CHEM 11/SCH3U0 FULL COURSE REVIEW
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These are really bad I would not recommend studying with these but if you do, pls turn true/false questions off and only have "answer with definition" on
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
What is the charge of a cation?
POSITIVE (“cat has paws”)
What is the charge of an anion?
NEGATIVE
What is the suffix for non-metal compounds?
-ide
When an acid only has two elements, it is named like this:
hydro-ic
-ate compounds create acids that end with:
-ic acid
-ite compounds create acids that end with:
-ous acid
What determines the number of protons?
Atomic number
What determines the number of NEUTRONS AND PROTONS in an element?
Mass number
Isotope (definition)
Two or more forms of an element that differ in their number of neutrons (By rounding atomic mass)
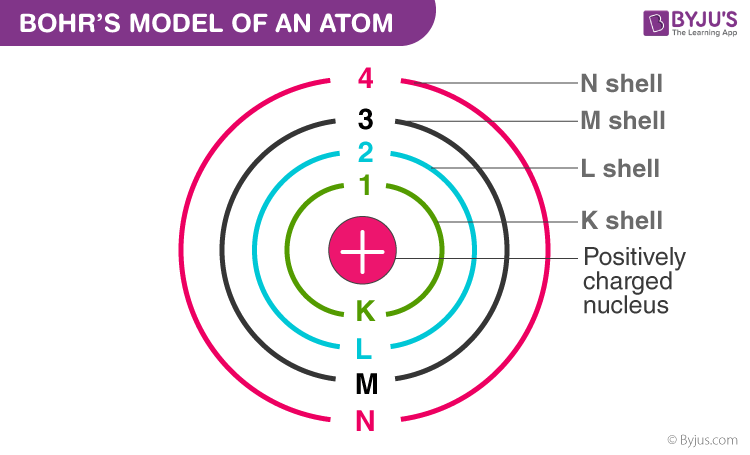
What is this?
Bohr model of an atom
How many electrons can fit in the -s orbital?
2
How many electrons can fit in the -p orbital?
6
How many electrons can fit in the -d orbital?
10
How many electrons can fit in the -f orbital?
14
What does it mean when two ions are isoelectronic?
They have the same number of electrons.
Effective Nuclear Charge(definition)
Strength of the pull between an atom’s nucleus and valence electrons.
I.E/Ionization Energy(definition)
Amount of energy required to remove an electron from an ion in a GASEOUS STATE
(T/F) As you move across a period, atoms on the LEFT SIDE hold electrons more tightly
False.
What does a big jump in IE values (When compared to other IE increases) suggest?
Change in electron shells.
Electron Affinity(definition)
Amount of energy released when a gaseous atom gains an electron.
Electronegativity(definition)
Ability of an atom to ATTRACT ELECTRONS
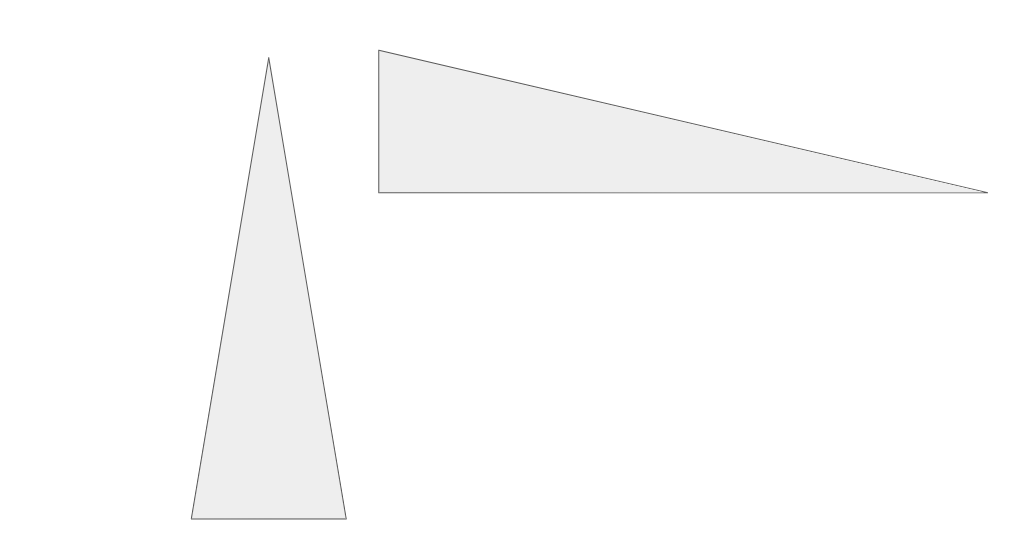
What atomic trend does this diagram demonstrate?
