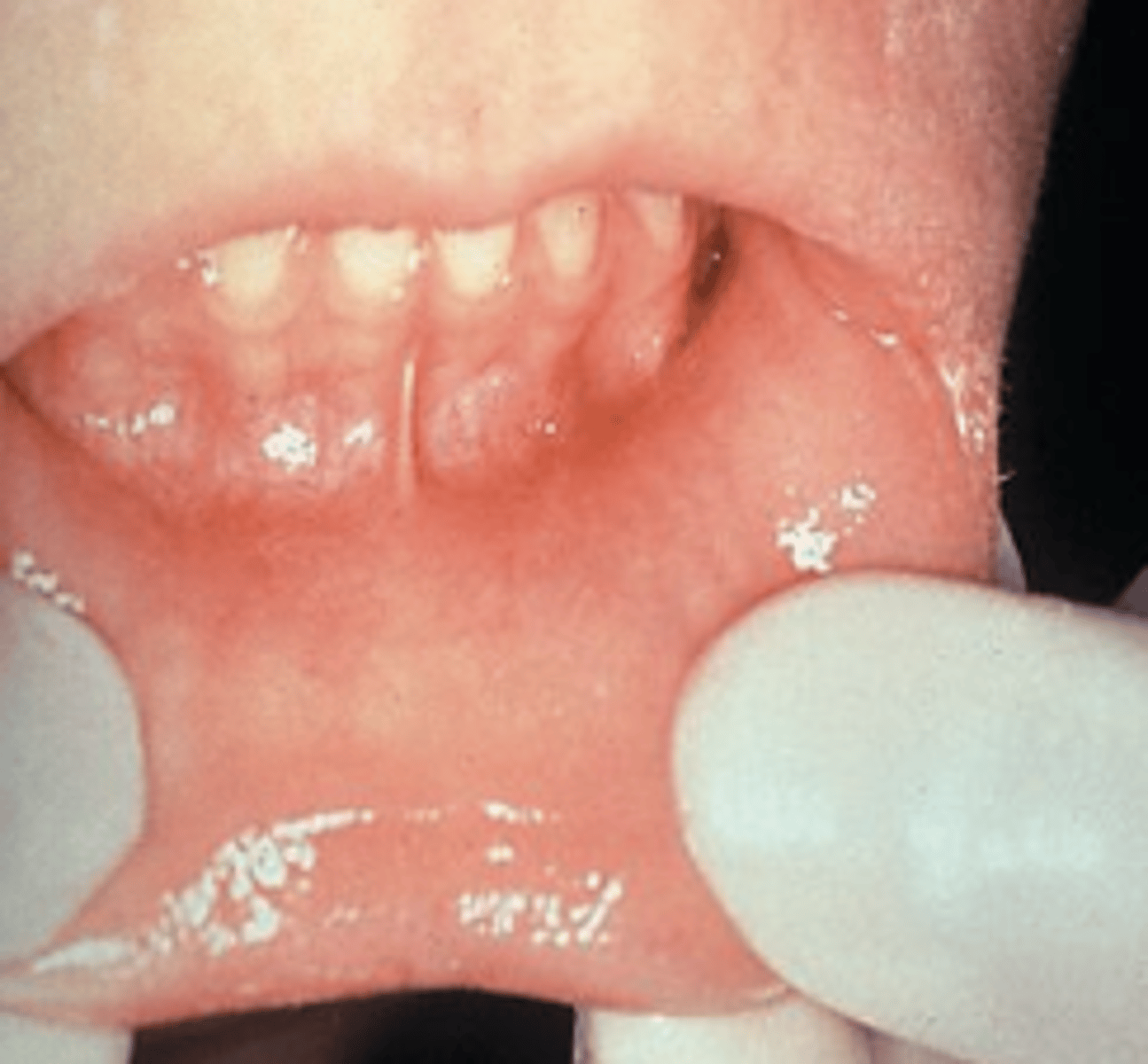
Characteristics of grade 2 mucositis
Erythema
ulcers
patient CAN swallow solid food
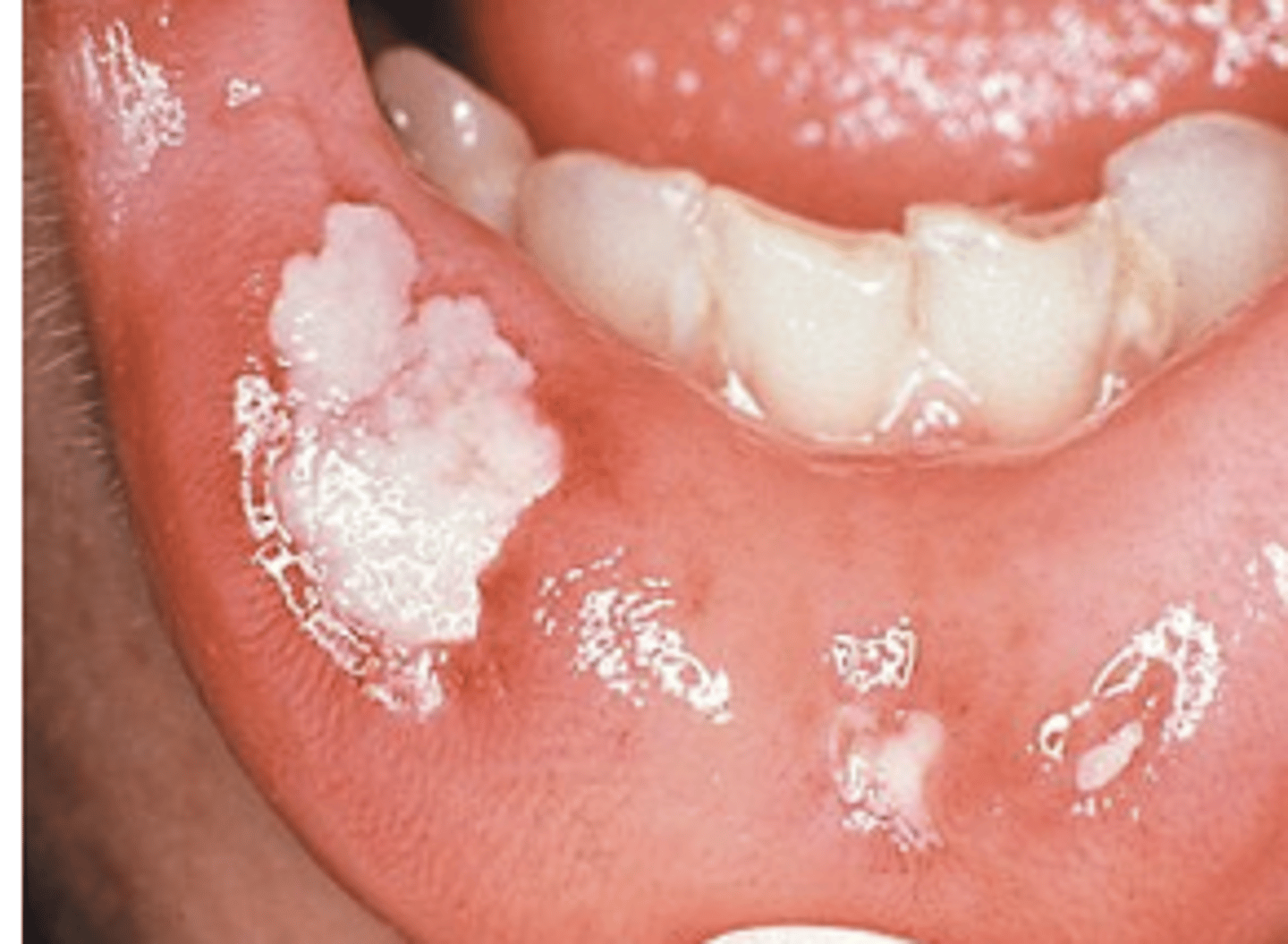
Characteristics of grade 3 mucositis
Ulcers with extensive erythema
Patient CANNOT swallow food, only liquid diet only
*considered severe mucositis
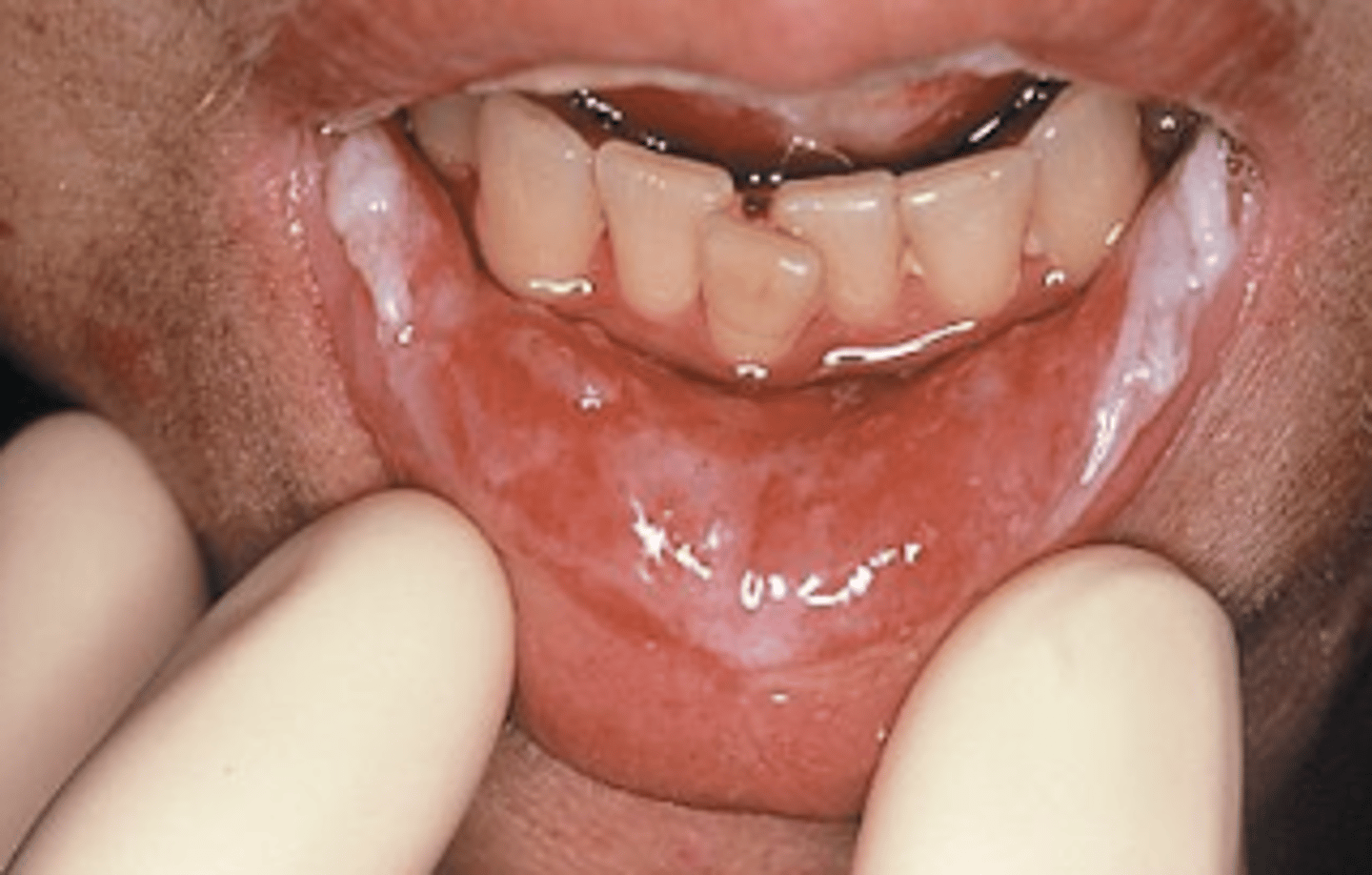
Characteristics of grade 4 mucositis
Mucositis to the extend that alimentation is not possible
patient cannot eat/drink
LIFE-THREATENING
*considered severe mucositis
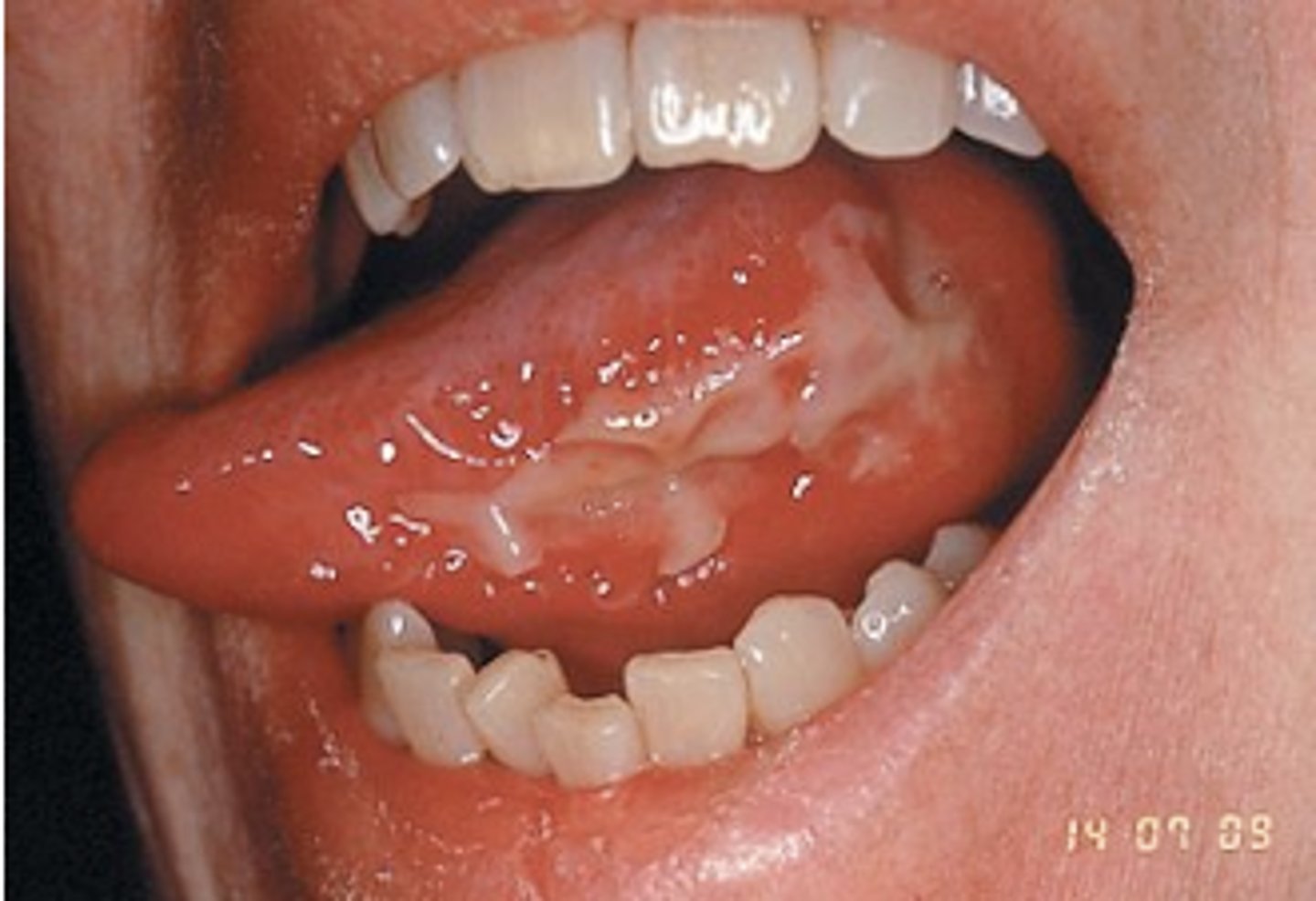
What is the treatment for mucositis?
No prevention exists
Increased risks for infections
topical analgesics and coating agents
Trismus
Inability to open the mouth completely
Max. incisal opening <35 mm
Affects quality of life