Atom size
What is shielding effect?
When innermost electrons “block” valence electrons from being attracted to the nucleus.
(T/F) As the number of protons increases, the atom gets larger
False. (The attraction between the electrons and nucleus increases, pulling them closer and making the atom smaller.)
What happens as you move down the periodic table?
The number of electron shells increases.
Formula for total number of electrons in a Bohr model.
Number of electrons = 2n²
n-value of Bohr model
Energy level
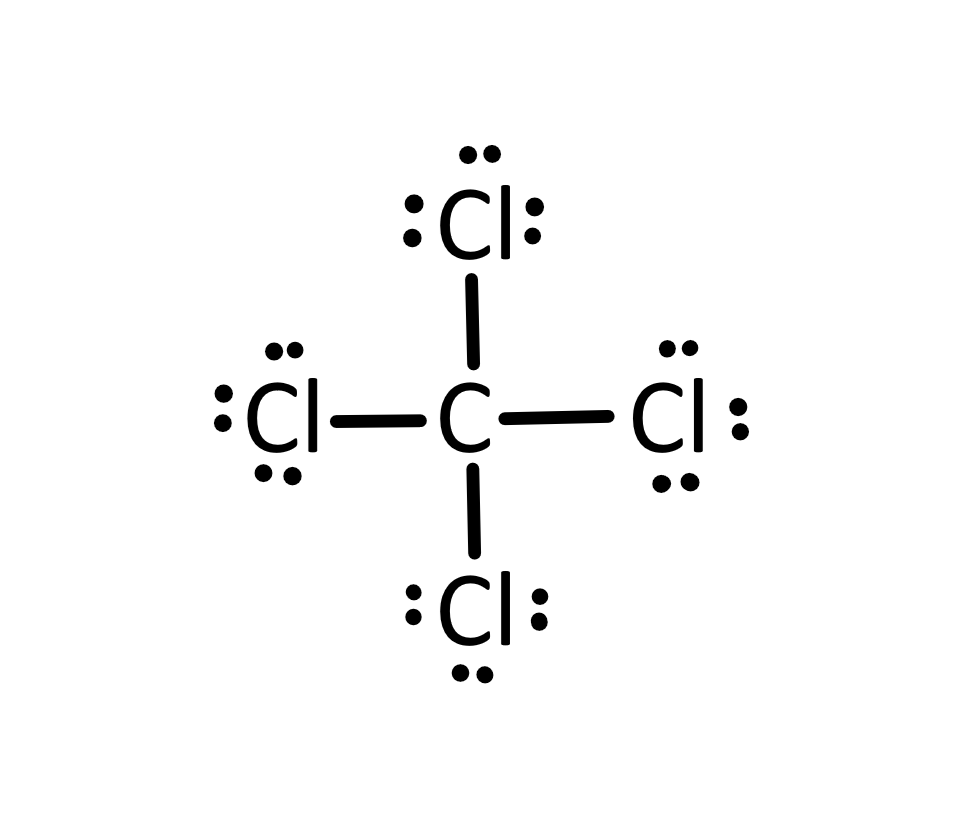
What is this?
Lewis Structure
What is bonding capacity?
How many bonds an atom can form with surrounding ions.
Covalent/molecular bond (definition)
A bond between two non-metals
What is a polar bond?
A bond between two ions that have a difference in electronegativity larger than 0.4
A bond is likely ionic if:
the difference in electronegativity is larger than 1.7
(T/F) COVALENT (nonmetal-nonmetal) compounds typically have higher boiling points
False. (Covalent bonds are weaker, so they’re easier to break apart.)
Dipole (definition)
A bond/molecule whose ends have opposite charges.

What molecular shape is this?
Linear
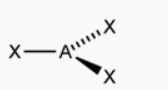
What molecular shape is this?
Trigonal Planar
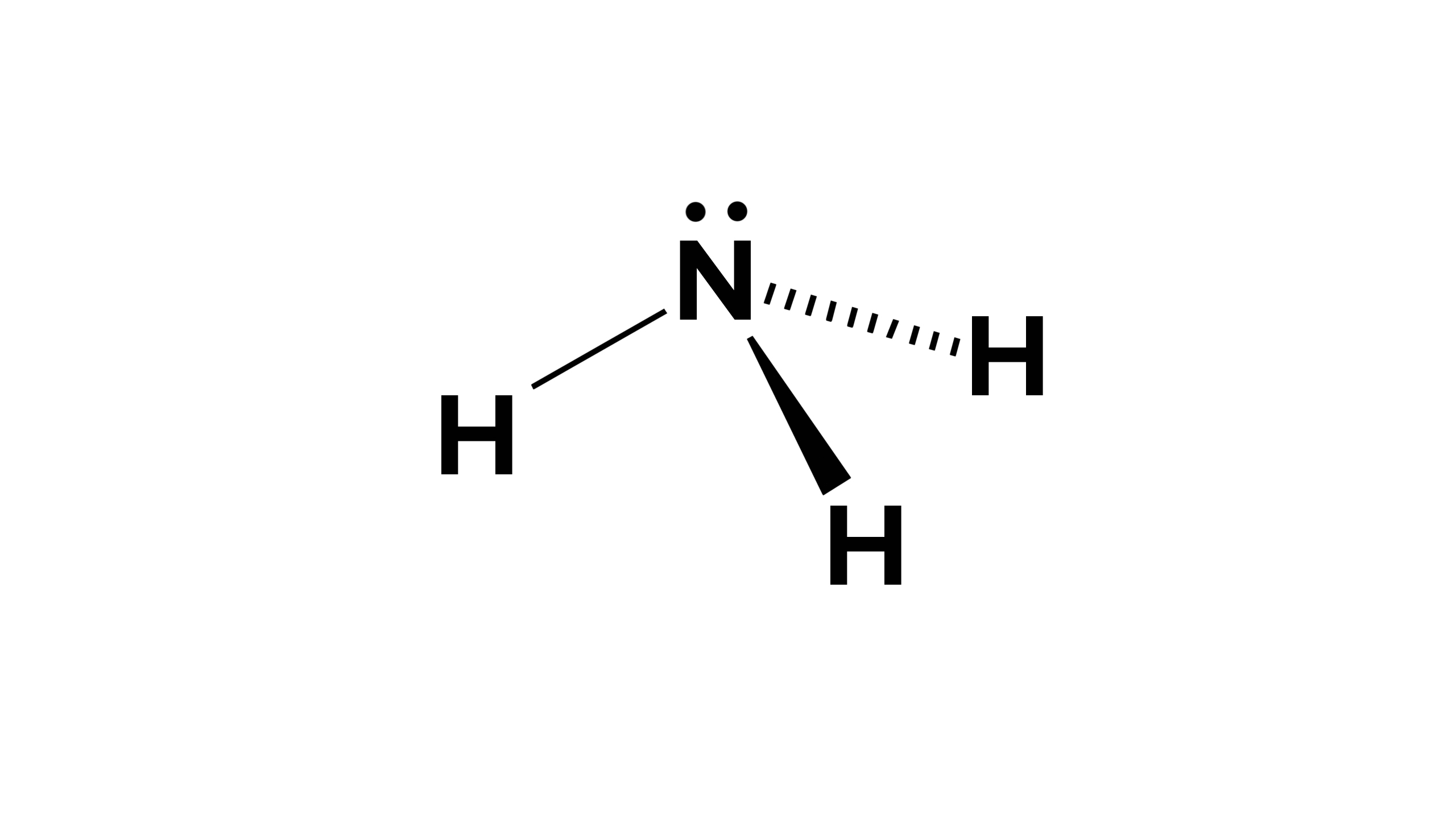
What molecular shape is this?