What is the treatment for trismus?
Exercise therapy
jaw opening devices (splints)
Emphasis on prevention
Xerostomia
Subjective feeling of decreased salivary flow
Hyposalivation
Objective reduction of salivary flow
Most common long term side effect in most patients undergoing head and neck radiation
Cholinergic agonists (parasympathetic) medications for xerostomia
Pilocarpine
Cevineline
Salivary flow stimulants
Sugarless gum
biotene
Xilifresh
Sugarless hard candy
Salix lozenges
What are other dental adjuncts to help xerostomia?
Fluoride
Acid buffer
Antif-ungals
Frequent dental visits
Sialogogues
What are things that interfere with a patient's nutrition once they start receiving treatment?
Mucositis
Loss of taste
Xerostomia
Loss of interest in eating
Comprised nutrition
Osteoradionecrosis
Exposed bone in a previously irradiated area
fail to heal over 3-6 months
NO history of anti-resorptive of metastatic tumors to jaw
What is the etiology of osteoradionecrosis?
Avascular effect of radiation to the bone causing hypoxia, hypovascularity, hypocellularity
T/F: Mucositis is a common side effect of both chemotherapy and radiation therapy
(video question)
True
What is the management of osteoradionecrosis?
Conservative management (routine prophylactic cleaning with 0.12% CHX)
Antibiotics + pain medication
T/F Osteoradionecrosis can develop at any point following radiation therapy?
True
Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ)
Pt has a HISTORY of anti-resorptive or anti-angiogenic medications
NO history of radiation or metastatic tumors of jaw
Exposed bone or probed bone >8 weeks
What are initiating events of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ)?
Spontaneous- 25%
Tooth extraction- 38%
Active perio disease-29%
Perio surgery- 11.2%
Dental implants- 3.4%
Apicoectomy - 0.8%
Who is more at risk for developing Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ)?
Females > males
Smokers
Obesity
Bisphosphonates
Inhibit bone resorption
Bind to bone surfaces and inhibit osteoblasts-- stays in body for 13yrs
increases bone density
Decreases fractures
excreted by kidneys
IV Bisphosphonates are contain _________ and are ______x more potent than oral Bisphosphonates
nitrogen, 100
Etidronate (Didronel)
IV bisphosphonate
Pamidronate (Aredia)
IV bisphosphonate
Zoledronate (Zometa)
IV bisphosphonate
Zoledronic Acid (reclast)
IV bisphosphonate