Trigonal Pyramidal
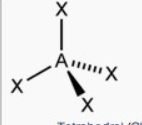
What molecular shape is this?
Tetrahedral
Are non-polar bonds soluble in water?
No.
What is the London dispersing force (LDF)?
Attraction between an ion’s nucleus and electron(s) from another atom.
What is a dipole-dipole bond?
A bond between 2 polar molecules.
When 2 molecules form a dipole-dipole bond…
The positive end of one molecule attracts the negative end of another.
What happens to electrons during an ionic bond?
A transfer of electrons
(T/F) Ionic bonds are the strongest type of bond.
True (because they involve a transfer of electrons.)
What type of reaction is A + B → AB?
Synthesis reaction
what type of reaction is AB → A + B?
Decomposition reaction
(T/F) When balancing equations, one should start with the simplest compounds.
False. (You should start with more complex/abundant compounds.)
What is a single displacement reaction?
A reaction in which one ion replaces another.
How is the replaced element determined in a single displacement reaction?
Activity Series
(T/F) In a double displacement reaction, positive ions switch with each other.
False. (Positive ions replace negative ions.)
What is “HOBrFiNCl” used to remember?
Diatomic atoms (atoms that must come in pairs.)
A combustion reaction is when a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen gas to produce:
H2O and CO2.
What is the meaning of aqueous(aq)?
Dissolved in water.
What is true about all compounds with elements in group 1?
They are always soluble.

What type of equation is this?
A skeletal(unbalanced) equation.
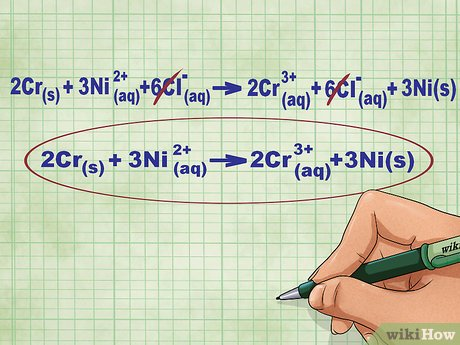
what type of equation is this?
Net ionic equation.
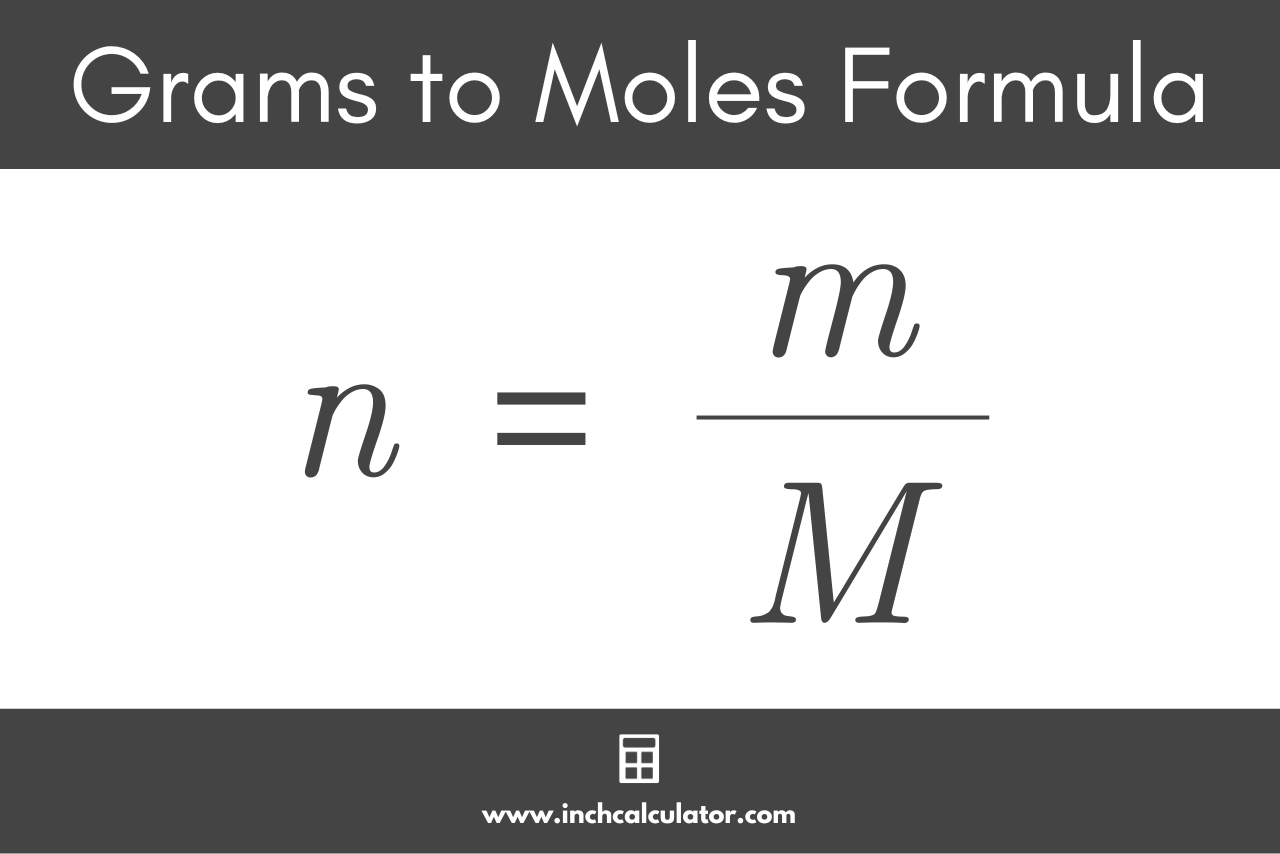
n = ?
Number of moles
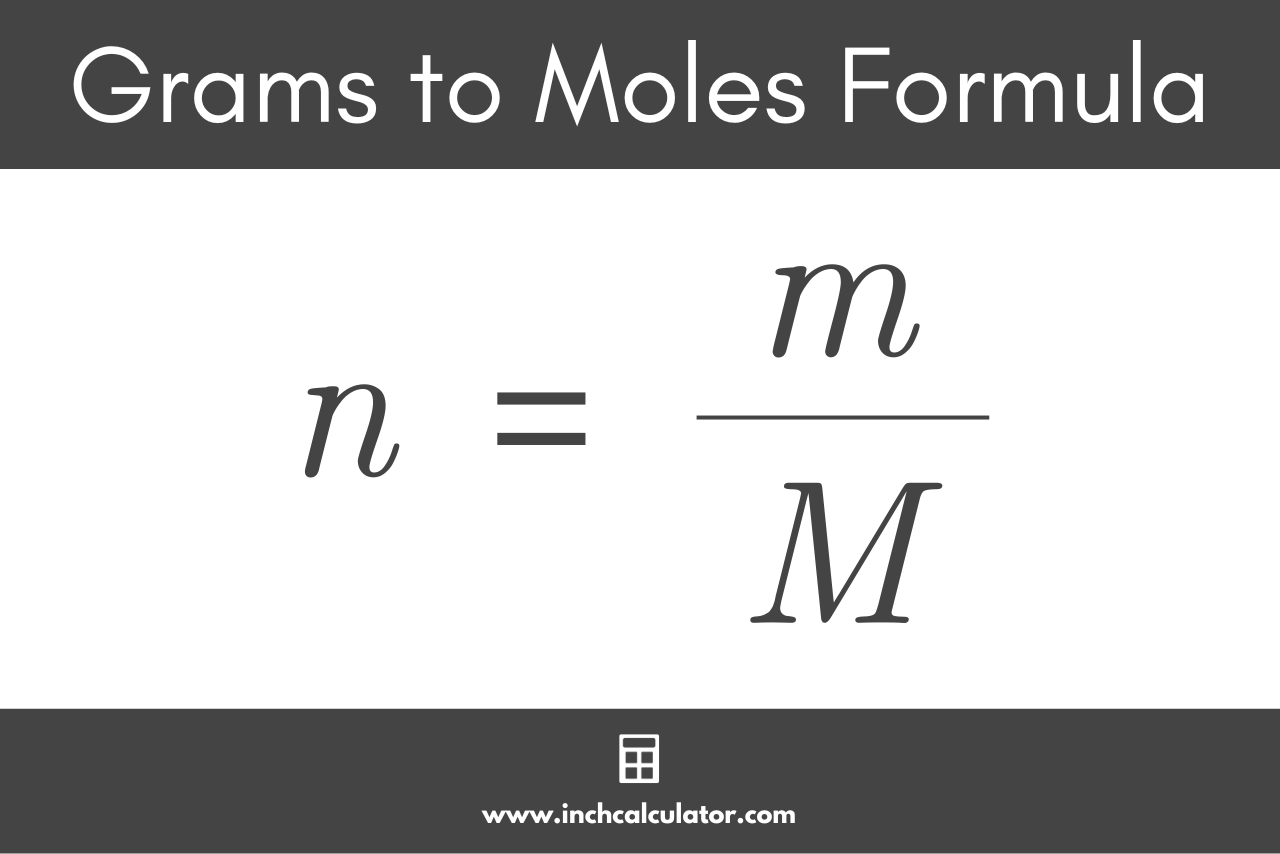
m = ?
Mass of compound (IN GRAMS)
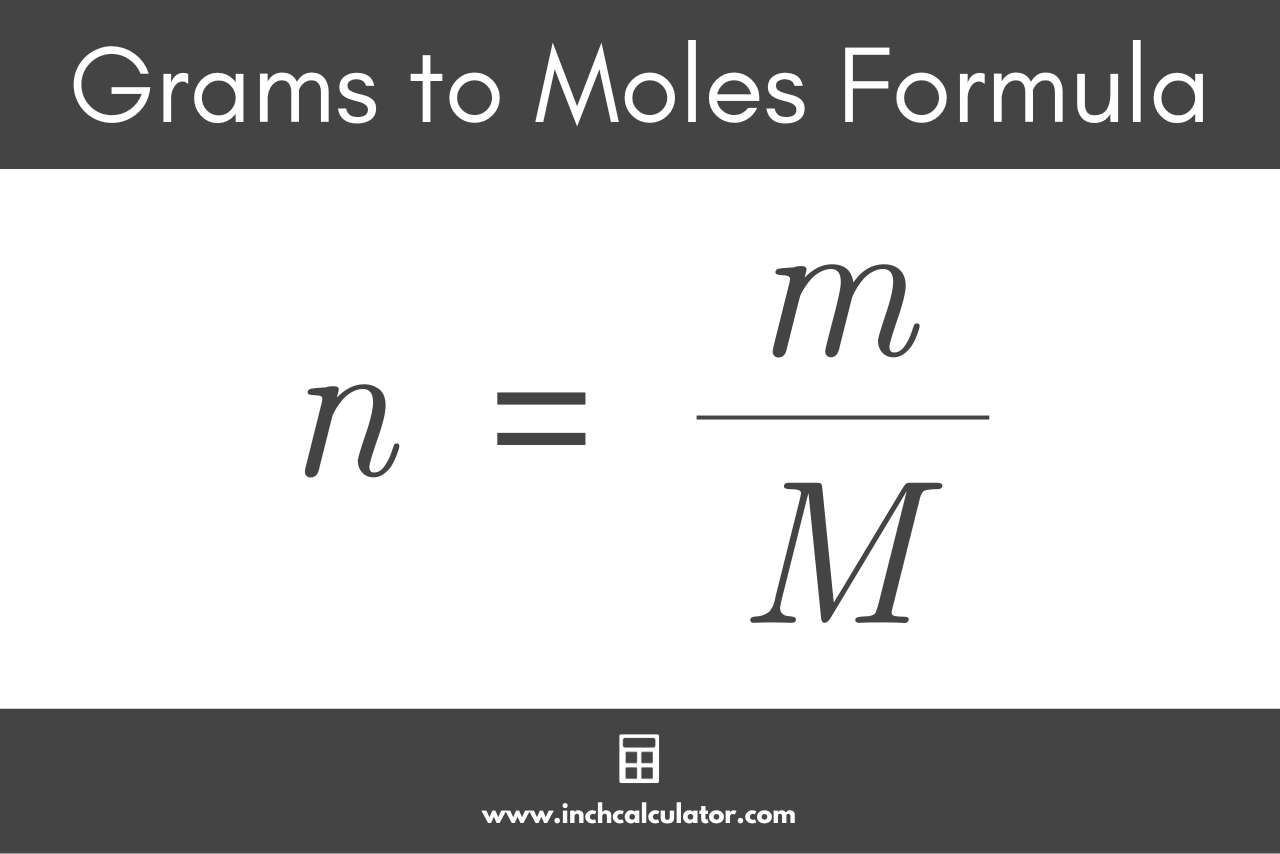
M = ?
Molar mass of compound (g/mol)
What unit is used for molar mass?
(Grams per mole) g/mol
What is avogadro’s number? (definition)
The number of particles found in one mole of a substance.
What is Avogadro’s number? (value)
6.02 × 10²³
To determine the empirical formula of a compound from its percentage, what must you determine first for each element present?
Mass (IN GRAMS) per 100g of compound
WHen determining the empirical formula of a compound, what must you divide each number of moles by?
Smallest number of moles.
What must you do to get the standard formula from a compound’s empirical formula?
Calculate molar mass of empirical formula
Divide molar mass by empirical formula molar mass
Multiply all subscripts in empirical formula by number obtained from above step.
Alkali metals are found in group:
1
What is a group on the periodic table?
Vertical column

What is a period on the periodic table?
Horizontal row.

Percentage yield formula
Actual / theoretical x 100 (ArtTrade)
What is “Theoretical Yield?”
Amount of product obtained from calculations.
What is the “Actual yield”?
Amount of product obtained from lab data.
(T/F) The limiting reactant/reagent is whichever compound has the least amount of moles.
True.
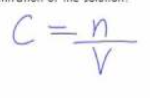
c = ?
Concentration (mol/L)
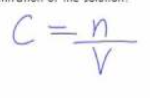
n = ?
Number of moles.
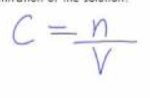
v = ?
Volume in LITRES
c1v1 = ?
c2v2
How do you convert ml to L?
Divide by 1000
How do you convert L to ml?
Multiply by 1000
What does a compound’s line on a solubility graph indicate?
A saturated solution.
ionic compounds ________ in water
dissociate
covalent/molecular compounds ________ in water
Ionise
How does dissociation separate ions?
Positive vs negative.
(T/F) acids taste bitter
False. (Acids taste sour)
(T/F) Acids are conductive, but bases arent.
False. Both acids and bases are conductive.
What do acids do to a blue litmus?
They turn it red
What do bases do to a blue litmus?
Nothing. They react with red litmus.
What happens when an aqueous solution has a higher concentration of ions?
It becomes more conductive.
What is the Arrhenius Theory?
An acid is anything that dissociates to produce H+ ions (protons), a base is anything that dissociates to produce OH- ions.
What is another word for an H+ ion?
Proton
(T/F) In Bronsted-Lowry’s theory, an acid is any species that can accept a proton.
False. (A BL acid is any ion capable of donating a proton.)
What is the Bronsted-Lowry Theory?
Acids are proton donors, bases are proton acceptors.
What is H3O+?
Hydronium ion.
What substance can act as an acid or base depending on what it’s reacting with?
Water (H2O)
(definition) Conjugate acid
An base that has received an extra proton
(definition) Conjugate base
An acid that has lost a proton
(definition) electrolyte
A substance that is conductive due to dissociation into +/- charged ions
(T/F) Any neutralization reaction (Involving acid + base) is simplified to H2O when broken down into a net ionic equation.
True.
(T/F) The strength of an acid depends on its concentration.
False. (The strength of an acid is based on how much it ionizes in water.)
(definition) Amphoteric
SUbstance with the ability to act as an acid or a base.
Amphiprotic (definition)
A substance that can both give and accept protons.